Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Table of English Tenses: Simple Present
Hochgeladen von
Norvin Treminio0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
21 Ansichten3 SeitenThe document provides a table summarizing English tenses, including their affirmative, negative, and question forms as well as common uses and signal words. It outlines 14 tenses - simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect, present perfect progressive, past perfect, past perfect progressive, future I simple, future I progressive, future II simple, future II progressive, conditional I, and conditional II. For each tense, example sentences are given to illustrate form and common time frames or situations of use are outlined.
Originalbeschreibung:
All English Tenses for studyinng,
Originaltitel
English Tense
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document provides a table summarizing English tenses, including their affirmative, negative, and question forms as well as common uses and signal words. It outlines 14 tenses - simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect, present perfect progressive, past perfect, past perfect progressive, future I simple, future I progressive, future II simple, future II progressive, conditional I, and conditional II. For each tense, example sentences are given to illustrate form and common time frames or situations of use are outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
21 Ansichten3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Simple Present
Hochgeladen von
Norvin TreminioThe document provides a table summarizing English tenses, including their affirmative, negative, and question forms as well as common uses and signal words. It outlines 14 tenses - simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect, present perfect progressive, past perfect, past perfect progressive, future I simple, future I progressive, future II simple, future II progressive, conditional I, and conditional II. For each tense, example sentences are given to illustrate form and common time frames or situations of use are outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
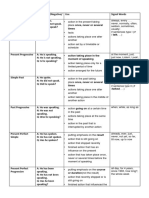
TABLE OF ENGLISH TENSES
TENSE AFFIRMATIVE/NEGATIVE/QUESTION USE SIGNAL WORDS
Simple Present A: He speaks. action in the present taking place regularly, never always, every …, never, normally, often,
N: He does not speak. seldom, sometimes, usually
or several times
Q: Does he speak? if sentences type I (If I talk, …)
facts
actions taking place one after another
action set by a timetable or schedule
Present Progressive A: He is speaking. action taking place in the moment of speaking at the moment, just, just now, Listen!,
N: He is not speaking. action taking place only for a limited period of time Look!, now, right now
Q: Is he speaking?
action arranged for the future
Simple Past A: He spoke. action in the past taking place once, never or yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in 1990, the
N: He did not speak. other day, last Friday
several times
Q: Did he speak? if sentence type II (If I talked, …)
actions taking place one after another
action taking place in the middle of another action
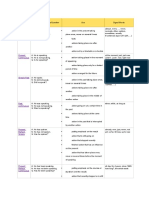
Past Progressive A: He was speaking. action going on at a certain time in the past while, as long as
N: He was not speaking. actions taking place at the same time
Q: Was he speaking?
action in the past that is interrupted by another
action
Present Perfect A: He has spoken. putting emphasis on the result already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till
Simple N: He has not spoken. now, up to now
action that is still going on
Q: Has he spoken?
action that stopped recently
finished action that has an influence on the
present
action that has taken place once, never or several
times before the moment of speaking
Present Perfect A: He has been speaking. putting emphasis on the course or duration (not all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?,
Progressive N: He has not been speaking. the whole week
the result)
Q: Has he been speaking?
action that recently stopped or is still going on
finished action that influenced the present
Past Perfect Simple A: He had spoken. action taking place before a certain time in the already, just, never, not yet, once, until
N: He had not spoken. that day
past
Q: Had he spoken? if sentence type III (If I had talked, …)
sometimes interchangeable with past perfect
progressive
putting emphasis only on the fact (not the
duration)
Past Perfect A: He had been speaking. action taking place before a certain time in the for, since, the whole day, all day
Progressive N: He had not been speaking.
past
Q: Had he been speaking?
sometimes interchangeable with past perfect
simple
putting emphasis on the duration or course of an
action
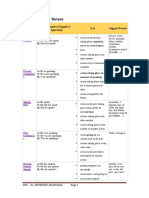
Future I Simple A: He will speak. action in the future that cannot be influenced in a year, next …, tomorrow
N: He will not speak. If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her, she will
spontaneous decision
Q: Will he speak? help you.)
assumption with regard to the future assumption: I think, probably, perhaps
Future I Simple A: He is going to speak. decision made for the future in one year, next week, tomorrow
(going to) N: He is not going to speak. conclusion with regard to the future
Q: Is he going to speak?
Future I Progressive A: He will be speaking. action that is going on at a certain time in the in one year, next week, tomorrow
N: He will not be speaking.
future
Q: Will he be speaking?
action that is sure to happen in the near future
Future II Simple A: He will have spoken. action that will be finished at a certain time in the by Monday, in a week
N: He will not have spoken.
future
Q: Will he have spoken?
Future II A: He will have been speaking. action taking place before a certain time in the for …, the last couple of hours, all day
Progressive N: He will not have been speaking. long
future
Q: Will he have been speaking?
putting emphasis on the courseof an action
Conditional I Simple A: He would speak. action that might take place if sentences type II
N: He would not speak. (If I were you, I would go home.)
Q: Would he speak?
Conditional I A: He would be speaking. action that might take place
Progressive N: He would not be speaking. putting emphasis on the course/ duration of the
Q: Would he be speaking?
action
Conditional II A: He would have spoken. action that might have taken place in the past if sentences type III
Simple N: He would not have spoken. (If I had seen that, I would have helped.)
Q: Would he have spoken?
Conditional II A: He would have been speaking. action that might have taken place in the past
Progressive N: He would not have been speaking. puts emphasis on the course / duration of the
Q: Would he have been speaking? action
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Eng Grammar Parts of SpeechDokument3 SeitenEng Grammar Parts of Speechsami karemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMarko MillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument2 SeitenSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAdailton SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsInga ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNDokument2 SeitenTense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNMirela MarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- გრამატიკაDokument3 Seitenგრამატიკაgio903371Noch keine Bewertungen
- Times: I Talk, )Dokument11 SeitenTimes: I Talk, )mugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: I Talked, )Dokument2 SeitenSimple Present: I Talked, )Seminarski Radovi Iz IstorijeNoch keine Bewertungen
- InglesDokument3 SeitenInglesazoljamiaidounNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Dokument3 Seiten1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Adeel AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: GrammarDokument2 SeitenTable of English Tenses: GrammarGenesis Belen0% (1)
- Verbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésDokument242 SeitenVerbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésVioleta Patricia Molet100% (1)
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentSofiene GuedriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument7 SeitenTenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRajalakshmi Gajapathy100% (2)
- Tiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioDokument2 SeitenTiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioelisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My English Grammar Guide CompressDokument39 SeitenMy English Grammar Guide CompressBenny LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenVerb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsmllorenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument2 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentBogdan ChișcababiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument2 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenAffirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsKavitha RajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordslovely innocentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialDokument5 SeitenGuia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialLizzy Yessenia Torres 11- 8 BCHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRanjit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentCristina ArdeleanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple PresentDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple Presentmanchiraju raj kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses PDFDokument2 SeitenTenses PDFgeraskewesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument10 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMina SamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key WordsDokument2 SeitenSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key Wordsyadhi20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan Jul 15, 2023Dokument2 SeitenAdobe Scan Jul 15, 2023sumanta biswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGiannina Ailén MusacchioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument2 SeitenTable of English TensesRasta FariNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument3 SeitenEnglish Tensescoquin8816Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Chart With Examples Use and Signal WordsDokument1 SeiteTenses Chart With Examples Use and Signal WordsMustapha ElNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDiego GrañenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsDokument2 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsradivojerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDahliya DwitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAngi BraileanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument7 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument4 SeitenEnglish TensesLucaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TenseDokument2 SeitenTenseKlaudia TerjékNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument2 SeitenTable of English TensesOscar LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cours 2bac L en 04Dokument2 SeitenCours 2bac L en 04hkuuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument2 SeitenTenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsanamariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarinela AnghelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument2 SeitenTable of English TensesElmi Zulkarnain OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument2 SeitenTable of English Tensesjavier_adan82Noch keine Bewertungen
