Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
What Is Routing Loop and How To Avoid Routing Loop
Hochgeladen von
srkakarlapudiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is Routing Loop and How To Avoid Routing Loop
Hochgeladen von
srkakarlapudiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
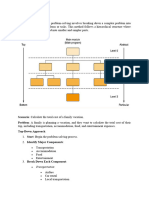
What is Routing Loop and how to avoid Routing Loop
A routing loop is a serious network problem which happens when a data packet is continually routed
through the same routers over and over. The data packets continue to be routed within the network in an
endless circle. A routing loop can have a catastrophic impact on a network, and in some cases, completely
disabling the network. Normally Routing Loop is a problem associated with Distance Vector Protocols.
How routing loops affect network performance?
• A major portion of the precious bandwidth which is available for normal user traffic of the affected
routers will be consumed by looping IP datagram packets.
• The major portion of the processing power of the affected routers is used to process the looping IP
datagram packets.
Routing Loop can happen in large internetworks when a second topology change emerges before the
network is able to converge on the first change. Convergence is the term used to describe the condition
when all routers in an internetwork have agreed on a common topology. Link state protocols tend to
converge very quickly, while distance vector protocols tend to converge slowly.
The following methods are used to avoid Routing Loops.
Maximum hop Count
Maximum hop count mechanism can be used to prevent Routing Loops. Distance Vector protocols use
the TTL (Time-to-Live) value in the IP datagram header to avoid Routing Loops. When an IP datagram move
from router to router, a router keeps track of the hops in the TTL field in the IP datagram header. For each
hop a packet goes through, the packet’s TTL field is decremented by one. If this value reaches 0, the packet
is dropped by the router that decremented the value from 1 to 0.
Split Horizon
A split horizon is a routing configuration that stops a route from being advertised back in the direction from
which it came. Split Horizon mechanism states that if a neighbouring router sends a route to a router, the
receiving router will not propagate this route back to the advertising router on the same interface.
Route Poisoning
Route Poisoning is another method for avoiding routing loops. When a router detects that one of its
connected routes has failed, the router will poison the route by assigning an infinite metric to it.
Hold-down Timers
Hold-down timer is another mechanism used to prevent bad routes from being restored and propagated
by mistake. When a route is placed in a hold-down state, routers will neither advertise the route nor accept
advertisements about it for a specific interval called the hold-down period.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Motherboard Parts Peripherals and Connectors ExplainedDokument31 SeitenMotherboard Parts Peripherals and Connectors Explainedsrkakarlapudi67% (3)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Paul W Browning - Farai Tafa - Daniel Gheorghe - Dario Barinic Cisco CCNA Simplified - Your Complete Gui - CompressedDokument692 SeitenPaul W Browning - Farai Tafa - Daniel Gheorghe - Dario Barinic Cisco CCNA Simplified - Your Complete Gui - CompressedCesarC.Arias100% (1)
- Ise 2 0 Atp HLD Template v0 4Dokument28 SeitenIse 2 0 Atp HLD Template v0 4Kanika GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wi-Fi Site Survey QuestionnaireDokument12 SeitenWi-Fi Site Survey QuestionnairePierre Gossen100% (1)
- TP 3200 ManualDokument11 SeitenTP 3200 ManualJean Carlos CâmaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massive MIMO: Omar Abu-EllaDokument23 SeitenMassive MIMO: Omar Abu-EllaTarek Tarek El-safraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- M 3 UDokument14 SeitenM 3 UIsaiasAristodemouNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANT ATR4518R7 DatasheetDokument2 SeitenANT ATR4518R7 DatasheetDelphine JahyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamklDokument13 SeitenExamklfatouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time ComplexityDokument3 SeitenTime ComplexitysrkakarlapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decimal To Binary 1Dokument2 SeitenDecimal To Binary 1srkakarlapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topdown Approach - 2Dokument5 SeitenTopdown Approach - 2srkakarlapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems Viva QuestionsDokument2 SeitenControl Systems Viva Questionssrkakarlapudi100% (1)
- I P Latex D M - B T A F E CV: Ndividual Roject OcumentationDokument36 SeitenI P Latex D M - B T A F E CV: Ndividual Roject OcumentationsrkakarlapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Array in C ProgrammingDokument9 SeitenArray in C ProgrammingsrkakarlapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netsim Experiment Manual - 1Dokument163 SeitenNetsim Experiment Manual - 1Rajiv PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do You Integrate An HMI Operator Panel Into A Local Network?Dokument12 SeitenHow Do You Integrate An HMI Operator Panel Into A Local Network?Bob YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis of MTech Nit RourkelaDokument79 SeitenThesis of MTech Nit RourkelaLogeeswaran MurugappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Okumura ModelDokument4 SeitenOkumura Modelchuck333Noch keine Bewertungen
- ANS 1 ProtocolsAndArchitectures 2223Dokument42 SeitenANS 1 ProtocolsAndArchitectures 2223FouziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access NOMA As A PDFDokument5 SeitenNon-Orthogonal Multiple Access NOMA As A PDFHanif KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sf1uwfjuu - Medical Image Distribution, Networks, and CommunicationsDokument17 SeitenSf1uwfjuu - Medical Image Distribution, Networks, and Communicationsivanne zaideNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8920A RF Communications Test Set Users Guide (Apr00) 08920 90219Dokument607 Seiten8920A RF Communications Test Set Users Guide (Apr00) 08920 90219JperezauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Bluetooth ConnectionDokument8 SeitenAndroid Bluetooth ConnectionSakshi GaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Data Sheet 6Es7414-3Xj00-0Ab0: Cir - Configuration in RunDokument10 SeitenProduct Data Sheet 6Es7414-3Xj00-0Ab0: Cir - Configuration in RunsadeghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beacon Frames: Linksys - Ses - 24086 Access Point? From The 30 Munroe St. Access Point? (Hint: ThisDokument4 SeitenBeacon Frames: Linksys - Ses - 24086 Access Point? From The 30 Munroe St. Access Point? (Hint: ThisJohan GustawssonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanceo de Carga Dinamico 4 Lineas ProbarDokument6 SeitenBalanceo de Carga Dinamico 4 Lineas ProbarMarlon UjpanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast SSHDokument1 SeiteFast SSHEdwin Santosa100% (1)
- FLY CompuWatch ENDokument1 SeiteFLY CompuWatch ENFelipe FrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP 477dw Web ServerDokument53 SeitenHP 477dw Web Servercovenant660Noch keine Bewertungen
- Helix Traveling Wave TubeDokument18 SeitenHelix Traveling Wave Tubeamvarman100% (1)
- Huawei ICT Skill Competition-Middle East Preparation KitsDokument29 SeitenHuawei ICT Skill Competition-Middle East Preparation Kitssamuel198100% (1)
- KRONOS Power Shield LQ mm08696Dokument2 SeitenKRONOS Power Shield LQ mm08696smsarmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- NGINX Container and Cloudflare PDFDokument6 SeitenNGINX Container and Cloudflare PDFLorieChampagneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yagi From PctelDokument51 SeitenYagi From PctelvictorantcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abit ZX-G31LM Rev1.4Dokument28 SeitenAbit ZX-G31LM Rev1.4datamarce2016 marceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Secure Appliance Series: Problems We SolveDokument3 SeitenPulse Secure Appliance Series: Problems We SolvearuninbaNoch keine Bewertungen