Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1 Ttests Handout Revised
Hochgeladen von
Leung Yi0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten1 SeiteThe document discusses one-sample and two-sample hypothesis testing. For one-sample testing, the null hypothesis is that the population mean is equal to a specified value. The research hypothesis can be one-tailed or two-tailed. The test statistic for means is calculated by taking the sample mean minus the population mean and dividing by the standard error. For proportions, the test statistic is calculated using the sample and population proportions. Two-sample testing compares two population means or proportions, with hypotheses of equality or inequality between the two. The test statistic for two means is calculated using the sample means, standard error, and sample sizes.
Originalbeschreibung:
Handout for t-test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document discusses one-sample and two-sample hypothesis testing. For one-sample testing, the null hypothesis is that the population mean is equal to a specified value. The research hypothesis can be one-tailed or two-tailed. The test statistic for means is calculated by taking the sample mean minus the population mean and dividing by the standard error. For proportions, the test statistic is calculated using the sample and population proportions. Two-sample testing compares two population means or proportions, with hypotheses of equality or inequality between the two. The test statistic for two means is calculated using the sample means, standard error, and sample sizes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten1 Seite1 Ttests Handout Revised
Hochgeladen von
Leung YiThe document discusses one-sample and two-sample hypothesis testing. For one-sample testing, the null hypothesis is that the population mean is equal to a specified value. The research hypothesis can be one-tailed or two-tailed. The test statistic for means is calculated by taking the sample mean minus the population mean and dividing by the standard error. For proportions, the test statistic is calculated using the sample and population proportions. Two-sample testing compares two population means or proportions, with hypotheses of equality or inequality between the two. The test statistic for two means is calculated using the sample means, standard error, and sample sizes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
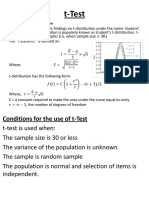
Hypothesis Testing (Chapter 9)
One-sample Hypothesis Testing
Null hypothesis is always one of no difference
H0: μy = some specified value
Possibilities for Research hypothesis:
H1: μy < some specified value (one‐tailed test, left‐tailed)
H1: μy > some specified value (one‐tailed test, right‐tailed)
H1: μy ≠ some specified value (two‐tailed test)
Calculating the Test Statistic for Means (one-sample)
𝑌�−µ𝑦
tobtained= 𝑆𝑦
√𝑁
Calculating the Test Statistic for Proportions (one-sample)
𝑃𝑠−𝑃𝑢
Zobtained= or T-obtained using df= ∞
𝑃𝑢(1−𝑃𝑢)
�
𝑁
𝑃𝑠−𝜋𝑦
Or
𝜋𝑦(1−𝜋𝑦)
�
𝑁
Two sample hypothesis testing
Hypotheses:
H0: μ1 = μ2
H1: μ1 ≠ μ2 or H1: μ1 < μ2 or H1: μ1 >μ2
Calculating the Test Statistic for Means (two-samples)
If σ𝑦� is known, use Z‐score and normal distribution:
𝑌�1 −𝑌�2
tobtained=
𝑆𝑦
� 1−𝑦
�2
where (Assuming equal variances)
((𝑁1 −1)𝑆𝑦 2 +(𝑁2 −1)𝑆𝑦 2 ) (𝑁 +𝑁 )
𝑆𝑦�1−𝑦�2 = � 1
(𝑁1 +𝑁2 )−2
2
� (𝑁1 𝑁 2)
1 2
And df=(𝑁1 +𝑁2 )-2
2
For Proportions, use X
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Stat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21Dokument7 SeitenStat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21PaolaCastelwhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Sample SolutionsDokument19 SeitenFinal Exam Sample SolutionsJung Yoon SongNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT361 Formulae 3Dokument2 SeitenMAT361 Formulae 3Fatin DewanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis TestingDokument6 SeitenHypothesis TestingAlishba NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- CORRELATIONAL FormuleDokument2 SeitenCORRELATIONAL FormuleIrenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Random Variables1d and 2DDokument31 SeitenRandom Variables1d and 2Dabhimanyusinghc6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 4 Hoja de FormulasDokument2 SeitenQuiz 4 Hoja de Formulaslsanc308Noch keine Bewertungen
- ST102 NotesDokument21 SeitenST102 NotesBenjamin Ng0% (1)
- Hypothesis testing in univariate statistics based on N (µ, σ)Dokument15 SeitenHypothesis testing in univariate statistics based on N (µ, σ)daniel3777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stat171 NotesDokument82 SeitenStat171 NotesnigerianhacksNoch keine Bewertungen
- StatsDokument8 SeitenStatsLeonardo ZapparoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variance of A Random VariableDokument7 SeitenVariance of A Random VariableMarvin TomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument32 SeitenChapter 10duynkhe163378Noch keine Bewertungen
- Section 4Dokument3 SeitenSection 4Yuzuru BlueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cornell CS578: Hypothesis TestingDokument2 SeitenCornell CS578: Hypothesis TestingIanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gsbiju MA202 3 5Dokument5 SeitenGsbiju MA202 3 5Jivin George ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Probability Distributionsi Math 217/218 Probability and StatisticsDokument10 SeitenCommon Probability Distributionsi Math 217/218 Probability and StatisticsGrace nyangasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Statistics - Chapter 10 Notes: Comparing Two Population Parameters 10.1: Comparing Two ProportionsDokument1 SeiteAP Statistics - Chapter 10 Notes: Comparing Two Population Parameters 10.1: Comparing Two ProportionsRhivia LoratNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Statistics - Chapter 10 Notes: Comparing Two Population Parameters 10.1: Comparing Two ProportionsDokument1 SeiteAP Statistics - Chapter 10 Notes: Comparing Two Population Parameters 10.1: Comparing Two ProportionsRhivia LoratNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Negative BinomialDokument9 Seiten20 Negative BinomialHarold FinchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics II Sol 2015-16Dokument6 SeitenStatistics II Sol 2015-16HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 251 PS1 SolutionsDokument5 SeitenEcon 251 PS1 SolutionsPeter ShangNoch keine Bewertungen
