Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Op Amps36
Hochgeladen von
lecuellarq85gmailcomOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Op Amps36
Hochgeladen von
lecuellarq85gmailcomCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
|A| [dB] |A| [dB]
0 0 ∆Ω
–3 –3
0 1 Ω 0 Ω1 1 Ω2 Ω
Figure 16–36. Low-Pass to Band-Rejection Transition
The corner frequency of the low-pass transforms to the lower and upper –3-dB frequen-
cies of the band-rejection filter Ω1 and Ω2. The difference between both frequencies is the
normalized bandwidth ∆Ω:
DW + W max * W min
Identical to the selectivity of a band-pass filter, the quality of the filter rejection is defined
as:
fm
Q+ + 1
B DW
Therefore, replacing ∆Ω in Equation 16–19 with 1/Q yields:
A 0ǒ1 ) s 2Ǔ
A(s) + (16–20)
1 ) Q1 ·s ) s 2
16.6.1 Active Twin-T Filter
The original twin-T filter, shown in Figure 16–37, is a passive RC-network with a quality
factor of Q = 0.25. To increase Q, the passive filter is implemented into the feedback loop
of an amplifier, thus turning into an active band-rejection filter, shown in Figure 16–38.
C C
R/2
VIN VOUT
R R
2C
Figure 16–37. Passive Twin-T Filter
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op Amps37Dokument1 SeiteOp Amps37lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Filter Design Techniques: Optimize Gain and Phase ResponseDokument15 SeitenActive Filter Design Techniques: Optimize Gain and Phase ResponseElíasJesúsDíazPanssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activefilters 141231042113 Conversion Gate02 PDFDokument46 SeitenActivefilters 141231042113 Conversion Gate02 PDFAbbas HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Filter DesignDokument66 SeitenActive Filter DesignLaura MariiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elektron DayaDokument5 SeitenElektron DayaRendy PoetraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A C C A 2C C R CC B 2C C R CC: High-Pass Filter DesignDokument26 SeitenA C C A 2C C R CC B 2C C R CC: High-Pass Filter Designlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronlecture 1Dokument18 SeitenElectronlecture 1Mohammed ShifulNoch keine Bewertungen
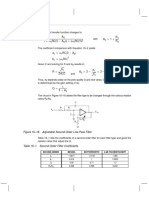
- Adjustable second-order low-pass filter transfer function and coefficientsDokument1 SeiteAdjustable second-order low-pass filter transfer function and coefficientslecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low-Pass to Band-Pass Filter TransitionDokument1 SeiteLow-Pass to Band-Pass Filter Transitionlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Introduction To Filter: RF Engineering - Passive Circuit Microstrip Filter DesignDokument20 Seiten1.0 Introduction To Filter: RF Engineering - Passive Circuit Microstrip Filter DesignraatkaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- L13Dokument29 SeitenL13ShreyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Integrated Circuit Design: Nagendra Krishnapura (Nagendra@ee - Iitm.ac - In) Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAnalog Integrated Circuit Design: Nagendra Krishnapura (Nagendra@ee - Iitm.ac - In) Assignment 1swarajboishya17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 8Dokument32 SeitenLecture 8Martian 07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hoja de Datos Del TDA 7439Dokument20 SeitenHoja de Datos Del TDA 7439_el_patriarca_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary IssueDokument3 SeitenPreliminary IssueThomas NoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei APE4518R20v06Dokument3 SeitenHuawei APE4518R20v06Marcelo Hernan LaurettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Filter (Part I)Dokument28 SeitenActive Filter (Part I)Dr-Ahmed ElkoranyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB REPORT 3 - FILTER DESIGN AND ANALYSISDokument26 SeitenLAB REPORT 3 - FILTER DESIGN AND ANALYSISgauruath_8967% (3)
- Baghdad Last: Table of Content: IDokument3 SeitenBaghdad Last: Table of Content: Ikhatab tawfeeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Band-pass and band-rejection filter design responsesDokument1 SeiteBand-pass and band-rejection filter design responseslecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8: Butterworth FiltersDokument5 SeitenLab 8: Butterworth FiltersJimtho MiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENTC 3320: Active FiltersDokument60 SeitenENTC 3320: Active FiltersAbdullah NisarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENTC 3320: Active FiltersDokument60 SeitenENTC 3320: Active FiltersMichael DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProblemSheet Chapter 8Dokument2 SeitenProblemSheet Chapter 8Bhen CalugayNoch keine Bewertungen
