Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Puppets and Communication
Hochgeladen von
pvaibhy100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
49 Ansichten2 Seitenhello
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenhello
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
49 Ansichten2 SeitenPuppets and Communication
Hochgeladen von
pvaibhyhello
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
NEWS
MEETING REPORTS
Puppetry: The perfect medium for edutainment and S&T
communication
Puppetry as an ancient mode of mass scientific topic relating to environment, B. K. Tyagi (NCSTC, New Delhi) and
communication, holds immense potential biodiversity, AIDS, blood donation, Binay Krushna Pattanayak (DPEP-
even in this high tech era. The age-old women’s health, leprosy eradication, safe MHRD, New Delhi) attended the work-
folk art puppetry is the synthesis of vari- drinking water, etc. In order to develop a shop as Master Resource Persons.
ous arts: sculpture, design, music, mime, scientific storyline with authentic scien- Among others, the eminent science
dance and theatre, and the puppet itself. tific message for the puppet-show script, communicator and activist Ramesh
It is the crystallization of the imagination eminent scientists and experts were in- Kothari, C. N. Pandey (GEER Founda-
and magic of the puppeteer. vited to deliver theme-based lectures on tion), Urvi D. Mehta (Obstetrician and
The National Council for Science and the above subjects. Gynaecologist), Parul Kotdawala (Adoles
Technology Communication (NCSTC)
has introduced the art of puppetry for
science and technology communication Advantages of puppetry as a communication medium arises from the facts that
for the first time in the country and has
also developed a training module for the (a) Puppets are moving
same. Working on the edge between en-
Puppets come to life as characters, a hero to cheer or a villain to boo, a tragic figure
tertainment and education, puppets can who can move us to tears or a comic figure who will make us laugh.
both teach and persuade and their crea- With a van, a portable stage, some battery-powered amplifiers and a few people
tive potential is just waiting to be used to for the ride, they can travel even to those areas inaccessible to the mass media. Not
help communities grow and change. only do they adopt local customs and costumes but they also get accepted as friends
Understanding the concept and know- and neighbours.
ing the immense potential of the me-
dium, the Gujarat Council of Science (b) Puppets are safe
City (GCSC) organized a State Level
Since they are characters, not people, puppets are the ideal medium for discussing
Workshop on Science and Technology
sensitive issues. They create a world in which we recognize ourselves and identify
Communication Through Puppetry from
with the characters as the drama unfolds. It is an extraordinary fact that the audience
18 to 24 February 2003 at Gujarat Sci- accepts from a puppet what would have caused offence or embarrassment if it came
ence City, Ahmedabad. The workshop from a live actor. That is why puppets are now widely used in teaching on AIDS and
was catalysed and supported by NCSTC, other sensitive matters.
Department of Science and Technology,
Govt. of India. About 50 participants (c) Puppets are for children
comprising primary and secondary
Children relate to puppets easily from their earliest years because they are used to
school science teachers, leading volun-
making inanimate characters come to life. Children are puppeteers themselves from
tary organizations and Vigyan Prasar
the first time they pick up a shoe, a squeezed-out half orange or a hairbrush and
Network science club members from make them move and talk. The puppet can say what the child thinks; feel what the
different parts of Gujarat attended the child feels and share a child’s sadness. It can show a poor child who knows only
workshop. poverty and hunger that there can also be joy and love and a happy ending.
The basic objective of the week-long
workshop was to train the science teach- (d) Puppets are for adults
ers and science communicators regarding
Despite the special relationships between puppets and children, puppets speak to
the art and craft of puppet making, sci-
adults too. The roots of puppetry are deeply connected with mystery, symbolism and
entific script writing and its manipulation
religion.
for science and technology education and
communication. The participants re- (e) Puppets develop skills and teamwork in school curriculum
ceived a complete training module for
puppetry that could be used as a low cost As an educational tool, puppets have become widely accepted because of their
teaching and communication aid for ex- value in helping children in personality development and the creative opportunities
plaining various concepts and themes in the making and operation of puppets provide. Through the medium of the puppet, the
child finds himself/herself able to express thoughts, ideas, and feelings that he/she
science and social science communica-
otherwise could not have. In puppetry, the teacher finds many possibilities for
tions.
