Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Csec Biology Scheme
Hochgeladen von
suggaballCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Csec Biology Scheme
Hochgeladen von
suggaballCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.
ARANGUEZ NORTH SECONDARY SCHOOL
SCHEME OF WORK
DEPARTMENT: SCIENCE
FORM IV
ACADEMIC YEAR: Term III (APRIL – JULY 2018)
WEEK NUMBER OF LEARNING CONTENT SCOPE TEACHING SUGGESTED
SESSIONS OUTCOMES STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT
SRATEGIES
SECTION B LIFE PROCESSES: Photosynthesis
Describe the process Two stages of Power Point CSEC Biology
of photosynthesis in photosynthesis: The light presentation Past Papers
green plants. dependent and the Light
independent. The evolution You Tube Videos
of oxygen as a result of the
splitting of water by light Associated labs
energy. The subsequent
reduction of carbon dioxide
to a carbohydrate (glucose).
The chloroplast is the site
of the reaction.
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 1
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Relate the structure The external features and Draw and lab the CSEC Biology
of the leaf of a internal features of a dicot external features. Past Papers
flowering plant to leaf as seen in cross section
its function in under the light microscope.
photosynthesis. Emphasis on adaptations
for photosynthesis.
Explain how Limiting factors in the Power Point CSEC Biology
environmental environment affect the rate presentation Past Papers
factors affect the rate of photosynthesis. Factors
of photosynthesis. such as light intensity and You Tube Videos
carbon dioxide affect the
rate at which photosynthesis Associated labs
occurs.
Discuss the Emphasis on the importance
importance of of nitrogen in the formation
minerals in plant of proteins and magnesium
nutrition using in the formation of
nitrogen and chlorophyll.
magnesium as
examples.
SECTION B LIFE PROCESSES: Diet and Nutrition
Perform tests to Starch, protein, lipids, Test for CSEC Biology
distinguish among reducing and non-reducing Biomolecules Past Papers
food substances. sugars. Chemical and
physical properties of Power Point
presentation
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 2
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
carbohydrates, proteins,
lipids. You Tube Videos
Associated labs
Discuss the Components of a balanced Test for CSEC Biology
importance of a diet including vitamins, Biomolecules Past Papers
balanced diet in minerals and their roles.
Humans. The results of their Power Point
deficiency or surplus presentation
(Malnutrition). The effects
of age, sex, gender and You Tube Videos
occupation on dietary
needs. Dietary Project: Analyze
recommendations for the items being
treating and preventing sold/made
diseases- diabetes and available to
hypertension. students in the
cafeteria. Assess if
these items meet
the needs of
developing
teenagers. Make
suggestions if
needed.
Relate the structures Simple diagrams of the Test for CSEC Biology
of the human alimentary canal and the Biomolecules Past Papers
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 3
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
alimentary canal to internal structure of a tooth.
their functions. Mastication and the role of Power Point
teeth in the mechanical presentation
breakdown of food to be
included. You Tube Videos
Explain the role and Inclusion of catalysis. Power Point CSEC Biology
importance of Properties of enzymes, role presentation Past Papers
enzymes. of digestive enzymes in the
mouth, stomach and You Tube Videos
pancreatic enzymes in the
small intestine. Associated labs-
Investigate the
effect of
temperature and
pH on the activity
of catalase or
amylase.
Describe what Simple diagram of villi and Power Point CSEC Biology
happens to the role of absorption of the presentation Past Papers
products of products of digestion. You Tube Videos
digestion after their Transport to the liver and
absorption. assimilation to be included. Associated labs-
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 4
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
TOPIC: Photosynthesis
ASSOCIATED LABS
Activity #01: Testing leaves for the presence of starch.
SBA SKILLS: ORR/AI/MM
Leaves that have been in sunlight contain starch, however placing Iodine on a fresh leaf would not yield any result. The
outer waxy surface will not absorb the solution and the green colour would hide the colour change. The leaf’s outer waxy
layer has to removed and the leaf decolourised.