- HA122 DatasheetDokument52 SeitenHA122 DatasheetAndi Awal JanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Stub and LC Matching CircuitDokument31 SeitenDouble Stub and LC Matching CircuitVijay ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-RC Filter Circuits and LCR Resonance CircuitsDokument13 Seiten2-RC Filter Circuits and LCR Resonance CircuitsaxelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.5.1 Second-Order Band-Pass Filter: A(s) A 1 S 1 S 1 SDokument1 Seite16.5.1 Second-Order Band-Pass Filter: A(s) A 1 S 1 S 1 Slecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- (MRK) Active Filter Design PDFDokument130 Seiten(MRK) Active Filter Design PDFDharmveer ModiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3Dokument66 SeitenChap 3Azimah Zainal OfficiqlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Stage Amplifier: Level-1Dokument6 SeitenMulti Stage Amplifier: Level-1kalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System Design by Using Frequency Response ApproachDokument73 SeitenControl System Design by Using Frequency Response ApproachDipti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.7 All-Pass Filter Design: Figure 16-41. Comparison of Q Between Passive and Active Band-Rejection FiltersDokument8 Seiten16.7 All-Pass Filter Design: Figure 16-41. Comparison of Q Between Passive and Active Band-Rejection FiltersseleneedithNoch keine Bewertungen
- N DSP6Dokument10 SeitenN DSP6sadhanatiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Filter Design by EricksonDokument49 SeitenInput Filter Design by EricksonshrikrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 2 Amplifier Frequency ResponseDokument33 SeitenUnit - 2 Amplifier Frequency ResponsePrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture18 18032019 PDFDokument132 SeitenLecture18 18032019 PDFabcdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Band Pass Filter DesignDokument11 SeitenActive Band Pass Filter DesignFarhan NitrateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sop DiareDokument22 SeitenSop DiareABEL SAINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- SC Chapter 15 - FiltersDokument35 SeitenSC Chapter 15 - Filterslornfate100% (1)
- Final Power Electronics Formulas ListDokument8 SeitenFinal Power Electronics Formulas ListJuan RaoofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act 17300Dokument371 SeitenAct 17300muhammad abdussalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Sciences EEE F111Dokument39 SeitenElectrical Sciences EEE F111Kriti TambareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.4.2.2 Multiple Feedback Topology: Figure 16-29. Second-Order MFB High-Pass FilterDokument25 Seiten16.4.2.2 Multiple Feedback Topology: Figure 16-29. Second-Order MFB High-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.1 Filters LPFDokument33 Seiten6.1 Filters LPFThanh HàNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP FiltersDokument60 SeitenDSP Filterspayalpaliwal014939Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16Dokument21 SeitenChapter 16Mahmoud AbdelghanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency Response Curve AnalysisDokument21 SeitenFrequency Response Curve AnalysisAC vlogNoch keine Bewertungen
- FilterDokument20 SeitenFilterAsheque IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Feedback CircuitDokument7 SeitenMultiple Feedback CircuitbelmontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-III Adc & DacDokument20 SeitenUnit-III Adc & DacK Krishna Murthy 184450Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseDokument28 SeitenAmplifier Frequency ResponseBenj MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LNA - Active Bandpass Filter For Receiver-Indicator of Glonass+GPSDokument4 SeitenLNA - Active Bandpass Filter For Receiver-Indicator of Glonass+GPSWael Abdelgadir AbdelazizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dac & Adc SCDokument4 SeitenDac & Adc SCsameer rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.multistage AmplifiersDokument17 Seiten11.multistage AmplifiersNitin Mehta - 18-BEC-030Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4Dokument53 SeitenLecture 4marcelineparadzaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor Active High Pass Filter Electronics NotesDokument2 SeitenTransistor Active High Pass Filter Electronics NotesRenato DeákNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEC MCQ Unit5Dokument7 SeitenAEC MCQ Unit5Chinmai NimgadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranes - Notable Features - RT775Dokument1 SeiteCranes - Notable Features - RT775lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAT Iflex5 Parte005Dokument2 SeitenPAT Iflex5 Parte005lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