enriching most educational situations. Creating a puppet show requires a wide range
The participants were divided into five of people and special skills. Puppets create teamwork even as they entertain and
groups and each group was asked to de- inform the audience. This gives a golden opportunity for forming alliances between
velop and present one model puppet creative artists and those involved in development work.
show after the workshop on a specific
976 CURRENT SCIENCE, VOL. 84, NO. 8, 25 APRIL 2003
NEWS
cent Health Committee) and M. N. Bhad (dealing with the importance of trees), messages mixed with a right blend of
(State Project Office, DPEP, Govt. of Kahi aapko hojae toa (dealing with action and music.
Gujarat), attended the workshop and AIDS), Jaduee sashalu (dealing with
delivered resource lectures on various science teaching of magnet), Bigyan vani
NAROTTAM SAHOO
scientific topics and also participated in (dealing with safe drinking water),
various interactive sessions with the par- Anader ki hartal (dealing with the under-
ticipants. standing of the human body), etc. The Gujarat Council of Science City,
On the final day, the participants pre- puppet shows were interesting and ex- Udyog Bhavan,
sented their group-wise puppet shows citing. As they progressed, they explored Gandhinagar 382 011, India
with titles like; Tum bina jivan kanha the science and technological issues with e-mail: narottam@scity.org
Nuclear terrorism perception: Some strategies and
recommendations to handle a disaster scenario
The Indian Society for Radiation Biology assessment in the moderate dose range of xanthine oxidoreductase system producing
(ISRB) organized a workshop, ‘Radiation 1–10 Sv – doses that are not lethal but free radicals in post-irradiation period
Risk in the Age of Nuclear Terrorism’, in which can potentially cause acute effects suggesting, thereby, that inhibition of the
collaboration with Research Centre, as cells continue to survive. K. P. Mishra system may contain radiation damage in
Juelich (Germany), Health Canada, (BARC, Mumbai) detailed need of more post-irradiation period. B. S. Dwarkanath
Ottawa (Canada) and School of Life Sci- extensive research to elucidate the role of (Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied
ences, Jawaharlal Nehru University free radicals in induction of membrane Sciences, Delhi) discussed possible use
(JNU), New Delhi (India) on 16 Novem- and DNA damages which may provide of minor groove-binding DNA ligands,
ber 2002 at School of Life Sciences, better understanding of apoptotic death such as Hoechst 33258 and 33342, in
JNU, New Delhi. Forty participants, and bystander effects. R. N. Sharan pre- protection of radiation-induced DNA dam-
including thirteen invited speakers/ sented evidence of nucleotide sequence age. The Hoechst ligands were shown to
panelists representing India, Germany, determined vulnerability of segments of scavenge free radicals as well as afford
Canada, Japan and the USA, attended the genomic DNA, suggesting that genome stabilization to DNA superstructure. A.
workshop. The speakers covered various instability or inherent radiosensitivity Chatterjee (NEHU, Shillong) elaborated
aspects of radiation risk assessment in a may, at least in part, be determined by upon the use of endogenous radioprotec-
nuclear disaster scenario in the six tech- the primary sequence of nucleotides. M. tor, GSH, in reducing post-irradiation
nical sessions of the workshop. R. N. S. Sasaki (University of Kyoto, Kyoto) damage to proliferating cells.
Sharan (NEHU, Shillong) in his opening presented a new model of biological The final technical session of the
remarks highlighted the need and dosimeter for a non-homogeneous radia- workshop was in the form of a plenary
urgency of the workshop and discussed tion exposure situation like the one dur- discussion with panelists P. N. Srivas-
its scope. The inaugural lecture was ing nuclear holocaust. The strategy is tava, M. S. Sasaki, F. H. A. Schneeweiss,
delivered by P. N. Srivastava (former based on scoring chromosome aberra- A. Trivedi and Vijayalaxmi. The session
Vice-Chancellor of JNU, Member of the tions in lymphocytes and spreading it was initiated by a short presentation on
Planning Commission and President of over a mixed Poisson distribution into ‘Chemical, biological radiological and
ISRB). Srivastava recalled the chrono- dose component to get most likely dose– nuclear research and technology initia-
logical events of the past where large response curve and a realistic biological tive’ by A. Trivedi. The deliberation
segments of population across the globe dose assessment. F. H. A. Schneeweiss made several recommendations:
were exposed to heavy doses of radia- (Research Center Juelich GmbH, Juelich)
tion. K. A. Dinshaw (Tata Memorial offered an alternative to this approach, in l International collaborations/partner-
Center, Mumbai) delivered a thematic which early cellular response could be ships, network and communication
talk titled ‘Managing radiation emergen- assessed by analyses of lymphocyte pro- channels be initiated and strengthened
cies – a physician’s view’ covering all teins by two-dimensional differential gel for free exchange of information and
aspects of health management during and electrophoresis and mass-spectropho- for collaborative research.
