Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
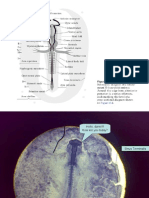
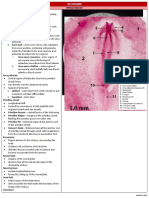
10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory Organs
Hochgeladen von
Marina of The Sea0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
131 Ansichten9 Seitenreviewer for embryo lab
Originaltitel
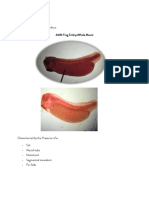
10 MM Frog
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenreviewer for embryo lab
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
131 Ansichten9 Seiten10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory Organs
Hochgeladen von
Marina of The Seareviewer for embryo lab
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 9
10 MM
Transverse Section
LEVEL OF TELENCEPHALON AND OLFACTORY ORGANS
Structure Location Mode of formation Embryonic Fate/Function 7MM
Origin precursor
Telencephalon Ectoderm As is
Lateral Cavity of Evagination of the side Ectoderm Telocoel
Ventricle telencephalon of the neural tube at the
anterior end of
neurocoel
Ependymal Immediately Ectoderm Cilia aids in the movement of
layer surrounding the the cerebrospinal fluid in the
neurocoel ventricles of the brain
Mantle layer Ectoderm Will form gray matter
Marginal layer Ectoderm Will form white matter
Nasal Organ Ventrolateral to Invagination of Ectoderm Olfactory vesicle
telencephalon ectoderm
Olfactory Ectoderm Gives rise to olfactory nerve Olfactory vesicle
epithelium that connects the olfactory
lobes to the brain
External naris Invagination of the Ectoderm
ectoderm
Internal naris Ectoderm
Frontal organ Evagination of the Ectoderm Contains photoreceptors
diencephalic roof with Function as third eye
epiphysis
Migrates toward
telencephalon
Jacobson’s Evagination of the nasal Ectoderm Picks up the smell of food
organ organ from the buccal region
Buccal cavity Where nasal Epithelial; Oral acvity
cavity and mouth derived
opens from
stomodeu
m
Ectoderm
Prechordal Beneath Hyaline Will form chondrocranium
cartilage telencephalon cartilage
Melanocytes Dorsolateral
region of the
brain and lateral
to nasal organs
Mesenchyme Mesoderm Outermost cells forms the
dermis
Epidermis Outer layer of the Composed
skin of two
strata of
ectodermal
cells
LEVEL OF THE DIENCEPHALON AND THE EYE
Structure Location Mode of Embryonic Origin Fate/Function 4MM
formation precursor
Diencephalon Ectoderm As is
III ventricle Cavity of Ectoderm Diocoel
diencephalon
Infundibulum Ectoderm Will evaginate the
posterior of
pituitary together
with stomodeum
Mesencephalon Dorsal to Ectoderm Bears the 3rd & 4th As is
diencephalon cranial nerves
Cerebral aqueduct Cavity of Ectoderm Mesocoel
mesencephalon
Pituitary body Oval mass Derived from Ectoderm Hypophysis
beneath infundibulum and
infundibulum solid ingrowth of
stomodeum
Optic cup Ganglian Innermost Ectoderm Axons form the Optic vesicle
(retina) cells sublayer optic nerve
Bipolar Middle layer Ectoderm Will synapse the
neurons receptor and
ganglian cells
Rods and Outermost Ectoderm Where
cones sublayer photoreceptoral
process is formed
Optic cup (pigmented Outer wall of the From the medial Ectoderm Iris
epithelium) optic cup half of optic
vesicle
Lens Lens One cell thick Thickenings of Ectoderm Lens vesicle
epithelium the inner wall of Epithelial cells
Lens fibers Core of the lens the lens vesicle Ectoderm Will become long
(lens) Columar epithelial fibers arranged in
cells layers
Cornea Assembly of Ectoderm Superficial covering Lens vesicle
ectodermal and of the eye
mesodermal cells
between
ectoderm and
lens
Choroid and Sclera Mesodermal cells Mesoderm
outside the
pigmented
epithelium
Pharynx Endodermal cells
(lining)
Hypobranchial Under the floor of Cartilage Makes up parts of
cartilages the foregut visceral skeleton
and support of
pharynx
Thyroid Beneath Endoderm Associated with
hypobranchial pharyx
cartilage
Skeletal muscle Lateral and Mesoderm Somites
ventral side of (Sclerotome)
pharynx
Oral suckers Ectoderm Glandular function Adhesive
Columnar Produce sticky glands
epithelial cells slime for
attachment to
floating objects
LEVEL OF THE MYELENCEPHALON AND AUDITORY VESICLE
Structure Location MOF Embryo Fate/Function 7MM
nic precursor
Origin
Myelencephalon Most posterior region Ectoder Roof will become vascularized Rhombencephal
with thick floor called m forming posterior choroid plexus on
basal plates
IV ventricle Cavity of Ectoder Rhombocoel
Myelencephalon m
Audito On each side of the Ectoder Otic vesicle
ry medulla m
vesicl Endolymph Thick-walled tube Ectoder Marks the course of
e atic duct between medulla and ear m invaginations of the auditory
vesicle vesicle from ectoderm
Utriculus Dorsal chamber Ectoder
m
Semicircula 3 perpendicular folds of Ectoder Sensory epithelium represented
r canals the ear vesicle (anterior, m by horizontal canal
posterior, horizontal)
Sacculus Ventral chamber Ectoder Lagena (lower vert), cochlea
m (higher vert)
Auditory capsule Mesench Will become cartilaginous ear
ymal capsule that surrounds and
cells protects the inner ear
Auditory ganglion Medial side of ear vesicle Nerve
cells
Notochord Mesoder Mesenchymal cells will give rise As is
m to notochordal sheath
Parachordals On each side of Cartilage
notochord
Heart Pericardial Mesoder Chamber enclosing the heart As is
cavity m
Conus Most anterior region Mesoder Connects ventricle with ventral As is
arteriosus m aorta
Ventricle Thicker muscular wall Mesoder Connects conus and atrium As is
m
Atrium Thin walled chamber Mesoder Receives blood from sinus As is
m venosus and delivers it to the
ventricle
Sinus Posterior-most chamber Mesoder Receives venous blood and As is
venosus lying anterior to the liver m delivers it to atrium
Opercular cavity Continuous with gut on Ectoder
each side of the heart m
Dorsal aorta Above each gill chamber Mesoder As is
m
Aortic arches (3-6) Within branchial arches Connects the dorsal and ventral
and encircling the aorta
pharynx
Visceral arch
Ganglia Facial Anterior to auditory Facial+auditoy ganglion=
(VII) ganglion acoustic-facialis ganglion
Trigemin Anterior and dorsal to
al (V) the acoustic-facialis
ganglion
Glossoph Below each auditory
aryngeal vesicle
(IX)
Operculum Formed Ectoder
by a body m
fold
Metencephalon Anterior subdivision of Ectoder Rhombencephal
rhombencephalon m on
Behind the optic lobes
and medial to V ganglion
LEVEL OF THE PRONEPHROS AND THE FIRST SPINAL GANGLION
Structure Location MOF Embryonic Fate/Function 7MM
Origin precurso
r
Spinal cord From posterior Ectoderm As is
region of
neural tube
Neural canal Laterally compressed cavity Ectoderm As is
with ciliated and pigmented
ependymal cells
Gray matter Inner layer of spinal cord Ectoderm Spinal
composed of neruoblasts cord
and neuroglia
White matter Peripheral layer containing Ectoderm
axons of the neurons in gray
matter
Meninges Ectoderm Membranous covering of CNS none
First spinal Nerve cells ventrolateral to none
ganglia spinal cord
Myotomes On each side of notochord Mesoderm Thickened primordial of Somite
skeletal muscles
Pleuroperiton Coelomic cavity containing the
eal cavity viscera except the heart
Esophagus Below the notochord Endoderm Tubular organ with folded As is
mucosal lining
Dorsal aorta Between notochord and Mesoderm As is
esophagus
Pronephros Ventrolateral region of the Arise from Mesoderm As is
body nephrotome
Pronephric Mesoderm As is
tubules Cuboidal
epithelium
Posterior Blood vessels within Mesoderm Supplies pronephros with blood
cardinal veins pronephros
Nephrostome Mesoderm Opening of pronephric tubules As is
into the coelom
Nephric duct Lone duct at most caudal Mesoderm Joins the cloaca where it
section of pronephros empties its contents
Glomus Mesoderm Functional componets of As is
pronephric kidney
Waste products diffuse from
glomi to coelomic fluid
Stomach Evaginations of Endoderm
the
endodermal
lining form the
rudiments of
gastric glands
Duodenum Between pyloric end of Endoderm
stomach and intestine
Intestine Posterior to duodenum filled Endoderm
with yolk platelets
Liver To the right of the midline Endoderm
Gallbladder One-cell thick Endoderm
Bile duct Thick walled tube that Endoderm
appears in the place of gall
bladder
Pancreas Within the curvature of Endoderm
stomach with alveoli
surrounding small ducts
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 4 MM FrogDokument5 Seiten4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 MM FrogDokument28 Seiten7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chick 33 HRDokument14 SeitenChick 33 HRaa628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Dokument17 SeitenEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Mm Frog Embryo: Lab Exercise 4 OrganogenesisDokument16 Seiten4Mm Frog Embryo: Lab Exercise 4 OrganogenesisDimple May Gianne DumaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDokument5 Seiten48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDokument7 SeitenEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 MM TadpoleDokument5 Seiten7 MM TadpoleKyla JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Dokument9 SeitenChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDokument3 Seiten24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDokument4 Seiten10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDokument18 Seiten24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDimple May Gianne DumaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyDokument34 Seiten48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyChristalie Bea Fernandez100% (2)
