Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SVRphy14 PDF
Hochgeladen von
anoetaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SVRphy14 PDF
Hochgeladen von
anoetaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
*01 Forces&Energy (8-45).
qxd 25/1/07 5:09 pm Page 14
Momentum
Key words
1 Transferred momentum
momentum
Newton’s laws of
motion
vector
velocity
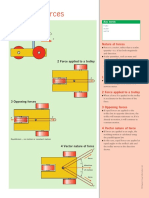
Momentum A B
● Momentum, a vector quantity is the B A
product of an object’s mass and
velocity.
● It is measured in kilogram meters per 2 Collision of two cars
second, kgms-1 or Newton seconds.
● Following Newton’s laws of motion, a
system’s total momentum is constant
unless a net external force acts. This
applies in cases of impact and Before:
disintegration. momentum to left + momentum
to right = zero
1 Transferred momentum After:
● The momentum of pendulum A is total momentum is zero
transferred to pendulum B.
2 Collision of two cars 3 Rocket propulsion
g f f liquid hydrogen
● If the cars were traveling with equal i g liquid oxygen
momentum in opposite directions
before impact they would remain at j h
the point of impact as the net
h combustion chamber
momentum would be zero. Rate of change of rocket momentum + rate of change of i nozzle
● If one car had more momentum than momentum of ejected hot gases j hot gasses
the other the cars would continue to
move after impact.
4 Conservation of momentum
3 Rocket propulsion A B
● The momentum of the rocket moving
in one direction is equal to the
momentum of the exhaust gases
moving in the opposite direction.
4 Conservation of
momentum Two mechanics trolleys that can be pushed apart by a compressed spring:
mass of trolley A = 2 × mass of trolley B
● In momentum calculations, movement
a trolley runway
to the right is considered positive, b point where trolleys physically separate +ve b
movement to the left negative.
● When the spring is released the
a trolley B
trolleys move apart as shown.
● Since momentum is conserved
momentum of trolley A + momentum
© Diagram Visual Information Ltd.
Velocity
of trolley B = 0. Time
Spring is released by hitting with a hammer 0
● Mass of trolley A = 2m; velocity = - vA.
Its momentum = - 2m x vA. Mass of
trolley B = m; velocity vB. Its trolley A
momentum = mvB.
As momentum is conserved, –ve
- 2mvA + mvB = 0; 2mvA = mvB Trolleys move apart Velocity-time graph
Trolley A's velocity is half trolley B's.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Quality Control of Rebar Couplers in Splicing of Reinforcement BarsDokument12 SeitenQuality Control of Rebar Couplers in Splicing of Reinforcement BarsDong-Yong KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Parts List: Converter CL9672-18 4265618Dokument42 SeitenService Parts List: Converter CL9672-18 4265618Chester Dalitso Mwanza100% (3)
- SVRphy19 PDFDokument1 SeiteSVRphy19 PDFanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRphy18 PDFDokument1 SeiteSVRphy18 PDFanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Machines 2: 1 Pulley SystemsDokument1 SeiteSimple Machines 2: 1 Pulley SystemsanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRphy9 PDFDokument1 SeiteSVRphy9 PDFanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRphy16 PDFDokument1 SeiteSVRphy16 PDFanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Fall and Terminal Velocity: 1 Gravity: Action at A DistanceDokument1 SeiteFree Fall and Terminal Velocity: 1 Gravity: Action at A DistanceanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRphy11 PDFDokument1 SeiteSVRphy11 PDFanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio114 - MolluscaDokument1 SeiteSVRbio114 - MolluscaanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's First Law of MotionDokument1 SeiteNewton's First Law of MotionanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRphy8 PDFDokument1 SeiteSVRphy8 PDFanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archimedes' Pump: Martin Gardner, Hendersonville, NC 28792Dokument1 SeiteArchimedes' Pump: Martin Gardner, Hendersonville, NC 28792anoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio126 MammaliaDokument1 SeiteSVRbio126 MammaliaanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
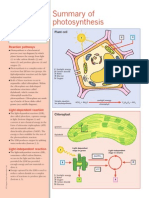
- Summary of Photosynthesis: Reaction PathwaysDokument1 SeiteSummary of Photosynthesis: Reaction PathwaysanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
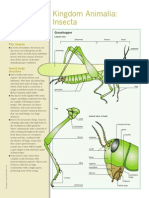
- Kingdom Animalia: Insecta: The InsectsDokument1 SeiteKingdom Animalia: Insecta: The InsectsanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio107 - CnidariaDokument1 SeiteSVRbio107 - CnidariaanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio120 EchinodermataDokument1 SeiteSVRbio120 EchinodermataanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