after a nuclear holocaust. tometer coupled with COMET-FISH l In the domain of preparedness, the
The next four sessions covered various analysis of DNA damage. P. Uma Devi following steps be initiated:
aspects of consequences of radiation (J. N. Cancer Hospital and Research – Public awareness initiatives for im-
exposure, new approaches to biological Center, Bhopal) presented results of parting correct perspectives on ef-
dosimetry, biological responses and research involving prenatal exposures of fects of radiation and perspective on
radioprotection strategies wherein nine mice and cancer incidence. Prenatal ex- nuclear disaster and its management.
invited speakers delivered their talks. A. posure was shown to significantly – School children awareness initia-
Trivedi (Health Canada, Ottawa) pre- increase genome instability. R. K. Kale tives to foster and strengthen con-
sented new strategies for radiation risk (JNU, New Delhi) presented evidence of cepts and possibilities of peaceful
CURRENT SCIENCE, VOL. 84, NO. 8, 25 APRIL 2003 977
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- en GoDokument75 Seitenen GoAsheke ZinabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science for Sustainable Living: NCSC Activity Guidebook 2020-2021Dokument204 SeitenScience for Sustainable Living: NCSC Activity Guidebook 2020-2021Rohan KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3211 7491 3 PBDokument22 Seiten3211 7491 3 PBPedro JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fonstsguide PDFDokument16 SeitenFonstsguide PDFMonroe OrtizanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of The Cordilleras: Unit 1: Nature of Science, Technology and SocietyDokument9 SeitenUniversity of The Cordilleras: Unit 1: Nature of Science, Technology and SocietyArvid JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AstronomyAcrossDisciplinesandBorders Mini ReviewDokument31 SeitenAstronomyAcrossDisciplinesandBorders Mini ReviewmarcbreglianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performing The Future: On The Use of Drama in Philosophy Courses For Science StudentsDokument27 SeitenPerforming The Future: On The Use of Drama in Philosophy Courses For Science StudentsWanessa Do Bomfim MachadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE 5 SIM - ULOhDokument7 SeitenGE 5 SIM - ULOhCarl Jonez BabieraNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Am VasundharaDokument4 SeitenI Am VasundharaVasundhara SindhudurgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enriching The Learning Space Using Digital StorytellingDokument7 SeitenEnriching The Learning Space Using Digital StorytellingEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: The Nature and Relationships of Science, Technology and SocietyDokument15 SeitenChapter 1: The Nature and Relationships of Science, Technology and SocietyJUFUER CITO JUATNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Modules 1Dokument15 SeitenSTS Modules 1Axis ViloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv Exp Soc Psychol - DeDreu Et Al - preprint-2023!06!10T11!30!30.013ZDokument89 SeitenAdv Exp Soc Psychol - DeDreu Et Al - preprint-2023!06!10T11!30!30.013Zoancea.simion07Noch keine Bewertungen
- STS Report Outline1Dokument14 SeitenSTS Report Outline1Gillian Amba100% (1)
- Introduction to STS: Science, Technology & SocietyDokument5 SeitenIntroduction to STS: Science, Technology & SocietyDrioden NuquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTB ScityDokument25 SeitenCTB ScityMukul ParasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- g2 - ArticleDokument5 Seiteng2 - Articleapi-405035830Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Press Release Science Film FestivalDokument3 SeitenNew Press Release Science Film FestivalLuana YunanevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3q1gqu68w - STS 100 - MODULE Readings 4 - Information SocietyDokument3 Seiten3q1gqu68w - STS 100 - MODULE Readings 4 - Information SocietyChristine Kate DalivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactive Science Museum DesignDokument13 SeitenInteractive Science Museum Designchristian de leonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interrogating the Anthropocene: Ecology, Aesthetics, Pedagogy, and the Future in QuestionVon EverandInterrogating the Anthropocene: Ecology, Aesthetics, Pedagogy, and the Future in Questionjan jagodzinskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - VosniadouDokument30 Seiten3 - VosniadouMaria BauleoNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Topic 1 3Dokument12 SeitenSTS Topic 1 3Micah Ruth Pascua100% (1)
- 2008 Anker& TechnogenesisDokument47 Seiten2008 Anker& TechnogenesisENoch keine Bewertungen
- SPECTRA-book-Learning Through Drawing in Art and ScienceDokument180 SeitenSPECTRA-book-Learning Through Drawing in Art and ScienceDiego BetancourtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicating Utility Value of Science For SocietyDokument4 SeitenCommunicating Utility Value of Science For SocietyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Centres: A Resource For School and CommunityDokument9 SeitenScience Centres: A Resource For School and Communitynuranis nabilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science, Technology and Society OBE-PPST Based SyllabusDokument26 SeitenScience, Technology and Society OBE-PPST Based SyllabusAndreaDimaculanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Education 15-16Dokument3 SeitenElementary Education 15-16RutadharmadhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making Sense and Made Sense: Design and Technology and The Playful Construction of Meaning in The Early YearsDokument7 SeitenMaking Sense and Made Sense: Design and Technology and The Playful Construction of Meaning in The Early YearsrodprNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contribution Fo WK CommunicationDokument8 SeitenContribution Fo WK CommunicationploetNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 100: UNDERSTANDING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETYDokument8 SeitenSCIENCE 100: UNDERSTANDING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETYJasmin T. TacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS READINGS No. 1Dokument5 SeitenSTS READINGS No. 1Maria Desiree AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 78, No. 2, 2020Dokument173 SeitenProblems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 78, No. 2, 2020Scientia Socialis, Ltd.Noch keine Bewertungen
- François Taddéi - PresentacionDokument36 SeitenFrançois Taddéi - PresentacionMikel AgirregabiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Syllabus 2020Dokument27 SeitenSTS Syllabus 2020AndreaDimaculangan100% (1)
- STS Lesson2 230221 075029Dokument3 SeitenSTS Lesson2 230221 075029yesha gyle angelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Var 12081 PDFDokument11 SeitenVar 12081 PDFLeyla JafarovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opening the Black Box of Cognition in ScienceDokument19 SeitenOpening the Black Box of Cognition in ScienceNauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 82, No. 1, 2024Dokument156 SeitenProblems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 82, No. 1, 2024Scientia Socialis, Ltd.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vol 11 No 2 - May 2015Dokument107 SeitenVol 11 No 2 - May 2015ijlter.orgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines for State Science ExhibitionsDokument35 SeitenGuidelines for State Science Exhibitionsiminluv143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science and Technology Solutions for Life's ChallengesDokument16 SeitenScience and Technology Solutions for Life's ChallengesPankaj PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Folk Stories Based On The Traditional Arts and RitualDokument12 SeitenUsing Folk Stories Based On The Traditional Arts and RitualayususantinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science, Technology and the Meaning of a Good LifeDokument18 SeitenScience, Technology and the Meaning of a Good LifeJoy Jane Mae OjerioNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Analysis of Change and Continuity of Riddles Among The NandiDokument12 SeitenAn Analysis of Change and Continuity of Riddles Among The NandiAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science City: Pre Thesis Report Jnias-SpaDokument13 SeitenScience City: Pre Thesis Report Jnias-SpaEFFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visions That Do Not Reproduce Another Nightmare (2006)Dokument4 SeitenVisions That Do Not Reproduce Another Nightmare (2006)湯凱傑Noch keine Bewertungen
- STS Final ModulesDokument13 SeitenSTS Final ModulesYoni MarindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ODN Biblio 2Dokument14 SeitenODN Biblio 2MrNewmanTCANoch keine Bewertungen
- v18n38 PDFDokument20 Seitenv18n38 PDFsiti sri mulyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Country Report: Department of Education in Arts & AestheticsDokument94 SeitenCountry Report: Department of Education in Arts & AestheticsNaveen GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Course Outline Focuses on Impacts of Science and TechDokument40 SeitenSTS Course Outline Focuses on Impacts of Science and TechElla Nika FangonNoch keine Bewertungen
- DISCONTINUATION OF ARTISTIC CREATIVITY FROM CHILDHOOD TO ADULTHOODDokument5 SeitenDISCONTINUATION OF ARTISTIC CREATIVITY FROM CHILDHOOD TO ADULTHOODAbilawon WandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural Heritage PreservationDokument12 SeitenCultural Heritage PreservationHerlina SyahputriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarah R. Davies, Maja Horst (Auth.) - Science Communication - Culture, Identity and Citizenship-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2016)Dokument265 SeitenSarah R. Davies, Maja Horst (Auth.) - Science Communication - Culture, Identity and Citizenship-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2016)eduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Nature: Art and Consciousness in the Post-Biological EraVon EverandEngineering Nature: Art and Consciousness in the Post-Biological EraNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Reviewer MidtermDokument11 SeitenSTS Reviewer MidtermMaricel PalawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Causal Effect of Transport Infrastructure: Evidence From A New Historical DatabaseDokument25 SeitenThe Causal Effect of Transport Infrastructure: Evidence From A New Historical DatabasepvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback Form One (BCH 3yr)Dokument18 SeitenFeedback Form One (BCH 3yr)pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiD Bias from Spatial SpilloversDokument35 SeitenDiD Bias from Spatial SpilloverspvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
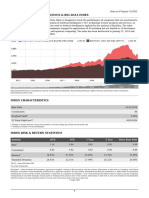
- Indxx Artificial Intelligence & Big Data Index: Statistic QTD YTD 1 Year 3 Year Since Base DateDokument1 SeiteIndxx Artificial Intelligence & Big Data Index: Statistic QTD YTD 1 Year 3 Year Since Base DatepvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGGSCC Alumni Rendezvous 2017Dokument14 SeitenSGGSCC Alumni Rendezvous 2017pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Cases PDFDokument1 SeiteTransfer Cases PDFpvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqar DduDokument85 SeitenAqar DdupvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback Form Two (BCH 3yr) .Dokument6 SeitenFeedback Form Two (BCH 3yr) .pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customizing Stata graphs made easy part 2Dokument17 SeitenCustomizing Stata graphs made easy part 2pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- StartupIndia ActionPlan 16january2016Dokument40 SeitenStartupIndia ActionPlan 16january2016Kaushik RudraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Union Budget 2017 18 Key Highlights PDFDokument7 SeitenUnion Budget 2017 18 Key Highlights PDFRakesh MistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test For Normality PDFDokument30 SeitenTest For Normality PDFShejj PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat A SteelDokument20 SeitenStat A SteelmailtorohitaquaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Public Sector in Developing India's InfrastructureDokument64 SeitenRole of Public Sector in Developing India's InfrastructurepvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working GroupDokument16 SeitenWorking GrouppvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravity Model PDFDokument43 SeitenGravity Model PDFpvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- T I 83 GuidebookDokument446 SeitenT I 83 GuidebookMarcelo AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Delhi Internal Assessment SchemeDokument8 SeitenUniversity of Delhi Internal Assessment SchemepvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan: AboutDokument4 SeitenBusiness Plan: AboutpvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finance 100: Corporate Finance: Professor Michael R. Roberts Quiz 3 November 28, 2007Dokument8 SeitenFinance 100: Corporate Finance: Professor Michael R. Roberts Quiz 3 November 28, 2007pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26618680Dokument16 Seiten26618680aaiiilllpsvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 &6 - 20180111213323Dokument24 SeitenChapter 5 &6 - 20180111213323pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - 20180111212848Dokument13 SeitenChapter 3 - 20180111212848pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaire Vs Social Networking SitesDokument18 SeitenQuestionnaire Vs Social Networking SitespvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Research Chap1Dokument26 SeitenMarketing Research