APPARATUS
1. Fresh leaves 2. A large beaker 3. Bunsen Burner
4. Tripod stand 5. Iodine Solution 6. Forceps
7. Ethanol 8. Petri Dish 9. White Tile
10. Test Tube 11. Test Tube rack
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 5
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 6
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Activity #02: Testing variegated leaves for the presence of starch.
SBA SKILLS: MM/AI/ORR
Starch is only made in the parts of the leaves that are green. This can be demonstrated by using a variegated leaf which
has green and white parts. The white regions, which lack the green pigment called chlorophyll would yield a negative test
for starch.
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 7
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Activity #03: Need for light for photosynthesis
SBA SKILLS: MM/AI/ORR
Use a destarched plant that has been kept in a cupboard for at least 48 hours.
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 8
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Activity #04: Testing leaves for reducing sugars.
SBA SKILLS: MM/AI/ORR
Instead of starch the leaves of some plants such as onions and chives store sugars. The leaves of these plants can be tested
for reducing sugars.
APPARATUS:
1. Onion/chive 2. Test Tubes 3. Benedict’s Solution
4. Large beaker 5. Bunsen Burner
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 9
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Activity #05: Drawing of a leaf section
Observation of a prepared slide.
SBA SKILL: D
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 10
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
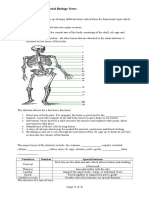
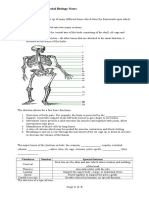
Activity #06: Drawing of the External features of a leaf
SBA SKILL: D
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 11
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Activity #07: Investigating the effects of the lack of minerals on the growth of seedlings.
SBA SKILL: PD
Design an experiment to investigate if seedlings need minerals to grow normally.
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 12
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Activity #08: Experiment with Chlorophyll and Chromatography
SBA SKILL: ORR/MM
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 13
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
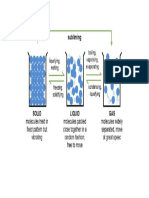
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food. Plants capture the energy from sunlight with their
leaves and other green parts of the plant. The green colour comes from a pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs
the energy from the sun, allowing the plant to use this energy to make its own food. Plants use carbon dioxide and water,
along with this energy from the sun, to make glucose, which is a sugar. This is photosynthesis.
At the height of photosynthesis, during the summer when the days are long, plants continually make chlorophyll. The
green from the chlorophyll covers up any other colour that may be in the leaf. However, when the days become shorter
and the temperatures become cooler, trees stop producing chlorophyll. Without chlorophyll present, the leaves change
colour as the other pigments are exposed. The yellow colour that we see in the fall is a pigment called carotenoid. We also
see carotenoids in carrots, corn, bananas and even canaries! The red colour that we also see is called anthocyanin, and
this is produced by the leaves only in the autumn when the days are short and the temperatures are cool, and only when
chlorophyll is no longer being produced. Anthocyanins can also be found in cranberries, red apples, cherries and
strawberries.
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 14
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
TOPIC: Diet and Nutrition
ASSOCIATED LABS
Activity #01: Determine the energy content of a food sample.
If a sample of food will burn well in air, you can measure its energy content using a simplified version of the food
calorimeter.
SBA SKILL: ORR/MM/AI
If the change in temperature is greater when the water is heated with the use of the fire caught by the food substance,
then the energy content in the food substance is higher because the heat energy is greater, since the heat energy is
absorbed by the water when the fire is kept under the test tube containing water. The formula indicates that if the change
in temperature is greater when the mass of the substances and the volume of water are constant, then the heat energy is
higher.
Apparatus
Test Tube
Measuring Cylinder
Laboratory Thermometer
Water
Needle with Handle
Scalpel (for cutting the substances into exactly 0.5 grams)
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 15
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Test tube holder
Burner
The following substances are the 5 different food items that are used to conduct the experiment, the substances
used are:
i. Biscuit
ii. Koko Crunch
iii. Cheetos
iv. Peanut
v. Candlenut
Variables
Independent Variable: Heat energy of the food substance used.
Dependent Variable: Temperature change in the water/Amount of energy absorbed.
