Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
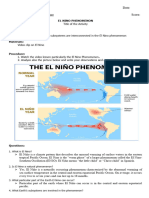
El Nino Student Activity Book
Hochgeladen von
Fred MontOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
El Nino Student Activity Book
Hochgeladen von
Fred MontCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
El Nino Student Activity Book
I. Introduction
El Nino refers to the irregular warming in the sea surface
temperatures from the coasts of Peru and Ecuador to the equatorial
central Pacific. This causes a disruption of the ocean-atmosphere
system in the tropical Pacific having important consequences for
weather around the globe. This phenomenon is not totally predictable
but on average occurs once every four years. It usually lasts for
about 18 months after it begins.
During the 1997-98 El Nino, sea surface temperatures in the central
and eastern equatorial Pacific were higher than normal. The sea
surface temperature for September 1997 was the highest in the last
50 years. Also, in late September easterly winds over the equatorial
Pacific between 150E and 120W decreased the most in the last 30
years.
Recent years in which El Nino events occurred are 1951, 1953, 1957-
1958, 1965, 1969, 1972-1973, 1976, 1982-1983, 1986-1987, 1991-
1992, 1994, and 1997. High sea surface temperatures and the
magnitude of increases in the westerly winds over the Pacific
suggest that the strength of the 1997 El Nino event could equal or
surpass that in 1982-1983, making it the strongest El Nino this
century.
The El Nino of 1982-1983 was responsible for the loss of nearly
2000 lives and displacement of hundreds of thousands from their
homes. Droughts and fires in Australia, Southern Africa, Central
America, Indonesia, the Philippines, South America and India caused
the losses. There were floods in the USA, Gulf of Mexico, Peru,
Ecuador, Bolivia and Cuba. More hurricanes than usual affected
Hawaii and Tahiti.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 1
You will learn about El Nino as you complete the following activities.
Get Info Objectives
1. Explain what El Nino is, where it is located, and how it occurs.
2. Describe the weather changes caused by El Nino.
3. Draw El Nino patterns on a world map.
Gather Data Objectives
1. List the years of previous EL Nino events.
2. Locate and graph precipitation for locations in the eastern and
western Pacific.
3. Analyze precipitation in the eastern and western Pacific in terms of
amount and when it occurred.
4. Compare precipitation amounts in the eastern and western Pacific to
occurrences of El Nino.
Application Objectives
1. Predict the economic effects El Nino will have on the areas it affects.
2. Predict when the next El Nino will develop.
3. Predict what would happen to coastal areas of the Atlantic Ocean if
El Ninos developed off the coast of Africa.
Before doing anything else, add the NOAA Research "El Nino" Web
page to Bookmarks or Favorites on your browser.
- From the NOAA Research "El Nino" main page, click "Get Info."
NOAA Research El Nino Page 2
II. Get Info
A. What is El Nino?
- Click on the "El Nino Definition" site.
Read and answer the following questions:
1. Explain what El Nino is.
2. What effect does El Nino have on the United States?
3. What effect does El Nino have on the western Pacific?
4. How are El Nino sea surface temperatures and weather conditions
different from normal conditions?
NOAA Research El Nino Page 3
5. What effects are there on Pacific sea life and productivity?
- Click "Back" to return to the El Nino "Get Info" web page.
- Click on the "El Nino Picture" site.
6. Using colored pencils, draw what the surface conditions/patterns
look like in the Pacific Ocean during a typical El Nino. (Use brown to
represent land and red for the warmest region, etc.)
NOAA Research El Nino Page 4
- Click "Back" to return to the El Nino "Get Info" web page.
B. El Nino Effects
- Click on the "El Nino Impacts" site and read the first paragraph.
1. In the space below, write the weather effects El Nino has on the
area where you live.
- Click on picture (a) of the United States that shows temperature
differences.
2. What difference in the average temperature does El Nino cause
where you live? (0 indicates zero difference from normal
temperature.) _____________ degrees Celsius
- Click "Back" one time.
- Click on picture (b) of the United States that shows precipitation
(rain, snow, hail) amounts.
3. What difference in average rainfall does El Nino cause where you
live? (0 indicates zero difference from normal normal.)
______________ centimeters
- Click "Back" to return to the NOAA Research "El Nino" home page,
or choose "El Nino" from your Favorites or Bookmarks.
- Click “Gather Data.”
NOAA Research El Nino Page 5
III. Gather Data
A. Comparison of Different El Ninos
- Click on the "El Nino Comparison Graph" site.
- Scroll down to the graph of El Ninos.
- Record the years of El Ninos in the chart below, then answer the
following questions about the El Ninos.
El Nino Years
19____ 19____ 19____ 19____ 19____ 19____ 19____
1. Which El Nino year before 1997 was the most severe? 19____
2. What was the greatest recorded sea surface temperature increase
above normal? __________ degrees Celsius
3. What is the approximate month/year of the greatest sea surface
temperature increase above normal? ______________________
4. What was the greatest recorded sea surface temperature
decrease below normal? _______________ degrees Celsius
5. What is the approximate month/year of the greatest sea surface
temperature decrease below normal? _____________________
6. In what year was El Nino weakest? 19____
7. During the period around June on the left side of the graph, what
was the difference in temperatures between the 1986 El Nino and
the 1997 El Nino? _______________ degrees Celsius
- Click "Back" to return to the El Nino "Gather Data.1" web page.
- Click "Forward" at the bottom of the page to go to the "Gather
Data.2" Web page.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 6
B. Comparison of Western Pacific Rainfall During El Ninos
- Click on the "Rainfall" site.
- Click on the statement, "I Agree to These Terms" to get the rainfall
data.
- Scroll down to the "Select a Graph Type" box.
- Choose "Graph total precipitation each year for a period of years."
- Scroll down to the world map.
Western Pacific – Rockhampton, Australia
- Click on the picture of Australia
- In the box that appears, click on Australia if it is not highlighted.
- Click "Okay."
- At the "Select a station" page, scroll down and click on Rockhampton
Airport.
- Scroll down to the "Select the type of units you prefer" section.
- Click metric units.
- Scroll down to the "Select a time period to graph" section. (You can
use the tab key to move to the next box without scrolling.)
- Enter the years 1955 and 1988 in the boxes.
- Click "Graph Data."
Answer the following questions about Rockhampton Airport.
Keep in mind the effects of an El Nino on the western Pacific.
1. Record the latitude and longitude of Rockhampton in the chart under
Question 2 below.
2. What are the rainfall amounts for Rockhampton in the El Nino years?
Fill in the rainfall amounts for each year.
Each horizontal line represents about 4 cm of rainfall.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 7
Rockhampton, Australia
Latitude = S Longitude = E
1957 1965 1972 1982 1986
1. When are the lowest annual precipitations shown?
19____ and 19____
2. What two back-to-back years show the greatest increase in rainfall
from year to year? ________________________
- Click "Back" to get information about Melbourne, Australia's rainfall
from the stations (city) directory.
- To leave the western Pacific and go to the eastern Pacific (U.S. and
South American) cities, click "Back" three times to get to the map
menu. Skip the rest of section B and go directly to section C.
- To continue with the western Pacific, answer the following questions.
Western Pacific 2 – Melbourne, Australia
- From the stations menu, scroll down and select Melbourne.
- Scroll down to the "Select the type of units you prefer" section.
- Click metric units.
- Click "Graph Data."
Answer the following questions about the graphed data.
Keep in mind the effects of an El Nino on the western Pacific.
1. Record the latitude and longitude of Melbourne in the chart under
Question 2 below.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 8
2. What are the rainfall amounts for Melbourne in the El Nino years?
Fill in the rainfall amounts for each year.
Each horizontal line represents about 2 cm of rainfall.
Melbourne, Australia
Latitude = S Longitude = E
1957 1966 1972 1982 1986
3. What was the most severe El Nino year in Melbourne? 19____
4. What was the rainfall total for the most severe El Nino year in
Melbourne? ____________ centimeters
5. What was the least severe El Nino year in Melbourne? 19____
6. What two back-to-back years show the greatest decrease in rainfall
from year to year? ___________________________
- Click "Back" twice to return to the country menu.
Western Pacific – Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia
- Select Malaysia.
- Click "Okay."
- At the "Select a station" page, select Kota Kinabalu.
- Scroll down to the "Select the type of units you prefer" section.
- Click metric units.
- Scroll or tab down to the "Select a time period to graph" section.
- Enter the years 1955 and 1988 in the boxes.
- Click "Graph Data,"
NOAA Research El Nino Page 9
Answer the following questions about Kota Kinabalu.
Keep in mind the effects of an El Nino on the western Pacific.
1. Record the latitude and longitude of Kota Kinabalu in the chart under
Question 2 below.
2. What are the rainfall amounts for Kota Kinabalu in the El Nino
years? Fill in the rainfall amounts for each year.
Each horizontal line represents about 7.4 cm of rainfall.
Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia
Latitude = N Longitude = E
1957 1965 1972 1982 1986
3. What was the most severe El Nino year in Kota Kinabalu? 19____
4. What was the rainfall total for the most severe El Nino year in Kota
Kinabalu? _____________ centimeters
5. What were the least severe El Nino years in Kota Kinabalu?
19____ and 19____
6. What was the increase in rainfall from 1972 to 1973?
___________ centimeters
- Click "Back" three times to return to the map menu.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 10
C. Comparison of Eastern Pacific Rainfall During El Ninos.
Eastern Pacific 1 – La Serina, Chile
- Click on western South America.
- At the country menu, select "Chile."
- Click "Okay."
- At the "Select a station" page, select "La Serina."
- Scroll down to the "Select the type of unit" section.
- Click metric units,
- Scroll or tab down to the "Select a time period to graph" section.
- Enter the years 1955 and 1988 in the boxes,
- Click "Graph Data."
1. Record the latitude and longitude of La Serina in the chart under
Question 2 below.
2. What are the rainfall amounts for La Serina in the El Nino years?
Fill in the rainfall amounts for each year.
Each horizontal line represents about 0.7 cm of rainfall.
La Serina, Chile
Latitude = S Longitude = W
1957 1965 1972 1982 1986/87
Answer the following questions about La Serina, Chile.
Keep in mind the effects of an El Nino on the eastern Pacific.
3. What was the most severe El Nino year in La Serina? 19____
4. What was the rainfall total for the most severe El Nino year in La
Serina? _____________ centimeters
NOAA Research El Nino Page 11
5. What was the least severe El Nino year in La Serina? 19____
6. What two back-to-back years show the greatest increase in rainfall
from year to year? 19____ and 19____
- To continue investigating the eastern Pacific, click "Back" three times
to return to the map menu. Go to the "Eastern Pacific – 2" section
below.
- To skip the eastern Pacific and go on to the next section, click "Back"
until you return to the "El Nino" main page, or choose the El Nino site
from your Favorites or Bookmarks.
Eastern Pacific 2 – Santa Cruz, California, USA
- Click on the United States.
- At the "Select a country" page, click "Okay."
- At the "Select a state" page, click Santa Cruz."
- Scroll down to the "Select the type of unit" section.
- Click metric units,
- Scroll or tab down to the "Select a time period to graph" section.
- Enter the years 1955 and 1988 in the boxes,
- Click "Graph Data."
Answer the following questions about Santa Cruz, California.
Keep in mind the effects of an El Nino on the eastern Pacific.
1. Record the latitude and longitude of Santa Cruz in the chart under
Question 2 below.
2. What are the rainfall amounts for Santa Cruz in the El Nino years?
Fill in the rainfall amounts for each year.
Each horizontal line represents about 3.5 cm of rainfall.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 12
Santa Cruz, California, USA
Latitude = N Longitude = W
1957 1966 1973 1983 1986
3. What as the most severe El Nino year in Santa Cruz? 19____
4. What was the rainfall total for the most severe El Nino year in
Santa Cruz? _____________ centimeters
5. What was the least severe El Nino year in Santa Cruz? 19____
6. What two back-to-back years show the greatest increase in rainfall
from year to year? ____________________
- Click "Back" once to return to the stations menu.
Eastern Pacific 32 – Los Angeles International Airport,
California, USA
- Select Los Angeles International Airport.
- Click "Graph Data."
Answer the following questions about Los Angeles International Airport.
Keep in mind the effects of an El Nino on the eastern Pacific.
1. Record the latitude and longitude of Los Angeles International
Airport in the chart under Question 2 below.
2. What are the rainfall amounts for Los Angeles in the El Nino years?
Fill in the rainfall amounts for each year.
Each horizontal line represents about 1.6 cm of rainfall.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 13
Los Angeles, California, USA
Latitude = N Longitude = W
1957 1965 1973 1983 1986
3. What as the most severe El Nino year in Loa Angeles? 19____
4. What was the rainfall total for the most severe El Nino year in Los
Angeles? _____________ centimeters
5. What was the least severe El Nino year in Los Angeles? 19____
6. What two back-to-back years show the greatest increase in rainfall
from year to year? _______________________
- Choose Favorites or Bookmarks in your browser to return to the
NOAA Research "El Nino" main page.
- Click on "Application."
IV. Application
A. Predictions
1. Predict what would happen to the coastal areas of the Atlantic
Ocean if El Ninos developed off the coast of Africa.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 14
2. Predict the effect of a severe El Nino on the salinity (saltiness) of
the northern Gulf of Mexico and write the reason for the effect
on salinity.
3. Predict what would happen to the U.S. Southwest if an El Nino
increased the sea surface temperature by 3 degrees and the
increase in temperature extended across the whole Pacific Ocean.
4. Using the dates of previous El Ninos, predict when the next El
Nino will occur.
- Click "Back" to return to the NOAA Research "El Nino" main page.
- Click "Enrichment."
NOAA Research El Nino Page 15
V. Enrichment Activities
A. Wind Patterns
If your class has studied global winds, explain in detail why El Nino sea
surface temperatures affect weather patterns and where the effects
occur.
B. Social Studies/Language Arts
- Click on the "Economic Impacts" site.
Read the data and write an explanation of the economic impacts of an El
Nino event.
- Click "Back" to return to the El Nino "Enrichment.1" Web page.
C. Math Activity
Predict the effect of the 1997 El Nino on Rockhampton, Australia based
on the departure from normal of sea surface temperature during the
1982 El Nino.
- Click on the "Rainfall" site to return to the Rockhampton data.
- Click on the statement "I Agree to These Terms" to get the data.
- Choose "Graph total precipitation each year for a period of years."
- Click on the picture of Australia.
- Click "Okay."
- At the "Select a station" page, select Rockhampton Airport.
- Scroll down to the "Select a time period to graph" section and enter
the years 1955 and 1988 in the boxes.
- Click "Graph Data."
- Scroll down to and click on "View the dataset."
NOAA Research El Nino Page 16
Follow the directions below to compare the abnormal sea surface
temperature during the 1982/1983 El Nino and the rainfall amount for
the same period in Rockhampton.
1. Compute the average rainfall amounts for Rockhampton, Australia
for the years 1955 to 1989 to obtain an average yearly rainfall.
Record the average below.
Average yearly rainfall = _____________ cm
2. Compute the average rainfall for 1982 and 1983, and then record the
1982/1983 average below.
1982/1983 rainfall = ______________ cm
3. Subtract the 1982/1983 rainfall from the average rainfall, then
record the difference below.
Deviation from normal = ____________ cm
- Choose Favorites or Bookmarks in your browser to return to the
NOAA Research "El Nino" main page.
- Click on "Enrichment" again.
- Click on the "El Nino Comparison Graph" site.
- Scroll to the graph of El Ninos.
4. Find the 1982/83 abnormality in temperature measured at the
March/April closest to the middle of the graph. Record the
temperature abnormality below.
Temperature Difference _____________ degrees
5. Divide the Deviation from Normal by the Temperature Difference.
This gives you a number telling you how much the rainfall should
increase for each degree that the sea surface temperature is above
normal. Record the answer below.
Rainfall Increase per degree = ______________
NOAA Research El Nino Page 17
Using your calculations, predict what the rainfall increase will be in
Rockhampton, Australia during the March/April period if an El Nino
occurred that was 4.1 degrees above normal.
6. Multiply your Rainfall Increase per Degree value times the 4.1-
degree increase.
Rainfall Increase per Degree x 4.1 = Predicted Rainfall
Your answer will give you an idea of how much additional rain will fall
(above normal) in Rockhampton if an El Nino of 4.1 degrees above
normal were to happen.
- Choose Favorites or Bookmarks in your browser to return to the
NOAA Research "El Nino" main page.
- Click on "Enrichment" again.
- Click "Forward" at the bottom of the page to go to the
"Enrichment.2" web page.
D. Research
1. Research other El Ninos using the Internet. Here's an idea of
information to look for:
a. When it occurred
b. How long it lasted
c. What countries and areas were most and least affected?
d. What happened to the weather as a result of each one?
e. On a map, draw the greatest sea surface area covered by an
El Nino.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 18
2. Collect newspaper and magazine articles about El Nino. Write a brief
summary of each one.
3. Find out differences between El Nino, La Nina, and El Viejo.
E. Interviews
1. Interview local weather people about the reports they have done on
El Ninos.
2. Interview 10 people to find out how much they know about El Ninos
and what effect they think El Nino has on the weather. Develop
eight to ten questions and write them out leaving space to write
their answers.
F. Class Reports
1. Prepare a two-minute news report on El Nino. If you have a video
camera, film your report. Interview one "expert" in your report.
2. Create a series of drawings on a map showing the increase and
decrease in the area (size) covered by the 1997 El Nino. Make sure
you include the date on each drawing.
NOAA Research El Nino Page 19
G. Related Web Sites
1. "Comparison of Different El Ninos" graph
http://www.cdc.noaa.gov/ENSO/enso.different.html
2. El Nino Theme Page
http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/toga-tao/el-nino
3. San Diego School District's "El Nino or El No-no"
http://powayusd.sdcoe.k12.ca.us/projects/ElNino/
4. Climate Prediction Center – El Nino/La Nina Home
http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/lanina/
5. Idealized El Nino Simulation
http://www.cdc.noaa.gov/~jjb/anim.html
6. Today's El Nino/La Nina Information
http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/tao/elnino/1997.html
NOAA Research El Nino Page 20
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Climate Extremes: Patterns and MechanismsVon EverandClimate Extremes: Patterns and MechanismsS.-Y. Simon WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Weather PatternsDokument4 SeitenGlobal Weather Patternsabbygurl10312008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptation to Climate Change: Agricultural Ecosystems and Gender DimensionsVon EverandAdaptation to Climate Change: Agricultural Ecosystems and Gender DimensionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- El NiñoDokument2 SeitenEl NiñoCheryl BolinawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity ENSODokument4 SeitenActivity ENSOBryan Agan0% (1)
- EL NINO and LA NINADokument2 SeitenEL NINO and LA NINAAshley QuinonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- El NinoDokument53 SeitenEl NinoMaesa Rizal MeilanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENSO As An Integrating Concept in Earth ScienceDokument24 SeitenENSO As An Integrating Concept in Earth ScienceSUSHOVAN GHOSH100% (1)
- 6 7 9 Final EBE S9 Q3 Week 6 7Dokument4 Seiten6 7 9 Final EBE S9 Q3 Week 6 7Leah CasanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Interannual Variability 2.3 Decadal Variability 2.4 Climate Prediction 2.5 Variability of High Impact WeatherDokument46 Seiten2.1 Introduction 2.2 Interannual Variability 2.3 Decadal Variability 2.4 Climate Prediction 2.5 Variability of High Impact WeatherJeremy FlNoch keine Bewertungen
- El NiñoDokument2 SeitenEl NiñoCheryl BolinawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EportfolioDokument9 SeitenEportfolioapi-313993715Noch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ScienceDokument29 SeitenEnvironmental ScienceReizel GaasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elnino Webquest For Ees 4 25 16 Honors EesDokument3 SeitenElnino Webquest For Ees 4 25 16 Honors Eesapi-262586446Noch keine Bewertungen
- El Niño/ Southern Oscillation: WMO-No. 1145Dokument12 SeitenEl Niño/ Southern Oscillation: WMO-No. 1145Ivonne MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al Nino Phenomena 2Dokument12 SeitenAl Nino Phenomena 2عبدالله محمد الحجاحجهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extreme LossesDokument14 SeitenExtreme LossesLuís MacedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Nino Stage Form (BOM, 2018)Dokument10 SeitenEl Nino Stage Form (BOM, 2018)anistiareyhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 Presentation: El NiñoDokument25 SeitenGroup 2 Presentation: El NiñoFernan Lee R. ManingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- El NiñoDokument2 SeitenEl NiñoNishanth ShanmugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The El Niño Event Project Worksheet: Team MembersDokument6 SeitenThe El Niño Event Project Worksheet: Team MembersVladimir Osorio CornejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Hydrometeorological HazardsDokument7 SeitenSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Hydrometeorological HazardsAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 Presentation: El NiñoDokument26 SeitenGroup 2 Presentation: El NiñoFernan Lee R. ManingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of El Nino and La LinaDokument41 SeitenEffects of El Nino and La LinaK Sai maheswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrometeorological Hazard StudentDokument26 SeitenHydrometeorological Hazard StudentMargaret Nicole100% (1)
- Winter Weather (Paul Kocin)Dokument41 SeitenWinter Weather (Paul Kocin)National Press FoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress in UnderstandingDokument9 SeitenProgress in Understandinglarenas23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityDokument18 SeitenEntering Uncharted Waters: El Niño and The Threat To Food SecurityOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- El NinoDokument14 SeitenEl NinojerezzakimraxioustalaverNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRRR - Hydro - Meteorological Hazards PhenomenaDokument15 SeitenDRRR - Hydro - Meteorological Hazards PhenomenaSheila Lacuesta PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 Q3 Week 7Dokument10 SeitenScience 9 Q3 Week 7Mervin LudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment 1Dokument10 SeitenAttachment 1HARSH KUMAR GAUTAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines, Region III-Central Luzon Department of Education, Division of Bulacan Calumpit National High SchoolDokument3 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines, Region III-Central Luzon Department of Education, Division of Bulacan Calumpit National High SchoolSanni Boy Baltazar EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is La Niña?Dokument8 SeitenWhat Is La Niña?Awatif MaisaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnsodiscDokument6 SeitenEnsodiscrais wrfNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Nino La Nina WS PDFDokument5 SeitenEl Nino La Nina WS PDFFriedeagle Oil0% (1)
- Ensodisc Elnino Advisory 09 03 2019 PDFDokument5 SeitenEnsodisc Elnino Advisory 09 03 2019 PDFDouglas LaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENSO El Niño & La NiñaDokument23 SeitenENSO El Niño & La NiñajohnosborneNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENSODokument25 SeitenENSOjohnosborneNoch keine Bewertungen
- El NinoPublicDokument4 SeitenEl NinoPublicJoao Carlos PolicanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021-22 Winter OutlookDokument60 Seiten2021-22 Winter OutlookRaindance WeatherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Climate PhenomenonDokument16 SeitenWorksheet Climate PhenomenonNelma Faye MadambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Implications of Global Warming: El NiñoDokument9 SeitenThe Implications of Global Warming: El Niñoarjay nombreNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITCZ (Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone) : Hydrometeorogical HazardsDokument9 SeitenITCZ (Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone) : Hydrometeorogical HazardsVjion BeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Niño and La Nina: PretestDokument3 SeitenEl Niño and La Nina: PretestKurt AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 Q3 Week 7Dokument10 SeitenScience 9 Q3 Week 7Alfred Villego SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enso EvolutiomDokument32 SeitenEnso Evolutiomibnu athoillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Nino and La NinaDokument23 SeitenEl Nino and La NinaLouis Miguel LauritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Nino WorksheetDokument1 SeiteEl Nino WorksheetVictoria WarrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnsodiscDokument6 SeitenEnsodiscrais wrfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study El NinoDokument5 SeitenCase Study El Ninojohn m0% (1)
- Jan Dec 2023Dokument14 SeitenJan Dec 2023Fred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- GZG Chanting Group Chantsheets October 2020Dokument30 SeitenGZG Chanting Group Chantsheets October 2020Fred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calendario 2017Dokument54 SeitenCalendario 2017Fred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesDokument4 SeitenPresent Simple Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesFred Mont100% (1)
- 451 - There Is There Are Some Any No Test A1 A2 Grammar ExercisesDokument4 Seiten451 - There Is There Are Some Any No Test A1 A2 Grammar ExercisesFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Have Got-Can Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesDokument4 SeitenHave Got-Can Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possessives Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesDokument4 SeitenPossessives Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- BsAsHerald-hushtagNiUnaMenos-edited For Written AssessmentDokument1 SeiteBsAsHerald-hushtagNiUnaMenos-edited For Written AssessmentFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesDokument4 SeitenPresent Continuous Test A1 - A2 Grammar ExercisesFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is BullyingDokument10 SeitenWhat Is BullyingFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Democratic Citizenship Education: A New Imperative For The AmericasDokument8 SeitenDemocratic Citizenship Education: A New Imperative For The AmericasFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- DGTipsheet1ChooseMyPlate PDFDokument1 SeiteDGTipsheet1ChooseMyPlate PDFFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- End-Of-term 1 Speaking TestDokument1 SeiteEnd-Of-term 1 Speaking TestFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Test A PDFDokument2 SeitenDiagnostic Test A PDFFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1. Structure Drills 1Dokument97 Seiten4.1. Structure Drills 1Fred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell (Biology)Dokument13 SeitenThe Cell (Biology)Fred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newsademic: The Informative Easy To Read Introduction To World NewsDokument20 SeitenNewsademic: The Informative Easy To Read Introduction To World NewsFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subordination, Coordination & EllipsisDokument2 SeitenSubordination, Coordination & EllipsisFred MontNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeteorologyDokument99 SeitenMeteorologymkzgroundNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meteorology (Questions) For CPL - ATPL - Subjects For CPL and ATPLDokument4 SeitenMeteorology (Questions) For CPL - ATPL - Subjects For CPL and ATPLSojin Soman100% (4)
- Tugas Saya M Ilham Arya PutraDokument2 SeitenTugas Saya M Ilham Arya PutraIlhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Optical PhenomenaDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Optical Phenomenahamzakoita2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural PlanDokument20 SeitenStructural PlanRaymond SuriagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28 Virudhunagar RainfallDokument1 Seite28 Virudhunagar RainfallSundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityDokument21 SeitenMET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityMalik ForbesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Got Water How The Water Cycle WorksDokument3 SeitenGot Water How The Water Cycle Worksapi-528795360Noch keine Bewertungen
- Language Development: General English I: Unit 3Dokument46 SeitenLanguage Development: General English I: Unit 3Sebastian NevarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Afternoon Teacher and ClassmatesDokument1 SeiteGood Afternoon Teacher and ClassmatesCristhianCastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meteorological PhenomenaDokument2 SeitenMeteorological PhenomenaMiller JonathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bragg & Co - 2020-2021 PDFDokument535 SeitenBragg & Co - 2020-2021 PDFnana fungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D3631-99Dokument5 SeitenAstm D3631-99johnsmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGPS Raas 7Dokument486 SeitenSGPS Raas 7gurvinder singh dhirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- What's The Forecast?: Cross-Curricular Focus: Earth ScienceDokument2 SeitenWhat's The Forecast?: Cross-Curricular Focus: Earth ScienceEduard AmuzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MmmmvfedgreDokument9 SeitenMmmmvfedgreLuisWMRomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hill Country South of Copperwood Pack 1Dokument4 SeitenHill Country South of Copperwood Pack 1GeoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define Types of Bioclimatic Charts. Explain The Applicability and Limitation of Bioclimatic Charts.Dokument4 SeitenDefine Types of Bioclimatic Charts. Explain The Applicability and Limitation of Bioclimatic Charts.Pooja SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word SearchDokument3 SeitenWord SearchnnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bai Luyen Thi Anh Van Dai Hoc 2016 Lesson 14Dokument3 SeitenBai Luyen Thi Anh Van Dai Hoc 2016 Lesson 14Linh ChiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hurricane Ian Is No AnomalyDokument5 SeitenHurricane Ian Is No Anomalykadyn tseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas 3vDokument4 SeitenTugas 3vRomie SyafitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HurricanesDokument25 SeitenHurricanesSwayamjit MohapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture On Air MassesDokument17 SeitenLecture On Air MassesSujit DebsarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKAA 3613-Lecture (SPACE UTMKL) Oct. 2017: Hydrology / Hidrologi Lecturer: Email: Tel: 012-7710825Dokument38 SeitenSKAA 3613-Lecture (SPACE UTMKL) Oct. 2017: Hydrology / Hidrologi Lecturer: Email: Tel: 012-7710825Azuan WahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Quarter Exam (Science)Dokument4 Seiten2nd Quarter Exam (Science)Rowena DivinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4000 Essential English Words 6 - Answer KeyDokument30 Seiten4000 Essential English Words 6 - Answer Key丁安然Noch keine Bewertungen
- State of The Global Climate 2022Dokument55 SeitenState of The Global Climate 2022NDTVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weather (Ielts Speaking Part 2-3)Dokument5 SeitenWeather (Ielts Speaking Part 2-3)Yaneth AtamariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Air Pressure in Daily LifeDokument3 SeitenApplication of Air Pressure in Daily Lifedbsiva0175% (4)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterVon EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersVon EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- So Others May Live: Coast Guard's Rescue Swimmers Saving Lives, Defying DeathVon EverandSo Others May Live: Coast Guard's Rescue Swimmers Saving Lives, Defying DeathBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastVon EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)
- Civilized To Death: The Price of ProgressVon EverandCivilized To Death: The Price of ProgressBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (215)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesVon EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (21)
- Ruthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterVon EverandRuthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeVon EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- The Big Burn: Teddy Roosevelt and the Fire that Saved AmericaVon EverandThe Big Burn: Teddy Roosevelt and the Fire that Saved AmericaBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (9)
- Alien Oceans: The Search for Life in the Depths of SpaceVon EverandAlien Oceans: The Search for Life in the Depths of SpaceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (26)
- A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersVon EverandA Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (113)
- The World Beneath: The Life and Times of Unknown Sea Creatures and Coral ReefsVon EverandThe World Beneath: The Life and Times of Unknown Sea Creatures and Coral ReefsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosVon EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Run the Storm: A Savage Hurricane, a Brave Crew, and the Wreck of the SS El FaroVon EverandRun the Storm: A Savage Hurricane, a Brave Crew, and the Wreck of the SS El FaroBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (39)
- Exploring Creation with Physical Science, 3rd EditionVon EverandExploring Creation with Physical Science, 3rd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeVon EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- When Humans Nearly Vanished: The Catastrophic Explosion of the Toba VolcanoVon EverandWhen Humans Nearly Vanished: The Catastrophic Explosion of the Toba VolcanoBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (34)
- Grand Transitions: How the Modern World Was MadeVon EverandGrand Transitions: How the Modern World Was MadeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)