Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Physics I - GS111
Hochgeladen von
Asghar Hussain ShahOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics I - GS111
Hochgeladen von
Asghar Hussain ShahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Course Outline
Rev No 2
SUIT Credit Hours : 2-1 Page 1 of 2 pages
Dated: 15.10.04
GS 111
Physics I
Engineering Physics
Text Books:- University Physics by Sears, Zemansky and Young, 7th Edition, Addison-
Wesley Publication company.
Reference Book:-
Fundamentals of Physics, 5th Edition by Halliday, Resnick and Walker
Course Description:-
This course introduces fundamental concepts of motion in one Dimension, freely falling
bodies, Projectile motion, Electromagnetism, Gauss' law and its application, Kirchoff's laws
and Complex Networks Analysis.
Pre-requisite:- Nil
Grading Policy:-
In Semester Evaluation: 30%
Final Evaluation: 70%
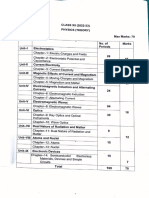
Week-Wise Breakdown
Week Topics/Activities Chapter
Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Standards and Units, Unit
consistency and conversion, Precision and significant figures,
1,2 Estimates and Order of magnitude, Vectors and vector addition & 1
subtraction, components of vectors, Unit vectors, product of
vectors
Motion along a Straight Line: Average and instantaneous velocities,
average and instantaneous accelerations, motion with constant
3,4 2
acceleration, velocity and coordinate by integration, freely falling
bodies, relative velocity
Work and Energy: Conservation of energy, work, work done by a
5 7
varying force, work and kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy
Elastic potential energy, conservative and dissipative forces, internal
6 7
work energy, power, automotive power
Impulse and momentum: Impulse and momentum, conservation of
7 momentum, collisions, inelastic and elastic collisions, recoils, centre 8
of mass
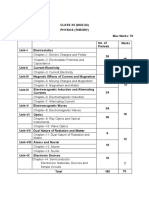
Course Outline
Rev No 2
SUIT Credit Hours : 2-1 Page 2 of 2 pages
Dated: 15.10.04
GS 111
Coulomb’s Law: Electric Charge, atomic structure, electrical
8 conductors and insulators, charging by induction, Coulomb’s law and 24
its applications
The Electric Field: Electric field and electrical forces, electric-field
9 forces, field lines, Gauss’s law and its applications, charges on 25
conductors
10 Mid Term Examination
Electrical Potential: Electrical potential energy, potential and its
11 calculations, equi-potential surfaces, potential gradient, the Millikan 26
Oil-Drop experiment, The Electron-Volt, The Cathode Ray tube
Capacitance and Dielectrics: Capacitors, the parallel-plate capacitors,
capacitors in series and parallel, energy of a charged capacitor, effect
12,13 27
of a dielectric, molecular model of induced charge, Gauss’s law in
dielectrics.
Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force: Current, Resistivity,
14 resistance, electromotive force, current-voltage relation, energy and 28
power in electrical circuits, theory of metallic conduction
Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces: Magnetism, magnetic field,
15 magnetic field lines and magnetic flux, motion of a charged particle in 30
a magnetic field, Thomson’s measurement of e/m
Isotopes and mass spectroscopy, Magnetic force on a conductor, force
16 30
and torque on a current loop, the direct current motor, the Hall Effect
Sources of Magnetic Field: Magnetic field of a moving charge, MF
of a current element, MF of a long straight conductor, forces between
17 31
parallel conductors, magnetic field of a circular loop, Ampere’s Law
and its applications
Induction Phenomenon, Motional electromotive force, Faraday’s Law,
18 32
Lenz’s Law, Eddy Currents
19 Revision
20 End Semester Exam
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Introduction To Physics GS 111Dokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Physics GS 111Areeb ÂhmēdNoch keine Bewertungen
- (B-Tech Elt Course Outline) Physics I - GS111Dokument2 Seiten(B-Tech Elt Course Outline) Physics I - GS111sherry420Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4: Work, Energy and Power: JEE MAIN 2022 PHYSICS SyllabusDokument4 SeitenUnit 4: Work, Energy and Power: JEE MAIN 2022 PHYSICS SyllabusAditya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4: Work, Energy and Power: JEE MAIN 2021 PHYSICS SyllabusDokument4 SeitenUnit 4: Work, Energy and Power: JEE MAIN 2021 PHYSICS SyllabusRukmini AdithyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units Topics: Remark (Completion)Dokument4 SeitenUnits Topics: Remark (Completion)siddanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aieee Physics SyllabusDokument5 SeitenAieee Physics SyllabusSarvesh KanaujiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Super 500 Questions With SolutionsDokument101 SeitenPhysics Super 500 Questions With SolutionsApurv MalviyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Syllabus For B.Tech. (4years) / Biotechnology-Dual Degree (B.Tech / M.Tech) & B.SC - NursingDokument11 SeitenPhysics: Syllabus For B.Tech. (4years) / Biotechnology-Dual Degree (B.Tech / M.Tech) & B.SC - NursingARYAN RATHORENoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET 2024 Physics Revised SyllabusDokument6 SeitenNEET 2024 Physics Revised Syllabusvaidsakshi43Noch keine Bewertungen
- Section: A (80% Weightage) Unit - 1Dokument9 SeitenSection: A (80% Weightage) Unit - 1maverickNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main Syllabus at A Glance Pages PDFDokument10 SeitenJEE Main Syllabus at A Glance Pages PDFSuman DewasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - Physics-1698910501601Dokument5 SeitenReduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - Physics-1698910501601manavsharma17012006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mains Syllabus ReducedDokument16 SeitenMains Syllabus ReducedbaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics-SyllabusDokument3 SeitenPhysics-Syllabusmohitabochare396Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers Physics-1Dokument545 SeitenArihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers Physics-1Krishna K70% (20)
- Joint Entrance Examination (Main) - 2023: PhysicsDokument5 SeitenJoint Entrance Examination (Main) - 2023: PhysicsLakshya SinghiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics PDFDokument517 SeitenPhysics PDFParth ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Physics Material PDFDokument273 Seiten12th Physics Material PDFMuraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- West Bangal State University: Syllabus B.Sc. (General) - PHYSICSDokument8 SeitenWest Bangal State University: Syllabus B.Sc. (General) - PHYSICSRikta DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Tech Le Sylabus For KiteeDokument3 SeitenB Tech Le Sylabus For KiteeRanjan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section - A: Physics Syllabus A Pertains To TheDokument12 SeitenSection - A: Physics Syllabus A Pertains To Thekushal bhatkal100% (2)
- Study Material 12th Physics 2023-24Dokument154 SeitenStudy Material 12th Physics 2023-24ayusanupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Syllabus SNUCEE 2022Dokument3 SeitenPhysics Syllabus SNUCEE 2022BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main 2024 Physics SyllabusDokument5 SeitenJEE Main 2024 Physics Syllabussardarrohan765Noch keine Bewertungen
- PC SyllabusDokument11 SeitenPC SyllabusRaunak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Physics 22 23Dokument9 SeitenSyllabus Physics 22 23the SkulptorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2022 23Dokument13 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2022 23PrahasNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE (Main) Physics Syllabus: UNIT 1: Physics and MeasurementDokument7 SeitenJEE (Main) Physics Syllabus: UNIT 1: Physics and Measurementmajji satishNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIPMT Syllabus 2012Dokument18 SeitenAIPMT Syllabus 2012Amit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SyllabusDokument4 SeitenPhysics SyllabusFroFee FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Syllabus 2022Dokument5 SeitenPhysics Syllabus 2022Ayan AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- My ProjectDokument15 SeitenMy Projectbhatr407Noch keine Bewertungen