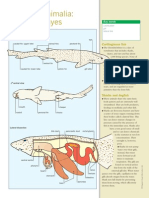
- Kingdom Animalia: Chondrichthyes: DogfishDokument1 SeiteKingdom Animalia: Chondrichthyes: DogfishanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio118-Chilopoda and DiplopodaDokument1 SeiteSVRbio118-Chilopoda and DiplopodaanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom Animalia: ClassificationDokument1 SeiteKingdom Animalia: ClassificationanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom Animalia: Annelida: EarthwormDokument1 SeiteKingdom Animalia: Annelida: EarthwormanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio123 Kingdom AnimaliaDokument1 SeiteSVRbio123 Kingdom AnimaliaanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio129-Nutrition Leaf StructureDokument1 SeiteSVRbio129-Nutrition Leaf StructureanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVRbio168 Respiration LungsDokument1 SeiteSVRbio168 Respiration LungsanoetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.N o Committee Number Committee Name Published StandardsDokument1 SeiteS.N o Committee Number Committee Name Published Standardsnarendar.1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Chassis Cab: Owner'S ManualDokument420 Seiten2022 Chassis Cab: Owner'S Manualmbadarau1206Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report: Fountain Design: October 2020Dokument32 SeitenProject Report: Fountain Design: October 2020alaa delewarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Pulsation Damper With A Reciprocating PumpDokument4 SeitenUsing Pulsation Damper With A Reciprocating PumpIkechukwu EjimNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEA PHE Fullywelded Phe en 1Dokument12 SeitenGEA PHE Fullywelded Phe en 1gemagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B16.5Dokument11 SeitenAsme B16.5jacquesmayol100% (1)
- Contourline / Pureline Warming Drawer: 8 Shown Above: Esw 6114Dokument5 SeitenContourline / Pureline Warming Drawer: 8 Shown Above: Esw 6114junjaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- JCTN SampleDokument8 SeitenJCTN Samplepalaniraj pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 4 Mesin FluidaDokument23 SeitenPart 4 Mesin FluidaARFAI020797Noch keine Bewertungen
- University Course Lecture NotesDokument332 SeitenUniversity Course Lecture NotesAlFakir Fikri AlTakiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- s5113 Mm39 F.O Supply UnitDokument408 Seitens5113 Mm39 F.O Supply UnitJorge AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Van de Graaff GeneratorDokument10 SeitenVan de Graaff GeneratorJihad AnadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Diesel ManualsDokument21 SeitenCAT Diesel Manualsaaguilarm100% (1)
- 15730-DX Cooling Units Rev 01Dokument10 Seiten15730-DX Cooling Units Rev 01abdullah amanullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Ribbed SlabDokument12 SeitenAnalysis of Ribbed Slabmickymat100% (1)
- SG6250HV-MV Container InstallationDokument3 SeitenSG6250HV-MV Container InstallationJesica SantibañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Lit-Up PDFDokument2 SeitenBoiler Lit-Up PDFHoncho Abhi Sinha100% (1)
- Internal Lubricating Oil System: GeneralDokument3 SeitenInternal Lubricating Oil System: GeneralAtanasio PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual: F2 SeriesDokument36 SeitenService Manual: F2 SeriesPramono DamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Line Catalog: P-SeriesDokument44 SeitenFull Line Catalog: P-Seriesyoopr2Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDF 5 Mechanics of DBDokument16 SeitenPDF 5 Mechanics of DBRizette PaloganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remanufactured Transmissions, Spare Parts, and Kits Catalog: 6S-750 Diesel UnitsDokument11 SeitenRemanufactured Transmissions, Spare Parts, and Kits Catalog: 6S-750 Diesel UnitsFernando CabildoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOP Choke Man Inspection ProcedureDokument13 SeitenBOP Choke Man Inspection ProcedureAhmed Imtiaz Rao100% (2)
- 9700-01053 SS Op Manual 2014-10-27 To PresentDokument48 Seiten9700-01053 SS Op Manual 2014-10-27 To PresentDaniel Castillo PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyundai H380 TrucksDokument12 SeitenHyundai H380 TrucksIrfan SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetic 2520acid 2520 - Design 2520of 2520equipments PDFDokument41 SeitenAcetic 2520acid 2520 - Design 2520of 2520equipments PDFTanuj HandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesDokument77 SeitenTypes of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesJyothish VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.daily Report Manufacture Steel Structure. TGL 09.07 2Dokument133 Seiten1.daily Report Manufacture Steel Structure. TGL 09.07 2Rusman LumbantoruanNoch keine Bewertungen