Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
E - C RCC: B I E R: Nergy Onsumption IN Ircuits A Rief Ntroduction TO Nergy Ecovery
Hochgeladen von
Dr. Sampatrao L PinjareOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
E - C RCC: B I E R: Nergy Onsumption IN Ircuits A Rief Ntroduction TO Nergy Ecovery
Hochgeladen von
Dr. Sampatrao L PinjareCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ENERGY-CONSUMPTION IN RC CIRCUITS: A BRIEF
INTRODUCTION TO ENERGY RECOVERY
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
Revisit Dynamic Energy Comsumption
Simple R-C model of Pass pMOS transistor
Consider a pMOS pass transistor
with a capacitive load C at the out
put. The voltage at the power
terminal swings from 0 to Vdd to
charge the node capacitance
through the transistor channel. The
channel is modeled by a normal
resistance R in fig (a).
Let us compute energy dissipated
while charging capacitance C from
0 to Vdd in time T with a linear
supply voltage as shown in fig (b).
Source: Intel
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
RC Circuit: Energy Dissipation
The voltage relations are dVC
shown here. RC ( ) VC
dt
The supply voltage can be
expressed as
0, t0
Vdd
VC ( ), 0 t T
T
Vdd , t T
Source: Intel
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
RC Circuits ( contd.)
Solving the voltage equation, we’ve
0,
t t0
RC
VC ( )Vdd (1 e RC ), 0 t T
T
t ( t T ) t T
RC ,
( )Vdd (1 e RC )e RC
T
The energy dissipation in the charging process can be calculated as
T
Elinear iVR dt iVR dt
0 T
Source: Intel
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
RC Circuits (contd.)
Term wise expanding, the first term can be expressed as
T T ( V ) 2
iVR dt C
dt
0 0 R
t
Vdd
T ( )
[ RC (1 e RC ] / Rdt
0 T
T
t
RC 2 t
2 RC
( ) CVdd (1 e RC ) 2 d ( )
T 0 RC
RC 3 RC RC (
T
) 1 RC (
2T
)
( )CVdd 1 ( ) 2( )e RC ( )e RC
2
T 2 T T 2 T
Source: Intel
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
RC Circuits (contd.)
The second term of the energy dissipation
( V ) 2
iVR dt C
dt
T T R
T ( t T )
RC 2
CVdd2 (1 e RC ) 2 e
RC dt
T T
T
RC 2 1
( ) CVdd2 [ (1 e RC ) 2 ]
T 2
Final energy expression
T
RC RC RC RC
Source: Intel Elinear ( )CVdd [1
2
e ]
T T T
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
Energy Dissipation: 2 Cases
Let us consider the two extreme cases, when T >> RC
RC
Elinear ( )CVdd2
T
And when T << RC, as in normal CMOS
RC RC RC T 1 T 2
Elinear ( )CVdd2 [1 (1 ( ) )]
T T T RC 2 RC
1
CVdd2
2
Source: Intel
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
Adiabatic Switching Concept
Source: Intel
Prof. Kaushik Roy
@ Purdue Univ.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- Eeen 301 Lecture IiDokument23 SeitenEeen 301 Lecture IiKabiru FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument77 SeitenChapter 7rizwanspirit11Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE123N RC-RL Circuits Post PDFDokument31 SeitenEE123N RC-RL Circuits Post PDFSHASHWA USOPNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Order Circuit: - Capacitors and Inductors - RC and RL CircuitsDokument14 SeitenFirst Order Circuit: - Capacitors and Inductors - RC and RL CircuitsNorhatini IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Domain Circuit Analysis First Order and Second Order Response of RL and RC CircuitDokument12 SeitenTime Domain Circuit Analysis First Order and Second Order Response of RL and RC CircuitROMIT RUNWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 122B Electricity and MagnetismDokument26 SeitenPhysics 122B Electricity and Magnetismbedjamkhed5010Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 First-Order Circuits NotedDokument67 Seiten9 First-Order Circuits NotedBrandon CilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Response of DC Circuits: V It e RDokument10 SeitenTransient Response of DC Circuits: V It e RAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SN CircuitsDokument18 SeitenSN CircuitsEscanor BanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem26 87Dokument1 SeiteProblem26 87IENCSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esc201t l10 RC RL CircuitsDokument34 SeitenEsc201t l10 RC RL CircuitsRachit MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionDokument18 SeitenLecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionShehroze TalatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9Dokument28 SeitenLecture 9sanyamjain51150Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitor Charging 2Dokument2 SeitenCapacitor Charging 2ManuBajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Simple RC and RL CircuitsDokument39 SeitenChapter 8: Simple RC and RL Circuitsdabs_orangejuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 209 Presentation 5 (1st and 2nd Order CCTS)Dokument88 SeitenEEE 209 Presentation 5 (1st and 2nd Order CCTS)Mert YılmazNoch keine Bewertungen
- RL TransientDokument35 SeitenRL Transientkrish104411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Time Domain AnalysisDokument94 SeitenTime Domain AnalysisAbhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionDokument18 SeitenLecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionMuhammad Hassan JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitance and Inductance: Learning GoalsDokument57 SeitenCapacitance and Inductance: Learning Goals김여명Noch keine Bewertungen
- ESC201T L11 RLC CircuitsDokument31 SeitenESC201T L11 RLC CircuitsRachit MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Square Wave ResponseDokument4 SeitenSquare Wave ResponseManjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eeng 455 LectureDokument174 SeitenEeng 455 Lectureezekielmuriithi34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Powersys 4Dokument39 SeitenPowersys 4setsindia3735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Powersys 3Dokument39 SeitenPowersys 3setsindia3735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2p4p2Dokument9 SeitenChapter 2p4p2Glenn VirreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- L33 ECEN5817 Out1Dokument14 SeitenL33 ECEN5817 Out1djyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah KapasitorDokument55 SeitenKuliah KapasitorCak RizNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB For Gate Ee: Power Electronics-Part-13Dokument9 SeitenQB For Gate Ee: Power Electronics-Part-13shivang agrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionDokument18 SeitenLecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionAhmad RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3 - Controlled Rectifiers (Autosaved)Dokument39 SeitenCH 3 - Controlled Rectifiers (Autosaved)fitwi halefomNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC DC Choper CirctDokument20 SeitenDC DC Choper Circtحسن علي جاسمNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3 - Controlled RectifiersDokument25 SeitenCH 3 - Controlled RectifiersGebremichael Teklay GebretsadikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionDokument18 SeitenLecture 02 Electrical Networks Transfer FunctionRammay SbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture # 5: Power Losses in Power Semiconductor SwitchesDokument23 SeitenLecture # 5: Power Losses in Power Semiconductor SwitchesShehroz BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alexander CH 08 Final R1Dokument18 SeitenAlexander CH 08 Final R1utpNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 - Uncontrolled Rectifiers (Autosaved)Dokument92 SeitenCH 2 - Uncontrolled Rectifiers (Autosaved)Gebremichael Teklay GebretsadikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmic Circuits With SolutionsDokument11 SeitenCosmic Circuits With SolutionsRaja SekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Part IDokument68 SeitenChapter 3 Part IDaniel MengeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Handout # 04Dokument7 SeitenEDC Handout # 04Rajendar SandiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mack Grady Fundamentals of Electric Power TAMU Relay Conf Tutorial 150331Dokument44 SeitenMack Grady Fundamentals of Electric Power TAMU Relay Conf Tutorial 150331Lawiii KkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buffer InsertionDokument47 SeitenBuffer InsertionAkhil MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt - 6: Linear Waveshaping CircuitsDokument8 SeitenExpt - 6: Linear Waveshaping CircuitssamarthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 Power Computation 2 in One 2023-09-09Dokument30 SeitenCh2 Power Computation 2 in One 2023-09-09hsiaopeihsuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Topics in Power - 1Dokument38 SeitenSpecial Topics in Power - 1Ravichandran SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- StepByStep Pulse8EdDokument24 SeitenStepByStep Pulse8Edpak tracksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alexander CH 08 Final R 1Dokument18 SeitenAlexander CH 08 Final R 1kifle203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam Formula Sheet ELEC1103 S1 2021Dokument1 SeiteMidterm Exam Formula Sheet ELEC1103 S1 2021Xin ZhaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low-Power Design and TestDokument39 SeitenLow-Power Design and TestvigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chp11-AC Power AnalysisDokument25 SeitenChp11-AC Power Analysisavishek aviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 and 4Dokument128 SeitenChapter 3 and 4selaroth168Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch7 Analysis+of+First +and+second Order+Transient+CircuitsDokument12 SeitenCh7 Analysis+of+First +and+second Order+Transient+Circuits김종혁Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 8 EDC-2Dokument8 SeitenExpt 8 EDC-2samarthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power and Energy Basics: Jan M. RabaeyDokument46 SeitenPower and Energy Basics: Jan M. Rabaey허완Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch07 First Order Circuits 16to9Dokument63 SeitenCh07 First Order Circuits 16to9avishek aviNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-DC ConvertersDokument22 SeitenDC-DC ConverterskanithanNoch keine Bewertungen
- System TheoryDokument17 SeitenSystem TheoryMichael CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actorization AND Pproximation: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDokument7 SeitenActorization AND Pproximation: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- A DSP: L - P, U E P, & E R: Pplication TO OW Ower Nequal Rror Rotection Rror EsiliencyDokument11 SeitenA DSP: L - P, U E P, & E R: Pplication TO OW Ower Nequal Rror Rotection Rror EsiliencyDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approximate Full Adder CellsDokument11 SeitenApproximate Full Adder CellsDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canonical Signed Digits (CSD)Dokument5 SeitenCanonical Signed Digits (CSD)Dr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- A - C L P - Application Domain: Multi-Media Systems, Recognition, Mining, SynthesisDokument4 SeitenA - C L P - Application Domain: Multi-Media Systems, Recognition, Mining, SynthesisDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lock Ating: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDokument8 SeitenLock Ating: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- R D R C C R: Educing THE Ynamic Ange OF Omputation AND Omplexity EductionDokument6 SeitenR D R C C R: Educing THE Ynamic Ange OF Omputation AND Omplexity EductionDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ariable Upply Oltage: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDokument7 SeitenAriable Upply Oltage: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulti Upply Oltage: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDokument5 SeitenUlti Upply Oltage: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- L - P Vlsi S P: L C D: OW Ower Ignal Rocessing OW Omplexity EsignDokument8 SeitenL - P Vlsi S P: L C D: OW Ower Ignal Rocessing OW Omplexity EsignDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ogic Tyle: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDokument10 SeitenOgic Tyle: Prof. Kaushik Roy at Purdue UnivDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Bit-Serial Adder Using Partially Reversible LogicDokument9 SeitenA Bit-Serial Adder Using Partially Reversible LogicDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Analog Design: Dr. S. L. PinjareDokument65 SeitenIntroduction To Analog Design: Dr. S. L. PinjareDr. Sampatrao L Pinjare100% (1)
- Analog Layout UTLDokument3 SeitenAnalog Layout UTLDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
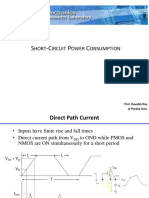
- S - C P C: Hort Ircuit Ower OnsumptionDokument7 SeitenS - C P C: Hort Ircuit Ower OnsumptionDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Average Number of Transitions: Source: IntelDokument2 SeitenEstimation of Average Number of Transitions: Source: IntelDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of MEMSDokument152 SeitenOverview of MEMSDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrothrusterDokument1 SeiteMicrothrusterDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLSI Implementation of Artificial Neural NetworkDokument26 SeitenVLSI Implementation of Artificial Neural NetworkDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of CMOS Low Dropout Voltage RegulatorDokument32 SeitenDesign of CMOS Low Dropout Voltage RegulatorDr. Sampatrao L PinjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMC No. 122 2022 9.6.2022Dokument6 SeitenRMC No. 122 2022 9.6.2022RUFO BULILANNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM011l E01 Exp.3 DeJuanDokument3 SeitenCM011l E01 Exp.3 DeJuanJarell De JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment PN1096617Dokument14 SeitenAssessment PN1096617Amr TarekNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOK Assessed Student WorkDokument10 SeitenTOK Assessed Student WorkPeter Jun Park100% (1)
- RESUME1Dokument2 SeitenRESUME1sagar09100% (5)
- Lecture No. 11Dokument15 SeitenLecture No. 11Sayeda JabbinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 PDFDokument85 SeitenCH 2 PDFSajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inqlusive Newsrooms LGBTQIA Media Reference Guide English 2023 E1Dokument98 SeitenInqlusive Newsrooms LGBTQIA Media Reference Guide English 2023 E1Disability Rights AllianceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top249 1 PDFDokument52 SeitenTop249 1 PDFCarlos Henrique Dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harish Raval Rajkot.: Civil ConstructionDokument4 SeitenHarish Raval Rajkot.: Civil ConstructionNilay GandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management 101Dokument36 SeitenSupply Chain Management 101Trần Viết ThanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debate Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenDebate Lesson Planapi-280689729Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basics PDFDokument21 SeitenBasics PDFSunil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read The Dialogue Below and Answer The Following QuestionDokument5 SeitenRead The Dialogue Below and Answer The Following QuestionDavid GainesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffrent Types of MapDokument3 SeitenDiffrent Types of MapIan GamitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arte PoveraDokument13 SeitenArte PoveraSohini MaitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Résumé Emily Martin FullDokument3 SeitenRésumé Emily Martin FullEmily MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power StationDokument8 SeitenApplication of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power Stationshinta sariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Successful School LeadershipDokument132 SeitenSuccessful School LeadershipDabney90100% (2)
- Shot Blasting Machine ApplicationsDokument7 SeitenShot Blasting Machine ApplicationsBhavin DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDokument11 SeitenModule 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesBilly Joel DasmariñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Personal StatementDokument2 SeitenModel Personal StatementSwayam Tripathy100% (1)
- A History of The Ecological Sciences, Part 1 - Early Greek OriginsDokument6 SeitenA History of The Ecological Sciences, Part 1 - Early Greek OriginskatzbandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dark Energy Survey DES CollaborationDokument38 SeitenDark Energy Survey DES CollaborationgeorgcantorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 009 Attached-1 NAVFAC P-445 Construction Quality Management PDFDokument194 Seiten009 Attached-1 NAVFAC P-445 Construction Quality Management PDFSor sopanharithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulk Separator - V-1201 Method StatementDokument2 SeitenBulk Separator - V-1201 Method StatementRoshin99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ojt Evaluation Forms (Supervised Industry Training) SampleDokument5 SeitenOjt Evaluation Forms (Supervised Industry Training) SampleJayJay Jimenez100% (3)
- SUNGLAO - TM PortfolioDokument60 SeitenSUNGLAO - TM PortfolioGIZELLE SUNGLAONoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric For Audio Speech DeliveryDokument2 SeitenRubric For Audio Speech DeliveryMarie Sol PanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 6 Product Disassembly ChartDokument5 SeitenActivity 6 Product Disassembly Chartapi-504977947Noch keine Bewertungen