Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reed Relays Switch Devices Using Magnetic Fields
Hochgeladen von
Asad KhanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Reed Relays Switch Devices Using Magnetic Fields
Hochgeladen von
Asad KhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
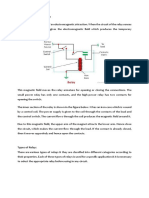
Reed Relays are a little, smaller, quick working switch design with one contact, which is NO.
Reed Relays
are hermetically fixed in a glass envelope, which makes the contacts unaffected by contaminants, smoke
or vapour, permits reliable switching, and gives contacts a higher future. The closures of the contact,
which are regularly plated with gold or another low resistance material to build conductivity, are drawn
together and shut by a magnet. Reed transfers are fit for switching industrial parts, for example,
solenoids, contactors and starter motors.
5.3 Functions of Relays
The basic parts and functions of Relays are these and explained
1. Frame: Heavy-obligation outline that contains and supports the parts of the relay.
2. Coil: Wire is twisted around a metal core. The loop of wire causes an electromagnetic field.
3. Armature: A relays moving part. The armature opens and shuts the contacts. An appended
spring restores the armature to its original position.
4. Contacts: The leading piece of the switch that makes (closes) and breaks (opens) a circuit.
Relays include two circuits: one is energizing circuit and the other is contact circuit. The coil is on
the Energizing side; and the relays contacts are on the contact side. When the current is pass
through the coil, by passing current the coil is energized and makes a magnetic field. In DC unit
the polarity is fixed and never but in AC unit the polarity is variable and changes 120 times each
second, but the fundamental functions remains the same: the ferrous plate which acts like a
armature and the one end of ferrous plate is pivoted with metal frame and the magnetic field attracts
the ferrous plate and attached with the metal frame., while the opposite end opens and close the
contacts.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Automatic Transmission GuideDokument34 SeitenAutomatic Transmission GuideAsad Khan100% (3)
- What is Contactor: Construction, Types and ApplicationsDokument7 SeitenWhat is Contactor: Construction, Types and ApplicationsDilip Gangopadhyay100% (1)
- Electromechanical Relay GuideDokument19 SeitenElectromechanical Relay GuideRajesh Naik Dharavath100% (1)
- Amta5 6 Applying Shielded Metal Arc Welding Smaw TechniquesDokument132 SeitenAmta5 6 Applying Shielded Metal Arc Welding Smaw TechniquesSaurav Kumaar GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is a RelayDokument13 SeitenWhat is a RelayJohn Carlo PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Know About Different Types of Relays PDFDokument17 SeitenKnow About Different Types of Relays PDFmohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RelayDokument11 SeitenRelayKishan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Electromagnetic RelayDokument7 SeitenTitle: Electromagnetic RelayCharidyChuahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A Magnetic ContactorDokument15 SeitenParts of A Magnetic ContactorPriince Dwi Ght100% (1)
- Relay DetailsDokument15 SeitenRelay DetailsstarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relays and Reed SwitchesDokument2 SeitenRelays and Reed SwitchesSamrat PvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relays Types Operations Specification SymbolsDokument12 SeitenRelays Types Operations Specification Symbolspradeep.nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coil of Wire Surrounding A Soft Iron CoreDokument15 SeitenCoil of Wire Surrounding A Soft Iron Coreprem035Noch keine Bewertungen
- RelayDokument89 SeitenRelayHarsh GajeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay Definition and Working PrincipleDokument33 SeitenRelay Definition and Working Principlevikas mauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Principle of A Contactor:: Holds The Moving and Fixed Contacts Together. in The ProcessDokument15 SeitenOperating Principle of A Contactor:: Holds The Moving and Fixed Contacts Together. in The ProcessAnand JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT 17503 AEE Session 27Dokument18 SeitenAT 17503 AEE Session 27pavanraneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Relays: DC Vs AC RelaysDokument7 SeitenElectromagnetic Relays: DC Vs AC RelaysAngel RacasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Relays: Name: Arpit Maheshwari ROLL NO:03896404914 EEE-6 DATE OF SUBMISSION: 27-9-2017Dokument15 SeitenElectric Relays: Name: Arpit Maheshwari ROLL NO:03896404914 EEE-6 DATE OF SUBMISSION: 27-9-2017Arpit MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Relays