Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sheet 3
Hochgeladen von
OmaroMohsen0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
43 Ansichten1 Seitesheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldensheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
43 Ansichten1 SeiteSheet 3
Hochgeladen von
OmaroMohsensheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
Cairo University
Faculty of Engineering
Mechanical Design Engineering
Credit Hours System
Fluid Power Systems – MDPN457
Sheet # 3
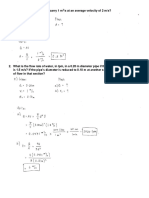
1. A hydraulic pump of 12.5 cm3 geometric volume runs at 1450 rpm
delivers the oil at 160 bar pressure. Assuming an ideal pump, calculate
the pump flow rate, the hydraulic power at the pump exit line, the driving
torque, and the driving power.
2. A hydraulic pump of 40 cm3 geometric volume runs at 1450 rpm
delivers the oil at 150 bar pressure. The pump has 80% volumetric
efficiency and 75% overall efficiency. Calculate the pump actual flow
rate, the required driving power, and the actual driving torque.
3. A hydraulic motor of 15 cm3 geometric volume and the pressure drop
across the motor is 12 MPa. Assuming an ideal motor, calculate the
torque delivered by this motor. If the speed of the motor is 820 rpm,
calculate the output power delivered.
4. A hydraulic motor of 20 cm3 geometric volume is required to provide
30 N.m torque to rotate a load at 1000 rpm. A hydraulic pump of 30 cm3
geometric volume is used. Assuming that the pump has 80% volumetric
efficiency and 75% overall efficiency, and an ideal hydraulic motor,
calculate the pump actual flow rate, the required driving power, and the
actual driving torque.
5. In problem 4, if the motor mechanical and volumetric efficiencies are
80% and 75% respectively, calculate the pump actual flow rate, the
required driving power, and the actual driving torque in this case.
6. A hydraulic cylinder of 100 mm piston diameter is required to move a
load of 150 KN at 0.1 m/s linear velocity. A hydraulic pump of 25 cm3
geometric volume is used. Assume the pump has 80% volumetric
efficiency and 75% overall efficiency. Calculate the pump actual flow
rate, the pump speed, the required driving power, and the actual driving
torque for the pump. Assume the outlet of the hydraulic cylinder is
directly connected to the tank.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TutorialDokument27 SeitenTutorialbassemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assigment IIDokument4 SeitenAssigment IIMurtesa KumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 2zul hilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Power AutomationquestonsDokument3 SeitenFluid Power AutomationquestonsSriram Nanjangud SubramanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic PumpsDokument32 SeitenHydraulic PumpsBasha MohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbo Assignment 1 - 2013Dokument2 SeitenTurbo Assignment 1 - 2013Shreyash SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Exercises in Agricultural PumpsDokument1 SeiteSolving Exercises in Agricultural PumpsInkel EitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AM 14201: Fluid Mechanics Assignment-4Dokument1 SeiteAM 14201: Fluid Mechanics Assignment-4arpan agnihotriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel HydroDokument1 SeiteDiesel HydroVon A. DamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam EnginesDokument6 SeitenSteam Engineschat2adiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 6Dokument5 SeitenSheet 6Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muzeyin FocusDokument3 SeitenMuzeyin FocuseyobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 4Dokument5 SeitenSheet 4Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Evaluation Questions and Answers: Lecture 7 To 9 - Hydraulic PumpsDokument6 SeitenSelf Evaluation Questions and Answers: Lecture 7 To 9 - Hydraulic Pumpspnjohn2822Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 5 HydraulicsDokument31 SeitenUNIT 5 Hydraulicsnandu20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Machines Question BankDokument11 SeitenHydraulic Machines Question BankAdit Gaur100% (3)
- L7 - Hydraulic Motors and AccumulatorsDokument33 SeitenL7 - Hydraulic Motors and Accumulatorsu1909030Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Components and SystemsDokument31 SeitenHydraulic Components and SystemsPrasad ChamarajanagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 6Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 6Muhammad Jawad IsmaeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oct 2012Dokument2 SeitenOct 2012Kasturie PillayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignemnt 04Dokument2 SeitenAssignemnt 04Abdalrhman SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11 PDFDokument11 SeitenLecture 11 PDFpsunmoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Fluid MachineryDokument1 SeiteActivity Fluid MachineryDryx LetranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet No2Dokument7 SeitenSheet No2Ismail SakrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 4sujay nayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment IIDokument3 SeitenAssignment IIPawan SubediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Power Systems - Sheet 2Dokument4 SeitenFluid Power Systems - Sheet 2Mohamed Maher100% (1)
- Pump ProblemsDokument1 SeitePump ProblemsRenz Magat100% (1)
- SQ - 4.7 - Pumps (Table Format)Dokument5 SeitenSQ - 4.7 - Pumps (Table Format)Amitav MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet5-Centrifugal PumpDokument5 SeitenSheet5-Centrifugal Pumpyousef mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Starup ProcedureDokument23 SeitenPump Starup ProcedureKrishnan ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 (Pumps)Dokument2 Seiten2 (Pumps)arsenic_94100% (1)
- Problem Set Number 1Dokument5 SeitenProblem Set Number 1Johnlloyd BarretoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Machinery - PumpsDokument32 SeitenFluid Machinery - PumpsIvan Jeremy AbilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PUMPSDokument8 SeitenPUMPSRyan Bicsur BulawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbo Assignment 3Dokument1 SeiteTurbo Assignment 3zuber369Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 EX Hydraulic MachineDokument13 SeitenCH 7 EX Hydraulic MachineBereket BegashawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-Centrifugal PumpDokument3 SeitenAssignment-Centrifugal PumpAbhilash Tilak100% (1)
- Sheet 4Dokument2 SeitenSheet 4ゞ『HaiDerツ98〆Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 1Dokument15 SeitenProblem Set 1Silva, Joe Mari T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Santosh G Kelshekar - AssortedDokument10 SeitenSantosh G Kelshekar - AssortedscemanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 2 HPDokument72 SeitenUnit - 2 HPVasanth MemoriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 4Krivai NagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumps (Problems)Dokument1 SeitePumps (Problems)Beesam Ramesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set MidtermDokument2 SeitenProblem Set MidtermKarl Sean Garma UbinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines - NumericalsDokument2 SeitenIC Engines - Numericalsaryansorout1612Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 Water PumpingDokument76 SeitenWeek 2 Water PumpingAbdullahi Dirie AbdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problem Turbine Fans and Blower and CompressorDokument3 SeitenPractice Problem Turbine Fans and Blower and CompressorRey Regaspi Tuyay50% (2)
- Quetions Turbo.................Dokument4 SeitenQuetions Turbo.................DICKSON SIMUTAMINoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set ADokument3 SeitenProblem Set AAldrich BaldonadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4-1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 4-1ashutoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Announcement 8755 PDFDokument1 SeiteS Announcement 8755 PDFKiah Taliwan100% (1)
- Ac Machinery Problem SetDokument2 SeitenAc Machinery Problem Setnet flix1230% (1)
- ComputationDokument18 SeitenComputationKaren Anne JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM Question Bank Unit 4Dokument3 SeitenFM Question Bank Unit 4cbeprabhugmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic TurbinesDokument2 SeitenHydraulic TurbinesmartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIRT, Bhopal Turbo Machinery (ME 502) Tutorial/Assignment Sheet 4 (Water Turbine)Dokument1 SeiteCIRT, Bhopal Turbo Machinery (ME 502) Tutorial/Assignment Sheet 4 (Water Turbine)AnkurTripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesVon EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Asi 04 00034 v2Dokument20 SeitenAsi 04 00034 v2OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Smart Tool Wear Prediction Model in Drilling ofDokument13 SeitenA Smart Tool Wear Prediction Model in Drilling ofOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace 08 00130Dokument13 SeitenAerospace 08 00130OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- RIndustry Certificates NREA - 2Dokument43 SeitenRIndustry Certificates NREA - 2OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- art3A10.10072Fs11668 016 0113 2Dokument16 Seitenart3A10.10072Fs11668 016 0113 2OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil + Air-Lubrication SystemDokument52 SeitenOil + Air-Lubrication SystemOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Filament Winding MachineDokument19 SeitenDesign of Filament Winding MachineOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Goals: Class FourDokument10 SeitenSetting Goals: Class FourOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutting Data Corrax EngDokument58 SeitenCutting Data Corrax EngOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applsci 12 02979 v2Dokument8 SeitenApplsci 12 02979 v2OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of EDM Electrode Passing Charge Role of Fluid Types of Wire EDMDokument2 SeitenDefinition of EDM Electrode Passing Charge Role of Fluid Types of Wire EDMOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report #2: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Experimentation MDE Department 4 YearDokument8 SeitenReport #2: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Experimentation MDE Department 4 YearOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDPN 363-Fall 2017-Project 2Dokument1 SeiteMDPN 363-Fall 2017-Project 2OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME307 091 Old-Exam Final-Exam SolvedDokument4 SeitenME307 091 Old-Exam Final-Exam SolvedOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLC Based Paper Cutting Machine: ComponentsDokument2 SeitenPLC Based Paper Cutting Machine: ComponentsOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report #1: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering GENN327 Selections of Life Long SkillsDokument9 SeitenReport #1: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering GENN327 Selections of Life Long SkillsOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faulty Product Detection and Separation System: ComponentsDokument2 SeitenFaulty Product Detection and Separation System: ComponentsOmaroMohsen100% (1)
- Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenLab ReportOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cairo University Faculty of EngineeringDokument15 SeitenCairo University Faculty of EngineeringOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By: 1-Omar Mohsen (113526) 2-Mahmoud Sayed Zaghlool (1135487) Presented To: Dr. Said Megahed Eng. ImanDokument9 SeitenPresented By: 1-Omar Mohsen (113526) 2-Mahmoud Sayed Zaghlool (1135487) Presented To: Dr. Said Megahed Eng. ImanOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcknowledgmentDokument9 SeitenAcknowledgmentOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Training MDE Department Year 4Dokument12 SeitenCairo University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Training MDE Department Year 4OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEPN345 - Lecture Slides - Pumps and CompressorsDokument2 SeitenMEPN345 - Lecture Slides - Pumps and CompressorsOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument53 SeitenPower ElectronicsOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEPN345 - Lecture Slides - Pumps and CompressorsDokument6 SeitenMEPN345 - Lecture Slides - Pumps and CompressorsOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Stoichiometry: Aqueous ReactionsDokument4 SeitenSolution Stoichiometry: Aqueous ReactionsOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vee Belt Fenner PDFDokument22 SeitenVee Belt Fenner PDFOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webinar Power PointDokument23 SeitenWebinar Power PointOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 1Dokument3 SeitenSheet 1OmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Power Systems Sheet # 2: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Design Engineering Credit Hours SystemDokument2 SeitenFluid Power Systems Sheet # 2: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Design Engineering Credit Hours SystemOmaroMohsenNoch keine Bewertungen