Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Material Management
Hochgeladen von
maulikpanchalOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Material Management
Hochgeladen von
maulikpanchalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1. MATERIAL MANAGEMENT
Material Management is an important element in any project’s management since it involves issues
related to buying, storing, billing and usage of materials. The basic elements of material management
are shown as follows:
Material Management
Stores Purchase
Procurement Accounts
Receiving Transportation
1. 1 PURCHASE AND MATERIAL REQUISITION
1.1.1 PURCHASING AND STORES ORGANIZATION
The organization on the project site is by function. Here, the materials management department is
structured on the basis of functions such as stores, procurement, transport, purchase etc. as shown in
the figure below:
STORE & PURCHASE I/C (Mr.L.RAMESH)
STORE OFFICER STORE OFFICER STORE CLERK
(Mr.PREM CHAND SHARMA)
1. S.BHATTACHARJEE (KRISHNA RAO) 2. LALAN KUMAR 3. RAMAKRISHNA (
5. SUSHIL KM. SHARMA
HELPERS DATA ENTRY OPERATOR
1.DINESH 2.GANESH RAM 3.MANAAL 1. A.BHATTACHARYA
The Stores and Purchasing organizations are kept under the same department so as to reduce the inter-
departmental issues and procedures and to have an efficient management system for materials.
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 1
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
Project execution requires use of construction materials of natural origin and manufactured items
materials for use in permanent/temporary works which should conform to the contract specifications in
both the cases.
The steps that will be adopted for control of these materials are taken for each of the above aspects of
materal management such as purchase, procurement, receiving and stores. The procedure for material
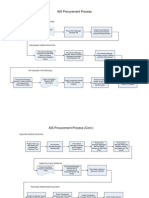
procurement will be as per the flow chart.
1.1.2 MATERIAL REQUISITION
The material requisition is made as per the demand of materials generated on site. The process is as
follows:
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 2
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
The purchase procedure after the material request generation at store is as follows:
Material request is generated at the store
Local purchase: For materials required in low quantity/ Purchase through Delhi Regional Office: For large
urgent requirement quantities
Selected vendors give quotation for materials System Material request is generated
Vendor selected on basis of lowest rate/ Availability/
Loading under ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
quantity & order is placed
Materials sent via store to the requestor Requisition sent to business unit
Indent Approval of that MR
Receipt note is generated Purchase is done
Payment done by Delhi Regional Office Material sent to store/ site to the requester
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is software used at Afcons which connects the people of the
organization and the entire working is co-ordinated through it. The material requisition posted on it is
sent to various sites and Delhi Regional Office and the regional office decides the source for material
supply. For local purchase, the vendors are supposed to be from the approved vendor list of the client
(CPWD approved vendor list).
1.1.3 SELECTION OF SUPPLIER AND ISSUE OF PURCHASE ORDER
Receive Purchase Requisition
NO
Check Letter of Award (LA) in place Purchase Requisition (PR) to be approved by PM
YES
Repeat order from approved vendor? Quotation assessment/ price comparison
NO
Sourcing Approved
NO YES
Supplier Information & quotations Recall quotation Raise Purchase Order (PO)
Vendor criteria assessment & Price comparison
Approved Register in approved Vendor list
Keep record for future purpose in Vendor Issue Purchase Order (PO)
selection file
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 3
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
For materials of natural origin, such as aggregates etc., the process is as follows:
Selection of Source
Sample and Test
Approved Source Non-Approved Source
Material is used from the source
Routine Tests
Not meeting specifications
Routine Tests meet specifications
Continue use Rework / Retest Discontinue use
Continue use if meeting specification
The following list provides a list of manufacturers as approved by the Client, in this case C.P.W.D:
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 4
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1.1.4 PURCHASING OF MATERIALS
There should be timely purchase of materials to avoid any disruption to the project schedule. Also it
is necessary to avoid any wastages etc.
The purchase process is initiated as and when there is a material requirement
1.1.4.1 Tools for Purchasing
The various tools required for purchasing are as follows:
Market Research
Price Charts
Codification
Funds Flow
Management Policies
1.1.4.2 Purchasing Process
The responsibility matrix for purchasing procedures along with necessary documents is as follows:
Sr. Procedure Description Responsibilit Reference Document Output
No y Record
.
A Supply items procured from HO/ Region
1 Receive kick off meeting minutes Planning Drawings/Specifications Minutes of
on procurement strategy on items Engineer , Contract documents kick off
to be procured from HO, Region meeting
and site
2 Send detailed construction Planning Construction
program indicating delivery Engineer program and
schedules to HO/ Regions delivery
schedule
3 Receive data sheet/ brochures Planning Data Sheet
from HO/ Region and submit to Engineer
customer for approval if required
contractually
4 Inform customer approval status Project In Notes
to HO/Region if any charge
5 Receive Purchase order (duplicate Planning Purchase Order copy
copy) and check the adequacies, Engineer
delivery status dates and inform
deviations if any to HO/ Region for
action
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 5
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
6 Follow up with purchase Project In Notes
department in case of delay charge
Receive materials and check
inspection report, MTC and
physical condition of materials
and inform concerned personnel
of the deviations/ damages if any
7 Follow corrective action if needed Project In
charge
B Construction materials procured from HO/ Region
1 Follow step A1 Planning
Engineer
2 ACE provisions and list of Planning Drawings/ Specs
approved vendors (contractually Engineer
agreed) to Purchase department
for HO/ Regional Procurement
3 Raise purchase requisition for Planning Drawings/ Specs Purchase
materials indicating approved Engineer Request
vendors agreed in contract,
specification of the product,
inspection and acceptance
criteria, delivery schedule and
requirements of QMS
4 Forward to Materials Department Project In ACE Purchase
through SPM though purchase charge/ Store Request List
keeper
5 Follow up with purchase Store keeper Inspection & Testing
department in case of delay Plan
Receive material and check the
conditions along with QC engineer
Construction materials procured from site
1 Follow step A1 Planning
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 6
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
Engineer
2 Identify vendors for material Planning Vendors list
procurement based on source of Engineer/
supply and capability of supply Store keeper
3 Prepare comparative statement and Project In Cost
select capable vendor charge comparison
statement
4 Take rate approval from SPM for Project In Note
material procured from site charge
5 Raise material request indicating Planning Drawings/ Specs Register
specifications Engineer
6 Approve MR and send to stores Project In Register
charge
7 Raise Purchase Order on the Store keeper Purchase
approved vendors with detailed Order
specification of the product,
quantity, inspection and acceptance
criteria, delivery schedule and
requirements of QMS and send to
Project In charge for approval
8 Approve purchase order and send to Project In Purchase
stores for procurement charge Order
9 Check quality of material at vendor Store keeper Inspection and testing
premises or on receipt at site
10 Accept approve material or follow
procedure for control of non-
confirming reports
D Services/ Sub contracts
1 Receive kick off minutes of meeting Project In Drawings/ specs/ Minutes of
on strategy on sub contracting to be charge contract documents kick of
initiated by HO and RO and site meeting
2 Obtain item rate approval from PM Project In Approval
charge notes
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 7
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
3 Identify potential agencies based on Sector
previous performance and Project
assessment Manager/
Project In
charge
4 Screen the subcontractors based on Project In
Technical/ financial competence charge
5 Obtain quotes from above parties Project In
and negotiate charge
6 Place order on the party offering Project In Purchase
best technical and commercial charge Order
terms after obtaining approval from
appropriate authority Comparative
statement
7 Evaluate the subcontractors Project In
periodically charge
8 Update master list of specialized Project In
contractors/ sub contractors charge
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 8
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1. 2 MATERIAL RECEIVING
The materials can be received from the following sources:
1. from vendor
2. from Delhi Regional Office
3. From Mumbai Head Office
The procedure involved in and after the receipt of materials is as follows:
Material Received
Received by inward Section of Stores In case of bulky material – weighed on Weigh Bridge – godown / yard
Verification of Quantity with delivery challan and
purchase order
Verification of all Documents:
Excise Gate pass
Octroi receipt
Third Party inspection / analysis
Delivery challan is stamped and signed
Material is received. In case of discrepancy- purchaser/
vendor / client / subcontractor to be intimated
Inspection - Inspection Authority is informed by the
inward section
Quality inspected by remarks on the MRN / Challan Copy.