Work: Electromechanical Relays Vs Solid State RelaysDokument5 SeitenHow Relays Work: Electromechanical Relays Vs Solid State RelaysSaad NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parte1-Description Material and ConclusionsDokument3 SeitenParte1-Description Material and ConclusionsLisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrically Switch ElectromagnetDokument16 SeitenElectrically Switch ElectromagnetThamarai Kannan RamajayamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contactor Ing LengkapsDokument6 SeitenContactor Ing LengkapsMuhammad Evan AryaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightning ProtectionDokument15 SeitenLightning ProtectionEnglish words BY Utkarsh johriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay: Fig 6.1: Automotive-Style Miniature Relay, Dust Cover Is Taken OffDokument12 SeitenRelay: Fig 6.1: Automotive-Style Miniature Relay, Dust Cover Is Taken OffmichealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay & ContactorDokument9 SeitenRelay & Contactorraj kharatNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 11 Effects of Electric Current – RBSE GuideDokument3 SeitenRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 11 Effects of Electric Current – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics About ContactorsDokument11 SeitenBasics About Contactorsrahulgoyal999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relay: HistoryDokument11 SeitenRelay: HistoryEngr WekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE-477 Protective Relays Course OverviewDokument29 SeitenEEE-477 Protective Relays Course OverviewMasud SarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument9 SeitenRelay: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaApri ZaldyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay: Navigation SearchDokument14 SeitenRelay: Navigation SearchAbhishek ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment no. 4 - Introduction to Electromagnetic Relay Construction and WorkingDokument1 SeiteExperiment no. 4 - Introduction to Electromagnetic Relay Construction and WorkingPhantom BeingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buy Products Send-In Repair On-Site Repair Engineered Systems Galco TV My AccountDokument8 SeitenBuy Products Send-In Repair On-Site Repair Engineered Systems Galco TV My AccountTanveer Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnets N Magnetic RelayDokument2 SeitenElectromagnets N Magnetic RelayRoshaan AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument13 SeitenRelay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediakghlkhglkghklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Design and Operation: Electrically SwitchDokument11 SeitenBasic Design and Operation: Electrically SwitchAnina JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Electrically Operated SwitchDokument18 SeitenAn Electrically Operated Switchfrancis abuchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RelayDokument10 SeitenRelayhighview1738Noch keine Bewertungen
- CLP U3A3.1 DiaGabRuiRenDokument5 SeitenCLP U3A3.1 DiaGabRuiRenDIANA GABRIELA RUIZ RENTERIANoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Basic Electrical ComponentsDokument17 Seiten14 Basic Electrical ComponentsShimpy MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechatronics CHAPTER 3Dokument39 SeitenMechatronics CHAPTER 3NahomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay: History Basic Design and Operation Terminology TypesDokument16 SeitenRelay: History Basic Design and Operation Terminology Typess prakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- ContactorsDokument3 SeitenContactorsGalco IndustrialNoch keine Bewertungen
- RelayDokument14 SeitenRelayKevin Ryan T. MaravillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitors Na AssignmentDokument3 SeitenCapacitors Na AssignmentnimraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Relays 692 Sar14phDokument21 SeitenElectric Relays 692 Sar14phSowmyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractDokument5 SeitenExperiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractKkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Construction of DC MachinesDokument3 SeitenBasic Construction of DC Machinesdev pawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- contactors moreDokument2 Seitencontactors moregopal sapkotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is RelayDokument8 SeitenWhat Is RelayLorenz BanadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Solenoid Engine: Students of Group 10 IEC College of Engineering & TechnologyDokument14 SeitenA Solenoid Engine: Students of Group 10 IEC College of Engineering & TechnologyArvind Kumar100% (4)
