Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Recommended limiting values for composition and properties of concrete
Hochgeladen von
Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Recommended limiting values for composition and properties of concrete
Hochgeladen von
Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Page 65
EN 206-1:2000
Table F.1 - Recommended limiting values for composition and properties of concrete
Exposure classes
No risk
of corro- Chloride-induced corrosion
sion or Carbonation-induced corrosion Sea water Chloride other Freeze/thaw attack Aggressive chemical envi-
attack than from sea ronments
water
X0 XC 1 XC 2 XC 3 XC 4 XS 1 XS 2 XS 3 XD 1 XD 2 XD 3 XF 1 XF 2 XF 3 XF 4 XA 1 XA 2 XA 3
Maximum --- 0,65 0,60 0,55 0,50 0,50 0,45 0,45 0,55 0,55 0,45 0,55 0,55 0,50 0,45 0,55 0,50 0,45
w/c
Minimum C12/15 C20/25 C25/30 C30/37 C30/37 C30/37 C35/45 C35/45 C30/37 C30/37 C35/45 C30/37 C25/30 C30/37 C30/37 C30/37 C30/37 C35/45
strength
class
Minimum --- 260 280 280 300 300 320 340 300 300 320 300 300 320 340 300 320 360
cement
content
(kg/m3)
Minimum air --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- 4,0a 4,0a 4,0a --- --- ---
content (%)
Other Aggregate in accordance with Sulfate-resisting
requirements prEN 12620:2000 with sufficient cementb
freeze/thaw resistance
a
Where the concrete is not air entrained, the performance of concrete should be tested according to an appropriate test method in comparison with a concrete for which
freeze/thaw resistance for the relevant exposure class is proven.
b
When SO24- leads to exposure classes XA2 and XA3, it is essential to use sulfate-resisting cement. Where cement is classified with respect to sulfate resistance,
moderate or high sulfate-resisting cement should be used in exposure class XA2 (and in exposure class XA1 when applicable) and high sulfate-resisting cement should
be used in exposure class XA3.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fly Ash - WikipediaDokument12 SeitenFly Ash - WikipediaBabar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ab Initio Interview Questions - HTML PDFDokument131 SeitenAb Initio Interview Questions - HTML PDFdigvijay singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety in Manufacturing: Ergonomics: Awkward PosturesDokument2 SeitenSafety in Manufacturing: Ergonomics: Awkward PosturesprashanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIS2103-202220-Group Project - FinalDokument13 SeitenCIS2103-202220-Group Project - FinalMd. HedaitullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Exposure Classes Sept2018 PDFDokument5 SeitenConcrete Exposure Classes Sept2018 PDFMohd.irfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chloride Attack On ConcreteDokument12 SeitenChloride Attack On Concretevikram kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROTON Preve 2012 On 4 DR Sal 1.6 Premium (CFE) AUTO 138Bhp (A) (04/12-)Dokument12 SeitenPROTON Preve 2012 On 4 DR Sal 1.6 Premium (CFE) AUTO 138Bhp (A) (04/12-)bluhound1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lifting Plan GuidelinesDokument45 SeitenLifting Plan GuidelinesFerry H. Sitohang100% (5)
- Concrete Exposure Classes A23.1-19Dokument7 SeitenConcrete Exposure Classes A23.1-19Steven Sebastian100% (1)
- Why The BS 8500 Durability Tables Are The Way They Are-Concrete June2016Dokument4 SeitenWhy The BS 8500 Durability Tables Are The Way They Are-Concrete June2016Vipin Kumar ParasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldVon EverandHydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Characterisation of self-flowing refractory material containing microsilicaDokument6 SeitenCharacterisation of self-flowing refractory material containing microsilicaAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement PDFDokument44 SeitenCement PDFEutimos ParamatatyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Britannia FinalDokument39 SeitenBritannia FinalNitinAgnihotri100% (1)
- 023 - Isomerization Unit (ISOM)Dokument5 Seiten023 - Isomerization Unit (ISOM)Raghavan VenkatramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 BPI Employee Union-Davao V BPI - DigestDokument1 Seite3 BPI Employee Union-Davao V BPI - DigestRonyr RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS en 206Dokument7 SeitenBS en 206amit_halcrow100% (1)
- 91 SOC Interview Question BankDokument3 Seiten91 SOC Interview Question Bankeswar kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SABIC ConcreteDokument14 SeitenSABIC ConcreteBasker BaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bro Sika Waterproofing BrochureDokument25 SeitenBro Sika Waterproofing BrochureArya ChunataNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Silos FailDokument14 SeitenHow Silos FailMedhat Hasanain100% (2)
- Manual Roof Drainage System HRWallingford SR620Dokument78 SeitenManual Roof Drainage System HRWallingford SR620hillamngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Boq AiiapDokument170 SeitenCivil Boq AiiapMuhammad ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unlock-Durcomet 100 (CD-4MCu)Dokument8 SeitenUnlock-Durcomet 100 (CD-4MCu)Dimas Pratama PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proportioning of A Concrete MixDokument11 SeitenProportioning of A Concrete MixSude FilizNoch keine Bewertungen
- DuplexDokument8 SeitenDuplexLoru GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de Propiedades de ConcretoDokument1 SeiteTabla de Propiedades de ConcretoHumberto MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Resistance Chart FlowserveDokument8 SeitenCorrosion Resistance Chart FlowserveLuis SudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duplex Steel (CD-4MCu)Dokument8 SeitenDuplex Steel (CD-4MCu)Anonymous CMS3dL1TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water-Soluble Salts - APPENDIXDokument1 SeiteWater-Soluble Salts - APPENDIXFelipe montanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Bullentin Rel. 2 CompacSOL-dataDokument4 Seiten2011 Bullentin Rel. 2 CompacSOL-dataBranko TodorovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05the Application of Nitrate Based Hi Density Completion Fluid Case Study of Workover in JRB 01 Well and Jas 02Dokument13 Seiten05the Application of Nitrate Based Hi Density Completion Fluid Case Study of Workover in JRB 01 Well and Jas 02Herry SuhartomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAES Q 001 Table ExposureDokument4 SeitenSAES Q 001 Table ExposureKhurram ShehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanicro35 Datasheet v9Dokument8 SeitenSanicro35 Datasheet v9cehamos882Noch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Formula Notes 1 17Dokument36 SeitenRCC Formula Notes 1 17Wajahat KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Christoph MuellerDokument55 Seiten03 Christoph MuellerKaren LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultra Sanicro35 Datasheet FINAL Digital-1Dokument6 SeitenUltra Sanicro35 Datasheet FINAL Digital-1Vaibhav KaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO M-80 (Año 2008)Dokument6 SeitenAASHTO M-80 (Año 2008)Roberto VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADDMIX 55-v3Dokument2 SeitenADDMIX 55-v3Ankita Baban GavadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2.1 Mixed Metal Oxide Tubular Anodes Rev 1Dokument2 Seiten2.2.1 Mixed Metal Oxide Tubular Anodes Rev 1Soltani AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Durability Requirement Based On ACI-318-19Dokument14 SeitenConcrete Durability Requirement Based On ACI-318-19MIL RABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitigation of Alkali-Silica Reaction While Using Highly Reactive Aggregates With Class C Fly Ash and Reduction in Water To Cementitious RatioDokument6 SeitenMitigation of Alkali-Silica Reaction While Using Highly Reactive Aggregates With Class C Fly Ash and Reduction in Water To Cementitious RatioArifsalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanbook General Detailing EC2 - English - 201223 NEWDokument24 SeitenHanbook General Detailing EC2 - English - 201223 NEWnguyendungnguyen92Noch keine Bewertungen
- CTB05 - Corrosion Resistance of Zinc in Water Sept 02Dokument2 SeitenCTB05 - Corrosion Resistance of Zinc in Water Sept 02Ravinesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex 4.1 - Technical Specifications - Civil WorksDokument6 SeitenAnnex 4.1 - Technical Specifications - Civil WorksMW ALSABRINoch keine Bewertungen
- Durimet 20: Bulletin A/1mDokument6 SeitenDurimet 20: Bulletin A/1mCarlosAlbertoRibeiroRuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Mix DesignDokument6 SeitenReport On Mix DesignForood Torabian IsfahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRPC Khaleej PCDokument2 SeitenSRPC Khaleej PCUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steelplant Refractories Containing Alphabond Hydratable Alumina BindersDokument31 SeitenSteelplant Refractories Containing Alphabond Hydratable Alumina BinderssonalisabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual Chapter IV - Portland CementDokument13 SeitenLab Manual Chapter IV - Portland Cementsalil dubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B320-60 (Reapproved 2013) PDFDokument4 SeitenB320-60 (Reapproved 2013) PDFStephen RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Rust - Article 2 PDFDokument11 SeitenSteel Rust - Article 2 PDFBalasubramanian MahadevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM C1097 Standard Specification For Hydrated Lime For Use in Asphalt Cement or Bituminous Paving MixturesDokument2 SeitenASTM C1097 Standard Specification For Hydrated Lime For Use in Asphalt Cement or Bituminous Paving MixturesRafael EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 A6 Concrete MixDokument33 Seiten3 A6 Concrete MixBabu SundararamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACI 318M-19 Exposure CategoriesDokument9 SeitenACI 318M-19 Exposure CategoriesMohammed AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN1361R2Dokument22 SeitenTN1361R2ClydeUnionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super Duplex Stainless Steel: Excellent Engineering SolutionsDokument3 SeitenSuper Duplex Stainless Steel: Excellent Engineering SolutionsshyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.4 Bituminous Materials: 3.4.1 DescriptionDokument5 Seiten3.4 Bituminous Materials: 3.4.1 DescriptionSujon AhmmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 1097-1 - 95 QzewotctotuDokument1 SeiteC 1097-1 - 95 Qzewotctotumohammad1361Noch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Formula Notes 66Dokument35 SeitenRCC Formula Notes 66Pavan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm C1097Dokument1 SeiteAstm C1097pfta_Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM C 1097 Hydrated Lime-Specification For Asphalt WorksDokument1 SeiteASTM C 1097 Hydrated Lime-Specification For Asphalt WorksVijayakrishna SingamsettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Cement Concrete Specifications AppendixDokument94 SeitenHydraulic Cement Concrete Specifications Appendixعلاء جبارNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 Portland CementDokument13 SeitenLecture 7 Portland Cementsalil dubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet-Sanicro-35-En-V2022-10-26 06 - 00 Version 1Dokument12 SeitenDatasheet-Sanicro-35-En-V2022-10-26 06 - 00 Version 1akbarul muttaqinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specifying For Performance: EngineeringDokument5 SeitenSpecifying For Performance: EngineeringJohn ShaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Carbide: Nitride Bonded (Cast/pressed), Ramming CFR, Castable CFCDokument3 SeitenSilicon Carbide: Nitride Bonded (Cast/pressed), Ramming CFR, Castable CFCdebasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlorimet 2 (N-7M) and Chlorimet 3 (CW-6M)Dokument6 SeitenChlorimet 2 (N-7M) and Chlorimet 3 (CW-6M)gullenariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1807 VS 1 Performance SpecificationsDokument89 Seiten1807 VS 1 Performance SpecificationsNiko TassigiannakisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latest Developments in Concrete StandardizationDokument48 SeitenLatest Developments in Concrete StandardizationDejana AnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure CAB O SIL PDMS Treated Fumed SilicasDokument4 SeitenBrochure CAB O SIL PDMS Treated Fumed Silicashery siregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0404501-H&W-Trojan AW SeriesDokument1 Seite0404501-H&W-Trojan AW SeriesHyungTae JangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion of Embedded Metal: (Carbonation-Induced and Chloride-Induced Corrosion)Dokument37 SeitenCorrosion of Embedded Metal: (Carbonation-Induced and Chloride-Induced Corrosion)Jagannathan KNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMO+Diesel+Motor+OilsDokument9 SeitenDMO+Diesel+Motor+OilssrcattozziNoch keine Bewertungen
- DYWIDAG Flat Multiplane Anchorage: Technical DataDokument1 SeiteDYWIDAG Flat Multiplane Anchorage: Technical DataAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SaltDokument2 SeitenSaltAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buiding Regulation Doc HDokument64 SeitenBuiding Regulation Doc HShailendra RamchurnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Slide Version 24 Sept 03Dokument6 SeitenAir Slide Version 24 Sept 03Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDIFICE Catalog 2014 PDFDokument16 SeitenEDIFICE Catalog 2014 PDFAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSI Geotechnic en PDFDokument44 SeitenDSI Geotechnic en PDFAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 196 NFGNDokument10 Seiten196 NFGNAnton FatoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing Guide Weld SymbolsDokument4 SeitenDrawing Guide Weld SymbolsAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Vapour Effect On ConcreteDokument225 SeitenWater Vapour Effect On ConcreteAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bond Strength of Concrete829-2520-1-PbDokument18 SeitenBond Strength of Concrete829-2520-1-PbjpkedahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bond Strength of Concrete829-2520-1-PbDokument18 SeitenBond Strength of Concrete829-2520-1-PbjpkedahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer 2013Dokument20 SeitenSummer 2013Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Production ProcessDokument2 SeitenCement Production ProcessNishant Ajitsaria100% (1)