Inspection to be completed within 7 days of receipt of
material
Inspected and Accepted material Inspected and rejected material
Handed to main store duly acknowledged on challan Kept separately
Tagged by a red tag indicating rejected material
Tagging done as follows:
Green tag – major materials
Blue tag – accessories in plant and machinery Returned to vendor, branch with a rejection challan
Yellow – other accepted material
Returned to vendor, branch with a rejection challan
Materials are checked by the Stores Department and the QA/QC in-charge. Separate details for storage
of materials shall be discussed later.
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 9
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1.2.1 FLOWCHART EXPLANATION
1.2.1.1 Material Receipt Note
A Material Receipt Note (MRN) shall be prepared on receipt of the material. The MRN should
distinguish the following receipts:
o Receipt from vendor
o Receipt from branch ( transfer of material whether from another site or Central stores)
o Receipts from within the site ( i.e. sub store, tools, sub contractor, rejected, - surplus,
client).
o Receipt of capital items, receipt will be taken into computer separately like General
store, spares etc.
o Receipt from sub-contactor
o Receipt from Client
o Receipt of Construction Assets, Receipt will be taken into computer in a separate
module.
The Receipt information shall be updated in the computer system for generating the MRN for
qty received vis-a-vis quantity mentioned in the Challan, rate etc.
The MRN for receipts from branches will be prepared in three copies. One copy will be sent to
the branch sending the material The MRN for receipts of Capital items should also be prepared
in three copies. One copy should be sent to the Equipment division at Head office. )For purchase
through vendor one copy of MRN may be given to vendor, in turn they will raise the bill
mentioning the MRN no. In each cased second copy of AMRN will be forwarded to Accounts
Department and third copy will remain as Store copy.
At the end of each day, Daily Receipt Report for each category shall be printed. Each entry shall
be verified against the respective document again. Adjustment entries should be passed in case
of errors in recording the receipts in the computer. A password system for authority to pass on
adjustment entry will be provided. Only In-charge stores can pass an adjustment entry. The
purpose is to ensure that there are no errors in receipt record and that it is correct. Hard copy of
these daily print outs shall be bound & kept as "Receipt Registers".
The system provides various reports based on "receipt of materials"
o Materials Received On Cash Purchase Basis
o Material Received From Contractors
o Material Received Form Client
o Material Received From HCC Branches
o Material Returned Back by Site (Works Return)
o Material Returned by Employees (Tools)
o Receipts Of Explosives
o Receipt History of Item(s)
o Receipt History of Vendor, Contractor, Client, Branch - Item wise
o Receipt History of Vendor, Contractor, Client, Branch - Date wise
Receipt report for major items such as steel, cement etc. may be sent to Procurement
Department weekly. Other reports may be furnished to Head Office as & when needed.
1.2.1.2 Inspection
The inspection authorities shall be informed for necessary inspection for all material by Inward
Section. The inspection authorities shall endorse the quality inspection remarks on the MRN or
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 10
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
in the Challan copy or by a separate Inspection report. The In-charge (Stores) shall inform these
details to Vendors, Customer (Client), Corporate Office, Subcontractors etc. as the case may be.
Inspection must be completed within seven days of receipt of the material.
MATERIAL INSPECTING AUTHORITIES
MATERIALS INSPECTING AUTHORITIES
Plant & Machinery spares & related Project mechanical engineer or any person authorized by him
Electrical
materials materials Project electrical engineer or any person authorized by him
General stores materials In-charge (Quality Assurance and Control) or any person
authorized by him
Building material & Construction In-charge (Quality Assurance and Control) or any person
chemicals authorized by him
Accepted Material:
The inspected and accepted material shall be handed over to the Main Store duly acknowledged
on Challan by person In-charge of stores for storage and preservation purpose. These shall be
tagged by Material Tag having Yellow colour for accepted material.
Rejected Material
All rejected Materials shall be kept separately duly identified by Material Tag -Red Colour. For
rejected materials Rejection Challan shall be prepared while returning them to Vendors,
Customer (Client), Subcontractors, Sending Branch as the case may be.
Treatment To Rejected Material:
Materials found defective at inspection stage shall be returned to the suppliers against Rejection
Challan. However, if any stock-material is found to be defective later on, issue entry shall be
made to take the qty out from the stock and then material shall be returned to the vendor
against Rejection Challan.
If the material is found to be defective after it is issued then a Rejection slip should be prepared
by the returning department. The Stores should account for the return on the basis of the
Rejection slip.
1.2.1.3 Weighment
The weighment will be verified by stores personnel through computer aided weighbridge. He
may be rotated every fortnight or as may be decided by the In-charge Stores. The name of the
Stores personnel supervising the weighment will be mentioned on the Material Receipt Note
(MRN) / Weightment slip. Weigh Bridge shall be calibrated once in a year, record shall be
available both in mechanical Section as well as in Stores.
1.2.1.4 Sending the Materials Out Of Site
Any item (materials, equipments, plant machinery etc) going out of HCC site shall be
accompanied by a Delivery Challan issued by stores, which will be generated from computer.
Apart from material code, full description, qty, value etc following information shall be clearly
mentioned on the delivery Challan.
Purpose for sending the item out. Eg. : Repairs, rejection, inter-branch transfer etc.
Expected date by which the item is supposed to be returned (if applicable)
In case it is not a sale transaction, it shall be clearly mentioned NOT FOR SALE and value
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 11
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
indicated is inclusive of sales tax, insurance.
Cross reference of relevant work order, disposal order, authority letter for transfer etc.
Gate pass is also needed for security purpose
Separate registers are to be maintained for all issues made from stores and necessary follow up
is to be carried out for materials sent out for repairs, works returns etc. Every dispatch is to be
entered in this register and as and when the materials are received the same is to be entered
and necessary follow-up is to be carried out for unreturned materials. A report is to be prepared
and sent by Stores to Accounts department at Head office through site accounts at the year-end.
1.2.1.5 Issue of Material to Subcontractor
Any subcontractor whom the material will be issued would request Project Manager in writing
mentioning name & Specimen Signature of their authorized representative who will draw the
material from stores. In turn Project Manager will inform stores mentioning the name of the
sub-contractors authorized representative. Section In-charge/ Engineers who are authorized by
Project Manager will give issue indent to stores requesting for issue of material to a particular
subcontractor mentioning free or chargeable basis.
The following cases may arise:
Free basis - As per Work Order
Chargeable basis.
In case of chargeable rate they may be of following two types:
Fixed Rate
System Rate + Service Charges as mentioned in Work Order or as decided by Project
Manager.
Computer system is so designed that it will take care of all options and stock valuation is not
affected. If any material is required to be issued to the sub-contractor directly from the site, then
appropriate work-return entry shall be made and then only issue shall be shown so as to have
complete record of issues in the computer system. Separate issue registers shall be generated from
computer for materials issued to Contractors. Sub-contractors shall be asked to certify the materials
drawn by them from stores on monthly basis. This shall be tallied with the issue record and
differences, if any, shall be settled forthwith.
1.2.1.6 Inter-branch transfer of material
Branch Transfer of any material can be made as per request of receiving branch. In case of
construction asset, approval from construction asset In-charge from H.O. has o be obtained. For
equipment & spares, clearance from equipment division at Head office has to be obtained. Branch
Transfer Challan may be generated by computer for that particular item.
1.2.1.7 Records to be up-dated while issuing materials
Bin cards
Computer System for issue information (Qty, rate, cost center code etc)
Every branch will have their Computer System installed and hence stocks shall be updated
simultaneously for quantity as well as value.
Issues shall be valued by Weighted Average method by computerized stores accounting system.
At the end of the day, Daily Issue Report shall be printed from the computer separately as per the
type of issue) and after checking the same will be filed separately to generate a Issue Registers.
Tools issued to employees shall be entered in "Personal Tool Register" (PTR). In case of tools
misplaced by employee 100% debit will be made for new one, whereas for broken tools 50% will be
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 12
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
debited on that particular employee.
Separate register shall also be maintained after taking printouts for items issued to sub-contractors.
In case any materials from the inventory are to be scrapped, requisition duly approved by Project
Manager shall be taken. Computer System shall be updated for showing issue for the purpose of
scrap disposal. Separate "Scrap Register" shall be maintained.
The registers shall be bound periodically say monthly/quarterly/half yearly depending upon the
volume of issues.
Issue slips also shall be properly bound and preserved as a record.
While issuing the materials Bin Card balance (and also the balance shown by the computer) shall be
verified with physical balance where items are stored in small quantity. In case of variance,
Discrepancy Report shall be made & Bin card as well as computer shall be updated by passing a
suitable adjustment entry.
It is essential that data entry in Computer System is always up-to-date. It is necessary to check
entries pertaining to Daily Receipts & Issues everyday. If any transaction entry is missing, it shall be
made before entering next day's records. If any mistake is found, adjustment entry shall be made
and then alone next day's entry work should be started. This is necessary since Computer System
shall not allow any backdated entries once adjustment is passed. Such corrected report (DRR & DIR)
shall be preserved as MR / MI registers. Separate register is maintained giving details about
adjustment entries made for issues.
The computer system has been provided with facility to do reconciliation of client materials (receipt,
issues, return to client & stock), materials issued to contractors (contractor-wise), Tools issued to
employees (employee-wise), reconciliation of explosives. It is necessary to run these reports
periodically & ensure proper reconciliation to have adequate control over materials.
1.2.2 INDENT OF MATERIAL
• The indent of material are prepared by site engineer, checked Indent of Material
by the team leader and approved by the project in-charge.
• The indent is prepared in a given standard format which is also Register Issue Record
Given to the stores.
Certificate for issue for various
• The store keeper takes up the follow up for the item
registers
intended with the purchase department or the supplier.
Security gate inward/ outward
• The pending indent is filed separately. register
Receipt of Material
Receipt of Steel Receipt of Cement
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 13
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1.2.3 REGISTER ISSUE OF MATERIAL
• This records the details of all issued register.
• This is essential for the verification of the responsible person.
• Whenever any register is issued or returned it is recorded in this register.
• Person who has been issued this register is responsible for maintaining the record and safe
custody of the register.
1.2.4 CERTIFICATE OF ISSUE FOR VARIOUS REGISTERS
• Issuance of letters should be only done through a system to avoid the chances of manipulation of
registers.
• This certificate is essential for the authenticity of the registers.
• For this a certificate is given while issuing each register mentioning the register name, no, page
no, name of person issued, his designation and the date of the issue.
• This certificate id printed or stamped on the first page of the register.
1.2.5 SECURITY GATE – INWARD/OUTWARD REGISTER
• As far as possible only 1 gate entry should be preferred.
• Security register is s standard form maintained at every site.
• The register is maintained by gate keeper.
• All incoming and outgoing materials are recorded in separate registers ie. material inward and
outward register.
1.2.6 RECEIPT OF MATERIAL
• The purchase order should be filed in pending purchase order file.
• When the material is received following actions should be initiated.
• If the material is a building material like sand, grit, kapchi, metal brick the store keeper should
physically measure the quantities.
• The measurement quantity is cross checked on the site by site engineers on regular basis.
• The store keeper in consultation with engineers should know well in advance the location for
loading and unloading of material at specified place only.
• The store keeper issues material receipt slip mentioning all details including actual measurement.
• Only one receipt book should be used for the issuing receipt.
• The material should be stacked to avoid breakage, wastage and pilferage.
1.2.7 RECEIPT OF STEEL
• The steel is unloaded preferably in the steel yard or at a place in consultation with the project in
charge.
• The steel received from client/supplier should be weighed at another weigh bridge other than
specified in the challan.
• The difference in challan weight and the actual weight should invariably be recorded and the
client’s driver’s signature should be obtained.
• Availability of manufacturers test certificate should be recorded and checked in consultation with
the QC engineer.
• Steel receipt document is checked by project in charge regularly.
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 14
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1.2.8 RECEIPT OF CEMENT
• The cement supplied by client /supplier shall be physically verified for quantities, brand type and
batch.
• Visual inspection is carried out in consultation with the QA/QC department whenever required.
• The cement bag weight is verified on sample basis.
• PROCEDURE FOR CONTROL OF MATERIALS
The responsibility matrix for control of materials is as follows:
S.N. Activity Personnel Remarks
1. Estimate material quantities with Planning Engineer
reference to drawings and
specifications
2. Prepare requirement plan Planning Engineer Recording in formats
3. Float enquiries enclosing specifications Purchase Officer/
Purchase Engineer
4. Collect samples, test independently QA/QC Incharge
5. Approve source Client’s Engineers Source approved by
consultants if required
6. Place order, receive materials sample, Purchase Officer/ Stores to stack untested
test Stores Incharge material at locations
designated for the purpose
7. Receive test reports, if within Stores Incharge Material Engineer to inform
specifications, approve for usage stores on standard formats
8. If routine tests not conforming, inform QA/QC Incharge
stores in writing. Segregate this
material
9. Rejected Material to be highlighted in Stores Incharge
front of location by flags and removed
to locations out of bounds for staff or
labour
10. If source fails consistently discard Project Manager
source
11. Qualify another source Planning Engineer
Project Manager
1.3.1 PROCEDURE FOR IDENTIFICATION AND TRACEABILITY
For identification of materials and traceability, the following methods and records are maintained:
IDENTIFICATION TRACEABILITY
Material Description Method Record Responsibility
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 15
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
Cement Board Material Receipt Note/ Stores In Charge
Manufacturers Test Certificate
Structural Steel Board Material Receipt Note/ Stores In Charge
Manufacturers Test Certificate
Re-bars Board Material Receipt Note/ Stores In Charge
Manufacturers Test Certificate
Consumables Board Material Receipt Note Stores In Charge
Pipes, Fittings & Gratings Board Material Receipt Note Stores In Charge
Electrical Items Tag/ case marking Material Receipt Note Stores In Charge
Tools and spares Tag/ case marking Material Receipt Note Stores In Charge
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 16
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1. 3 ISSUE OF MATERIALS
Issue of Material by duly authorized requisitions.
Issue to be accompanied by:
Delivery Challan, Material code and description
Quantity, purpose – repair / rejection / transfer / use
Issue of Material to Site Inter Branch Transfer of Material
Braanch Transfer Challan
Request PM in writing mentioning name and specimen
signature of their authorized representatives.
Section head gives list of authorized representatives
and their attested signatures.
Indents from authorized representatives
Procurement of Material
Daily Receipt goes to section Heads which informs them
regarding the availability
Material Issue Voucher
Material is issued for use. Gate pass is given to take the
material out of the store area.
Updating of bin cards and computer systems for issue
information
Daily Issue Reports
1.3.3 MATERIAL ISSUE VOUCHER (MIV)
Job No: 3555 Date:
Activity:
To stores: Please issue the following material
S.No Material Cost code/ Equip Quantity Remarks
Description UOM
. Code No. code Required Issued
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 17
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
Indented By: _______ Stores In charge: _______ Issued By: _______ Received By: _______
1. 4 PLANNING OF THE MATERIALS
Planning of materials involves identification and estimation of materials. In any project execution, it is
important to identify the type, nature, size and quantum of key and critical materials right at the start of
the project with the data /drawings available. It is important to know the total quantities and phase wise
requirement of critical materials likely to affect the progress of work so that the planning for
procurement of the same can be done in a systematic manner.
Planning involves forecasting the materials that would be required. This is done by the Planning
Department on site as per the construction schedule prepared. The monthly requirement of
materials was worked out at the beginning of the project.
According to the lead time of various materials it is forecasted when a material should be
ordered so that the construction process is not hampered.
The planning would include preparation of schedules indicating approximately the total quantity
of all essential materials such as aggregates, bricks, structural / reinforcement steel, formwork
materials, timber, roofing sheets etc. to be procured. The schedule can thus:
o Ensure availability of these items as per requirement to suit construction programmed.
o Constantly monitor procurement function such that no item is procured in excess of
requirement and the material cost is within control.
o Ensure sufficient lead-time for procurement of materials at best possible prices / terms
and avoid emergency purchases.
o Give sufficient time to arrange for inputs from sites / region / HQ offices for items like
structural steel, scaffolding and shuttering materials etc.
The procedure for preparation of the schedule is as follows:
Compute material requirements month wise for each item as per breakup of the quantities
Sum up requirement of the same material under different items of work under individual
material heads and finalize the schedule, taking to consideration the lead-time and stock level.
Factors like monsoon, price escalation, union budget etc. must be kept in view.
Prepare a separate list for the following items:
o Diameter wise requirement of reinforcement steel.
o Section wise requirement of structural steel.
o Section wise requirement of timber & plywood.
o Item wise / system wise requirement of formwork required for scaffolding and
shuttering purpose.
o Materials required as erection aids.
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 18
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1.4.1 STEPS FOR PREPARATION OF SCHEDULE
Preparation of Schedule Ensure availability of items
Constant Monitor Procure Function
Ensuring sufficient lead time
Sufficient time to arrange for input from offices
Preparation of
separate list for special Requirements for reinforcing steel
items
Requirements for structural steel
Requirements for timber and plywood
Requirements for erection aids
• For materials required in enabling works like formwork for concrete, erection of structural steel,
precast concrete items, work out construction methods first, compute quantities and place order /
requisition for the same.
• Material requirements will include provision for wastage, allowance for under weighment in
cement, rolling margin in reinforcement and structural steel.
1. 5 VENDOR MANAGEMENT
1.5.1 PROCEDURE
There is a detailed procedure prescribed by the Company for vendor management. This states that the
Purchasing authority shall strive to maintain the quality supplies from reliable sources only. To exercise
control over sources of Purchase, the purchasing authority shall follow the Procedure as below:
Preliminary work for vendor registration
Assessment of Vendors and their registration and selection
Performance evaluation of registered Vendors
Initiate action in case of unsatisfactory performance
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 19
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1.5.2 GUIDELINES FOR SELECTION OF VENDOR
Vendor is already registered agency in other unit of Afcons where ISO programme has been
implemented.
Vendor is a manufacturer of the commodity himself.
Vendor is an authorized Agent / Distributor / Stockist / Dealer of manufacture.
Vendor is a monopoly supplier.
Vendor is registered
Based on the site assessment i.e. assessment of his manufacturing facilities.
Based on client’s list and reputation enjoyed in the industry.
Based on evaluation of supplies made.
Supplier is an approved vendor of the client.
Any other valid reasons.
Nearness of vendor’s place of business to the branches of the company.
Credit period allowed by the vendor as compared to the industry norms.
1.5.3 VENDOR REGISTRATION
The site follows the Vendor Registration Procedure as given in ISO 9001.
The Site should follow the preliminary work for vendor registration, assessment and evaluation for
all items where the annual purchase value is likely to be over Rs 1,00,000 or as informed by Head
office.
For items below Rs 1,00,000 the system should give details of variation in rates of purchase as
compared to the last purchase.
1.5.3.1 Preliminary Work:
Vendor registration form shall be issued by the Purchase Department at Site to the vendors seeking
registration with the company.
Vendors are expected to submit the forms duly filled, signed and stamped back to the issuing
authority within 30 days from the date of collection of the registration form.
1.5.3.2 Assessment for Vendor Registration:
The Procurement Manager and Project Manager at the site shall assess the vendors capabilities for
registration based on the information available with the procurement department at site in any of
the following forms:
Profile of the Supplier
Catalogue / Literature of the supplier
Information from the internet, E-mail, Yellow Pages, Business Magazines, Newspapers,
Seminars.
