Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fatigue Cracking
Hochgeladen von
mohsen_2670 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
14 Ansichten1 Seitefatigue cracking
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenfatigue cracking
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
14 Ansichten1 SeiteFatigue Cracking
Hochgeladen von
mohsen_267fatigue cracking
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
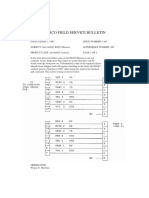
fatigue cracking
Although cracking can be caused by reduction of section
from corrosion, most cracking is caused by fatigue.
Fatigue is the process of the formation and propagation of
a crack caused by repeated or fluctuating loading. The
stresses caused by the repeated or fluctuating loading are
additive to the existing stresses which may be residual.
Ail welding processes result in high tensile residual
stresses in the weld and in the base metal adjacent to it.
These stresses are caused by the shrink of the weld as it
cools. They may approach the yield point. Any
discontinuity in the weld is also located in this region of
high residual stress. The stress rise caused by
discontinuity is added to the residual stress caused by
weakling. Most fatigue cracking in welded structures
initiates at or in the weld. The cracks start at an initial
discontinuity in the weld or at the edge of the weld and
grow perpendicular to the cyclic stresses. Attachments to
girders such as cover plates, stiffeners or other
components welded to a flange or web introduce a
transverse weld perpendicular to the live load stress thus
causing a local stress concentration. This can result in
fatigue cracking which starts at the small but sharp
discontinuities at the weld toe.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Material Datasheet Cu-OFDokument2 SeitenMaterial Datasheet Cu-OFmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Longines Technical Information PVD enDokument1 SeiteLongines Technical Information PVD enmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Choose A Right EDM Machine - Pro..Dokument3 SeitenHow To Choose A Right EDM Machine - Pro..mohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- 316 MaterialDokument1 Seite316 Materialmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma Prof 80Dokument31 SeitenPlasma Prof 80mohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radial Drilling Machine Invema KT 65Dokument2 SeitenRadial Drilling Machine Invema KT 65mohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- API-653 Now Permits Lap-Welded Patch Plates For Shell Repairs - Carmagen EngineeringDokument2 SeitenAPI-653 Now Permits Lap-Welded Patch Plates For Shell Repairs - Carmagen Engineeringmohsen_267100% (1)
- C12200 PD Copper - Austral Wright Metals - AustraliaDokument3 SeitenC12200 PD Copper - Austral Wright Metals - Australiamohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metric DIN 2093 SpecDokument5 SeitenMetric DIN 2093 Specmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 RacePacingDokument2 Seiten2 RacePacingmohsen_267100% (1)
- Design - Hyperbaric FacilitiesDokument7 SeitenDesign - Hyperbaric Facilitiesmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Nitric Acid in The Presence of Hydrofluoric AcidDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of Nitric Acid in The Presence of Hydrofluoric Acidmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stitch Welding vs. Seam Welding - Vista Industrial Products, IncDokument5 SeitenStitch Welding vs. Seam Welding - Vista Industrial Products, Incmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- C 45Dokument10 SeitenC 45mohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Composition and Physical Properties of AlloysDokument22 SeitenComposition and Physical Properties of Alloysmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 2768-Mk - Solidworks ForumsDokument3 SeitenIso 2768-Mk - Solidworks Forumsmohsen_267100% (1)
- S 960 QDokument2 SeitenS 960 Qmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison Chart - CASIO WEW Worldwide Education WebsiteDokument2 SeitenComparison Chart - CASIO WEW Worldwide Education Websitemohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitive SensingDokument5 SeitenCapacitive Sensingmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- SODECA. Manufacturer of Fans and Industrial ExtractorsDokument3 SeitenSODECA. Manufacturer of Fans and Industrial Extractorsmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- American Welding Society Forum Topic Welding Industry / General Welding Discussion / Plug Weld by MJF Date 10-26-2005 14:58Dokument1 SeiteAmerican Welding Society Forum Topic Welding Industry / General Welding Discussion / Plug Weld by MJF Date 10-26-2005 14:58mohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plug Weld Hole Size - Tekla User AssistanceDokument1 SeitePlug Weld Hole Size - Tekla User Assistancemohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hurco Connection 1987Dokument1 SeiteHurco Connection 1987mohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amrhein AA T 2015Dokument78 SeitenAmrhein AA T 2015mohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- WheelDokument3 SeitenWheelmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Master Backstroke: in This SectionDokument2 SeitenMaster Backstroke: in This Sectionmohsen_267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)