- BQQ6214 Statistical FormulaeDokument3 SeitenBQQ6214 Statistical FormulaeRobert OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Proof of A Classical FormulaDokument5 SeitenA New Proof of A Classical FormulaKonstantinos MichailidisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential EquationsDokument8 SeitenDifferential EquationsJong CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article A Generalization of Powers-StørmerDokument8 SeitenArticle A Generalization of Powers-StørmerThuy LanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Test-5Dokument32 SeitenHypothesis Test-5Said VarshikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Statistical ConceptsDokument14 SeitenBasic Statistical ConceptsVedha ThangavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endterm QAM II 2021 DEFDokument4 SeitenEndterm QAM II 2021 DEFABHISHEK KUMAR SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 2Dokument8 SeitenChapter 2 2Uni StuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Likelihood Ratio TestsDokument5 SeitenLikelihood Ratio Testsgibadew959Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical MethodsDokument3 SeitenStatistical MethodsRed VillaluzNoch keine Bewertungen
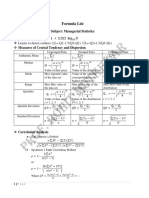
- List of Formula - Managerial StatisticsDokument6 SeitenList of Formula - Managerial Statisticsmahendra pratap singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Design I Lecture 6 070915Dokument17 SeitenExperimental Design I Lecture 6 070915Marlvin PrimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Unit 1-2Dokument6 SeitenSTATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Unit 1-2theresaperez298Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math204 NonParOneTwoDokument4 SeitenMath204 NonParOneTwoNeeti JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final03 SolsDokument3 SeitenFinal03 SolssdaetwylerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Values:: 1. Average Value: The Average Value of The Data Set Is The Average of All DataDokument3 SeitenValues:: 1. Average Value: The Average Value of The Data Set Is The Average of All DataHiền ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Physics AnswerDokument3 SeitenFor Physics AnswerLiuweimingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Mohammad Saifuddin: Discrete or ContinuousDokument7 SeitenPrepared By: Mohammad Saifuddin: Discrete or ContinuousHRIDOYNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022-2023 Final ExamDokument9 Seiten2022-2023 Final ExamPavle PakalovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6eDokument4 SeitenChapter 6eAdmasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECMT1020 Formulas 2021Dokument9 SeitenECMT1020 Formulas 2021Darius ZhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation Theory EngDokument40 SeitenEstimation Theory EngVe EKNoch keine Bewertungen
- QT Question TemplateDokument7 SeitenQT Question TemplateSahaana DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pekan XIDokument47 SeitenPekan XINuzul Cahyani AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Calculus Differentiation Increment Method 4Dokument11 SeitenBasic Calculus Differentiation Increment Method 4sijeysanchez56Noch keine Bewertungen
- Random VariablesDokument37 SeitenRandom Variables20-051 Vigneshwar PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question One: Data Analysis and Decision Statistics:: Variable 1 Variable 2Dokument5 SeitenQuestion One: Data Analysis and Decision Statistics:: Variable 1 Variable 2Andrei CristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2asl D2 15 16Dokument2 SeitenMath 2asl D2 15 16houcine72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Analysis With Application: Statistics and Informatics Second Stage 2021-2022Dokument26 SeitenNumerical Analysis With Application: Statistics and Informatics Second Stage 2021-2022Rebar QaraxiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question DPP 1 Continuity and Differentiability Mathongo Jee Main 2022 Crash CourseDokument6 SeitenQuestion DPP 1 Continuity and Differentiability Mathongo Jee Main 2022 Crash CoursePc xoixaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 6 Solutions - 441Dokument4 SeitenHW 6 Solutions - 441adnan_mahboob_1100% (1)
- Legendre Equation ProblemsDokument2 SeitenLegendre Equation ProblemsShahbaz AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Reference Sheet - Revision 2Dokument6 SeitenCourse Reference Sheet - Revision 2mattbutler1401Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum Likelihood Methods: Data Analysis in HEP 2.4 2.6Dokument38 SeitenMaximum Likelihood Methods: Data Analysis in HEP 2.4 2.6MioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Von EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting Statistics in APA FormatDokument3 SeitenReporting Statistics in APA FormatJiss PalelilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Curve HandoutDokument1 SeiteNormal Curve HandoutLeung YiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1551496602Dokument2 Seiten1551496602Leung YiNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Math Lab: AXP Internal 8/14/16 1Dokument16 SeitenMy Math Lab: AXP Internal 8/14/16 1Leung YiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics Hypothesis TestingDokument6 SeitenStatistics Hypothesis TestingLeung YiNoch keine Bewertungen