Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tutorial Nucleic Acid
Hochgeladen von
Nazirah Arba'inOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tutorial Nucleic Acid
Hochgeladen von
Nazirah Arba'inCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tutorial Nucleic Acid
Name: Matric number:
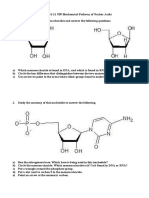
1. Draw a structural formula for the DNA dinucleotide TG that is phosphorylated at the 5’-end only.
2. Name the type of covalent bonds joining monomers in these biopolymers?
a. Protein-
b. Nucleic acid-
3. The DNA of sea urchins contains about 32% A. What percentage of the other three bases would
you expect in sea urchin DNA? Explain.
4. What is the difference between DNA & RNA?
5. What nonapeptide is coded for by the following fragment of mRNA?
a. 5’-AAA-GUU-GGC-UAC-CCC-GGA-AUG-GUG-GUC-3’
6. What is the sequence of bases in the template strand of DNA that codes for mRNA in 5(a)?
7. What is the sequence of bases in the sense strand of DNA that codes for mRNA in 5(a)?
8. Name amino acids that do the following ribonucleotide triplets code?
a. AAU-
b. GAG-
c. UCC-
9. The job of tRNA is to do which one of the following? (circle it)
a. Read the mRNA and tell the ribosome to bring a specific amino acid to the growing
protein
b. Bring any amino acid to the ribosome so it can be added to the growing protein
c. Bring a specific amino acid to the ribosome so it can be added to the growing protein
d. Bring a codon to the ribosome so it can be added to the growing protein
10. What enzyme is used in polymerase chain reaction (PCR). What is the function of this enzyme
and what unique feature does it possess that is critical for the success of PCR.
11. Why is PCR helpful to forensic scientists? And how does it help them solve crimes?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Preclinical Biochemistry and Medical Genetics Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Von EverandPreclinical Biochemistry and Medical Genetics Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- RNA Methodologies: A Laboratory Guide for Isolation and CharacterizationVon EverandRNA Methodologies: A Laboratory Guide for Isolation and CharacterizationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encode SequenceDokument212 SeitenEncode SequenceRaj Naithik100% (1)
- Gene Expression AssignmentDokument5 SeitenGene Expression AssignmentLauren EatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 1St Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument32 SeitenGenetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 1St Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFPhilipHoustoncamy100% (12)
- Self Quizzes: See This Figure Below Then Answer The Question (8-10)Dokument4 SeitenSelf Quizzes: See This Figure Below Then Answer The Question (8-10)Dr DolittleNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Dokument6 SeitenSEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Brian Chi Yan Cheng 鄭智仁Noch keine Bewertungen
- Translation Notes SheetDokument5 SeitenTranslation Notes SheetKelsey BakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Translation - Transcription WorksheetDokument7 SeitenTranslation - Transcription Worksheethanatabbal19Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH4 Genetic Material and Protein SynthesisDokument6 SeitenCH4 Genetic Material and Protein SynthesisMohamed Ali AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To ProteinDokument18 SeitenChapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To Protein蔡旻珊100% (1)
- Biology A Level, MCQ Problem Sets, Protein Synthesis, Dna and RnaDokument5 SeitenBiology A Level, MCQ Problem Sets, Protein Synthesis, Dna and RnaAcep AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directions: Read Each Question Carefully. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer OnDokument23 SeitenDirections: Read Each Question Carefully. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer OnFreshel Arra LeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDokument5 SeitenProtein Synthesis WorksheetAlyssa Jacobs100% (3)
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDokument22 SeitenMolecular Basis of InheritancePavithraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyq Cbse 2021-1-2Dokument19 SeitenPyq Cbse 2021-1-2Yuvraj MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4 Quiz and Homework PDFDokument5 SeitenWeek 4 Quiz and Homework PDFMilkiDuranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021Dokument11 SeitenLab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021thesoccerprince.10Noch keine Bewertungen
- RnaproteinsynthesisseDokument6 SeitenRnaproteinsynthesisseapi-551950987Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsDokument20 SeitenCH 7 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsRokia GhariebNoch keine Bewertungen
- N - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeDokument5 SeitenN - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeMa Anna Cris LumongsudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possible Exam QuestionsDokument2 SeitenPossible Exam QuestionsJofreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL662 HW3Dokument5 SeitenCL662 HW3Prathamesh KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Protein Synthesis Practice WorksheetDokument4 SeitenDNA Protein Synthesis Practice WorksheetAmbrielle WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Dogma Review KEYDokument8 SeitenCentral Dogma Review KEYeula faith miracle andam0% (1)
- Genetic Analysis An Integrative Approach 1St Edition Sanders Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument34 SeitenGenetic Analysis An Integrative Approach 1St Edition Sanders Test Bank Full Chapter PDFyhenryhnorc5100% (10)