- XII PhysicsDokument283 SeitenXII PhysicsNripendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0000Dokument16 SeitenWa0000subhajit mondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SrSec 2023-24Dokument5 SeitenPhysics SrSec 2023-24Abhishek SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class12th Syllabus 2023-24 (PCM+Ec+ PE)Dokument39 SeitenClass12th Syllabus 2023-24 (PCM+Ec+ PE)om9213720Noch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main Physics SyllabusDokument5 SeitenJEE Main Physics SyllabusRanjit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii Physics Split Up 2022-23 (27.07.22)Dokument6 SeitenXii Physics Split Up 2022-23 (27.07.22)HADINoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Brochure For SAAT 2015Dokument18 SeitenInformation Brochure For SAAT 2015Neepur GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument5 SeitenPhysicsamazon audibleNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main Syllabus PDFDokument44 SeitenJEE Main Syllabus PDFAkash KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS (Code No. 042) : Besides, The Syllabus Also Attempts ToDokument11 SeitenPHYSICS (Code No. 042) : Besides, The Syllabus Also Attempts ToRanit MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics of HS 2nd Year 2023 24Dokument6 SeitenPhysics of HS 2nd Year 2023 24Swapan DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 12th SyllabusDokument6 SeitenPhysics 12th SyllabusYuvraj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SyllabusDokument9 SeitenPhysics SyllabusHAPPYVALLEYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SrSec 2022-23 RemovedDokument13 SeitenPhysics SrSec 2022-23 RemovedVanshi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- C B S E Physics - SrSec - 2022-23Dokument12 SeitenC B S E Physics - SrSec - 2022-23divyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics I ST Grade 12122013Dokument6 SeitenPhysics I ST Grade 12122013mittalnipun2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Syllabus 2024Dokument5 SeitenPhysics Syllabus 2024C1B-33-AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Syllabus For Jee Mains 2018Dokument5 SeitenPhysics Syllabus For Jee Mains 2018Addhyan TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 PhysicsDokument15 SeitenClass 12 Physicsanand maheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I: Electrostatics: PhysicsDokument2 SeitenUnit I: Electrostatics: PhysicsAyush GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Rajasthan CCT Integrated MDokument13 SeitenUniversity of Rajasthan CCT Integrated Mjain_akshi_29Noch keine Bewertungen
- NEETDokument13 SeitenNEETazeemahamad134Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Principles of Modern Theoretical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyVon EverandFundamental Principles of Modern Theoretical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 1: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #1Von EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 1: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steady Electric Fields and Currents: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryVon EverandSteady Electric Fields and Currents: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schaum's Outline of Electromagnetics, Fifth EditionVon EverandSchaum's Outline of Electromagnetics, Fifth EditionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Lecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahDokument9 SeitenLecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACI The New Model Code Feb 2013Dokument87 SeitenACI The New Model Code Feb 2013Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture#15: Sub Structure: Sub-Structure or Foundation Is The Lower Portion of The Building, UsuallyDokument3 SeitenLecture#15: Sub Structure: Sub-Structure or Foundation Is The Lower Portion of The Building, UsuallyAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Management MGT 427Dokument2 SeitenIndustrial Management MGT 427Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Analysis - II - EE150 - New - 09-08-12Dokument1 SeiteNetwork Analysis - II - EE150 - New - 09-08-12Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communications Skills - ENG 112Dokument1 SeiteCommunications Skills - ENG 112Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Architecture - CS252Dokument2 SeitenComputer Architecture - CS252Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 7thDokument15 SeitenClass 7thAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Class NurseryDokument1 SeiteSyllabus Class NurseryAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage Technology - EE463Dokument1 SeiteHigh Voltage Technology - EE463Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abid 1 PDFDokument1 SeiteAbid 1 PDFAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaka G Tangarr-ModelDokument1 SeiteKaka G Tangarr-ModelAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abid 2Dokument1 SeiteAbid 2Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- KG Teacher Ist Teacher 2NDDokument4 SeitenKG Teacher Ist Teacher 2NDAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abid 1Dokument1 SeiteAbid 1Asghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abid 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteAbid 2 PDFAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abid 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteAbid 2 PDFAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of ContentsDokument1 SeiteTable of ContentsAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6 MetalsDokument4 SeitenLec 6 MetalsAsghar Hussain ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Work Sheet-SS JCT - AIATS-02 - SolDokument3 SeitenPhysics Work Sheet-SS JCT - AIATS-02 - Solhari kroviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 630 Volt and 400 Volt FILM Capacitors Electrolytic & Safety Capacitors MICA and 1000V, 1600V & 6000VDokument8 Seiten630 Volt and 400 Volt FILM Capacitors Electrolytic & Safety Capacitors MICA and 1000V, 1600V & 6000VwilfredoinimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - FUNGAT: (Chapter 1+2 B-I)Dokument3 SeitenPhysics - FUNGAT: (Chapter 1+2 B-I)XXXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Load ListDokument2 SeitenElectrical Load ListAhmed EssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfa Laval Pump HandbookDokument257 SeitenAlfa Laval Pump HandbookMiodrag RakićNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - First Law of ThermodynamicsDokument20 Seiten01 - First Law of ThermodynamicsFabio BosioNoch keine Bewertungen
- NullDokument10 SeitenNullapi-25932525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mitsubishi PS21767-VDokument9 SeitenMitsubishi PS21767-VMadai Sanchez TopeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- v vλ v vλ= γmc h h γmv c vDokument6 Seitenv vλ v vλ= γmc h h γmv c vkurnia febriantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Physics and Measurement: 1.1 Basic and Derived UnitsDokument18 SeitenChapter 1: Physics and Measurement: 1.1 Basic and Derived UnitsMin NaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- An 4134Dokument14 SeitenAn 4134shri.bhairavkar6977Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPM-D11 Series: Load Share SynchronizerDokument4 SeitenSPM-D11 Series: Load Share Synchronizersivana rodiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- QS1QS1A LATAM CertifacationDokument13 SeitenQS1QS1A LATAM Certifacationsteven6diaz-2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of FluidDokument21 SeitenProperties of FluidUnfit NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument41 SeitenUntitledSushant Kumar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Julabo-Service Manual Shaking Water Bath SW21cDokument20 SeitenJulabo-Service Manual Shaking Water Bath SW21cAugusto Vieira100% (1)
- Improvement in Patel Teja Eqn of StatesDokument10 SeitenImprovement in Patel Teja Eqn of StatesSumukh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Accesorios de Los Transformadores (Parte2)Dokument63 Seiten10 - Accesorios de Los Transformadores (Parte2)LOURDES JANNETH LIMON ROMERONoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar Junction Transistors Talha Syed NaqviDokument51 SeitenBipolar Junction Transistors Talha Syed NaqviMuhammad AwaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Out of Step Protection Schemes For GeneratorsDokument78 SeitenApplication of Out of Step Protection Schemes For Generatorsrahul100% (1)
- Alfanar Eletra Type Raysan Load Centers CatalogDokument24 SeitenAlfanar Eletra Type Raysan Load Centers CatalogKANSNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force, Work, Power and Energy - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Victory 2024 - ICSE)Dokument2 SeitenForce, Work, Power and Energy - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Victory 2024 - ICSE)44 A Ritam BeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 5 Quarter 3 Module 3 Week 3: Transmission-RefersDokument4 SeitenScience 5 Quarter 3 Module 3 Week 3: Transmission-RefersALLYSSA MAE PELONIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugeuse Br4iDokument36 SeitenCentrifugeuse Br4iKada HaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- DARBY - Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics 3edition PDFDokument578 SeitenDARBY - Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics 3edition PDFMiguel Zuniga100% (2)
- Thermistor 100KDokument2 SeitenThermistor 100KDiego RicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ena Design Standard For Earthing SystemDokument110 SeitenEna Design Standard For Earthing SystemNADEEM KHALID100% (1)
- Mini Launcher Manual ME 6825ADokument39 SeitenMini Launcher Manual ME 6825AShanzae FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar ReportDokument15 SeitenSeminar ReportNipesh MAHARJANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic PropertiesDokument20 SeitenMagnetic Propertiespatrick saliwanNoch keine Bewertungen