- Relay: This Article Is About The Electronic Component. For Other Uses, SeeDokument11 SeitenRelay: This Article Is About The Electronic Component. For Other Uses, SeeAkash MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure For Making ProjectDokument24 SeitenProcedure For Making ProjectAnkit BishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condenser.: Capacitor - in A Way, A Capacitor Is A Little Like A Battery. Although They Work in Completely Different WaysDokument8 SeitenCondenser.: Capacitor - in A Way, A Capacitor Is A Little Like A Battery. Although They Work in Completely Different WaysJuan DelacruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relays vs Contactors - Electromagnetic switches for low and high voltage applicationsDokument4 SeitenRelays vs Contactors - Electromagnetic switches for low and high voltage applicationsOMSURYACHANDRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Electromechanical Relays WorkDokument11 SeitenHow Electromechanical Relays WorkKevin FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolenoidDokument4 SeitenSolenoidDannfil ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task4 ClarDokument14 SeitenTask4 ClarSteve ClarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statitical Table of Equipment Hidden Risk InspectionDokument3 SeitenStatitical Table of Equipment Hidden Risk InspectionAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Mar Daily Work ReportDokument2 Seiten14 Mar Daily Work ReportAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic Equipment: 4.1 Components of An Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorDokument11 SeitenUltrasonic Equipment: 4.1 Components of An Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loto SystemDokument27 SeitenLoto SystemAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Ultrasonics: 2.1 Mechanical Wave PropagationDokument20 SeitenFundamentals of Ultrasonics: 2.1 Mechanical Wave PropagationAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DensityDokument27 SeitenDensityAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDTDokument28 SeitenGeneral Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDTAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibration of The Testing SystemDokument7 SeitenCalibration of The Testing SystemAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Socially Maladjustment Vs Emotional DisturbanceDokument4 SeitenSocially Maladjustment Vs Emotional DisturbanceAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Techniques and Their Limitations: 3.1 Pulse Echo TechniqueDokument10 SeitenTesting Techniques and Their Limitations: 3.1 Pulse Echo TechniqueAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of Fuel Free Electric CarDokument18 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of Fuel Free Electric CarAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall Protection Harness Inspection ChecklistDokument2 SeitenFall Protection Harness Inspection ChecklistAsad Khan100% (2)
- Personality PresentationDokument7 SeitenPersonality PresentationAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Design For Ultra-Long Needle Probe Card For Digital Light Processing Wafer TestingDokument2 SeitenGeometric Design For Ultra-Long Needle Probe Card For Digital Light Processing Wafer TestingAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolling Friction CoefficientsDokument1 SeiteRolling Friction CoefficientsAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adhesion and Tractive EffortDokument1 SeiteAdhesion and Tractive EffortAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- R22 Phase Out SummaryDokument1 SeiteR22 Phase Out SummaryAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bugatti Veyron EB Is A Grand Sport CarDokument2 SeitenThe Bugatti Veyron EB Is A Grand Sport CarAsad Khan0% (1)
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics (ME 326) Fluid Mechanics - II)Dokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics (ME 326) Fluid Mechanics - II)Asad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUMMARYDokument1 SeiteSUMMARYAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Octahedral Stress TheoryDokument18 SeitenOctahedral Stress TheoryAsad Khan100% (1)
- R-22 Being Phased Out, Not EliminatedDokument6 SeitenR-22 Being Phased Out, Not EliminatedAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
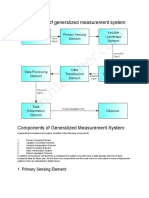
- Block Diagram of Generalized Measurement SystemDokument2 SeitenBlock Diagram of Generalized Measurement SystemAsad Khan100% (1)
- CalculusDokument51 SeitenCalculusAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A History of The CalculusDokument6 SeitenA History of The CalculusAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- R-22 Being Phased Out, Not EliminatedDokument6 SeitenR-22 Being Phased Out, Not EliminatedAsad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen