Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Alopecia: Dermatosis: Erythema: Hirsutism: Hyperpigmentation: Hypopigmentation: Keratin: Langerhans Cells
Hochgeladen von
Prince K. Tailey0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
22 Ansichten2 SeitenMedical Surgical Chapter 60
Originaltitel
Ch 60 Med Surg
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMedical Surgical Chapter 60
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
22 Ansichten2 SeitenAlopecia: Dermatosis: Erythema: Hirsutism: Hyperpigmentation: Hypopigmentation: Keratin: Langerhans Cells
Hochgeladen von
Prince K. TaileyMedical Surgical Chapter 60
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
MED SURG Chapter 60 Glossary
alopecia: loss of hair from any cause
dermatosis: any abnormal skin condition
erythema: redness of the skin caused by congestion of the capillaries
hirsutism: the condition of having excessive hair growth
hyperpigmentation: increase in the melanin of the skin, resulting in an
increase in pigmentation
hypopigmentation: decrease in the melanin of the skin, resulting in a loss of
pigmentation
keratin: an insoluble, fibrous protein that forms the outer layer of skin
Langerhans cells: dendritic clear cells in the epidermis that carry surface
receptors for immunoglobulin and complement and that are active
participants in delayed hypersensitivity of the skin
melanin: the substance responsible for coloration of the skin
melanocytes: cells of the skin that produce melanin
Merkel cells: cells of the epidermis that play a role in transmission of
sensory messages
petechiae: pinpoint red spots that appear on the skin as a result of blood
leakage into the skin
rete ridges: undulations and furrows that appear at the dermis–epidermis
junction and are responsible for cementing together the two layers
sebaceous glands: glands that exist within the epidermis and secrete sebum
to keep the skin soft and pliable
sebum: fatty secretion of the sebaceous glands
telangiectasias: red marks on the skin caused by distention of the superficial
blood vessels
vitiligo: a localized or widespread condition characterized by destruction of
the melanocytes in circumscribed areas of the skin, resulting in white
patches
Wood’s light: ultraviolet light used for diagnosing skin conditions
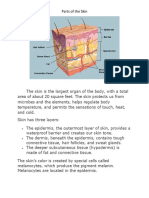
Skin disorders are encountered frequently in nursing practice. Skin-related
disorders are common causes for ambulatory patient visits in the United
States. Because the skin mirrors the general condition of the patient, many
systemic conditions may be accompanied by dermatologic manifestations.
Any patient who is hospitalized may suddenly develop itching and a rash
from the treatment regimen. The psychological stress of illness or various
personal and family problems may be exhibited outwardly as dermatologic
problems. In certain systemic conditions, such as hepatitis and some
cancers, dermatologic manifestations may be the first sign of the disorder
and the main reason a patient seeks health care.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Von EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Complete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisVon EverandComplete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductionDokument58 SeitenIntroductionv_vijayakanth7656Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatology 1Dokument47 SeitenDermatology 1Edwin OkonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Form and FunctionDokument2 SeitenAnimal Form and FunctionAbdus samiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Manifestations of Metabolic DisordersDokument22 SeitenSkin Manifestations of Metabolic DisordersGiovanni AnggastaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 54 IntegumentaryDokument5 SeitenChapter 54 IntegumentaryRebeccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of The SkinDokument5 SeitenParts of The SkinJudith M AleriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Function of The SkinDokument9 SeitenAnatomy & Function of The Skinعبدالعزيز احمد علي عتشNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lichen Simplex ChronicusDokument1 SeiteLichen Simplex ChronicusAnonymous Af24L7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of SkinDokument60 SeitenAnatomy of SkinYashdeepMalik100% (3)
- Presentation PhytoDokument57 SeitenPresentation Phytoyasmeenelraouf16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - IntegumentaryDokument63 SeitenChapter 6 - Integumentaryapi-297069611Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary Skin Hair NailsDokument2 SeitenVocabulary Skin Hair NailsdavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System: Functions of SkinDokument7 SeitenIntegumentary System: Functions of SkinSoniyaJI84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System: Chapter OutlineDokument7 SeitenIntegumentary System: Chapter OutlineRiy KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The SkinDokument28 SeitenAnatomy of The Skinay254Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6 IntegumentDokument43 Seiten6 Integumentgabbs_123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System: Skin and Accessory Structures Hair NailsDokument117 SeitenIntegumentary System: Skin and Accessory Structures Hair NailsSunita RaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sistem IntegumentariDokument42 SeitenSistem IntegumentariVani Taah GNoch keine Bewertungen