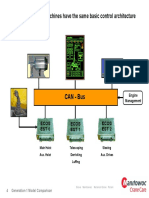
- All Generation 1 Machines Have The Same Basic Control ArchitectureDokument1 SeiteAll Generation 1 Machines Have The Same Basic Control Architecturelecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAT Iflex5 Parte004Dokument2 SeitenPAT Iflex5 Parte004lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- F 10 KHZ 1.036 9.653 KHZ F 10 KHZ 1.036 10.36 KHZ: Filter 1: Filter 2Dokument1 SeiteF 10 KHZ 1.036 9.653 KHZ F 10 KHZ 1.036 10.36 KHZ: Filter 1: Filter 2lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notice: Service Manual iFLEX5Dokument2 SeitenNotice: Service Manual iFLEX5lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAT Iflex5 Parte003Dokument2 SeitenPAT Iflex5 Parte003lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Band-pass and band-rejection filter design responsesDokument1 SeiteBand-pass and band-rejection filter design responseslecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Filter: R 1 2 F A C 1 2 10 HZ 0.756 100 10 F 2.105 KDokument1 SeiteSecond Filter: R 1 2 F A C 1 2 10 HZ 0.756 100 10 F 2.105 Klecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 16-6. Fourth-Order Butterworth Band-Pass FilterDokument1 SeiteExample 16-6. Fourth-Order Butterworth Band-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- A) A DW) A) A DW +: Table 16-2. Values of For Different Filter Types and Different QsDokument1 SeiteA) A DW) A) A DW +: Table 16-2. Values of For Different Filter Types and Different Qslecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 16-5. Second-Order MFB Band-Pass Filter With F 1 KHZDokument1 SeiteExample 16-5. Second-Order MFB Band-Pass Filter With F 1 KHZlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.5.1.2 Multiple Feedback Topology: Figure 16-34. MFB Band-PassDokument1 Seite16.5.1.2 Multiple Feedback Topology: Figure 16-34. MFB Band-Passlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.5.1 Second-Order Band-Pass Filter: A(s) A 1 S 1 S 1 SDokument1 Seite16.5.1 Second-Order Band-Pass Filter: A(s) A 1 S 1 S 1 Slecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.5.1.1 Sallen-Key TopologyDokument1 Seite16.5.1.1 Sallen-Key Topologylecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low-Pass to Band-Pass Filter TransitionDokument1 SeiteLow-Pass to Band-Pass Filter Transitionlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- C C 4b A: Example 16-2. Second-Order Unity-Gain Tschebyscheff Low-Pass FilterDokument1 SeiteC C 4b A: Example 16-2. Second-Order Unity-Gain Tschebyscheff Low-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- A C C A 2C C R CC B 2C C R CC: High-Pass Filter DesignDokument26 SeitenA C C A 2C C R CC B 2C C R CC: High-Pass Filter Designlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op Amps22Dokument24 SeitenOp Amps22lecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.4.2.2 Multiple Feedback Topology: Figure 16-29. Second-Order MFB High-Pass FilterDokument25 Seiten16.4.2.2 Multiple Feedback Topology: Figure 16-29. Second-Order MFB High-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- First-Order High-Pass Filter Circuit Diagrams and Transfer FunctionsDokument1 SeiteFirst-Order High-Pass Filter Circuit Diagrams and Transfer Functionslecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Filter: Figure 16-21. Second-Order Unity-Gain Sallen-Key Low-Pass FilterDokument1 SeiteSecond Filter: Figure 16-21. Second-Order Unity-Gain Sallen-Key Low-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 16-24. Developing The Gain Response of A High-Pass FilterDokument21 SeitenFigure 16-24. Developing The Gain Response of A High-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjustable second-order low-pass filter transfer function and coefficientsDokument1 SeiteAdjustable second-order low-pass filter transfer function and coefficientslecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.4 High-Pass Filter Design: Figure 16-22. Fifth-Order Unity-Gain Butterworth Low-Pass FilterDokument1 Seite16.4 High-Pass Filter Design: Figure 16-22. Fifth-Order Unity-Gain Butterworth Low-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- C C 4b A: Example 16-2. Second-Order Unity-Gain Tschebyscheff Low-Pass FilterDokument1 SeiteC C 4b A: Example 16-2. Second-Order Unity-Gain Tschebyscheff Low-Pass Filterlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op Amps13 PDFDokument1 SeiteOp Amps13 PDFlecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 16-15. General Sallen-Key Low-Pass Filter: A(s) A 1 C R R 1 A R C S R R C C SDokument1 SeiteFigure 16-15. General Sallen-Key Low-Pass Filter: A(s) A 1 C R R 1 A R C S R R C C Slecuellarq85gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen