Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
JECFA Additive-108-M1 Carmine PDF
Hochgeladen von
Grisselda PriliacitaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
JECFA Additive-108-M1 Carmine PDF
Hochgeladen von
Grisselda PriliacitaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CARMINES
Prepared at the 55th JECFA (2000) and published in FNP 52 Add 8 (2000),
superseding specifications prepared at the 44th JECFA (1995) and
published in FNP 52 Add 3 (1995). Metals and arsenic specifications revised
at the 59th JECFA (2002). A group ADI of 0-5 mg/kg bw for carmines, as
ammonium carmine or the equivalent of Ca, K and Na salts was established
at the 26th JECFA (1982) and maintained at the 55th JECFA (2000).
SYNONYMS Cochineal carmine, Carmine, CI Natural Red 4, CI (1975) No. 75470; INS
No. 120
DEFINITION Obtained by aqueous extraction of cochineal, which consists of the dried
bodies of the female insect Dactylopius coccus Costa; the colouring principle
is a hydrated aluminium chelate of carminic acid in which aluminium and
carminic acid are thought to be present in the molar ratio 1:2.
In commercial products the colouring principle is present in association with
ammonium, calcium, potassium or sodium cations, singly or in combination,
and these cations may also be present in excess. Products may also contain
proteinaceous material derived from the source insect, and may also contain
free carminate or a small excess of aluminium cations.
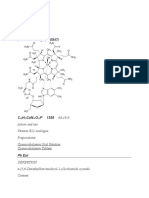
Chemical names Hydrated aluminium chelate of carminic acid (7-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-
3,5,6,8-tetrahydroxy-1-methyl-9,10-dioxo-anthracene-2-carboxylic acid)
C.A.S. number 1390-65-4 (carmine)
1260-17-9 (carminic acid)
Chemical formula Carminic acid: C22H20O13
Structural formula Carminic acid:
Possible structural formula for the aluminium complex of carminic acid:
M+: cation ½ Ca++, Na+, K+, NH4+
Formula weight Carminic acid: 492.39
Assay Not less than 50% of C22H20O13 on the dry basis
DESCRIPTION Red to dark red, crumbly solid or powder
FUNCTIONAL USES Colour
CHARACTERISTICS
IDENTIFICATION
Solubility (Vol. 4) The solubility of carmine preparations varies depending on the nature of the
cations present. Products where the major cation is ammonium (ammonium
carminate) are freely soluble in water at pH 3.0 and pH 8.5. Products where
the major cation is calcium (calcium carminate) are very slightly soluble in
water at pH 3.0 but freely soluble at pH 8.5.
Colour reactions Make a solution of the sample slightly alkaline by adding 1 drop of 10%
sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solution. A violet colour is
produced.
Add a small sodium dithionite (Na2S2O4) crystal to acid, neutral or alkaline
solutions of the sample. The solutions are not decolourized.
Dry a small quantity of the sample in a porcelain dish. Cool thoroughly and
treat the dry residue with 1 or 2 drops of cold sulfuric acid TS. No colour
change occurs.
Acidify a dispersion of the sample in water with 1/3 volume of hydrochloric
acid TS and shake it with amyl alcohol. Wash the amyl alcohol solution 2-4
times with an equal volume of water to remove hydrochloric acid. Dilute the
amyl alcohol solution with 1-2 volumes of petroleum ether (40-60o) and
shake with a few small portions of water to remove colour. Add, dropwise,
5% uranium acetate, shaking thoroughly after each addition. A characteristic
emerald-green colour is produced.
PURITY
Loss on drying (Vol. 4) Not more than 20% (135 o, 3h)
Total ash (Vol. 4)) Not more than 12%
Test 1 g of the sample as directed in the test for Ash (Total Ash)
Protein (Vol. 4) Not more than 25%
Proceed as directed under Nitrogen Determination (non-ammonia N x 6.25)
Matter insoluble in dilute Not more than 1%
ammonia (Vol. 4) Dissolve about 0.25 g of the sample, previously dried and accurately
weighed, in 2.5 ml of dilute ammonia solution (160 ml of strong ammonia TS,
made up to 500 ml) and dilute to 100 ml with water: the solution is clear.
Filter through a sintered glass filter (British Standard Grade No. 3). Wash
with a 0.1% ammonia solution and dry to constant weight at 105º.
Lead (Vol. 4) Not more than 5 mg/kg
Determine using an atomic absorption technique appropriate to the specified
level. The selection of sample size and method of sample preparation may
be based on the principles of the method described in Volume 4,
“Instrumental Methods.”
Microbiological criteria Salmonella: Negative per test
(Vol. 4)
METHOD OF ASSAY Weigh accurately about 100 mg of the sample, dissolve in 30 ml of boiling
2N hydrochloric acid and cool. Transfer quantitatively to a 1000-ml
volumetric flask, dilute to volume with water, and mix. Determine the
absorbance of the solution in a 1 cm cell at the wavelength of maximum
absorbance (about 494 nm) using water as the blank. Calculate the
percentage of carminic acid in the sample analysis using the formula:
where
A = absorbance of the sample solution;
W = weight, in mg, of the sample taken; and
1.39 = absorbance of a solution of carminic acid having a concentration of
100 mg per 1000 ml
If the measured absorbance of the solution is not within the range 0.650 to
0.750, prepare another sample and adjust the weight accordingly.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresVon EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisVon EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Cochineal ExtractDokument3 SeitenCochineal ExtractAnggriani BusinessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 377Dokument2 SeitenAdditive 377Mayra MayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Ammonium Sulfate Fao CriteriaDokument2 SeitenAluminium Ammonium Sulfate Fao CriteriaVictor Hugo HinojosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B AsulamDokument7 SeitenB Asulamjessica montielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferrous Glycinate (Processed With Citric Acid) : SynonymsDokument3 SeitenFerrous Glycinate (Processed With Citric Acid) : SynonymsIfra AkhlaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium ChlorideDokument2 SeitenPotassium ChlorideRajesh RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ca-Laktate JecfaDokument2 SeitenCa-Laktate JecfaAslih N PT SIGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processed Eucheuma Seaweed: SynonymsDokument8 SeitenProcessed Eucheuma Seaweed: SynonymsLabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Method of Mercury, Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead and Chromium in FertilizersDokument8 SeitenAnalytical Method of Mercury, Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead and Chromium in FertilizersGenaro PalacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- EUsalt AS014-2005 Total Cadmium - Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric MethodDokument5 SeitenEUsalt AS014-2005 Total Cadmium - Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric MethodThuc Quyen TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5 Carboxylic AcidDokument12 SeitenLab 5 Carboxylic AcidalihusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monografi JECFA Additive-390-M11 SALP BasicDokument2 SeitenMonografi JECFA Additive-390-M11 SALP BasicM. Amalul AhliNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSFA - Fosfato Tricálcico (Additive 341)Dokument2 SeitenGSFA - Fosfato Tricálcico (Additive 341)andreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 475Dokument2 SeitenAdditive 475ayu kristiyaningrumNoch keine Bewertungen
- AOCS CD 8 53 Peroxido Con CL PDFDokument2 SeitenAOCS CD 8 53 Peroxido Con CL PDFIvone Sulistya92% (13)
- JECFA Carrageenan MonographDokument5 SeitenJECFA Carrageenan MonographSurya SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Ammonium Sulfate: SynonymsDokument2 SeitenAluminium Ammonium Sulfate: SynonymsadriaanvarelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 117Dokument9 SeitenAdditive 117Heru KristanokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TESTING PB, CD, As, HG FOR FRUITY FLV POWDERDokument9 SeitenTESTING PB, CD, As, HG FOR FRUITY FLV POWDERNguyễn Ngọc MaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acesulfame Potassium: SynonymsDokument2 SeitenAcesulfame Potassium: SynonymsAslih N PT SIGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 091 m1Dokument2 SeitenAdditive 091 m1Patel HitendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascorbic AcidDokument2 SeitenAscorbic AcidMulayam Singh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Practical'sDokument38 SeitenChemistry Practical'sTvara PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - Xii Subject: Chemistry (Practical) Term-2 Experiments (2021 - 22)Dokument34 SeitenClass - Xii Subject: Chemistry (Practical) Term-2 Experiments (2021 - 22)CarbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5Dokument10 Seiten5Syahira YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disodium Salt Tests For Detecting Fe%Dokument4 SeitenDisodium Salt Tests For Detecting Fe%NIKHIL SHINDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 164Dokument3 SeitenAdditive 164izzybjNoch keine Bewertungen
- EUsalt AS 013-2005 Total Lead - Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric MethodDokument5 SeitenEUsalt AS 013-2005 Total Lead - Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric MethodThuc Quyen TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Amónicas Del Ácido Fosfatídico SIN 442Dokument4 SeitenSales Amónicas Del Ácido Fosfatídico SIN 442Andrea Sanchez AbarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- $ro4a6yq (2017 - 11 - 27 15 - 16 - 35 Utc)Dokument6 Seiten$ro4a6yq (2017 - 11 - 27 15 - 16 - 35 Utc)Rob DamhuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 096 m17Dokument3 SeitenAdditive 096 m17lox agencyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amla Dry ExtractDokument4 SeitenAmla Dry ExtractHarrizul RivaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (Cod)Dokument8 SeitenChemical Oxygen Demand (Cod)evreddy05100% (4)
- Lab Report Environmental Engineering 2 (CEL304)Dokument40 SeitenLab Report Environmental Engineering 2 (CEL304)Shivang KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metode Analisis BTPDokument30 SeitenMetode Analisis BTPNurlaela ElaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive-021 2 PDFDokument2 SeitenAdditive-021 2 PDFGunjan KalyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benzyl Alcohol: SynonymsDokument3 SeitenBenzyl Alcohol: SynonymsArroNoch keine Bewertungen
- EuSalt AS007-2005 Potassium - Sodium Tetraphenylborate Volumetric MethodDokument5 SeitenEuSalt AS007-2005 Potassium - Sodium Tetraphenylborate Volumetric MethodNguyễn Khắc HảiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Environmental Engineering 2 (CEL304)Dokument40 SeitenLab Report Environmental Engineering 2 (CEL304)Shivang KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium SaccharinDokument2 SeitenPotassium SaccharinNguyễn LinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th ChemistryDokument39 Seiten12th Chemistryanonymous3256tNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iodine ValueDokument4 SeitenIodine ValueRobert Gilmore100% (4)
- Test Method - AlumDokument9 SeitenTest Method - AlumAqmar Aqeem Bin Azhar100% (1)
- Chemical Test Procedure FinalDokument51 SeitenChemical Test Procedure Finallekshmi_remesh100% (2)
- Cyanocobalamin BPDokument4 SeitenCyanocobalamin BPjaimurugeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive-323-M16polyoxyethylene Sorbitan Monostearate (POS)Dokument2 SeitenAdditive-323-M16polyoxyethylene Sorbitan Monostearate (POS)Benni IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD ChlorineDokument30 SeitenSTD ChlorineMunawar HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods For Estimation of Preservatives in Treated Timber and in Treating SolutionsDokument7 SeitenMethods For Estimation of Preservatives in Treated Timber and in Treating SolutionsSajidAliKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titrimetric Determination of CO2 in EthanolaminesDokument3 SeitenTitrimetric Determination of CO2 in EthanolaminesDavinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit Tests: by Mohneet Chitkara B Pharma Semester 1 2150991058Dokument13 SeitenLimit Tests: by Mohneet Chitkara B Pharma Semester 1 2150991058Mohneet ChitkaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AOCS - CD - 8-53 Peroxido Con CLDokument2 SeitenAOCS - CD - 8-53 Peroxido Con CLmanuelsnic100% (5)
- 12th Chemistry PracticalDokument88 Seiten12th Chemistry Practicalsavitristiching100% (1)
- Chemistry Practical T1 XIIDokument15 SeitenChemistry Practical T1 XIIlegendmitthu002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ammonium GlycyrrhizateDokument2 SeitenAmmonium GlycyrrhizateAndré C. de PaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 043 PDFDokument2 SeitenAdditive 043 PDFokikwmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt of Fatty AcidDokument9 SeitenSalt of Fatty AcidFermi Dio AlfatyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterVon EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryVon EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Mailard ReactionDokument16 SeitenMailard ReactionGrisselda PriliacitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A I0345eDokument141 SeitenA I0345eGrisselda PriliacitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JECFA Beta Carotenes - (Vegetable) - INS-No.-160a (Ii) PDFDokument2 SeitenJECFA Beta Carotenes - (Vegetable) - INS-No.-160a (Ii) PDFGrisselda PriliacitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mozzarella ProcessingDokument28 SeitenMozzarella ProcessingGrisselda PriliacitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konver PPM Ke MikrosiemensDokument1 SeiteKonver PPM Ke MikrosiemensGrisselda PriliacitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Worksheet: Conceptual QuestionsDokument2 SeitenPhysics Worksheet: Conceptual QuestionsGuliverov DedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- q1 ST 2 Gr.4 Science With TosDokument6 Seitenq1 ST 2 Gr.4 Science With TosJunaly GarnadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gia Ingles Faase1 Parte 33Dokument7 SeitenGia Ingles Faase1 Parte 33yodaimefredyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis & Working Patial Structre in Haldi Ram'sDokument95 SeitenRatio Analysis & Working Patial Structre in Haldi Ram'sAnkit Singh0% (2)
- Eco Straw - Mid Exam Group Entrepreneur PDFDokument3 SeitenEco Straw - Mid Exam Group Entrepreneur PDFJUNITA WAFOMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tsaa Laya Brochure 2015Dokument12 SeitenTsaa Laya Brochure 2015Elijah MahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euroland Food SA Case Study - Syndicate ABD2GDokument11 SeitenEuroland Food SA Case Study - Syndicate ABD2Gghazian luthfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third ConditionalDokument1 SeiteThird ConditionalLuisa Joanna Falcón OrdazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Containers: Activity TypeDokument2 SeitenContainers: Activity TypeТарас РовенськийNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frenchsem 6Dokument21 SeitenFrenchsem 6Ritesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- About SaffronDokument9 SeitenAbout SaffronVishal Sharma100% (1)
- First Class Menu Long Haul FlightsDokument16 SeitenFirst Class Menu Long Haul FlightsVivek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- LABELDokument2 SeitenLABELerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Luff Schoorl MethodDokument4 SeitenLuff Schoorl MethodrheamaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roti CookBookDokument11 SeitenRoti CookBookMKPashaPashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSADokument54 SeitenRSAAlexander Rueda OrduzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budget Meal Plan 1 PDFDokument14 SeitenBudget Meal Plan 1 PDFAnaLiggiaSamayoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 & 8 Bar Design and Layout & Bar Operation BHM 2nd SEM F&B ServiceDokument11 SeitenUnit 7 & 8 Bar Design and Layout & Bar Operation BHM 2nd SEM F&B ServiceAryan Mahto67% (6)
- PREFER (Tercih Etmek) : Question FormDokument2 SeitenPREFER (Tercih Etmek) : Question Formasfasfasdfasfasfaf100% (1)
- Pre-Columbian Surface MetallurgyDokument8 SeitenPre-Columbian Surface MetallurgyAantchuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Everest Base Camp Trekking OfferDokument2 SeitenSpecial Everest Base Camp Trekking OfferNepal Trekking GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument50 SeitenReportDeavoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quit Caffeine 1.3 PDFDokument113 SeitenQuit Caffeine 1.3 PDFNawaf Almahdi100% (2)
- Engg Chem Lab ManualDokument45 SeitenEngg Chem Lab ManualShariq Farooqui0% (1)
- Einstein's Riddle For Children and AdultsDokument19 SeitenEinstein's Riddle For Children and Adultsa2kmHamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moldova PresentationDokument39 SeitenMoldova Presentationm1eme1mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production of Yogurt With Enhanced Levels of Gamma Aminobutyric Acid and Valuable Nutrients Using Lactic Acid Bacteria and Germinated Soybean ExtractDokument5 SeitenProduction of Yogurt With Enhanced Levels of Gamma Aminobutyric Acid and Valuable Nutrients Using Lactic Acid Bacteria and Germinated Soybean ExtractMuhammad Subchi Wira PutratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1. Prepare A List of Bar Equipment With Pictures and Their UsesDokument7 SeitenQ1. Prepare A List of Bar Equipment With Pictures and Their UsesYash Chhabra100% (1)
- 2 Determine Critical Control Points (CCPS)Dokument5 Seiten2 Determine Critical Control Points (CCPS)Andre MarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAHEHE DanoneDokument2 SeitenWAHEHE DanoneJovin0% (1)