Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sap Abap Programming Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
dhivyaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sap Abap Programming Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
dhivyaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SAP ABAP PROGRAMMING SYLLABUS Overall introduction to ERP Introduction SAP R/3 architecture,
Introduction to SAP ABAP/4 ABAP/4 editor (Focus on the functionalities of new ABAP editor) Data
types Output statements Writing small programs Arithmetic operations String operations
Control statements Parameters Open SQL –statements (insert, modify, delete, update). Simple
reporting Selection screens Transaction code creation Data Dictionary o Tables o Data element o
Domain o Structures o Search helps o Views o Type Groups o Table maintenance generator and T-code
creation o Primary and foreign keys. o Check and value tables. REPORTING Debugging techniques. o
Breakpoint creation. o Watch point creation. o Emphasize on the usage of New Debugger. Internal
tables. o Declaration o Processing. o Population. Control Break Statements. Modularization
techniques. o Includes. o Subroutines. o Function modules. o Macros Variants. Conversion exits.
For all entries and joins (inner and left outer). Message class creation & message types and handling
messages. Events for classical reports. Events for interactive reports. Hide and hotspot. Creating
and handling buttons. Menu painter. ALV Introduction. Types of ALV Simple report to display
simple ALV List using Function Modules Simple report to display simple ALV grid using Function
Modules. Interactive ALV Reports. Adding new buttons in the ALV toolbar and handling events.
Working with ALV using classes (List, Grid and Tree). Usage of latest class library in ECC 6.0 for ALV.
DIALOG PROGRAMMING Introduction to screen painter and dialog programming. Flow logic. o PAI. o
PBO. o POV. o POH. Screen designing. Programming in object browser. Field validations. Creation
of o Normal Screens o Sub Screens. o Table Controls. o Tab Strips. Dynamic Screen. o Call Screen. o Set
Screen. o Leave to Screen. o Leave Screen. Processing of list from transaction and vice versa. Screen
table and its fields. Lock objects. INTERFACE PROGRAMMING Why Data Transfers Introduction to
BDC. File Handling. o Presentation server. o Application server. Recordings. Methods in BDC. o Call
transaction. o Session method. Error Handling in Call Transaction. Handling Table Controls in BDC and
Screen Resolutions. Mass Updation. o Vendor master. o Customer master. Legacy System Migration
Workbench (LSMW) o Different methods. o Steps to Create an LSMW Project. o Flat file creation. o
Uploading data. SAP Scripts Introduction. Layout Sets. SAP Script Elements. Modifying standard
layout sets (by using subroutines). Uploading logo. SMARTFORMS Working with smart forms.
Standard Texts. Graphics management. Writing print program and designing layouts. Output type
configuration to standard orders. ADOBE FORMS / INTERACTIVE FORMS (PDF) Introduction Overview
on Form Interface and Layout sets MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS SAP System Landscape. Correction and
Transport System (CTS). Transport Organizer. Workbench Request. Task Creation. Merging
Requests Release Requests. SAP memory. o SET/GET parameters. ABAP memory. o Imports/
Exports. Logical Database and Handling Events (LDB). Field symbols. SD flow. MM flow. CROSS
APPLICATION Introduction to CA. RFC destination. Working with RFC function modules. IDOCS
Concepts of IDOCS. Structure of IDOCS and Types. Creation of segments Creation of IDOCS. o Basic.
o Extension. Creation of message types. Monitoring tools of IDOC interface. o Statistics. o Display
IDOCS. o IDOCS list. ALE Defining logical systems used for ALE interfaces. Outbound / Inbound
processing. Transferring of master data from one system to another system. Distribution modal view.
IDOC filtering. Segment filtering using filter objects. Reduced IDOC. Outbound using change
pointers methods. EDI Overview and architecture. BAPI and Business Objects Introduction to BAPI
Overview of Business Objects. Step By Step Approach followed to create BAPI. ENHANCEMENTS
Introduction to enhancements. Different Ways of doing Enhancements. Types of User Exits. Field
Exits Menu Exit Function Exit. Screen Exi
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PLM - BasicsDokument8 SeitenPLM - BasicsdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Books To Refer CSEDokument3 SeitenBooks To Refer CSEdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
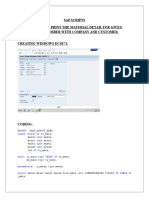
- Sap Scripts 1. Program To Print The Material Detail For Given Material Number With Company and Customer Details. Creating Windows in Se71Dokument4 SeitenSap Scripts 1. Program To Print The Material Detail For Given Material Number With Company and Customer Details. Creating Windows in Se71dhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPSC - Books To ReferDokument2 SeitenUPSC - Books To ReferdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Under Loop in Main Window Table, in Sort Window, Event Log Header Doc No Output Item Doc Wa'sDokument1 SeiteUnder Loop in Main Window Table, in Sort Window, Event Log Header Doc No Output Item Doc Wa'sdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- If Sfsy-Count 001' Text Bank Copy Elseif Sfsy-Count 002' Text Customer Copy Elseif Sfsy-Count 003' Text College Copy EndifDokument1 SeiteIf Sfsy-Count 001' Text Bank Copy Elseif Sfsy-Count 002' Text Customer Copy Elseif Sfsy-Count 003' Text College Copy EndifdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Abap Q & ADokument3 SeitenSap Abap Q & AdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap TblesDokument37 SeitenSap TblesdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection Screen Field Validations:: 'F4 - FILENAME'Dokument3 SeitenSelection Screen Field Validations:: 'F4 - FILENAME'dhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prerequistes: Create Three Internal TablesDokument5 SeitenPrerequistes: Create Three Internal TablesdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packing List ProcessDokument19 SeitenPacking List ProcessdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oops Concept Alv Report ExampleDokument18 SeitenOops Concept Alv Report ExampledhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Search Help Dynamic in Abap ReportsDokument2 SeitenSearch Help Dynamic in Abap ReportsdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create A Report For Following Detail: RequirementDokument12 SeitenCreate A Report For Following Detail: RequirementdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Abap Sample ProgramsDokument5 SeitenSap Abap Sample ProgramsdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Pool Sap ProgrammingDokument19 SeitenModule Pool Sap ProgrammingdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Program in AbapDokument7 SeitenSample Program in AbapdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important PP Table List:: Work CenterDokument5 SeitenImportant PP Table List:: Work CenterdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of SAP CRMDokument5 SeitenOverview of SAP CRMdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- T Codes in SAPDokument6 SeitenT Codes in SAPdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BapiDokument11 SeitenBapidhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
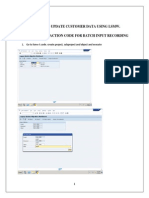
- Program To Update Customer Data Using Lsmw. Xd01 - Transaction Code For Batch Input RecordingDokument15 SeitenProgram To Update Customer Data Using Lsmw. Xd01 - Transaction Code For Batch Input RecordingdhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
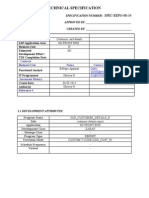
- Technical Specification: General DataDokument3 SeitenTechnical Specification: General DatadhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Example of Praxis TicketDokument3 SeitenExample of Praxis TicketEmily LescatreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link Belt Rec Parts LastDokument15 SeitenLink Belt Rec Parts LastBishoo ShenoudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fund For Local Cooperation (FLC) : Application FormDokument9 SeitenFund For Local Cooperation (FLC) : Application FormsimbiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Law 1Dokument2 SeitenCivil Law 1Len Sor Lu100% (3)
- Thermal Hybrids R5Dokument9 SeitenThermal Hybrids R5amir.kalantariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maturity AssessmentDokument228 SeitenMaturity AssessmentAli ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOVAL Dati Tecnici Caldaie IngleseDokument57 SeitenHOVAL Dati Tecnici Caldaie Ingleseosama alabsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Baseboard StelproDokument4 SeitenElectric Baseboard StelprojrodNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTAG 1 2nd EditionDokument36 SeitenGTAG 1 2nd EditionChristen Castillo100% (2)
- Project SummaryDokument59 SeitenProject SummarynaseebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970Dokument2 SeitenComprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970Bryan AbestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS 531 2006 Code of Practice For Lighting of Work Places Part 1 PDFDokument13 SeitenSS 531 2006 Code of Practice For Lighting of Work Places Part 1 PDFEdmund YoongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Framework For Durable ConcreteDokument8 SeitenFramework For Durable ConcreteDai ThanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normas FieldbusDokument3 SeitenNormas FieldbusAlielson PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Payment (Telecom Operatoers)Dokument12 SeitenE-Payment (Telecom Operatoers)Ahmed SelimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 580N 580SN 580SN WT 590SN With POWERSHUTTLE ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICDokument2 Seiten580N 580SN 580SN WT 590SN With POWERSHUTTLE ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICEl Perro100% (1)
- Arab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2Dokument7 SeitenArab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2samiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Planer PDFDokument8 SeitenHand Planer PDFJelaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tingalpa Green New Townhouse Development BrochureDokument12 SeitenTingalpa Green New Townhouse Development BrochureMick MillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACC 101 - 3rd QuizDokument3 SeitenACC 101 - 3rd QuizAdyangNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument2 SeitenAẄâQâŗÂlïNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS Company RecordsDokument2 SeitenBS Company RecordstNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDMI CABLES PERFORMANCE EVALUATION & TESTING REPORT #1 - 50FT 15M+ LENGTH CABLES v3 SMLDokument11 SeitenHDMI CABLES PERFORMANCE EVALUATION & TESTING REPORT #1 - 50FT 15M+ LENGTH CABLES v3 SMLxojerax814Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arvind Textiles Internship ReportDokument107 SeitenArvind Textiles Internship ReportDipan SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Termsconditions of JionetDokument3 SeitenTermsconditions of JionetskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usb - PoliDokument502 SeitenUsb - PoliNyl AnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Khrone 5 Beam Flow Meter DatasheetDokument16 SeitenKhrone 5 Beam Flow Meter DatasheetAnoop ChulliyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gamesa Wind Turbine Element UpgradesDokument1 SeiteGamesa Wind Turbine Element Upgradesstanislav uzunchevNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS 671Dokument9 SeitenSS 671OwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigger: Business Process Procedure OverviewDokument11 SeitenTrigger: Business Process Procedure Overviewcalalitbajaj100% (1)