- GLOSSARY - Integumentary System - MQCDokument10 SeitenGLOSSARY - Integumentary System - MQCPilar SNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accessory Structures of The Skin: The Skin - Glands, HairDokument4 SeitenAccessory Structures of The Skin: The Skin - Glands, HairGabriel FrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manifestasi Kulit DAN HipotiroidDokument26 SeitenManifestasi Kulit DAN HipotiroidAa SsNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Hargeisa Facualt of Applied ScienceDokument5 SeitenUniversity of Hargeisa Facualt of Applied ScienceAwdahir JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of SkinDokument2 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of SkinMohammed RafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To Terminology SectionDokument1 SeiteAnswers To Terminology Sectionapi-263755297Noch keine Bewertungen
- Permasalahan Kulit Pada UsilaDokument31 SeitenPermasalahan Kulit Pada UsilaetylienNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9-Patologi Skin PDFDokument34 Seiten9-Patologi Skin PDFririnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch25 SkinDokument124 SeitenCh25 SkinMorozovschi VitalieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asuhan Keperawatan Gangguan Sistem Integumentum Pada LansiaDokument50 SeitenAsuhan Keperawatan Gangguan Sistem Integumentum Pada LansiadwiinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBRC DermatologyDokument83 SeitenSBRC DermatologyErin HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q3 - Perform Facial TreatmentDokument19 SeitenQ3 - Perform Facial TreatmentAzucenas, Mycha Blace V.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatology NotesDokument59 SeitenDermatology NotesAbdullah Matar Badran50% (2)
- Kuliah Sindrom Rabu 19112008.Dokument65 SeitenKuliah Sindrom Rabu 19112008.Nurdiana RahmadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument21 SeitenIntegumentary SystemErnie SyarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amyloidosis SkinDokument6 SeitenAmyloidosis SkinGoran MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stephanie Ocampo - DermatologyDokument14 SeitenStephanie Ocampo - DermatologystephocmpoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Tumor AgusDokument54 SeitenSkin Tumor AgusHafida AuliaristaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of Sebaceous GlandDokument54 SeitenDisorders of Sebaceous GlandAnurag PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin, Hair & Nail ChangesDokument66 SeitenSkin, Hair & Nail ChangesUmut YücelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - Toronto Notes 2011 - DermatologyDokument46 Seiten6 - Toronto Notes 2011 - DermatologyqobsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 LabDokument75 SeitenModule 1 Labkrystal ongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Localized Area of Color or Texural Changes in The Skin. Macule May Me HypoDokument4 SeitenLocalized Area of Color or Texural Changes in The Skin. Macule May Me Hypo123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- DMS. K12. DermatopathologyDokument64 SeitenDMS. K12. DermatopathologymissirenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 PowerPointDokument28 SeitenChapter 5 PowerPointHilary OliverioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDokument49 SeitenChapter 5 Integumentary System蔡嘉慧Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Glossary: Integumentary System-Skin and Accessory OrgansDokument24 SeitenMedical Glossary: Integumentary System-Skin and Accessory OrgansFev BanataoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DermaDokument30 SeitenDermalydia_chandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin-PathologyDokument32 SeitenSkin-PathologyArfa BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatology Updated 2020Dokument57 SeitenDermatology Updated 2020ElvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skin As An Organ at CBCDokument45 SeitenThe Skin As An Organ at CBCEmmanuel DanielsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi KuliitDokument40 SeitenAnatomi Dan Fisiologi KuliitZulfani AdhiyatmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prev Next: © 2014 Webmd, Llc. All Rights ReservedDokument5 SeitenPrev Next: © 2014 Webmd, Llc. All Rights ReservedOlfaktorius GoenawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Integumentary SystemDokument5 SeitenThe Integumentary SystemVivi rikkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammatory-Skin-Diseases 231101 174335 (2462)Dokument37 SeitenInflammatory-Skin-Diseases 231101 174335 (2462)Moayad IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin and Body MembranesDokument44 SeitenSkin and Body Membranesquiaballares19Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4integumentary SystemDokument139 Seiten4integumentary SystemMargreth MontejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of SkinDokument33 SeitenHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- SkinDokument116 SeitenSkinhajer hajerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument34 SeitenIntegumentary SystemALAN MAGPANTAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample USAjobs Resume Builder Federal ResumeDokument1 SeiteSample USAjobs Resume Builder Federal ResumePrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomedical Equipment Maintenance Division (Biomed) OperationsDokument32 SeitenBiomedical Equipment Maintenance Division (Biomed) OperationsPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thank You Note TemplateDokument1 SeiteThank You Note TemplatePrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Position WorksheetDokument11 SeitenJob Position WorksheetPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSS Specialized ExperienceDokument2 SeitenHSS Specialized ExperiencePrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering The Federal ResumeDokument1 SeiteMastering The Federal ResumePrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Mini Lecture ReviewDokument9 SeitenChapter 1 Mini Lecture ReviewPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usaid Covid PositionsDokument2 SeitenUsaid Covid PositionsPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working BulletsDokument5 SeitenWorking BulletsPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte NCLEXDokument4 SeitenElectrolyte NCLEXPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Federal Resume Guide: What You Should Know When Applying For A Federal CareerDokument24 SeitenThe Federal Resume Guide: What You Should Know When Applying For A Federal CareerPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes For Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDokument4 SeitenStudy Notes For Sexually Transmitted DiseasesPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creative Résumé Techniques For Marketing Your Skills: Debbie Lashbaugh, CPRWDokument18 SeitenCreative Résumé Techniques For Marketing Your Skills: Debbie Lashbaugh, CPRWPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - 4 To 1 - 6 Mini Lecture ReviewDokument3 SeitenChapter 1 - 4 To 1 - 6 Mini Lecture ReviewPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes For Upper GI ProblemsDokument5 SeitenStudy Notes For Upper GI ProblemsPrince K. Tailey100% (1)
- 01-02 ReviewDokument2 Seiten01-02 ReviewPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini-Lecture 0.5: Learning ObjectivesDokument2 SeitenMini-Lecture 0.5: Learning ObjectivesPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Management: Nutritional Problems (Chapter 40) : MalnutritionDokument2 SeitenNursing Management: Nutritional Problems (Chapter 40) : MalnutritionPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System (Chapter 39) : Structures and FunctionsDokument4 SeitenNursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System (Chapter 39) : Structures and FunctionsPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19 Nutrition Through The Life Cycle: The Later YearsDokument18 SeitenChapter 19 Nutrition Through The Life Cycle: The Later YearsPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes For Breast DisordersDokument4 SeitenStudy Notes For Breast DisordersPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obesity Study NotesDokument2 SeitenObesity Study NotesPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes For Breast DisordersDokument4 SeitenStudy Notes For Breast DisordersPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 - Antioxidant and VisionDokument20 SeitenChapter 10 - Antioxidant and VisionPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 41: Nursing Management: ObesityDokument2 SeitenChapter 41: Nursing Management: ObesityPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes For Female Reproductive ProblemsDokument4 SeitenStudy Notes For Female Reproductive ProblemsPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes For Breast DisordersDokument4 SeitenStudy Notes For Breast DisordersPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EthicsDokument4 SeitenEthicsPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes For Reproductive SystemDokument2 SeitenStudy Notes For Reproductive SystemPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Care EnvironmentDokument4 SeitenEffective Care EnvironmentPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen