Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case 1: Impairment On Local Level: Tax Rate 25% Change in Value T 1 vs. T 2
Hochgeladen von
singhsanjOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case 1: Impairment On Local Level: Tax Rate 25% Change in Value T 1 vs. T 2
Hochgeladen von
singhsanjCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tax rate 25%
Change in value
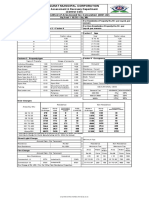
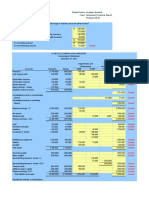
T=1 vs. T=2 Case 1: Impairment on local Level
T=1 T=2
Asset Liability Property -80 Asset Liability
local GAAP Property 100 90 Equity Equities 0 Property 20 10 Equity
Insurance Insurance Insurance
Equities 200 210 Liabilities Liabilities 0 Equities 200 210 Liabilities
Property 50 Property 0
Equities 50 Equities 50
Revaluation
Insurance Insurance
Liabilities -90 Liabilities -90
Change in value SII
T=1 vs. T=2
T=1 T=2
Asset Liability Property -130 Asset Liability
SII
Property 150 232.5 Equity Equities 0 Property 20 115 Equity
Insurance Insurance Insurance
Equities 250 120 Liabilities Liabilities 0 Equities 250 120 Liabilities
47.5 DTL 35 DTL
50.00 Property to Equity 37.50 50.00 Equities to Equity 37.50
DTL 12.50 DTL 12.50
50.00 Equities to Equity 37.50 90.00 Ins. Liab. to Equity 67.50
DTL 12.50 DTL 22.50
90.00 Ins. Liab. to Equity 67.50
DTL 22.50
T=1
Due to market consistent economic valuation assets rise in value (in comparison to local GAAP/Tax GAAP) and technical provisions are reduced due to the best
estimate calculation. The value increases/decreases trigger temporary differences in between SII/Tax GAAP. Therefore from the 190 CU of Value Increase only
142,5 CU run directly into an increase of equity, whereas 25 % (tax rate) run into the building of a deferred tax liability amounting to 47,5 CU.
T=2 (Case 1)
Property shows an extreme decrease in value, which results both in local GAAP and in SII in a necessary impairment. Therefore the temporary difference
triggering (for property) the building of a DTL amounting to 12,5 CU in T=1 falls away and less DTL is necessary. So the value decrease in SII from T=1 to T=2
amounts to 130 CU whereas equity is just reduced by 117,5. The DTL works as loss absorbing.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- An Introduction To Debt Policy and Value - Syndicate 4Dokument9 SeitenAn Introduction To Debt Policy and Value - Syndicate 4Henni RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE Jan 2011Dokument7 SeitenPE Jan 2011nawwar ukeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop 1 - Accounting Statements and Posting Entries Solution v2Dokument12 SeitenWorkshop 1 - Accounting Statements and Posting Entries Solution v2Karina BenítezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Structure with Market ImperfectionsDokument11 SeitenCapital Structure with Market ImperfectionsNishantShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex GroupsDokument12 SeitenComplex GroupsRaquibul HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 2 Shared 2021Dokument25 SeitenSession 2 Shared 2021Puneet MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deferred Taxes and Accelerated Depreciation ExplainedDokument15 SeitenDeferred Taxes and Accelerated Depreciation Explainedtarun19191919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Balance SheetDokument3 SeitenBasic Balance SheetJean Marc LouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 2 Shared 2023Dokument34 SeitenSession 2 Shared 2023VAKIL YATHARTH NILESH 18110184Noch keine Bewertungen
- Castro Maryliam T 3Dokument4 SeitenCastro Maryliam T 3Kyle KuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation FP ExampleDokument4 SeitenConsolidation FP ExampleSuryaRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of RatiosDokument5 SeitenList of RatiosKappala AbhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step-by-step guide to goodwill translation and consolidationDokument4 SeitenStep-by-step guide to goodwill translation and consolidationuser mrmysteryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 DEC QuestionDokument10 Seiten05 DEC Questionkhengmai100% (1)
- January 2022 Balance SheetDokument1 SeiteJanuary 2022 Balance Sheet14 - LUSI FITRIANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet and Income StatementDokument7 SeitenBalance Sheet and Income StatementAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Httpsproperty.ulbharyana.gov.InBillReportPrintBillPID=1KD14OO0&UlbID=61Dokument1 SeiteHttpsproperty.ulbharyana.gov.InBillReportPrintBillPID=1KD14OO0&UlbID=61roopumgautam95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dux Company Statement of Cash Flows for 2021 (indirect methodDokument6 SeitenDux Company Statement of Cash Flows for 2021 (indirect methodJuliana CaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation FP ExampleDokument4 SeitenConsolidation FP ExampleYoooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation FP ExampleDokument4 SeitenConsolidation FP ExampleYAUHANoch keine Bewertungen
- IRRDokument5 SeitenIRROlivier MNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Consolidate Group AccountsDokument1 SeiteHow to Consolidate Group AccountsMohammad BaratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokument37 SeitenFinancial Statement AnalysisShilpa AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- P&L and Balance Sheet AnalysisDokument6 SeitenP&L and Balance Sheet AnalysisMauricio SernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 - 29th March 2021 - Group FS - Interpretation - IFRS ApplicationDokument6 SeitenAssignment 1 - 29th March 2021 - Group FS - Interpretation - IFRS ApplicationGanbilegBatnasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Flow Statement SAMPLEDokument4 SeitenCash Flow Statement SAMPLEShaira BaltazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acstran - Assignment 1.3Dokument2 SeitenAcstran - Assignment 1.3Tricia Nicole DimaanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting AssignmentDokument2 SeitenAccounting AssignmentRomyah CornwallNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7918final Adv Acc Nov06Dokument20 Seiten7918final Adv Acc Nov06ஆக்ஞா கிருஷ்ணா ஷர்மாNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projected One-Year Balance Sheet Lip Redux Balance Sheet As of October 2020 Account Titles Debit Credit AssetsDokument2 SeitenProjected One-Year Balance Sheet Lip Redux Balance Sheet As of October 2020 Account Titles Debit Credit Assetsmjmj.lorenzo0805Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2 - Cost of Equity - ExerciseDokument7 Seiten4.2 - Cost of Equity - ExerciseHTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Discussion Questions Rev 0Dokument6 SeitenChapter 2 Discussion Questions Rev 0Hayley SNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocxDokument7 SeitenDocxRenelyn FiloteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight ProblemsDokument39 SeitenStraight ProblemsJev CastroverdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equity Method Versus ConsolidationDokument4 SeitenEquity Method Versus ConsolidationGing freexNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 July 2023Dokument12 Seiten05 July 2023sajedulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statements: Problem 14-1: True or FalseDokument13 SeitenFinancial Statements: Problem 14-1: True or FalseMichael Brian TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFRS-3 Business Combination Accounting for Miracle Ltd Acquisition of Hand LtdDokument1 SeiteIFRS-3 Business Combination Accounting for Miracle Ltd Acquisition of Hand LtdBabu babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Account AccountDokument12 SeitenAccount AccountblackghostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surat Municipal CorporationDokument1 SeiteSurat Municipal CorporationTonny HiktonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projected One-Year Balance Sheet Lip Redux Balance Sheet As of October 2020 Account Titles Debit AssetsDokument2 SeitenProjected One-Year Balance Sheet Lip Redux Balance Sheet As of October 2020 Account Titles Debit Assetsmjmj.lorenzo0805Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assets Liabilities + Owners Equity Income Statement InformationDokument2 SeitenAssets Liabilities + Owners Equity Income Statement Informationamitmehta29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sunsquare Company Was Created As A Wholly Owned Subsidiary of Times CorporationDokument5 SeitenSunsquare Company Was Created As A Wholly Owned Subsidiary of Times Corporationloanltt88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ratios CalculatorDokument6 SeitenRatios CalculatorQuyen TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exceltemplate Company Inc. Balance Sheet: Assets Current AssetsDokument8 SeitenExceltemplate Company Inc. Balance Sheet: Assets Current AssetsAlex100% (1)
- 20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX: You Are Likely To Have Change The Number of YearsDokument6 Seiten20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX: You Are Likely To Have Change The Number of Yearsmalishka1025Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Reporting in HyperinflationDokument12 SeitenFinancial Reporting in HyperinflationShane KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis Numericals Including Reverse RatiosDokument6 SeitenRatio Analysis Numericals Including Reverse RatiosFunny ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting - Semester-3: Suggested Solutions/ Answers Fall 2015 ExaminationsDokument2 SeitenFinancial Accounting - Semester-3: Suggested Solutions/ Answers Fall 2015 ExaminationsAsimsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- f3 AssignmentDokument6 Seitenf3 Assignmentnoumanchaudhary902Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project 4 - Chap 5Dokument3 SeitenProject 4 - Chap 5Waqar ZulfiqarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Analysis and Working Capital: Mba (Tech) Sem Vii Mpstme Course Facilitator: Dr. Nupur GuptaDokument53 SeitenFinancial Analysis and Working Capital: Mba (Tech) Sem Vii Mpstme Course Facilitator: Dr. Nupur GuptaJake RoosenbloomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet As On July 31, 2017 Liabilities AssetsDokument18 SeitenBalance Sheet As On July 31, 2017 Liabilities AssetsKanmani FX21015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis Problems-1Dokument10 SeitenRatio Analysis Problems-1Aditya DalviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acc Cap M - 2019 - Exercise Pack - With SolutionsDokument26 SeitenAcc Cap M - 2019 - Exercise Pack - With SolutionsValentinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seran MamaDokument1 SeiteSeran MamachauhantonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Ratios ExplainedDokument5 SeitenAccounting Ratios ExplainedParas VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rand Inc. Balance SheetDokument1 SeiteRand Inc. Balance SheetKri BanayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imo Sample Paper Class-2Dokument2 SeitenImo Sample Paper Class-2srijani pal0% (1)
- NF21121247803688 E-Ticket PDFDokument2 SeitenNF21121247803688 E-Ticket PDFsinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bandhan Bank DRHP PDFDokument482 SeitenBandhan Bank DRHP PDFsinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis: R K MohantyDokument30 SeitenRatio Analysis: R K Mohantybgowda_erp1438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aging AnalysisDokument2 SeitenAging AnalysissinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBI Master Circular on Prudential Norms for Capital AdequacyDokument124 SeitenRBI Master Circular on Prudential Norms for Capital Adequacysushil_raj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deffered TaxDokument7 SeitenDeffered TaxsinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Ways To Group Times in ExcelDokument15 Seiten3 Ways To Group Times in ExcelsinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Finance MCQDokument11 SeitenCorporate Finance MCQsinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aging AnalysisDokument2 SeitenAging AnalysissinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Capital AssessmentDokument33 SeitenWorking Capital AssessmentzydusNoch keine Bewertungen
- UP Budgetbhashan2016 2017Dokument68 SeitenUP Budgetbhashan2016 2017singhsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customs Act 1962 OverviewDokument83 SeitenCustoms Act 1962 OverviewipragalbhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Excel TestDokument980 SeitenAdvanced Excel TestsinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- App Store Optimization: A Beginners Guide ToDokument13 SeitenApp Store Optimization: A Beginners Guide TosinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valuing Banking Stocks Pros and ConsDokument5 SeitenValuing Banking Stocks Pros and ConssinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutual FundsDokument29 SeitenMutual FundssinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Mobile HandsetsDokument45 SeitenReport On Mobile HandsetssinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument29 SeitenPresentation 1prakashkashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- U S Economic Recession & Its Impact On Indian EconomyDokument32 SeitenU S Economic Recession & Its Impact On Indian EconomysinghsanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tikona broadband bill detailsDokument2 SeitenTikona broadband bill detailsabhietwup50% (2)
- Confirmation Note: D D C DDokument1 SeiteConfirmation Note: D D C DZurruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ola BillDokument3 SeitenOla BillMohit TanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory and Basis of Taxation: Lifeblood Principle and Benefit-Received ConceptDokument4 SeitenTheory and Basis of Taxation: Lifeblood Principle and Benefit-Received ConceptJiyu50% (2)
- EY Tax Alert: Malaysian DevelopmentsDokument10 SeitenEY Tax Alert: Malaysian DevelopmentsSirius StarNoch keine Bewertungen
- InvocalDokument1 SeiteInvocalbaiju bawraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Guidelines For Issuance and Operation of Prepaid Payment Instruments in IndiaDokument12 SeitenDraft Guidelines For Issuance and Operation of Prepaid Payment Instruments in IndiaSidharath GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Quiz2 Answer KeyDokument5 SeitenTax Quiz2 Answer Keycloy aubreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVO Unit Progress ReportDokument2 SeitenDVO Unit Progress ReportNeeraj KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Number. 999RCU1022960: Ruaha Catholic University (Rucu)Dokument2 SeitenControl Number. 999RCU1022960: Ruaha Catholic University (Rucu)Maria MadalambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalimuthu Kayalvizhi GST Profile PDFDokument4 SeitenKalimuthu Kayalvizhi GST Profile PDFRam CharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authorization Letter To Pag IBIGDokument1 SeiteAuthorization Letter To Pag IBIGattyjamaputi62% (13)
- Page 1 of 1: Statement Period: February 2019Dokument1 SeitePage 1 of 1: Statement Period: February 2019Yuliana Alexandra Echeverri PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sun Developers & Consultants: Date Invoice # Bill Amount Credit Amount Balance RemarksDokument7 SeitenSun Developers & Consultants: Date Invoice # Bill Amount Credit Amount Balance Remarksrajts singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- TejbirDokument1 SeiteTejbirTejbir SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 PDFDokument19 SeitenModule 4 PDFRAJASAHEB DUTTANoch keine Bewertungen
- (TAX) Income Taxation Updated Jan 9 2022Dokument133 Seiten(TAX) Income Taxation Updated Jan 9 2022Reginald ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invoices CR - Sale 129 VDPM Lnd4nTfROp4mieDokument1 SeiteInvoices CR - Sale 129 VDPM Lnd4nTfROp4mieAcer UserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icp Receipt - Icp 129309Dokument1 SeiteIcp Receipt - Icp 129309Sadiq KhattakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atc 1 PDFDokument2 SeitenAtc 1 PDFSatvik ManaktalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSTR1 Excel Workbook Template-V1.0Dokument39 SeitenGSTR1 Excel Workbook Template-V1.0palanisathiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VITA Volunter Resource GuideDokument232 SeitenVITA Volunter Resource Guidefefasqewweq100% (1)
- Outgoing Payment Advice: Payment Debit Analysis Commission & Charges AnalysisDokument1 SeiteOutgoing Payment Advice: Payment Debit Analysis Commission & Charges AnalysisDiJúDiJúNoch keine Bewertungen
- FATCA COMPLIANCEDokument13 SeitenFATCA COMPLIANCEMuhammed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Account Statement (Online) Page 1 of 65Dokument65 SeitenAccount Statement (Online) Page 1 of 65Noorul Hassan100% (2)
- Effect of Cashless Payment Methods A Case Study Perspective AnalysisDokument4 SeitenEffect of Cashless Payment Methods A Case Study Perspective AnalysisAaryan Singh100% (1)
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDokument1 SeiteIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruMahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RR 1-95Dokument9 SeitenRR 1-95matinikki0% (1)
- Federal Income Tax Computation and DefinitionsDokument42 SeitenFederal Income Tax Computation and Definitionsabmo33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gross Income (Tax)Dokument52 SeitenGross Income (Tax)HOOPE JISONNoch keine Bewertungen