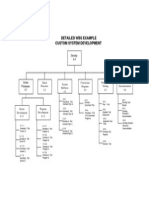
- Detailed WBS Example for Custom System DevelopmentDokument1 SeiteDetailed WBS Example for Custom System DevelopmentAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies: Combustion of Corn Stover Bales in A Small 146-kW BoilerDokument10 SeitenEnergies: Combustion of Corn Stover Bales in A Small 146-kW BoilerAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apron FeederDokument4 SeitenApron FeederMineria28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Heaters and Pre Calci NersDokument6 SeitenPre Heaters and Pre Calci NersPandega Ikhramul UzlahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies: Combustion of Corn Stover Bales in A Small 146-kW BoilerDokument10 SeitenEnergies: Combustion of Corn Stover Bales in A Small 146-kW BoilerAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Memorize 47 PMP Processes - Using PMBOK 5th Edition ReferenceDokument4 SeitenHow To Memorize 47 PMP Processes - Using PMBOK 5th Edition ReferenceAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomass Burn CharacteristicsDokument7 SeitenBiomass Burn CharacteristicsAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- M150Dokument9 SeitenM150Ajit ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Exterior Doors Inspection ChecklistDokument10 Seiten5 Exterior Doors Inspection ChecklistAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dewatering Refractory Castable Monoliths Aachen 1999Dokument11 SeitenDewatering Refractory Castable Monoliths Aachen 1999Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSCI5273 PS3 KiranJojareDokument11 SeitenCSCI5273 PS3 KiranJojareSales TeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agro Chems MrRGAgarwalDokument17 SeitenAgro Chems MrRGAgarwalapi-3833893Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product Models Comparison: Fortigate 1100E Fortigate 1800FDokument1 SeiteProduct Models Comparison: Fortigate 1100E Fortigate 1800FAbdullah AmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDokument11 SeitenCapital Asset Pricing ModelrichaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Vulnerability Index Helps Emergency ManagementDokument24 SeitenSocial Vulnerability Index Helps Emergency ManagementDeden IstiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS221 - Artificial Intelligence - Machine Learning - 3 Linear ClassificationDokument28 SeitenCS221 - Artificial Intelligence - Machine Learning - 3 Linear ClassificationArdiansyah Mochamad NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aegis SGR BrochureDokument2 SeitenAegis SGR BrochureAmazonas ManutençãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modicon Quantum - 140DDI85300Dokument5 SeitenModicon Quantum - 140DDI85300Samdan NamhaisurenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Lecture PSBCDokument83 SeitenPython Lecture PSBCPedro RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Fluid-Conveying Beams: Governing Equations and Finite Element ModelsDokument22 SeitenDynamics of Fluid-Conveying Beams: Governing Equations and Finite Element ModelsDario AcevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MongoDB vs RDBMS - A ComparisonDokument20 SeitenMongoDB vs RDBMS - A ComparisonShashank GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment # 4 26 CH 22Dokument6 SeitenAssignment # 4 26 CH 22Ibrahim AbdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accor vs Airbnb: Business Models in Digital EconomyDokument4 SeitenAccor vs Airbnb: Business Models in Digital EconomyAkash PayunNoch keine Bewertungen
- FTC470XETDokument2 SeitenFTC470XETDecebal ScorilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS Corrosion SlidesDokument36 SeitenSS Corrosion SlidesNathanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Advances in Mobile Robotics - TopalovDokument464 SeitenRecent Advances in Mobile Robotics - TopalovBruno MacedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Selling ProcessDokument21 SeitenPersonal Selling ProcessRuchika Singh MalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kj1010-6804-Man604-Man205 - Chapter 7Dokument16 SeitenKj1010-6804-Man604-Man205 - Chapter 7ghalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Waste On GHG Gas in MalaysiaDokument10 SeitenSolid Waste On GHG Gas in MalaysiaOng KaiBoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam SolutionsDokument11 SeitenMidterm Exam SolutionsPatrick Browne100% (1)
- Torta de Riso Business PlanDokument25 SeitenTorta de Riso Business PlanSalty lNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCW Armored Composite OMNICABLEDokument2 SeitenCCW Armored Composite OMNICABLELuis DGNoch keine Bewertungen