Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pump Components Guide for Maintenance and Repair
Hochgeladen von
Lutfi ArdiansyahOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pump Components Guide for Maintenance and Repair
Hochgeladen von
Lutfi ArdiansyahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pump Components
There are a number of standard components for pumps and pump systems.
Parts of a Pump
When a pump breaks down, sometimes buying replacement parts or components is an alternative to
buying a new pump. Most centrifugal pumps consist of a few basic components:
• Housing/casing – The outer shell of the pump which protects most of the components from the
outside elements. The casing of the pump should be of materials suitable to withstand the
environmental conditions of the application (e.g. submersible pumps should be water and rust
corrosion resistant
• Impeller – A rotating disk with a set of vanes coupled to a shaft. When the impeller rotates, it imparts
energy to the fluid to induce flow. Flow characteristics of the pump vary widely based on the impeller
design.
• Motor – The power source of the pump which drives the shaft. AC motors and DC motors are the
most common power sources for pumps, but internal combustion engines (ICEs), hydraulic power,
and steam power are other possibilities.
• Shaft – The shaft connects the impeller to the motor/engine that provides power for the pump.
• Volute – The inner casing that contains the impeller and collects, discharges, and (sometimes)
recirculates the fluid being pumped. The materials used to construct the lining of the pump volute
must be compatible with the handled media.
Other components:
• Bearing assembly – The mechanical support that allows continuous rotation of the impeller and is
continuously lubricated.
• Hub – Device attached to the bearing assembly which is the connecting point for the motor or
engine.
• Seal – Protects the bearing assembly from being contaminated by the pumped media. Some pump
designs are sealless, meaning the pumping mechanism is completely contained within a pressurized
volute chamber with static seals (e.g. gaskets or O-rings).
Parts of the Pump System
Outside of the pump itself are a number of additional components which are part of a complete pumping
system.
• Controllers – Used in conjunction with probes and sensors to provide operational information as
well as automatic or manual control of different pumping functions.
• Fittings and adapters – Parts which connect different system components (pumps, motors,pipe,
hose, etc.) to one-another.
• Mounting devices – Used to allow pumps to be mounted in different ways, such as on walls, on
the ground, or on/near associated stationary equipment.
Pump motor adapters – mounting devices used to connect dissimilar motor and pump bolt
configurations.
• Probes and sensors – Used to measureliquid level,pressure, temperature, and other important
system factors during system operation. Data from probes and sensors are sent to controllers or
computers for system analysis or response.
• Valves – Used to control flow within different parts of the system, including the pump inlet and outlet.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Centrifugal Pump Selection: - Part OneDokument3 SeitenCentrifugal Pump Selection: - Part Oneمنير أحمد100% (1)
- 1.2 Pumps PresentationDokument25 Seiten1.2 Pumps PresentationKristian UretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About Industrial PumpsDokument25 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About Industrial PumpsKristian UretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumps, Valves, FansDokument34 SeitenPumps, Valves, Fansm_alodat6144Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Accessory Gear Box Drives Hydraulic SystemsDokument22 SeitenAircraft Accessory Gear Box Drives Hydraulic SystemsFaisal AwaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics & Pneumatics Chapter 1: Hydraulics (Hydraulic Components)Dokument16 SeitenHydraulics & Pneumatics Chapter 1: Hydraulics (Hydraulic Components)gkhnNoch keine Bewertungen
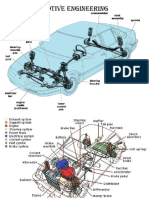
- Unit-I Vehicle Structure and EnginesDokument31 SeitenUnit-I Vehicle Structure and EnginesSirajAyeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Power - (ME353) - Lec6Dokument37 SeitenFluid Power - (ME353) - Lec6Mohamed MaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and Working of Fluid Power SystemsDokument14 SeitenParts and Working of Fluid Power SystemsnidhidarklordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Lift: Abdullah Bin ZiadDokument39 SeitenArtificial Lift: Abdullah Bin ZiadGilbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSC QB 1-7Dokument9 SeitenCSC QB 1-7Vedang ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsDokument7 SeitenHydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsMayur ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chassis Components of Construction EquipmentDokument87 SeitenChassis Components of Construction EquipmentSujit RegmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydraDokument2 SeitenHydraMagesssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and maintenance of gasoline and diesel enginesDokument3 SeitenParts and maintenance of gasoline and diesel enginesErman DeanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air CompressorsDokument26 SeitenAir Compressorskabbilaash kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumps and Pumping Systems1Dokument42 SeitenPumps and Pumping Systems1Pradyumna DhamangaonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Case Study: PumpsDokument43 SeitenTechnical Case Study: Pumpsfahad670Noch keine Bewertungen
- Subject of Technical Report Date Submitted: June 16, 2020 Plasencia, Jerome G. TMEC 5-1Dokument14 SeitenSubject of Technical Report Date Submitted: June 16, 2020 Plasencia, Jerome G. TMEC 5-1Bimby FaggotNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Seminar Report ON Air Powered EngineDokument46 SeitenA Seminar Report ON Air Powered EngineAsif SkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Centrifugal Pumps PDFDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To Centrifugal Pumps PDFOscar DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engine Components GuideDokument7 SeitenInternal Combustion Engine Components GuideengineeringdesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICE Components & SystemsDokument50 SeitenICE Components & Systemssukku18121991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Process Plant Utilities: Submitted ToDokument17 SeitenAssignment Process Plant Utilities: Submitted ToMaham FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automobile Engineering: Prepared by Dr.T.Yuvaraj Asp / MechDokument173 SeitenAutomobile Engineering: Prepared by Dr.T.Yuvaraj Asp / MechGetachew TikueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ae 1 90Dokument90 SeitenAe 1 90Er Dinesh ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To IC EngineDokument48 SeitenIntroduction To IC EngineNur JemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLOW MORE PUMPS LTD. INDUSTRIAL TRAINING REPORTDokument40 SeitenFLOW MORE PUMPS LTD. INDUSTRIAL TRAINING REPORTAbu Obaidah Khan100% (1)
- IHP Micro ProjectDokument13 SeitenIHP Micro ProjectROHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumps: Created By-Suneth Bombuwela Student Number - 6622313Dokument32 SeitenPumps: Created By-Suneth Bombuwela Student Number - 6622313Suneth Dilusha BombuwelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Morning Everyone: Reporters For Today: Mr. President: Denis Celocia Body Guard: General Patrick CagandeDokument44 SeitenGood Morning Everyone: Reporters For Today: Mr. President: Denis Celocia Body Guard: General Patrick CagandeUps YamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AirSystem - Hydraulic SystemDokument2 SeitenAirSystem - Hydraulic SystemYves CaraangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass. 2Dokument18 SeitenAss. 2Ramez RaymonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumps - Hassan ElBanhawiDokument20 SeitenPumps - Hassan ElBanhawijesus_manrique2753Noch keine Bewertungen
- First SeminarDokument30 SeitenFirst SeminarNan OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ActuatorsDokument86 SeitenActuatorsSrinivasan V PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Brake System PDFDokument61 SeitenAutomotive Brake System PDFwanaw100% (2)
- Presentation ON Hydraulic Control System Control Engineering (2151908)Dokument26 SeitenPresentation ON Hydraulic Control System Control Engineering (2151908)Marwan NasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 503 Rotating Equipment I Pump: Aiman Nazmi Bin Rosli Faculty of Chemical Engineering Uitm 012-3929445Dokument30 SeitenCHE 503 Rotating Equipment I Pump: Aiman Nazmi Bin Rosli Faculty of Chemical Engineering Uitm 012-3929445Nurtasha AtikahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument27 SeitenModule 2Salt PapiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PumpsDokument36 SeitenPumpsNo NameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Ii Robot Drive Systems AND End Effectors: Prepared by B.Balasubramanian Ap/Mech CcetDokument89 SeitenUnit Ii Robot Drive Systems AND End Effectors: Prepared by B.Balasubramanian Ap/Mech CcetBala mechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic ActuatorDokument55 SeitenHydraulic ActuatorMASOUD75% (4)
- Screw Pump: Presented By: Padon, Mric Kimjim JDokument24 SeitenScrew Pump: Presented By: Padon, Mric Kimjim JJohn A. CenizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel PPDokument58 SeitenDiesel PPManvendra Pratap Singh Bisht100% (1)
- Unit 5 ActuatorsDokument18 SeitenUnit 5 ActuatorsKAMALJEET SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Pumps Pumping SystemsDokument42 SeitenLecture 4 Pumps Pumping SystemsKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal PumpsDokument24 SeitenCentrifugal PumpsHari Babu DharmavarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic DrivesDokument56 SeitenUNIT-1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic DrivesChetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Pump Characteristics and Energy Efficiency GuideDokument69 SeitenHVAC Pump Characteristics and Energy Efficiency Guidekarthikraja21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pump System Design GuideDokument21 SeitenPump System Design GuideP Priya100% (1)
- MintenaceDokument26 SeitenMintenaceAdugna GosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical study of a centrifugal pumpDokument82 SeitenPhysical study of a centrifugal pumpArthur Maderse Ramo Jr.100% (1)
- An Overview of Pumps - ReportDokument14 SeitenAn Overview of Pumps - ReportCraigWoolvineNoch keine Bewertungen
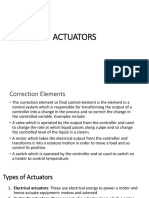
- Correction ElementDokument20 SeitenCorrection ElementKelvin Oscar nsituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryVon EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operator’S Guide to Centrifugal Pumps: What Every Reliability-Minded Operator Needs to KnowVon EverandOperator’S Guide to Centrifugal Pumps: What Every Reliability-Minded Operator Needs to KnowBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Misumi OilFreeBushing p281 282Dokument1 SeiteMisumi OilFreeBushing p281 282Lutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misumi OilFreeBushing p399 400Dokument1 SeiteMisumi OilFreeBushing p399 400Lutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Free Bushings Oil Free Bushings: Copper Alloy, Flanged, Standard C-VALUE Products - Copper Alloy, Flanged, StandardDokument1 SeiteOil Free Bushings Oil Free Bushings: Copper Alloy, Flanged, Standard C-VALUE Products - Copper Alloy, Flanged, StandardLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM Substation Connector PeakWithstandCurrentDokument16 SeitenFEM Substation Connector PeakWithstandCurrentLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creep Age and ClearanceDokument9 SeitenCreep Age and ClearancearashengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altair SimSolid 2019 - Thermal Analysis Concepts GuideDokument13 SeitenAltair SimSolid 2019 - Thermal Analysis Concepts GuideLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Std-Comp Dead Ends-ACSRDokument12 SeitenStd-Comp Dead Ends-ACSRLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanic Corrosion White PaperDokument7 SeitenGalvanic Corrosion White Paperleo_hindartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapping ISO 14001 - 2015 To ISO 14001 - 2004 PDFDokument3 SeitenMapping ISO 14001 - 2015 To ISO 14001 - 2004 PDFsuresh kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bimetallic CorrosionDokument20 SeitenBimetallic CorrosionchristophedepaepeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnet pump for chemical and sea water applicationsDokument6 SeitenMagnet pump for chemical and sea water applicationsLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Carbon Steel - Chemical Composition & Application SummaryDokument11 SeitenAn Overview of Carbon Steel - Chemical Composition & Application SummaryLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perbedaan ISO9001 PDFDokument6 SeitenPerbedaan ISO9001 PDFdevanyactqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bimetallic CorrosionDokument20 SeitenBimetallic CorrosionchristophedepaepeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultramid BASF BrochureDokument68 SeitenUltramid BASF BrochureLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACSR BS215 Part 2Dokument1 SeiteACSR BS215 Part 2Ade Y SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SATA Master Catalogue-2014 PDFDokument83 SeitenSATA Master Catalogue-2014 PDFLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanic Action ChartDokument1 SeiteGalvanic Action ChartLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understand The Basics of Centrifugal Pump Operations (CEP)Dokument5 SeitenUnderstand The Basics of Centrifugal Pump Operations (CEP)Ari Firmansyah100% (1)
- Corona EffectDokument4 SeitenCorona EffectArturo MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1189 MATS1 Definition With TYPSTRN in Optistruct1Dokument2 Seiten1189 MATS1 Definition With TYPSTRN in Optistruct1Lutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- F-Production MethodsDokument2 SeitenF-Production MethodsLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOC 217076 Facts About Plasma Technology FA Low ResDokument32 SeitenBOC 217076 Facts About Plasma Technology FA Low ResAndrei SavvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastomer PropertiesDokument1 SeiteElastomer PropertiesLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dulmison, Helpful Reference TablesDokument16 SeitenDulmison, Helpful Reference TablescheesobeachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Range Stress Strain CurvesDokument45 SeitenFull Range Stress Strain CurvesLoffegutt100% (1)
- Method For Determining The Quality of A Crimped Connection Between A Conductor and A ContactDokument16 SeitenMethod For Determining The Quality of A Crimped Connection Between A Conductor and A ContactLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stranded Copper Conductor Sizes ChartDokument1 SeiteStranded Copper Conductor Sizes ChartLutfi ArdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bomag Bw141 151 154 Acad 4 Service TrainingDokument20 SeitenBomag Bw141 151 154 Acad 4 Service Trainingyvonne100% (40)
- Main Business Lines and ServicesDokument15 SeitenMain Business Lines and ServicesTrellindo Solusi TeknikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volkswagen Golf Brochure 2014Dokument33 SeitenVolkswagen Golf Brochure 2014xxSRAMxx67% (3)
- L28 32H Manual PDFDokument512 SeitenL28 32H Manual PDFYurii0% (1)
- Automated Power Assessment For Turboshaft EnginesDokument15 SeitenAutomated Power Assessment For Turboshaft EnginesMustafaAl-ShawafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Drive Positioner System GuideDokument138 SeitenAutomatic Drive Positioner System GuideMrihexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drive Unit Guide CompleteDokument46 SeitenDrive Unit Guide CompleteRonald Fernandez ManubuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citroen Bosch EDC16 PDFDokument104 SeitenCitroen Bosch EDC16 PDFNenad Chip Tuning Aleksic100% (2)
- ISO-9001:2008 Blower O&M ManualDokument33 SeitenISO-9001:2008 Blower O&M Manualfaqdani100% (1)
- Engine Number GuideDokument4 SeitenEngine Number GuideMksreekanthMkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salient Features of RA 4136Dokument5 SeitenSalient Features of RA 4136Mhaebilyn Dizon100% (2)
- P938-1 CM20190226-27990-63519Dokument6 SeitenP938-1 CM20190226-27990-63519ANDRE LUIZ RAMOS DE FREITASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Owners Manual QSL9 CM2350 L102: Cummins Customer Assistance Center 1-800-DIESELS Applicable Only in U.S.A. and CanadaDokument201 SeitenOwners Manual QSL9 CM2350 L102: Cummins Customer Assistance Center 1-800-DIESELS Applicable Only in U.S.A. and Canadajodhraj.gurjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae.Dokument3 SeitenCurriculum Vitae.Isaya cosmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article 516 FordFocusFCVDokument7 SeitenArticle 516 FordFocusFCVbxlmichael8837Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Propulsive and Thermal Management System Design For Optimal Hybrid Electric Aircraft PerformanceDokument17 SeitenIntegrated Propulsive and Thermal Management System Design For Optimal Hybrid Electric Aircraft PerformanceAli DENİZNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Conservation GuidelinesDokument6 Seiten05 Conservation GuidelinesRIAN NOFENDRINoch keine Bewertungen
- ETL Yanmar Schneefraese YSR 1820 - 2220 - 2720Dokument115 SeitenETL Yanmar Schneefraese YSR 1820 - 2220 - 2720linnorman123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Sciences: TEG Design For Waste Heat Recovery at An Aviation Jet Engine NozzleDokument21 SeitenApplied Sciences: TEG Design For Waste Heat Recovery at An Aviation Jet Engine NozzlemeracarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT Inspection IntervalsDokument19 SeitenCT Inspection IntervalsSantiago67% (3)
- Catalogo Lambda SensorsDokument2 SeitenCatalogo Lambda SensorsRogério MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0K4291-G SG0100 9.0 INDUSTRIAL 20 Mar 2020 PDFDokument6 Seiten0K4291-G SG0100 9.0 INDUSTRIAL 20 Mar 2020 PDFGustavoCalderonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-How Many Minutes Should The Aircraft Battery Last? 2 - What Is The Correct Exterior Light Usage? Phase of Flight Light UsageDokument4 Seiten1-How Many Minutes Should The Aircraft Battery Last? 2 - What Is The Correct Exterior Light Usage? Phase of Flight Light UsageLucinda AdamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switched Reluctance Drives For Electric Vehicle ApplicationsDokument7 SeitenSwitched Reluctance Drives For Electric Vehicle ApplicationsHuynh Thanh AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series II Wheel LoaderDokument24 SeitenSeries II Wheel LoaderCARLA EMANOELE LABIAPARI NASCIMENTONoch keine Bewertungen
- Coffee Tumbler Power BankDokument6 SeitenCoffee Tumbler Power BankMatt Julius CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineer Muhib Ur Rehman ResumeDokument3 SeitenElectrical Engineer Muhib Ur Rehman ResumeEngr Muhib KhÅñNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deutz Silnik Tcd2012-2013Dokument102 SeitenDeutz Silnik Tcd2012-2013Mateusz Gmiąt100% (1)
- 12H Frein TestDokument13 Seiten12H Frein TestaniriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grove GMK 4090aDokument12 SeitenGrove GMK 4090aMarco Torres HenrriquezNoch keine Bewertungen