Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Answers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2e
Hochgeladen von
Ressurct SnyOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Answers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2e
Hochgeladen von
Ressurct SnyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Gillespie: Business Economics 2e
Chapter 07
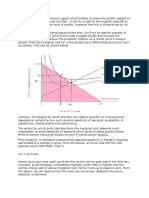
1. Discuss the factors that influence the impact of a new indirect tax on the market price.
Answers may include:
An indirect tax is placed on producers. It increases costs and leads to an inward shift of
supply. This leads to a higher market price and lower equilibrium quantity.
The relative impact on price compared to quantity depends on the price elasticity of
demand. The more price inelastic demand is the more that price increases relative to the
fall in the equilibrium quantity i.e. the more the incidence of the tax is shifted on to the
consumer.
Demand is more likely to price inelastic if:
There are few substitutes
In the short run when it is difficult to switch to alternatives
The product is heavily branded
2. Discuss the case for and against the free market system as a way of analysing
resources.
Answers may include:
The free market relies on market forces to allocate resources. The price mechanism acts
as a signal and rationing device to bring about equilibrium.
The free market has advantages:
It relies on the “invisible hand” of the price mechanism. Individuals and businesses pursue
their own objectives (e.g. to maximize utility or profit) and the price will adjust to find the
equilibrium. Millions of individual decisions are effectively coordinated by the price.
It can maximize the community surplus (i.e. the combination of consumer surplus and
producer surplus) maximizing society’s welfare.
It encourages innovation and customer services as businesses seek high returns.
However there are many potential failures and imperfections such as monopolies,
externalities, merit goods, public goods, price instability and asymmetric information.
These move markets away from the optimal price and quantity.
3. Discuss the factors that would determine how effectively the price mechanism could
adjust to bring equilibrium if there was a change in supply or demand conditions.
Answers may include:
The free market relies on market forces to allocate resources. The price mechanism acts
as a signal and rationing device to bring about equilibrium. If there is excess demand, for
example, the price increases reducing the quantity demanded and increasing the quantity
supplied until equilibrium is restored
However there may be barriers to the price mechanism working such as:
Monopoly power dominating a market and setting the price
Contracts negotiated fixing prices for a set time
© Oxford University Press, 2013. All rights reserved.
Gillespie: Business Economics 2e
Chapter 07
Information problems so difficult to identify the extent of excess demand or supply
Costs of changing prices meaning prices are left at a given level for a while
Intervention by governments to fix prices
© Oxford University Press, 2013. All rights reserved.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Market in Action 1Dokument9 SeitenMarket in Action 1Stan DitonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Economics BCADokument25 SeitenBusiness Economics BCAamjoshuabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Supply and Demand: Unraveling Market Dynamics: IntroductionDokument4 SeitenTheory of Supply and Demand: Unraveling Market Dynamics: IntroductionSharan RarhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall 2017Dokument11 SeitenFall 2017Kripaya ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Key TermsDokument3 SeitenChapter 6 Key TermsEvan CrewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics TheoryDokument19 SeitenEconomics TheoryadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics 22:23Dokument70 SeitenEconomics 22:23dongsara2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supply and DemandDokument3 SeitenSupply and DemandSamita ChunaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParnikaDokument3 SeitenParnikaJust BasumataryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price ElasticityDokument4 SeitenPrice ElasticityBrian NyamuzingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SupplyDokument2 SeitenSupplyJosh Lander MatugasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics : SupplyDokument55 SeitenEconomics : SupplyFaisal Raza SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management Microeconomics ConceptsDokument15 SeitenFinancial Management Microeconomics ConceptsmiolataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument15 SeitenChapter 1James SitohangNoch keine Bewertungen
- walras lawDokument6 Seitenwalras lawFolarin Ademola PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law of demand and supply explainedDokument7 SeitenLaw of demand and supply explainedBodapati Sai bhargav2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dmba105 - Managerial EconomicsDokument12 SeitenDmba105 - Managerial EconomicsMuhammed AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1.2 The Allocation of Resources in Competitive MarketsDokument5 Seiten3.1.2 The Allocation of Resources in Competitive MarketsFattyschippy1Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECONOMICSDokument7 SeitenECONOMICSmilse moralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is MicroeconomicsDokument6 SeitenWhat Is MicroeconomicsjuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EABD Solve Qquestion PaperDokument25 SeitenEABD Solve Qquestion Papernikwankhade19Noch keine Bewertungen
- SUPPLYDokument5 SeitenSUPPLYNeha RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price ActDokument5 SeitenPrice ActJohny TumaliuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assingment #4Dokument11 SeitenAssingment #4kaszulu1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Economics Practise Extended ResponseDokument3 SeitenPreliminary Economics Practise Extended Responseoiu7hjjs100% (2)
- Asynch - 6 TABUGDokument3 SeitenAsynch - 6 TABUGPogi OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Development Strategies for Developing NationsDokument17 SeitenEconomic Development Strategies for Developing NationsVher Christopher Ducay100% (1)
- Price ControlsDokument5 SeitenPrice ControlsAnanya ShardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yutae Lee - ECON 11 UNIT TEST On Government Intervention 60 MarksDokument1 SeiteYutae Lee - ECON 11 UNIT TEST On Government Intervention 60 Marks이유태Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surplus Happens When The Quantity Supplied Is Less Than The Quantity DemandedDokument12 SeitenSurplus Happens When The Quantity Supplied Is Less Than The Quantity DemandedJannah GasangueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics AssignmentDokument6 SeitenEconomics Assignmentsolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Failure PSEDokument12 SeitenMarket Failure PSEnawtamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case-1: People Respond To Incentives. It Is Important, Therefore, That These Have The Desired EffectDokument13 SeitenCase-1: People Respond To Incentives. It Is Important, Therefore, That These Have The Desired EffectHarikrushan DholariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply and Demand Chapter SummaryDokument15 SeitenSupply and Demand Chapter SummarysweettejuNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Economics - Unit OneDokument46 SeitenIB Economics - Unit OneTLinhTCDLALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eabd NotesDokument3 SeitenEabd Notesnikwankhade19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5C: The Functions of The Price MechanismDokument3 SeitenChapter 5C: The Functions of The Price MechanismAmmaar KIMTI100% (1)
- Assignment: Management EconomicsDokument24 SeitenAssignment: Management EconomicsHarendra SilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- TextDokument2 SeitenTextMinakshi RajaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Departmental N Fabra EEL 105Dokument58 SeitenDepartmental N Fabra EEL 105shared classroomNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 2 - The Global Economy (20230220083403) PDFDokument8 SeitenLESSON 2 - The Global Economy (20230220083403) PDFNovelyn DuyoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS1197 - 289862 PDFDokument9 SeitenBS1197 - 289862 PDFCameron MoraisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand EcoDokument6 SeitenDemand Ecoaditya singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply and Demand: The Market Mechanism ExplainedDokument19 SeitenSupply and Demand: The Market Mechanism Explainedvaibhav4yadav-4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity of Demand: Understanding How Prices Affect QuantitiesDokument3 SeitenElasticity of Demand: Understanding How Prices Affect QuantitiesnattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA 240 Comprehensive ExaminationDokument4 SeitenBA 240 Comprehensive ExaminationRichille D Sordilla - PaladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics NotesDokument37 SeitenEconomics Notesrafehsd100% (1)
- Aplayd Ekonomhie 1Dokument56 SeitenAplayd Ekonomhie 1Daphne Gesto SiaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 SummaryDokument8 SeitenChapter 1 SummaryTejpal LathherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market EquilibriumDokument7 SeitenMarket Equilibriumunicornsarecoolasice100% (2)
- Economic System, Advantages, Disadvantages NotesDokument6 SeitenEconomic System, Advantages, Disadvantages NotesPRACHI DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial EconomicsDokument14 SeitenManagerial EconomicsRishi DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13Dokument14 SeitenChapter 13dongsara2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Economics 1Dokument6 SeitenMicro Economics 1mandisanothando60Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Basic Elements of Supply and Demand: A. The Demand ScheduleDokument2 SeitenChapter 3: Basic Elements of Supply and Demand: A. The Demand ScheduleMichelle LonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Microeconomics: Strategic Barriers to EntryDokument9 SeitenPrinciples of Microeconomics: Strategic Barriers to EntryCameron MoraisNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument23 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAnand MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain The Functions of Price in A Market EconomyDokument6 SeitenExplain The Functions of Price in A Market Economyhthomas_100% (5)
- China's price controls distort market equilibriumDokument3 SeitenChina's price controls distort market equilibriumWai HponeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Factbook: Central America and Caribbean:: AnguillaDokument6 SeitenThe World Factbook: Central America and Caribbean:: AnguillaWajahat GhafoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Factbook: North America:: BermudaDokument9 SeitenThe World Factbook: North America:: BermudaRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Australia-Oceania:: Americansamoa: (Territory of The Us)Dokument7 SeitenAustralia-Oceania:: Americansamoa: (Territory of The Us)Ressurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Factbook: Middle East:: BahrainDokument11 SeitenThe World Factbook: Middle East:: BahrainRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antarctica Factbook IntroductionDokument6 SeitenAntarctica Factbook IntroductionWajahat GhafoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Countrypdf An PDFDokument8 SeitenCountrypdf An PDFRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashmore and Cartier IslandsDokument2 SeitenAshmore and Cartier IslandsWajahat GhafoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Factbook: Europe:: AkrotiriDokument3 SeitenThe World Factbook: Europe:: AkrotiriRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central America and Caribbean:: Aruba: (Part of The Kingdom of The Netherlands)Dokument8 SeitenCentral America and Caribbean:: Aruba: (Part of The Kingdom of The Netherlands)Ressurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eDokument2 SeitenAnswers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wikileaks Document Release: Congressional Research Service Report Rl32465Dokument13 SeitenWikileaks Document Release: Congressional Research Service Report Rl32465Chinmay KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing Financial Statements For Profitability Liquidity and SolvencyDokument44 SeitenAnalyzing Financial Statements For Profitability Liquidity and SolvencyRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Resources, Recycling, and Recovery: Lean 6-Sigma Green Belt ProjectDokument15 SeitenDepartment of Resources, Recycling, and Recovery: Lean 6-Sigma Green Belt ProjectYatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Antiquities and Art Treasure Act 1972Dokument18 SeitenThe Antiquities and Art Treasure Act 1972Anzil FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eDokument2 SeitenAnswers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05gillespie Business Economics 2e To What Extent Do Economies of Scale Matter PDFDokument2 Seiten05gillespie Business Economics 2e To What Extent Do Economies of Scale Matter PDFRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eDokument2 SeitenAnswers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eRessurct Sny0% (1)
- History of HeinekenDokument11 SeitenHistory of HeinekenSargam RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eDokument2 SeitenAnswers May Include:: Gillespie: Business Economics 2eRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BudweiserDokument6 SeitenBudweiserRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gillespie: Business Economics 2e: © Oxford University Press, 2013. All Rights ReservedDokument1 SeiteGillespie: Business Economics 2e: © Oxford University Press, 2013. All Rights ReservedRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study HeinekenDokument2 SeitenCase Study HeinekenRessurct SnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posc ActDokument7 SeitenPosc ActPrem ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monetary Economics II: Theory and Policy ECON 3440C: Tasso Adamopoulos York UniversityDokument60 SeitenMonetary Economics II: Theory and Policy ECON 3440C: Tasso Adamopoulos York UniversityPulki MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCF Commerce CSR 13 Sem. 1Dokument2 SeitenCCF Commerce CSR 13 Sem. 1Toshani VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cvru Regular Syllabus - Bachelor of Business Administration 2013-16Dokument54 SeitenCvru Regular Syllabus - Bachelor of Business Administration 2013-16vivek patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Econ600Dokument8 SeitenSyllabus Econ600Thijs772Noch keine Bewertungen
- Service MarketingDokument35 SeitenService MarketingDipak sagathiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Syllabus, ECE Department HSTUDokument46 SeitenECE Syllabus, ECE Department HSTUIrfan NabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EconomicsDokument8 SeitenEconomicsGosheealee SewruttunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 Com, Annual Exam, 2023-24Dokument5 SeitenGrade 11 Com, Annual Exam, 2023-24AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 & 12 Economics Split-UpDokument9 Seiten11 & 12 Economics Split-UpMadhuryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions For IB EconomicsDokument26 SeitenDefinitions For IB EconomicsMohamed Mohideen50% (2)
- Student Handouts For BananaDokument8 SeitenStudent Handouts For Bananaapi-271596792Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMIS Insights - Colombia Food and Beverage Sector Report 2019 - 2020Dokument77 SeitenEMIS Insights - Colombia Food and Beverage Sector Report 2019 - 2020Alvaro AcunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet For Chapter 13 (2023)Dokument39 SeitenWorksheet For Chapter 13 (2023)Ncebakazi DawedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Chapter 5 - CompressDokument11 SeitenSolutions To Chapter 5 - CompressSadia ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam QuestionsDokument11 SeitenNUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam QuestionsYin Hau100% (2)
- Feasibility Study (MATS CNG Filling Station) : Students of MBA 3 SemesterDokument61 SeitenFeasibility Study (MATS CNG Filling Station) : Students of MBA 3 SemesterMCDABC0% (1)
- Demand and Supply of Smart Phone in UAE2Dokument23 SeitenDemand and Supply of Smart Phone in UAE2Dendukuri varmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Manuscript in PracticalDokument21 SeitenFinal Manuscript in PracticalRochelle Khate SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vorlesung 05 PDFDokument16 SeitenVorlesung 05 PDFSakshi AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECO 372 Final Exam GuideDokument15 SeitenECO 372 Final Exam GuideECO 372 Week 5 Final ExaminationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 May TZ2 MsDokument14 Seiten2016 May TZ2 MsSeoHyun KIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Memo InstructionsDokument4 SeitenCase Memo InstructionsVish KamdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Order Quantity & Its Determination: Dr. S. C. Singh Shivam SrivastavaDokument16 SeitenEconomic Order Quantity & Its Determination: Dr. S. C. Singh Shivam Srivastavashivamsrivastava85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Public Policy Connect AnswersDokument11 SeitenPublic Policy Connect AnswersMargarita ArnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 1550 Assignment 1: Analysis of Graphs, Slopes, Production Possibilities Frontier & MoreDokument19 SeitenECON 1550 Assignment 1: Analysis of Graphs, Slopes, Production Possibilities Frontier & Morenekkmatt100% (1)
- 12.18 Marketing12.18 MarketingDokument31 Seiten12.18 Marketing12.18 MarketinggoerginamarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- British Tourist Authority Price Sensitivity of Tourism To BritainDokument132 SeitenBritish Tourist Authority Price Sensitivity of Tourism To BritainLaura AndreeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics For Quick RevisionDokument224 SeitenManagerial Economics For Quick RevisionSuparna2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Specimen Paper 3 Mark SchemeDokument20 Seiten2023 Specimen Paper 3 Mark Schemetafadzwa tandawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lu Bba SyllabusDokument10 SeitenLu Bba SyllabusTalha SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldVon EverandKleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (25)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereVon EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsVon EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (94)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumVon EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (12)
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentVon EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (92)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesVon EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (8)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaVon EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomVon EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingVon EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (97)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyVon EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (227)
- The Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldVon EverandThe Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (16)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenVon EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyVon EverandThe Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (69)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetVon EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsVon EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassVon EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailVon EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (237)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationVon EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (46)
- Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistVon EverandDoughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (37)
- Kaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineVon EverandKaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (36)
- The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the WorldVon EverandThe Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (132)
- Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of RiskVon EverandAgainst the Gods: The Remarkable Story of RiskBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (352)
- How an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionVon EverandHow an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (102)