Controlled Variable: Amount of water, Temperature of surroundings, Type of needle used, Temperature of water.
Manipulation
Independent Variable: As we vary the food items that we use, their heat energy/ they themselves become the
independent variable.
Dependent Variable: The change in temperature/ Heat energy absorbed is varied as the heat energy of the
substance is varied.
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 16
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Controlled Variable: The temperature is not varied in any case or does not depend on anything during this
experiment, amount of water equals 20ml in each trial of experiment for each food substance.
Procedure
Measure 20ml water in the measuring cylinder and pour in the test tube.
Place the test tube in the holder and lock it tight.
If the food substance measures 0.5 grams on the electrical balance, then use the substance, otherwise use the scalpel
to divide it into smaller pieces and make sure it measures exactly 0.5 grams.
Measure the initial temperature of water using the thermometer
Poke through a food substance measuring 0.5 grams using the needle with the handle.
Turn on fire on the burner.
Set the food substance on the needle to fire on the burner.
Once the food substance starts to burn, place it under the test tube so the water inside it can absorb heat.
Measure the temperature change in the water using the thermometer.
Measure the energy content in the food item by using the following formula:
https://schoolworkhelper.net/lab-answers-energy-from-burning-food/
Activity #02: Food tests
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 17
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
This experiment allows the students to become familiar with both the positive and negative colour results for identifying
biomolecules such as – sugars (reducing and non-reducing), starch, lipids and proteins. Additionally, a food sample can
be tested and the biomolecules it contains identified.
10 Test tubes
2 Test tube racks
Test tube holder
2 Measuring cylinders
Large beaker
Bunsen burner
Gauze and tripod stand
Labels
Stop clock
Distilled water
Glucose solution (reducing sugar)
Sucrose solution (non-reducing sugar)
Starch solution
Oil (vegetable)
Protein solution (albumen)
Benedict’s solution
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Copper sulphate (CuSO4)
Iodine solution
*Food sample ____________ (optional)
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 18
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
METHOD:
(A) BENEDICT’S TEST (REDUCING SUGAR TEST):
1. Label 2 clean test tubes – R1 and R2. Add 1cm3 distilled water to R1 and 1cm3 glucose to R2.
2. In each test tube add 2 cm3 of Benedict’s solution.
3. Place both test tubes into a boiling water bath for 2 minutes.
4. Observe and record the initial and final colours of each test tube in an appropriate table.
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 19
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
(B) NON-REDUCING SUGAR TEST:
1. Label 2 clean test tubes – N1 and N2. Add 1cm3 distilled water to N1 and 1cm3 sucrose to N2.
2. In each test tube add 2 cm3 hydrochloric acid (HCl).
3. Boil each tube in a water bath for exactly 1 minute, then remove from the water bath and neutralize with 2cm3
sodium hydroxide (NaOH) – until the fizzing stops.
4. Carry out the Benedict’s test as above (A -steps 2 – 4).
5. Observe and record the initial and final colours of each test tube in an appropriate table.
(C) STARCH TEST (IODINE TEST)
6. Using cleaned test tubes – S1 and S2 – add 1cm3 distilled water to S1 and 1cm3 starch to S2.
7. Add 3 drops of iodine solution to each test tube.
8. Observe and record the initial and final colours of each test tube in an appropriate table.
(D) PROTEIN/ BIURET TEST
9. Using cleaned test tubes – P1 and P2 – add 1cm3 distilled water to P1 and 1cm3 protein to P2.
10. To each test tube add 1 cm3 of dilute sodium hydroxide (NaOH) followed by 4 drops of 5% Copper Sulphate
solution (CuSO4), shake gently to mix each test tube.
11. Observe and record the initial and final colours of each test tube in an appropriate table.
(E) EMULSION TEST FOR LIPIDS
1. Using cleaned test tubes – L1 and L2 – place 1cm3 distilled water to L1 and 1cm3 oil to L2.
2. To each test tube add 1 cm3 of ethanol, and shake each vigorously.
3. Pour cold distilled water into each test tube.
4. Observe and record the initial and final colours of each test tube in an appropriate table.
Name of Test Substance tested Main reagents/ treatment
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 20
Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2
Benedict’s test/ Reducing R1 - water - Benedict’s solution
sugar test R2 – glucose solution - Heat
Non-reducing sugar test N1 - water - HCl + heating
N2 – sucrose solution - NaOH
- Benedict’s solution + heat
Starch/ Iodine test S1 - water - Iodine solution
S2 – starch solution - (no heating)
Protein/ Biuret test P1 - water - NaOH or KOH
P2 – protein solution - 5% CuSO4 (no heating)
Emulsion test L1 - water - Ethanol + shaking
L2 - oil - Cold water
Document Prepared by Ms. Rambaran 25/04/2018 Page 21
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Csec BiologyDokument79 SeitenCsec BiologysuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSB Section ADokument12 SeitenHSB Section AAshford Thom100% (1)
- Edited Lab Manual For CSEC BiologyDokument16 SeitenEdited Lab Manual For CSEC BiologyKLASSIQUE BROOKS100% (1)
- Handout On Planning and DesigningDokument4 SeitenHandout On Planning and DesigningJuliene HindsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living Organisms and The Environment PDFDokument29 SeitenLiving Organisms and The Environment PDFOsmany MadrigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sba Lab CompilationDokument2 SeitenSba Lab CompilationDevi Rambaran0% (1)
- Csec Biology Laboratory Manual: Grades 10 and 11Dokument44 SeitenCsec Biology Laboratory Manual: Grades 10 and 11Kristen100% (2)
- CSEC Biology - EcologyDokument74 SeitenCSEC Biology - EcologyRic Flamboyant FraserNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC BIOLOGY - Ecological StudiesDokument36 SeitenCSEC BIOLOGY - Ecological StudiesNabeel Uddin86% (7)
- PDF DocumentDokument53 SeitenPDF Documentbrie100% (2)
- The Csec HelperDokument71 SeitenThe Csec Helperapi-291242485100% (1)
- Csec Biology Work BookletDokument77 SeitenCsec Biology Work BookletDevi Rambaran100% (4)
- CSEC Biology SBA GuidelinesDokument4 SeitenCSEC Biology SBA GuidelinesMichelle Benskin100% (3)
- Csec BiologyDokument79 SeitenCsec Biologysuggaball100% (4)
- Endocrine System (CSEC Integrated Science)Dokument20 SeitenEndocrine System (CSEC Integrated Science)Nabeel Uddin100% (2)
- CSEC Biology Revision Guide AnswersDokument29 SeitenCSEC Biology Revision Guide AnswersCharlobabooram50% (2)
- CSEC Biology Manual 2018-2020Dokument49 SeitenCSEC Biology Manual 2018-2020Shakira100% (6)
- Human & Social Biology 4th FormDokument23 SeitenHuman & Social Biology 4th Formhedasdudh100% (1)
- CSEC BIOLOGY Nervous Coordination - EyeDokument29 SeitenCSEC BIOLOGY Nervous Coordination - EyeTamicka BonnickNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC CHEMISTRY LABsDokument32 SeitenCSEC CHEMISTRY LABsCryus Lipid100% (1)
- F5 T1 HSB P1 2010-2011Dokument13 SeitenF5 T1 HSB P1 2010-2011asjawolverine81% (27)
- CSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers PDFDokument31 SeitenCSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers PDFSimon PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSB Past PapersDokument43 SeitenHSB Past PapersAretha Dawes33% (6)
- BHS CSEC Grade 10 Lab Manual 2019-2020Dokument12 SeitenBHS CSEC Grade 10 Lab Manual 2019-2020Abby Shay GayleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec H&s Biology 2008Dokument7 SeitenCsec H&s Biology 2008Marshalee Francis75% (4)
- Section 1 - Living Organisms and The EnvironmentDokument11 SeitenSection 1 - Living Organisms and The EnvironmentOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- CSEC Biology 2014 RevisionDokument44 SeitenCSEC Biology 2014 RevisionNabeel Uddin89% (9)
- CXC Biology Practical - Ecological StudiesDokument1 SeiteCXC Biology Practical - Ecological StudiesNabeel Uddin33% (3)
- Csec Bio. Digestion MCDokument8 SeitenCsec Bio. Digestion MCShav Mad Swizz50% (4)
- CAPE Bio Mark SchemeDokument4 SeitenCAPE Bio Mark Schemeron97150% (2)
- CSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesDokument10 SeitenCSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesAnasha Éttienne-Taylor100% (2)
- CSEC Biology Jan 2021 P2 - OCRDokument28 SeitenCSEC Biology Jan 2021 P2 - OCRJonathan RamsundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Study Guide - September 11, 2012Dokument11 SeitenCSEC Study Guide - September 11, 2012ChantelleMorrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Biology January 2013 P1 PDFDokument11 SeitenCSEC Biology January 2013 P1 PDFCarl Agape Davis0% (3)
- HSB 80 Mark Paper (CSEC)Dokument9 SeitenHSB 80 Mark Paper (CSEC)Gregory SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSB January2014 Paper 2 Past PaperDokument16 SeitenHSB January2014 Paper 2 Past PaperTrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSB Mock Paper 2Dokument17 SeitenHSB Mock Paper 2Nadege Roach50% (2)
- CSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDokument4 SeitenCSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesLeon Abel80% (5)
- Csec HSB January 2009 p2Dokument24 SeitenCsec HSB January 2009 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec Biology Sba Mark SchemesDokument22 SeitenCsec Biology Sba Mark Schemesaj jaikaran100% (1)
- Biology 09 p2 CsecDokument15 SeitenBiology 09 p2 CsecGiovanni Dubii Daba Hutton86% (7)
- CSEC Biology Quiz Section ADokument3 SeitenCSEC Biology Quiz Section AViCtOrIa M.100% (2)
- 1 States of MatterDokument27 Seiten1 States of MatterRaymond FrederickNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Unit 1 P2 BiologyDokument19 Seiten2022 Unit 1 P2 BiologyMartyn PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec Lab Manual 2017 PDFDokument36 SeitenCsec Lab Manual 2017 PDFCamaya Rumble100% (3)
- Csec HSB June 2007 p2Dokument17 SeitenCsec HSB June 2007 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date: 11/02/2020 Lab#1 Title: Ecology Aim: To Determine The Density of Plant Species Within A Given Study Area. ApparatusDokument7 SeitenDate: 11/02/2020 Lab#1 Title: Ecology Aim: To Determine The Density of Plant Species Within A Given Study Area. ApparatusTabitha Darrell100% (1)
- Cape Communication Studies: Practical Exercises for Paper 02 EssaysVon EverandCape Communication Studies: Practical Exercises for Paper 02 EssaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryDokument8 SeitenFORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryJennifer ElliottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Useful Formulae For Csec Physic1Dokument2 SeitenUseful Formulae For Csec Physic1Britney valladaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDokument4 SeitenCSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology Notessmbdy tbhhh100% (1)
- Practice Exam - CXC CSEC English A Exam Paper 1 - CaribExams2Dokument6 SeitenPractice Exam - CXC CSEC English A Exam Paper 1 - CaribExams2Sam fry0% (1)
- CSEC Biology June 2009 P2Dokument20 SeitenCSEC Biology June 2009 P2Joy Boehmer50% (2)
- Csec HSB January 2014 p2Dokument21 SeitenCsec HSB January 2014 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms. Moses CSEC Chemistry 2017 (2484)Dokument19 SeitenMs. Moses CSEC Chemistry 2017 (2484)Anna Lyse Moses100% (1)
- Biology CXC 2022 ReviewDokument46 SeitenBiology CXC 2022 ReviewLatoya Scottland100% (2)
- Jamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideVon EverandJamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module b4 The Processes of Life Scheme of Work and Lesson PlanDokument30 SeitenModule b4 The Processes of Life Scheme of Work and Lesson PlanSaba FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL For Energy TransformationDokument5 SeitenDLL For Energy TransformationArman VillagraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDokument44 SeitenPHOTOSYNTHESISsuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELLSDokument37 SeitenCELLSsuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIFFN&OSMOSISDokument56 SeitenDIFFN&OSMOSISsuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arrangement of ParticlesDokument1 SeiteArrangement of ParticlessuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turning Primary Scientists Into CSEC Level ScientistsDokument35 SeitenTurning Primary Scientists Into CSEC Level ScientistssuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Unit PlanDokument7 SeitenCells Unit PlansuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEY Ecological-Pyramids-Worksheet - 2013Dokument2 SeitenKEY Ecological-Pyramids-Worksheet - 2013suggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Supple Me Nary Questions and Suggested AnswersDokument1 SeiteAssessment Supple Me Nary Questions and Suggested AnswerssuggaballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec BiologyDokument79 SeitenCsec Biologysuggaball100% (4)