Chap1pvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPI ManualDokument97 SeitenWPI ManualNarendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Da Vinci's Mona Lisa Entering The Next Dimension: Short ReportDokument7 SeitenDa Vinci's Mona Lisa Entering The Next Dimension: Short ReportpvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPI ManualDokument97 SeitenWPI ManualNarendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- December 2016), Based On General Indices and Cfpis Are Given As FollowsDokument5 SeitenDecember 2016), Based On General Indices and Cfpis Are Given As FollowspvaibhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- David L. Bergman and Charles W. Lucas, Jr. - Physical Models of MatterDokument23 SeitenDavid L. Bergman and Charles W. Lucas, Jr. - Physical Models of MatterJuiomSDF100% (1)
- Nature of LightDokument2 SeitenNature of LightDhanBahadurNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDT Radiography Techniques for Weld InspectionDokument56 SeitenNDT Radiography Techniques for Weld InspectionIrfan Mehmood100% (3)
- Emissivity PaperDokument6 SeitenEmissivity PaperbasitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Propagation (Unit VI)Dokument65 SeitenWave Propagation (Unit VI)Nuzhath FathimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refractive Index of Liquids Using Laser LightDokument7 SeitenRefractive Index of Liquids Using Laser LightPrashant100% (1)
- Light Lesson 1Dokument20 SeitenLight Lesson 1rajesh duaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 CIE Physics IGCSEDokument6 SeitenSummary Notes - Topic 3 CIE Physics IGCSEYousef SyeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory Project On TIRDokument21 SeitenPhysics Investigatory Project On TIRDenyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cswip 3.2.2 Preparatory Material Yr 2020Dokument12 SeitenCswip 3.2.2 Preparatory Material Yr 2020UmaibalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3 Photoelectron Spectroscopy: X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (UPS)Dokument8 Seiten5.3 Photoelectron Spectroscopy: X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (UPS)Ajay Sharma ShankyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 8Dokument35 SeitenClass 8Pooja MantriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ProjectDokument15 SeitenPhysics ProjectRELAXATION MUSICNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS Waves 2Dokument5 SeitenWS Waves 2Hannah LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Techniques in Drug DevelopmentDokument16 SeitenAnalytical Techniques in Drug DevelopmentLeonard Goh Zhong Ning100% (3)
- Lecture Notes On X RayDokument6 SeitenLecture Notes On X RayHyacinthe KOSSINoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluoroscopy Fundamentals ModuleDokument10 SeitenFluoroscopy Fundamentals ModuleErshad SohailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves 1 QPDokument18 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves 1 QPNaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy T1Dokument23 SeitenPhy T1SivaSaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Remote Sensing and Gis Ce 333 Unit - 1 Remote SensingDokument13 SeitenBasics of Remote Sensing and Gis Ce 333 Unit - 1 Remote SensingShanmuga SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 TNHDokument2 Seiten2 TNHLe My YenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Image Processing: Dr. Lavdie RADADokument15 SeitenDigital Image Processing: Dr. Lavdie RADAMukarram SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WinWave Power Point PresentationDokument34 SeitenWinWave Power Point PresentationpatrizziamarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Fluorescence SpectrosDokument10 SeitenMolecular Fluorescence Spectrosleo mark100% (1)
- AP Unit 1 Question BankDokument4 SeitenAP Unit 1 Question BankBuy OnlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Lib24.Vn) de Thi Vao 10 Chuyen Tieng Anh Truong THPT Chuyen Hung Vuong Phu Tho Nam Hoc 2020 2021Dokument7 Seiten(Lib24.Vn) de Thi Vao 10 Chuyen Tieng Anh Truong THPT Chuyen Hung Vuong Phu Tho Nam Hoc 2020 2021dieu linhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Police PhotographyDokument52 SeitenPolice PhotographyTerrencio Reodava100% (13)
- Physics: Class 10th (KPK)Dokument21 SeitenPhysics: Class 10th (KPK)Muhammad naveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - 2022Dokument15 SeitenUnit 2 - 2022Nyashadzashe ChikarakaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Optical Fiber PDFDokument96 SeitenChapter 2 Optical Fiber PDFNguyễnMinhTháiNoch keine Bewertungen