Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Quant Finance For Dummies Notes
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous 9qJCv5mC0Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Quant Finance For Dummies Notes
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous 9qJCv5mC0Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 1 – What is quant finance?
- Quant finance is the application of probability and stats to finance.
- It’s the empirical observation of prices, exchange rates, and interest rates
Efficient Markets
o Markets that are efficient means the prices reflect known info and thus follow a random
walk.
3 types of efficiency
Weak – When prices cant be predicted from past prices
Semi String – is when prices cant be predicted with all available public
info.
Strong – cant be predicted at all
o Markets are efficiently but not perfect.
3 functions of Money
o Store of value
o Means of exchange
o Unit of account
Borrowings
o Bonds – Form of a loan where a lender gives the borrower $ in return of the principal
and interest payments called coupons
Lender can sell the bond to someone else
o Stocks – represent ownership in company.
Options
o Gives you the right but not obligation to buy or sell a financial asset such as a bond at a
time in the future at a price agreed now.
Price of a option depends on:
Risk free rate
Volaitility of asset
Time to expiry
Strike price
o Can be used for leverage or the returns can be similar to using borrowed $ to buy shares
or hedging against market moves.
Managing risk
o Options allow you to protect yourself against adverse price movements but for a
premium up front.
o Typically value at risk or VaR is used to measure portfolio riskiness
o For a portfolio you should know
Expected return of your assets
Volatility of your assets
Correlations between assets
o Try to apply MPT but it can be hard
Chapter 2 – Probability and Statistics
Define a return r_n of an asset on day n and price on day n p_n to be r_n= (p_n-P_n-1)/P_n-1
What is a random variable?
o Measurement or characteristic that takes on its value by chance.
o Don’t know the value till the xperiment is done
o Can be discrete/continuous
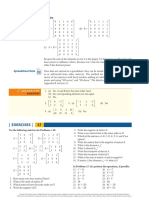
o Expected Value: E[X] = ∑𝑀 𝑗=1 𝑥𝑗 𝑝𝑗 where M is the # of possible outcomes.
Weighted average
What is statistics?
o All about fitting distributions to data
o Normal Distribution
CLT – States that if you have a sum of many random variables it tends to a
normal distribution
x_i represents the ith elements in a sample of size N
A distribution can be characterized by following statistics
Average, STDDEV
Skew – measures how lob sided a distribution is. Positive is right skewed
vice versa.
Kurtosis – measures how fat the tails of the distribution are.
Chapter 3 – Taking look @ Random Behaviors
Factors affecting price of a stock despite stock prices being random
1) Global economic activity
2) Factors affecting a specific company
3) Sale of stock or commodity
Setting up the Random Walk
1) Suppse that X_i is a step in a RW taking on +1 or -1.
2) R_N = X_1+…+X_N is the position after N Steps
3) 𝐸[𝑅_𝑁] = ∑𝑁 𝑖=1 𝑋_𝑖 = 0 𝑎𝑠 𝐸[𝑋𝑖 ] = 0
2
4) 𝐸[𝑅_𝑁^2] = ∑𝑁
𝑖=1 𝑋𝑖 = 0 = 𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒(𝑅𝑁 )
Suppose now we have a RW with drift so now there is bias introduced.
Let
1) ∆ : Time it takes for each step
2) ∂ : distance of each step
3) The RW goes ∂ with probability p and -∂ with (1-P)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Guide To Syndicated Leveraged FinanceDokument11 SeitenGuide To Syndicated Leveraged FinanceMrigank Agarwal100% (1)
- Business Law TestDokument11 SeitenBusiness Law Testmaikypr100% (6)
- Exercises - : SolutionDokument5 SeitenExercises - : SolutionDang Cong SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buyback of SharesDokument93 SeitenBuyback of SharesDipock Mondal86% (7)
- Cole Harris IndictmentDokument14 SeitenCole Harris IndictmentJennifer Van LaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul Wilmott - Intro To Quanitiative Finance NotesDokument13 SeitenPaul Wilmott - Intro To Quanitiative Finance NotesAnonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ting Ting Pua v. Sps. Lo Bun TiongDokument2 SeitenTing Ting Pua v. Sps. Lo Bun TiongRalph Deric EspirituNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 2Dokument3 SeitenHW 2Anonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet: Week 4: NAMEDokument2 SeitenWorksheet: Week 4: NAMEAnonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pidd Pidd LKJHLKHJ Piss JKGK LKJ L JLKJ KLJDokument1 SeitePidd Pidd LKJHLKHJ Piss JKGK LKJ L JLKJ KLJAnonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- HW 4Dokument7 SeitenHW 4Anonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 4Dokument4 SeitenHomework 4Anonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- HW 2 SolutionDokument7 SeitenHW 2 SolutionAnonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- CSCI 40 / ENGR 40 - Term Project Assignment - Part I 2014 FallDokument5 SeitenCSCI 40 / ENGR 40 - Term Project Assignment - Part I 2014 FallAnonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sol HMK9Dokument2 SeitenSol HMK9Anonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice MidtermDokument4 SeitenPractice MidtermAnonymous 9qJCv5mC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Weekender Vol 6 Issue 2Dokument40 SeitenIndian Weekender Vol 6 Issue 2Indian WeekenderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pricing of ServicesDokument30 SeitenPricing of ServicesAnand VANoch keine Bewertungen
- Balancing and Closing AccountsDokument2 SeitenBalancing and Closing AccountsMildred C. WaltersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unclaimed DepositsDokument2 SeitenUnclaimed DepositsRajesh RamachandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viceroy CapitecDokument33 SeitenViceroy CapitecPrimedia Broadcasting100% (5)
- JANKIDokument47 SeitenJANKIJankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Letters: 1) Somatie de PlataDokument7 SeitenBanking Letters: 1) Somatie de PlataMireanu ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essar OilDokument20 SeitenEssar OilVinay PrabhakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- (City, Municipality, Province) : Cash InflowsDokument2 Seiten(City, Municipality, Province) : Cash InflowsMara ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICICI Vehical LoanDokument49 SeitenICICI Vehical Loanjagdish80% (5)
- Cost Accounting Unit 1Dokument16 SeitenCost Accounting Unit 1archana_anuragiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research NotesDokument41 SeitenBusiness Research NotesGorishsharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instru Manual English - CodesDokument32 SeitenInstru Manual English - Codeslalapo1100Noch keine Bewertungen
- MetLife Alico at A GlanceDokument10 SeitenMetLife Alico at A GlanceRejul KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On Mega Merger of Sbi With Its Associate Banks and Bhartiya Mahila BankDokument34 SeitenA Case Study On Mega Merger of Sbi With Its Associate Banks and Bhartiya Mahila BankMihirParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- INVESTMENT AND COMPETITION LAW - Unit 2Dokument62 SeitenINVESTMENT AND COMPETITION LAW - Unit 2saif aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co Act On Loans Accepted & GivenDokument43 SeitenCo Act On Loans Accepted & GivendkdineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Ca-Cpt - Quick Revision VersionDokument14 SeitenEconomics For Ca-Cpt - Quick Revision VersionCA Suman Gadamsetti75% (4)
- Distinguishing Between Simple and General AnnuitiesDokument2 SeitenDistinguishing Between Simple and General AnnuitiesErnie Caracas Lahaylahay100% (1)
- 001 - Icon Jan-Feb 05Dokument70 Seiten001 - Icon Jan-Feb 05gendrivef1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Premier Discover BrochureDokument8 SeitenPremier Discover BrochuredfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lisa Foley Statement of Financial ConditionDokument37 SeitenLisa Foley Statement of Financial ConditionYTOLeaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview Questions For Finance StudentsDokument12 SeitenInterview Questions For Finance Studentsradhika1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Bu AprilDokument29 SeitenMateri Bu AprilQorry Aini HaniNoch keine Bewertungen