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following and Take Notes On Your PaperDokument2 SeitenProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following and Take Notes On Your PaperLemonade BlinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDU BIOINFORMATICS The Central DogmaDokument6 SeitenCDU BIOINFORMATICS The Central DogmaKrisha Mae VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceeDokument4 SeitenMolecular Basis of InheritanceePROFESSORNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNAProtein Synthesis SEDokument7 SeitenRNAProtein Synthesis SEAmbrielle WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 HandoutDokument13 Seiten2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Handoutaidar.seralinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers PGR Week7Dokument8 SeitenAnswers PGR Week7kkk13whyNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-B-5-3 - From Gene To Protein KEYDokument5 SeitenS-B-5-3 - From Gene To Protein KEYcokcreNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ MolecularDokument11 SeitenMCQ MolecularMahmOod Gh100% (2)
- Practice Problems HourlyDokument2 SeitenPractice Problems Hourlyjls tjhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch17Answers PDFDokument11 SeitenCh17Answers PDFalbert601873% (15)
- Q3 Proteins and NaDokument2 SeitenQ3 Proteins and NaAbegail FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis 2Dokument5 SeitenProtein Synthesis 2SHARIFAH BINTI HASSAN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Tut 2 Block 1Dokument10 SeitenRevision Tut 2 Block 1Matsiri ImmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Review WSDokument11 Seiten12 Review WSJASON WILLSNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Dokument14 SeitenC Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Daisy Soriano Prestoza100% (1)
- RevewipacketanswerkeyrevisedDokument5 SeitenRevewipacketanswerkeyrevisedapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class Xii Biology Chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of InheritanceDokument8 SeitenClass Xii Biology Chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of InheritanceAkshit Sharma VIII Diasy Roll no 6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nelson Biology Answers 4Dokument2 SeitenNelson Biology Answers 4ritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Analysis An Integrative Approach 1st Edition Sanders Test BankDokument38 SeitenGenetic Analysis An Integrative Approach 1st Edition Sanders Test Bankcarlarodriquezajbns100% (16)
- Ch4 Study Guide and Practice Questions - StudentDokument2 SeitenCh4 Study Guide and Practice Questions - StudentdfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 DNA and Genomics QuestionsDokument18 SeitenH2 DNA and Genomics QuestionsWesley TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Dokument5 SeitenScience-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Marl Rina EsperanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis GizmoDokument6 SeitenProtein Synthesis GizmomInd prOceSsNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Transcription and TranslationDokument132 SeitenDNA Transcription and TranslationThe GadiatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDokument5 SeitenProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Followingapi-39708077950% (2)
- RNAProteinSynthesisSEDokument6 SeitenRNAProteinSynthesisSEsmol ukeleleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentDokument27 SeitenProtein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentAydan BadalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and Translation Practice WorksheetDokument4 SeitenTranscription and Translation Practice Worksheetsmith joeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Questions - MCQDokument4 SeitenGenetics Questions - MCQManisanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biol 2334 - Molecular Biology Translation WorksheetDokument3 SeitenBiol 2334 - Molecular Biology Translation WorksheetCassandra BoduchNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCDB 1A Midterm 1 2012Dokument10 SeitenMCDB 1A Midterm 1 2012Kenji SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.central DogmaDokument4 Seiten4.central DogmaAnanthan C.RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chris Copy of Pretein Synthesis GizmoDokument6 SeitenChris Copy of Pretein Synthesis GizmoChris EffiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch11 QuizDokument6 SeitenCh11 QuizcatlovesfoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahan Tisab Fluor in Drinking WaterDokument6 SeitenBahan Tisab Fluor in Drinking WaterRatriKiranaPrabaningtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolybutadieneDokument10 SeitenPolybutadieneNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolybutadieneDokument10 SeitenPolybutadieneNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.6.4 NematodaDokument12 Seiten11.6.4 NematodaNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.6.1 2 Domain Eukarya AnimaliaDokument35 Seiten11.6.1 2 Domain Eukarya AnimaliaNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21.1 Nervous SystemDokument35 Seiten21.1 Nervous SystemNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21.1 Action PotentialDokument43 Seiten21.1 Action PotentialNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunityDokument42 SeitenImmunityNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.2 Immune Response: at The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToDokument63 Seiten11.2 Immune Response: at The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToNazirah Arba'inNoch keine Bewertungen