- 33 Hour Chick Embryo Transverse SectionDokument36 Seiten33 Hour Chick Embryo Transverse SectionSasha GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoDokument13 SeitenActivity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoFerhaeeza KalayakanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmbryoLab 10mm FrogDokument13 SeitenEmbryoLab 10mm FrogpauNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10mm Frog TadpoleDokument30 Seiten10mm Frog TadpoleSarah Margaret Chong33% (3)
- Chick EmbryoDokument24 SeitenChick Embryonabilalk100% (1)
- 7 MM Frog EmbryoDokument20 Seiten7 MM Frog EmbryoCourtneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDokument14 SeitenEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsDokument22 Seiten48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsNathan Bantayan100% (1)
- Exercise 22 Serial Section of A 10 MM Pig Embryo PDFDokument16 SeitenExercise 22 Serial Section of A 10 MM Pig Embryo PDFMichaela Faye100% (1)
- ANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Dokument6 SeitenANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Junko TsukudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 Hour Chick EmbryoDokument27 Seiten24 Hour Chick Embryoaa6280% (1)
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoDokument28 Seiten48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 72 HR ReviewerDokument8 Seiten72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of The Pig EmbryoDokument12 SeitenDevelopment of The Pig EmbryoKarmina SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Chick EmbryoDokument74 SeitenEarly Chick EmbryoMinette EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2 4.1 1Dokument11 SeitenExp 2 4.1 1Carlo MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Ex1-2 and Chick OrganogenesisiDokument20 SeitenLab Ex1-2 and Chick OrganogenesisiLardel CarayNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEVBIOLAB Exercise1 REVIEWER Outside-SourceDokument24 SeitenDEVBIOLAB Exercise1 REVIEWER Outside-SourceDimple May Gianne Dumaguit100% (1)
- Development of Frog EmbryoDokument13 SeitenDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDokument8 Seiten24-Hr Chick EmbryopauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dumaguit (2021)Dokument12 SeitenDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick 72 HR DDokument35 SeitenChick 72 HR Daa628Noch keine Bewertungen
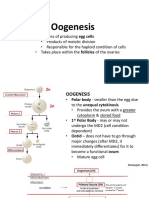
- DEVBIOLAB OogensisDokument91 SeitenDEVBIOLAB OogensisDimple May Gianne Dumaguit100% (1)
- Frog EmbryosDokument43 SeitenFrog EmbryosNics Martinez100% (7)
- Histo Ra 3 - Barbosa, Azenith VincentDokument7 SeitenHisto Ra 3 - Barbosa, Azenith VincentMinamiSapphire BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDokument48 SeitenChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvNoch keine Bewertungen
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDokument5 Seiten33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- PigDokument34 SeitenPigVanessa CarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDokument4 SeitenExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Hour Chick EmbryoDokument7 Seiten18 Hour Chick Embryoaa628100% (2)
- Chick Embryo WMDokument6 SeitenChick Embryo WMdhyan_ajjah67% (3)
- Embryo Lab Org 2Dokument14 SeitenEmbryo Lab Org 2pauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDokument23 SeitenExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDokument9 SeitenBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lbybio4 PDFDokument8 SeitenLbybio4 PDFstudent10100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Dokument16 SeitenExercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Gail AmuraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 30 LAB: Pattens 72-hr Chick SummaryDokument19 SeitenBIO 30 LAB: Pattens 72-hr Chick SummaryFaith VillahermosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 Hour Chick LabelledDokument89 Seiten48 Hour Chick LabelledSasha Gutierrez100% (1)
- 7mm Frog ATLAS 2Dokument28 Seiten7mm Frog ATLAS 2aemilianneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 33.48,72 From 2011Dokument63 Seiten33.48,72 From 2011aa628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chick GastrulationDokument6 SeitenChick GastrulationAlyssa Gail de VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 72-HR ChickDokument16 Seiten72-HR Chick411452123100% (1)