Workshops, Trainings, Technical Exhibitions, JV consortium Partner, clients or competitors.
Standard Registration Form
Suppliers suggested by any of the AFCONS sites or by experienced senior level personnel
through e-mail, IOM or free style note.
Order executed successfully by unregistered suppliers under urgent situation.
Preliminary assessment of any Vendor's capability shall be recorded in the prescribed format within
15 days from the date of submission of the registration form.
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 20
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
Based on the recommendations of the Vendor Assessment, the vendor's registration status shall be
identified in Approved Vendors List (AVL) as follows:
For vendors chosen by the client: Status - by Client (CL)
For new vendors to whom the trial order is not placed or the trial order is placed but the
confirmation about the acceptance of quality of material supplied by them is not yet received.
Status - Waiting (W)
For registered vendors: Status - Confirmed (C)
For disqualified Vendors: Status - Cancelled (CN)
The status mentioned above shall be updated as and when need arises.
After registration, result shall be conveyed to the awarded vendor by a letter duly signed by the
Project Manager.
1.5.4 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF VENDORS
All the Vendors shall undergo performance evaluation at least once in six months, but as a routine site
will send an evaluation on monthly basis. Each consignment from each Vendor shall be evaluated on the
basis of Quality, Delivery Schedule and price as per the norms given in Data Sheet.
For the purpose of performance evaluation of the vendor, following data should be included for each
vendor:
Total quantity ordered and details of Acceptance/ Rejections against the order / quantity.
Total quantity ordered and details of quantity, which was delivered later
than the scheduled time.
Average period taken to replace Rejections. Delays in replacement of rejections should be specified.
Average period taken to provide After Sales Service. Delays in providing After Sales Service should be
specified.
These Reports should be prepared and sent to the procurement department (Head Office) by the
Stores-in- charge on monthly basis.
For performance evaluation, quality and delivery of each lot shall be compared with corresponding
purchase order. Vendor's Performance Evaluation shall be based on monthly evaluation from stores at
site, mentioning receipt details, i.e. quantity of accepted materials and actual delivery at site.
1.5.5 EVALUATION CRITERIA AND TECHNIQUE
The evaluation Technique followed is the Weighted Point Method. Depending upon the needs of the
parent unit, four evaluation factors are identified. Their relative weights can be expressed in numerical
terms so that a composite performance index can be determined and supplier can be compared.
1.5.5.1 Evaluation Criteria
Quality 70
Delivery 30
Price 20
Service, Cooperation and others 30
Total 150
The detailed breakup of the evaluation criteria is as follows:
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 21
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
Sr. No. Factors for Assessment Weightage Method of Award
1. Quality 70 Total Quality Accepted during evaluation period x 70
2. Delivery Schedule 30 Quality supplied on schedule x 30
Total Quality scheduled during evaluation period
3. Price 20 Lowest Tender price x 20
4. Prompt replacement of 10 Qualitative Factors of Assessment
Rejections
5. Prompt after Sales Services 10 Qualitative Factors of Assessment
6. Co-operation from Vendors 10 Qualitative Factors of Assessment
1.5.5.2 Minimum Marks to be scored for passing
Sr. No. Criteria Minimum Marks
1. Quality alone 50
2. Delivery alone 10
3. Price alone 10
4. Prompt replacement of rejections 5
5. Prompt after sales services 5
6. Co-operation from vendors 5
Aggregate 85
1.5.5.3 Composite Rating Schedule
Vendor Total % Quality On Delivery Service Service
shipment accepted Rating schedule rating Rating
recd.
A 100 90 64 80 16 Fair 21
B 60 80 48 90 18 Poor 12
C 50 70 42 100 20 Good 30
Vendor Average price / unit Lowest price / actual price Price Rating Total Rating
A Rs. 40 40/40 = 100 20 121
B Rs. 50 40/50 = 80 16 94
C Rs. 60 40/60 = 67 14 106
Thus, Vendor A would be selected
1.5.6 VENDOR GRADING
Vendor Grading should be done and on the basis of the grade points given to the respective vendors
they should be classified as follows:
Grade Points Classification
125-150 Excellent
80-125 Good
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 22
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
55-80 Satisfactory
00-55 Un-satisfactory
Thus, Vendor A would be graded as Good
1.5.7 VENDOR EVALUATION PROCESS AT A GLANCE
Pre- qualification & Evaluation of Vendors & Contractors
Project Manager
Obtain company profiles of Vendors/Contractors
Engineer
Evaluate Capacity & Capability of Vendors/ Contractors
QA/QC
F&A Pre-qualify Vendor/Contractor
Maintain Databank Category – wise/ Discipline wise/ Size wise
Evaluate the existing Databank periodically at six months intervals
Revise/ Update Databank
1.5.8 DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FROM NEW VENDOR
A new Vendor is required to submit the following details:
Certificates for ISO Certification
Certificate for ISI Certification
Details like sales tax registration, excise registration, income tax registration are mandatory.
Manufacturers, Indian agents, Indian representatives of Foreign principals for machinery/
Computers and peripherals/ Office automation equipment must give full details of
service facility available in India. The availability of spares / trained service personnel/
warranty terms etc. must also be mentioned.
All vendors should attach relevant certificates, order copies, proof of registration with major
customers etc. along with the application. Manufacturers / Authorized dealers/ Indian
agents of Foreign Principals must attach relevant catalogues/ technical literature for the
Products listed.
Any change of in the status above mentioned information should be communicated within one
week. This information is required for updating the vendor database
Filled in applications with enclosures should be sent to the “The Purchase Dept AFCONS ECC
Construction Company Limited.
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 23
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1.5.9 PARAMETERS OF VENDOR EVALUATION
1. Building and General Impression of Good Maintenance
a. Check floor space available against that stated in Same/Different
questionnaire form
b. What material handling equipment is used? Crane/ Hoist/ Fork – lift/ Other
c. Level of Housekeeping, cleanliness and maintenance Poor/ Good/ Very Good
order
d. Age of the plant 5 to 10/15/more old/ modernized/ new and modernized
e. Is care and maintenance of plant a planned programme? Yes/ No
f. Does the presence of clever methods and set ups show Yes/ No
adaptability in the type of working being done?
g. Is there space for expansion? Yes/ No
2. Production and Technical Competence
a. Check list of machines attached to the questionnaire Same/ Different (Why?)
form
b. No. of technically qualified engineers/ Staff and level of E.E/ M.E/ I.E/ Other
qualification
c. No. of Skilled workers and type of training i.e. trade
apprenticeship, etc.
d. Can design assistance be given by the vendor? Yes/ No
e. Is any basic research being done? Yes/ No
f. What other work is in progress? Yes/ No
g. General level of precision and finish of work in progress Poor/ Good/ Very good
compared to what his machines can achieve
h. Is any production planning method used? Yes/ No
i. Are job orders followed up? Yes/ No
j. Are there regular contracts for raw materials? Yes/ No
k. Limitations of work due to this size or capacity of the Yes/ No
tools and machine?
3. Quality control and Inspection of Facilities
a. Is there a regular quality control dept/ section? Yes/ No
b. Are gauges and instruments used for quality control and Yes/ No
inspection?
c. Are gauges and instruments calibrated and corrected Yes/ No
d. Are gauges bought or borrowed Bought/ borrowed
e. Are SQC methods used? If so what is the sampling plan Yes/ No
f. Are records kept of the results of instrument checks and Yes/ No
production inspection?
g. Is incoming materials inspected and evaluated? Yes/ No
h. To whom does the head of QC report? Yes/ No
i. No. of people full – time on inspection Trained/ Untrained
j. What is present per cent rejection (5/5-10) 10 years
4. Financial Resources
a. What is the approximate value of work in progress? Rs
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 24
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
b. What is the approximate value of raw materials and Rs
finished goods?
c. Has vendor any raw materials license or allocation? If so Yes/ No
how much of which material(s) and from which source?
d. What is the approximate annual turnover of sales? Rs
e. What were last year’s approximate profits (gross)? Yes/ No
f. Does he have any future plans for expansion/ Yes/ No
diversification?
g. Names of associate companies Yes/ No
5. Other Companies Supplied to
a. Check names mentioned in the questionnaire from Same/ Different
b. What work was done for these companies?
c. How long has vendor been supplying to these
companies?
d. Does vendor do entire job or does he further sub Entire job/ further sub contract
contract?
e. IS so, list names of parties work sub contracted to:
f. Timing performance of delivery of a few typical cases Poor/ Good/ Very good
g. Quantity performance of delivery of a few typical cases Poor/ Good/ Very good
h. Obtain reference from other companies if large order is
to be given
6. General Observations
a. How would you rate the morale of the total Poor/ High/ Very high
organization?
b. How would you rate the progressiveness and Poor/ Good/ Very good
competence of vendor’s management?
7. Conclusion
Should this vendor be added to our list of approved Yes/ No
suppliers?
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 25
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1. 6 MATERIAL CODIFICATION
1.6.1 INTRODUCTION
Since the number of items of stores run into large numbers, a proper method of identifying them,
using a common language is a must. Codification is a process representing each item by number. The
digit will indicate group, sub-group, type and dimension of the item.
Purpose served by codification
Proper identification Accounting and control
There are number of methods of building of coding system, but method should be:
o Simple
o Capable of being understood by all
o Each code should uniquely represent one item
1.6.2 REQUIREMENT FOR CODIFICATION
A stock code to group and identify items with similar physical characteristics in a logical pattern
permits simple and precise material identification as an aid to production, stores, purchasing and
accounting. This stock code should be kept as short as possible, starting with a class designation for
like items keyed to major commodity group, e.g. electrical hardware, fastener, pipe fittings,
sanitorial supplies and so on. First two digits will be sufficient for this purpose, followed by a single
digit to denote subclass. The codification of materials in such a way helps in quick identification of
the material. In fact elaborate coding will provide the information regarding details descriptions of
the materials very easily. This helps in reducing waste of time.
1.6.3 OBJECTIVES OF CODIFICATION
In order to identify the items correctly and logically for processing the transactions and to facilitate
each location in stores, a codification system should be evolved with the following objectives:
• Accurate and Logical Identification: A separate code is allotted to each of the items available
in the storehouse indicating the size, quality, price, usability, special characteristics,
specification etc.
• Prevention of Duplication: All items are separately codified and are arranged in a logical
order. Since each item has a different code number and various items are kept in different
bins at different places, there can be no duplication in placing the orders and no piling up of
the materials will take place in the storehouse.
• Standardization and Reduction in Varieties: For codification, grouping of identical items is
done and it enables the stores to examine the entire range of items. It facilitates the
elimination of those varieties in place of which other varieties of the like quality can be used,
this reduces the number of varieties to the minimum.
• Efficient Purchasing: The filling up of purchase requisition and preparation of purchase orders
are simplified by the use of codes, which easily indicate the materials required. Buying
instructions to the suppliers become easy and quick if there is proper understanding of
codification by the supplier.
• Efficient Recording and Accounting: Codes lead to effective stock control, efficient recording
and result-yielding accounting. Chances of mistakes are minimized.
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 26
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
• Easy Locating, Indexing and Inspection: The materials in the store have to be kept in an order,
which may facilitate their placement and location.
• Easy Computerization: Small size computers such as personal computers are finding their
wide applications in materials management.
1.6.4 CODIFICATION - FEATURES
There could be many possible arrangements of coding symbols (numbers, alphabets, etc.), which can
be used to design a code. The following considerations must be kept in mind when designing codes.
i. Brevity: The codification system should avoid long and unwieldy description. This implies that the
codes should consist minimum possible number of digits.
ii. Logical: The coding system should be logically fit for the needs of the users and the methods of
data processing employed.
iii. Flexibility: The code design should be flexible to accommodate changes without disturbing
existing codes. We are familiar with the library coding system in which codes do never get
disturbed by addition of new books and all books to come in future are easily accommodated by
the existing code structure.
iv. Uniqueness: Each code must be a unique representation for the item it identifies. For example, an
inventory item number or employee identification code must identify one and only one inventory
item or employee.
v. Easy Understandability: The code structure must be easily understood by various users. It should
be as simple, practical and meaningful as possible.
vi. Proper Choice of the Coding Symbols: While a code may have numbers, alphabets or a mixture of
both, certain precautions should be taken in selection of the symbols.
vii. Layout of codes: The layout of codes should be equal in length. Codes longer than four alphabetic
or five numeric characters should be divided into smaller segments for human judgments.
1.6.5 REQUIREMENTS OF MATERIAL CODIFICATION
Material Codification it is required for the following reasons:
For Proper Identification Of Item By All Departments
To Avoid Use Of Long Description Of Item
To Avoid Duplicate Stocks Under Different Description
To Enable Reduction In Varieties And Sizes
To Arrange Bin Cards, Stock Control Cards, and A/C Records Etc. In Uniform Manner
To Ensure Receipt & Issue Document Are Posted In Appropriate Records
1.6.6 METHODS OF CODIFICATION
Codification of materials
Alpha-Numerical Numerical Colour codification
1.6.7 MATERIAL CODE STRUCTURE
Head Office (Mumbai)’s material code is a 9-digit all numeral one.
Item is identified in first four digits and the rest five digits are for specific identification.
o 1st Digit specifies the class,
o 2nd Digit specifies major group in that class,
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 27
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
o 3rd & 4th Digits specify minor group within the respective major group.
1.6.7.1 Classification Of Items
Items are classified as follows:
FIRST DIGIT CLASS
0 Capital Items
1 Heavy Tools & Tackles
2 Small Tools
3 Consumables
4 Reserved for Future Use
5 Electrical Main Items
6 Construction Materials
7 Special / One-Time Items
8 Reserved For Future Use
9 Spares (P&M)
1.6.7.2 Class 1: Heavy Tools & Tackles (Nc Items)
Class & Major Group (1st & 2nd Digits) Description
10 & 11 Equipments
12 Electrical Items
15 Form Work (DOKA System)
17 OTHER SYSTEMS (ACROW, APOLLO, EWL, Etc.)
19 Temporary Structure
13, 14, 16 & 18 Reserved For Future Needs
1.6.7.3 Class 2: Small Tools
There is no major group in this “class”.
There is only sequential codification for all type of small tools.
For example – measuring tape, drill bits lab items, etc.
1.6.7.4 Class 3: Consumables
Class & Major Group (1st
Description
& 2nd Digits)
31 Chemical, Etc (Oils, Gases, Paints, Chemicals, Admixtures, Etc. )
32 Electrical Items
33 Pipe Fittings
34 Hardwares (All Metals Included)
35 Welding Electrodes
36 Cutting Tools
37 Abrasives
38 Others (Wire Ropes, Packing Materials, Stationery Etc.)
39 Common Spares (Bearings, Tyres, “V” Belts Etc.)
30 Reserved For Future Needs
1.6.7.5 Class 6: Construction Materials
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 28
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
Class & Major Group (1st & 2nd Digits) Description
61 Major Items (Aggregates, Bricks, Cement Etc.)
62 Ferrous Items
64 Non-Ferrous Items
65 Timber And Plywood
60, 63, 66, 67, 68 & 69 Reserved For Future Needs
1.6.7.6 Codification of Spare Parts
1. 7 MATERIAL RECONCILATION
Reconciliation is the process to identify the unaccountable use of materials during various construction
activities at site. It is the record keeping of the materials at site.
The total quantity, Consumption, Wastage and balance of the material at the site are accounted in the
Reconciliation reports.
It is being prepared for most of the materials- Cement, sand, aggregates, reinforcement etc.
It helps to identify the wastage out of the unaccountable consumption of the material during activities,
transportation, test samples, and poor workmanship etc.
Reconciliation forms are as follows:
1.7.1 RECONCILATION FORM FOR THE MAIN STORE
The main store maintains the following Reconcilation form for all materials to keep stock of the material
quantities issued and available:
MATERIAL IN MATERIAL OUT
Purchased Quantity To Site Store Quantity
From Other Site Quantity To Other Site Quantity
BALANCE QUANTITY = MATERIAL IN - MATERIAL OUT
1.7.2 RECONCILATION FORM FOR THE SUB STORE
The sub store at site maintains Reconcilation forms for all materials in the following format to keep
stock of materials received, materials issued, billed materials, wastage in materials and balance stock.
The reconciliation form is as follows:
Sl. No. Details QUANTITY
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 29
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT PROJECT-2
1. Material received from Main Store 100 T
2. Material Issue 75 T
3. Material Balance 25 T
4. Material Billed 70 T
5. Material Wastage 2.5 T
6. Work in Progress 2.5 T
KUSHAL JAIN | MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 30
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Material ManagementDokument36 SeitenMaterial ManagementDamodharan RathanaveluNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPM FinalDokument49 SeitenPPM FinalTadele DandenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procurement FlowchartDokument3 SeitenProcurement FlowchartAhmed Mustafa AlabadlehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material ManagementDokument20 SeitenMaterial Managementgkataria110100% (1)
- Men - Machines - Methods - Money - MaterialsDokument42 SeitenMen - Machines - Methods - Money - MaterialsAbhirup MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material ManagementDokument175 SeitenMaterial Managementbhaskarjadhav100% (3)
- Procedure For StoresDokument25 SeitenProcedure For StoresSanthosh Kumar Ch100% (5)
- Types of Purchases in A Purchasing ProcessDokument3 SeitenTypes of Purchases in A Purchasing ProcessJonnah Fernandez Dalogdog100% (1)
- Procurement and Materials ManagementDokument44 SeitenProcurement and Materials ManagementAshish JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stock VerificationDokument26 SeitenStock VerificationRishi MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchase Management.Dokument41 SeitenPurchase Management.ajitthomas98100% (1)
- Faculty: Intro: Author S. A. ChunawallaDokument30 SeitenFaculty: Intro: Author S. A. Chunawallaswapnilharal100% (1)
- Warehouse SupervisorDokument2 SeitenWarehouse SupervisorJethro Stanly100% (1)
- Procedure of Material Management SyestemDokument25 SeitenProcedure of Material Management SyestemNitesh Bhura100% (1)
- Material Purchasing ProcedureDokument3 SeitenMaterial Purchasing ProcedureRahul Kumawat100% (2)
- Organization For Materials ManagementDokument60 SeitenOrganization For Materials ManagementNaushad PulikkandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6: Materials ManagementDokument21 SeitenTopic 6: Materials Managementcareermotions50% (2)
- Material Management Presentation (New 1)Dokument73 SeitenMaterial Management Presentation (New 1)Prabhu RavindranNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProcurementDokument99 SeitenProcurementMoiez AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arjun Kumar: Contact: +91-9779503016 E-MailDokument3 SeitenArjun Kumar: Contact: +91-9779503016 E-MailArjun Danoch100% (1)
- Store Purchase RulesDokument90 SeitenStore Purchase Ruleskashyap_873823904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Procurement GlossaryDokument12 SeitenProcurement GlossaryMichael Schmitt100% (2)
- Procedure For ProcurementDokument9 SeitenProcedure For ProcurementTrust EmmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure of Material Procurement and Use (Final)Dokument29 SeitenProcedure of Material Procurement and Use (Final)asadfarooqi4102100% (6)
- Store SopDokument6 SeitenStore SopRAJESH KUMAR100% (1)
- Stocks - Physical Verification Guidance NoteDokument2 SeitenStocks - Physical Verification Guidance NoteJoão Henrique Machado100% (1)
- SC Purchasing and ProcurementDokument22 SeitenSC Purchasing and ProcurementAhmedAbdallahLordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template - Procurement Management ProcessDokument10 SeitenTemplate - Procurement Management ProcessGryswolf100% (1)
- Test Purchasing Procurement QuizletDokument4 SeitenTest Purchasing Procurement Quizletkeith ryan lapizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchase Policy and Procedure by Puruhutjit SurjitDokument2 SeitenPurchase Policy and Procedure by Puruhutjit SurjitSurjit PuruhutjitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Management ManualDokument198 SeitenMaterials Management ManualNaveen Bansal100% (1)
- Purchasing and Material Management PDFDokument60 SeitenPurchasing and Material Management PDFAlfred Allotey PappoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Handling and Material Storage SystemDokument56 SeitenMaterial Handling and Material Storage SystemRishi vardhiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Control For PurchasesDokument2 SeitenInternal Control For PurchasesMuhammad AyubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sourcing Procurement Category Manager in USA Resume Evgeny (Eugene) RomakinDokument1 SeiteSourcing Procurement Category Manager in USA Resume Evgeny (Eugene) RomakinEvgenyEugeneRomakinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchasing, Receipt & Inspection of MaterialDokument11 SeitenPurchasing, Receipt & Inspection of MaterialDr. Rakshit SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchasing ProcessDokument54 SeitenPurchasing Processraks_mechnadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centralized Procurement ProcedureDokument1 SeiteCentralized Procurement ProcedurePugal100% (1)
- How To Audit Warehouse Inventory ChecklistDokument4 SeitenHow To Audit Warehouse Inventory ChecklistClaire Charess AjiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Purchase:: Business Organization Goods ServicesDokument14 SeitenCompany Purchase:: Business Organization Goods ServicesNoman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplier Evaluation MatrixDokument48 SeitenSupplier Evaluation MatrixJohn Moshiro71% (7)
- Kamlesh Kumar Resume of Material ControllerDokument3 SeitenKamlesh Kumar Resume of Material ControllersumeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchase ManagementDokument34 SeitenPurchase Managementshweta_4666475% (8)
- Material Management & ControlDokument146 SeitenMaterial Management & Controlmatrixworld20Noch keine Bewertungen
- SOP Material ManagementDokument7 SeitenSOP Material Managementwasee99Noch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionnaireDokument3 SeitenQuestionnaireabdul rehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchase Manual of Complete ProcurementDokument177 SeitenPurchase Manual of Complete ProcurementKarthik NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchase ManagementDokument38 SeitenPurchase ManagementSiva KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material ManagementDokument24 SeitenMaterial ManagementdeeptiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warehouse ProcedureDokument6 SeitenWarehouse Procedurengmodi100% (4)
- Stores ManagementDokument7 SeitenStores ManagementVinay SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Civil & Structure - Rev - 01Dokument24 Seiten02 Civil & Structure - Rev - 01Yasir MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Main Criterion: 1.price 2.quality 3.deliveryDokument9 SeitenStandard Main Criterion: 1.price 2.quality 3.deliverybunny_ankur77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Management - Class NotesDokument76 SeitenMaterials Management - Class NotesKarthick Sivaraman84% (31)
- Expediting of Equipment and MaterialsDokument1 SeiteExpediting of Equipment and Materialsrylar999Noch keine Bewertungen
- SOPDokument17 SeitenSOPJinal K Shah0% (1)
- Purchasing ProcedureDokument3 SeitenPurchasing ProcedureMark Roger Huberit IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Purchasing ProcedureDokument7 SeitenSample Purchasing ProcedureJemuel GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qms-Pro-Pur - Purchase SopDokument8 SeitenQms-Pro-Pur - Purchase SopRajkumar Prajapati100% (2)
- Lesson 4 - Materials ManagementDokument39 SeitenLesson 4 - Materials ManagementJacques OsmeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Bridge Evaluation: A Global Nondestructiv Approach Using Impact Generated FrfsDokument7 SeitenTimber Bridge Evaluation: A Global Nondestructiv Approach Using Impact Generated FrfsmaulikpanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darcy's Law & FlowDokument19 SeitenDarcy's Law & FlowmaulikpanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genting Highlands قنتنيق تاعفترم .: ... city of entertainment in Asia..Dokument33 SeitenGenting Highlands قنتنيق تاعفترم .: ... city of entertainment in Asia..maulikpanchal100% (1)
- Purpose of ValuationDokument21 SeitenPurpose of ValuationmaulikpanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helena Monolouge From A Midsummer Night's DreamDokument2 SeitenHelena Monolouge From A Midsummer Night's DreamKayla Grimm100% (1)
- Reviewer For Fundamentals of Accounting and Business ManagementDokument4 SeitenReviewer For Fundamentals of Accounting and Business ManagementAngelo PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Agency and Credit Transactions 1Dokument144 SeitenSales Agency and Credit Transactions 1Shaneen AdorableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sitras RSC: FeaturesDokument4 SeitenSitras RSC: FeaturesAnonymous m1cSnEavoNoch keine Bewertungen
- X7 User Manual With ConnectionDokument15 SeitenX7 User Manual With Connectionanup nathNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Defense of The Faith Cornelius Van TilDokument8 SeitenThe Defense of The Faith Cornelius Van TilEmanuel Gutiérrez100% (1)
- CresumeDokument2 SeitenCresumeapi-315133081Noch keine Bewertungen
- TFC On Double LineDokument9 SeitenTFC On Double LineSoumen BhattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Dyer CaseDokument3 SeitenGeneral Dyer CasetimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Villaber Vs ComelecDokument13 SeitenVillaber Vs ComelecJAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epartment of Hemical Ngineering: Muhammad Nawaz Sharif University of Engineering & Technology, Multan, PakistanDokument3 SeitenEpartment of Hemical Ngineering: Muhammad Nawaz Sharif University of Engineering & Technology, Multan, PakistanMina ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSME - Pratham Heat TreatmentDokument2 SeitenMSME - Pratham Heat TreatmentprathamheattreatmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Macabre Motifs in MacbethDokument4 SeitenThe Macabre Motifs in MacbethJIA QIAONoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Motion To Strike For Unlawful Detainer (Eviction) in CaliforniaDokument5 SeitenSample Motion To Strike For Unlawful Detainer (Eviction) in CaliforniaStan Burman91% (11)
- Bases Conversion and Development Authority vs. Commission On Audit G.R. No. 178160, 26 February 2009 FactsDokument1 SeiteBases Conversion and Development Authority vs. Commission On Audit G.R. No. 178160, 26 February 2009 Factsaudrich carlo agustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Loved Aussie Poems Ballads SongsDokument36 SeitenBest Loved Aussie Poems Ballads SongsMartina BernieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Significance of The StudyDokument8 SeitenThesis Significance of The Studyafcnenabv100% (2)
- Deped Format of A Project Proposal For Innovation in SchoolsDokument6 SeitenDeped Format of A Project Proposal For Innovation in SchoolsDan Joven BriñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions Internal TradeDokument4 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions Internal TradeAryan Dev SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sport in The Eastern Sudan - 1912Dokument308 SeitenSport in The Eastern Sudan - 1912nevada desert ratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complaint Affidavit Rape CaseDokument3 SeitenComplaint Affidavit Rape CaseMa Krissa Ellaine Bundang100% (1)
- Account StatementDokument12 SeitenAccount StatementNarendra PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting Harrison 10th Edition Test BankDokument24 SeitenFinancial Accounting Harrison 10th Edition Test BankNicoleHallrktc100% (46)
- EssayDokument6 SeitenEssaylinhJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anglais L3 FinanceDokument10 SeitenAnglais L3 FinanceRomaric YapoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEST 8th Grade (Had Better+needn't)Dokument2 SeitenTEST 8th Grade (Had Better+needn't)anacincaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS Sample Speaking Test 2: Lesson 4Dokument4 SeitenIELTS Sample Speaking Test 2: Lesson 4nọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument26 SeitenPDFAjay Kumar GantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEIL Engineers Annexure ADokument2 SeitenCEIL Engineers Annexure AZeeshan PathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boston TV EEO Public File Report 2022-2023Dokument4 SeitenBoston TV EEO Public File Report 2022-2023Boston 25 DeskNoch keine Bewertungen