- Practical Carbohydrates PDFDokument22 SeitenPractical Carbohydrates PDFJoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology OreoDokument25 SeitenBiology Oreoapi-3740416Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Molecules (Multiple Choice) QPDokument12 SeitenBiological Molecules (Multiple Choice) QPSuman JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying NutrientsDokument7 SeitenIdentifying NutrientsDorcas ChiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of CarbohydratesDokument3 SeitenQualitative Analysis of CarbohydratesJylla AngwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes and KetonesDokument4 SeitenAldehydes and KetonesAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud50% (2)
- Carbohydrate AnalysisDokument63 SeitenCarbohydrate AnalysisWinda EngkesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted To: Vidyasagar UniversityDokument126 SeitenSubmitted To: Vidyasagar UniversitySANKHADEEP BAKLYNoch keine Bewertungen
- PracticalsDokument33 SeitenPracticalsNo NameNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9700 Nos Ps 22Dokument6 Seiten9700 Nos Ps 22Samer Ehab100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Testing For Nutrients LabDokument16 SeitenChapter 10 Testing For Nutrients Labm_frajmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Lab Report (G2) PDFDokument10 SeitenBio Lab Report (G2) PDFAina NabihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Postlab MidtermDokument68 SeitenBiochemistry Postlab MidtermNash Deniega50% (4)
- Physics IPDokument21 SeitenPhysics IPParthiban ParthibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reducing and Non-Reducing Sugars Test: Lab Activity in Preparation For Practical Exam AS Level BiologyDokument36 SeitenReducing and Non-Reducing Sugars Test: Lab Activity in Preparation For Practical Exam AS Level BiologyAmisha JuraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS1005 Wet Lab ReportDokument12 SeitenBS1005 Wet Lab ReportDoug A. HoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathological Urine ConstituentsDokument22 SeitenPathological Urine Constituentsmanni1001100% (3)
- BIO 101 Lab Manual 2017 - 2018 FinalDokument43 SeitenBIO 101 Lab Manual 2017 - 2018 FinalOlerato TeddieNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB 1108 L05 ChemLifeDokument3 SeitenIB 1108 L05 ChemLifeKaya Dawn0% (2)
- 9700 m18 QP 33 PDFDokument16 Seiten9700 m18 QP 33 PDFIG UnionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benedicts TestDokument3 SeitenBenedicts TestEsther AgyapongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytochemical Screening Tests SartajDokument3 SeitenPhytochemical Screening Tests SartajJarvis WillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Olympiad Forensics Qualitative AnalysisDokument4 SeitenScience Olympiad Forensics Qualitative Analysisesthersim714100% (1)
- Color Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesDokument6 SeitenColor Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesRüveyda AkçinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Test Lab 1Dokument16 SeitenFood Test Lab 1Oksana40% (15)
- Amali 26oktDokument15 SeitenAmali 26oktJun Hong TeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of Biology - Lab ManualDokument43 SeitenConcepts of Biology - Lab ManualUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characterization of Carbohydrates (Formal Report)Dokument11 SeitenCharacterization of Carbohydrates (Formal Report)Man Dejelo100% (6)
- Experiment 1: CarbohydratesDokument6 SeitenExperiment 1: CarbohydratesEM Alberts100% (2)
- BCM 202Dokument49 SeitenBCM 202Naufal QaweimNoch keine Bewertungen