- ÖzetDokument2 SeitenÖzetEnes PolatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: Italk, )Dokument2 SeitenSimple Present: Italk, )Enes PolatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart of English TensesDokument2 SeitenChart of English TensesMaria ArtilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Cuadro ResumenDokument4 SeitenTenses Cuadro ResumenGuillermo NarvaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Table Illustrates The Tenses in A Simple Way: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument2 SeitenThis Table Illustrates The Tenses in A Simple Way: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRafik RafNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar OnlineDokument6 SeitenEnglish Grammar OnlineNasir IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- All TensesDokument3 SeitenAll TenseskarenNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Course: Like I, Me (Personal Pronouns) or My, Mine (Possessive Pronouns)Dokument12 SeitenEnglish Course: Like I, Me (Personal Pronouns) or My, Mine (Possessive Pronouns)Luis AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English TensesMelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument2 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJosé LiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument1 SeiteTensesNucă EvelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument4 SeitenTensesLiliia RakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tenses 3ºDokument1 SeiteVerb Tenses 3ºaitana katherine barcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3Von EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7th GradeDokument44 Seiten7th GradeNorvin TreminioNoch keine Bewertungen
- IrregularDokument23 SeitenIrregularNorvin TreminioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phrasal Verbs List 3 PDFDokument9 SeitenPhrasal Verbs List 3 PDFNorvin TreminioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Common IdiomsDokument5 Seiten50 Common IdiomsNorvin TreminioNoch keine Bewertungen
- LINKERSDokument5 SeitenLINKERSIonela Loredana Batog100% (1)
- Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Unversitas Muhammadiyah TangerangDokument3 SeitenFakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Unversitas Muhammadiyah TangerangFitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 5 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisDokument4 SeitenModul 5 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisSiti NurzulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten Grammar ErrorsDokument2 SeitenTen Grammar ErrorsSK SurazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class VII Direct & Indirect SpeechDokument24 SeitenClass VII Direct & Indirect SpeechApparna BalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syntactical Analysis of Newspaper Headlines by Fitri Maharani English Department Faculty of Letters and Culture Udayana UniversityDokument8 SeitenSyntactical Analysis of Newspaper Headlines by Fitri Maharani English Department Faculty of Letters and Culture Udayana UniversityTHÚY NGUYỄNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Ujian Tengah Semester Genap Tahun Ajaran 2021/2022 UNIBADokument3 SeitenSoal Ujian Tengah Semester Genap Tahun Ajaran 2021/2022 UNIBAWilly RizkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modal Kullanimlari Ve Turkce Karsiliklari 1Dokument1 SeiteModal Kullanimlari Ve Turkce Karsiliklari 1ArasIlgazNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument9 SeitenUntitledapi-233604231Noch keine Bewertungen
- ComparisonDokument25 SeitenComparisonIndahMeiliianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Adverb PowerPointDokument10 SeitenThe Adverb PowerPointAyça Atakan DenizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect Speech For Exclamatory and Imperative SentencesDokument8 SeitenIndirect Speech For Exclamatory and Imperative SentencesRizwan BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smash 1 TB Resource PackDokument72 SeitenSmash 1 TB Resource PackGV Malta English Centre100% (1)
- Bracket: Quotation MarkDokument2 SeitenBracket: Quotation MarkraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure of The Present Perfect Continuous Tense IsDokument3 SeitenThe Structure of The Present Perfect Continuous Tense IsAlejandra RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Due Dates COM111 1 3 1Dokument9 SeitenTable of Due Dates COM111 1 3 1Daniel OkazakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerund and Infinitive DominoesDokument2 SeitenGerund and Infinitive DominoesBlanca Ruiz de SomocurcioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article Writing-Guidelines & Sample ArticleDokument2 SeitenArticle Writing-Guidelines & Sample ArticleLiliana Alexandra Paraipan100% (1)
- English Yearly Plan For Year 6Dokument8 SeitenEnglish Yearly Plan For Year 6Masnizan Binti HamdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aab College-Department of English Lexicology Assignment, Nov 2020Dokument2 SeitenAab College-Department of English Lexicology Assignment, Nov 2020Fatjona BerishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Perfect Tense MAMDokument8 SeitenPresent Perfect Tense MAMset netNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRACTICEDokument14 SeitenPRACTICEThùy DươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future SimpleDokument1 SeiteFuture SimpleEduard Lisogor100% (1)
- Classifications of Noun: Week 1: Lessons On NounDokument3 SeitenClassifications of Noun: Week 1: Lessons On Nounjaocent brixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive GrammarDokument35 SeitenDescriptive GrammarJoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communications Question BankDokument15 SeitenCommunications Question BankChembula Jahnavi100% (2)
- Chapter ThreeDokument110 SeitenChapter ThreeBethelhem YetwaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb TensesDokument6 SeitenVerb TensesReiner ZambranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Technical Knowledge GrammarDokument4 Seiten12 Technical Knowledge GrammarMargielyn100% (1)
- Series of Adjectives LPDokument5 SeitenSeries of Adjectives LPApril Dela Cruz RojoNoch keine Bewertungen