- Chick 48 HRDokument50 SeitenChick 48 HRaa628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Development. Cap 1Dokument32 SeitenPrinciples of Development. Cap 1Gre Vega ÁlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4mm Frog EmbryoDokument3 Seiten4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7Mm Frog: Structure GL Derivative Fate Function Cavity Misc. Info StructureDokument3 Seiten7Mm Frog: Structure GL Derivative Fate Function Cavity Misc. Info StructureJannah DangananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeDokument2 SeitenTail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gametogenesis LayersDokument1 SeiteGametogenesis LayersMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xenopus Reviewer Inductive InteractionsDokument2 SeitenXenopus Reviewer Inductive InteractionsMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spermatogenesis: Grasshopper TestisDokument5 SeitenSpermatogenesis: Grasshopper TestisMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Biological DesignDokument1 SeiteChapter 4 Biological DesignMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 6 KardongDokument8 SeitenCHAPTER 6 KardongMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zelfstudie Van Blastula Naar 3 KiemlagenDokument18 SeitenZelfstudie Van Blastula Naar 3 KiemlagenCheyenne ProvoostNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDokument4 Seiten10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryonic InductionDokument11 SeitenEmbryonic Inductionsourya jyoti dashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esophagus - Anatomy and Development - GI Motility OnlineDokument21 SeitenEsophagus - Anatomy and Development - GI Motility OnlineMaria Fernanda VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Development: Neurulation and Extra-Embryo MembranDokument45 SeitenAnimal Development: Neurulation and Extra-Embryo MembranNurul JasminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal ReproductionDokument7 SeitenPlant and Animal Reproductionhellohelloworld100% (2)
- Gastrulation and Formation of Germ Layers PDFDokument5 SeitenGastrulation and Formation of Germ Layers PDFElla LagramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fate Maps & Fate of Germ LayersDokument5 SeitenFate Maps & Fate of Germ LayersAmar Kant JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDokument48 SeitenChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal DevelopmentDokument43 SeitenAnimal DevelopmentZach ThorpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greek and Latin Roots HandoutDokument4 SeitenGreek and Latin Roots HandoutSiam SarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sclera PDFDokument334 SeitenThe Sclera PDFMaría Soledad Romero LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third Week of DevelopmentDokument34 SeitenThird Week of DevelopmentAriba Asif100% (1)
- Developmental BiologyDokument9 SeitenDevelopmental BiologyZahraa TermosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Anodontia PDFDokument4 SeitenJurnal Anodontia PDFTadjul Arifin Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDokument8 Seiten24-Hr Chick EmbryopauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zhou Xuedong Eds. Dental Caries Principles and ManagementDokument187 SeitenZhou Xuedong Eds. Dental Caries Principles and ManagementFreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 3. Photoperiodism and EmbryogenesisDokument7 SeitenWorksheet 3. Photoperiodism and EmbryogenesisSukmagita RahajengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex234.1 Ascaris Eggz PDFDokument7 SeitenEx234.1 Ascaris Eggz PDFCarlo MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Origin and Development of Organ Systems NotesDokument4 SeitenOrigin and Development of Organ Systems NotesimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aitana Manuela Castro Colabianchi, PDFDokument21 SeitenAitana Manuela Castro Colabianchi, PDFKerry RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDokument23 SeitenExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- Embryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainDokument100 SeitenEmbryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainAya Sobhi100% (4)
- Stiles-Jernigan - The Basics of Brain DevelopmentDokument22 SeitenStiles-Jernigan - The Basics of Brain DevelopmentBrunela SperanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrulationin MammalsDokument16 SeitenGastrulationin MammalsHarsha MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The EctodermDokument30 SeitenThe EctodermRey Bonnin Gonzaga NaparanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth Theories.Dokument40 SeitenGrowth Theories.Maha Ahmed Soliman100% (1)
- The Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomyDokument18 SeitenThe Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomymeseniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 1Dokument7 SeitenGroup Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 1Kayl Dustin MalalisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Craniofacial Biology Notes Unit 1Dokument37 SeitenCraniofacial Biology Notes Unit 1nohacksNoch keine Bewertungen