Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Trabajo Ingles Presente Simple
Hochgeladen von
Лиз МагалиOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trabajo Ingles Presente Simple
Hochgeladen von
Лиз МагалиCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
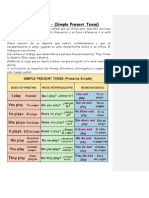
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
(PRESENTE SIMPLE)
El Presente Simple es un tiempo verbal que se utiliza para describir acciones habituales
que suceden con cierta frecuencia y no hace referencia a si está ocurriendo en el momento
actual.
EL "SIMPLE PRESENT" SE UTILIZA:
Rutinas y habitos
I work in a silver mine
(Trabajo en una mina de plata)
I smoke
(yo fumo)
Situaciones permanentes
She has a car
(Ella tiene un coche)
Leyes naturales o físicas
The Sun appears in the East
(El Sol sale por el este)
For things that are always / generally true.
They speak English at work.
Por cosas que siempre son / generalmente verdaderas.
It rains a lot in winter.
(Llueve mucho en invierno.)
The Queen of England lives in Buckingham Palace.
(La Reina de Inglaterra vive en el Palacio de Buckingham.)
Para dar instrucciones o indicaciones:
You walk for two hundred meters, then you turn left.
Para hablar de eventos programados, presentes o futuros:
Your exam starts at 09.00.
Para referirse al futuro, detrás de algunas conjunciones: after, when, before, as
soon as, until:
He'll give it to you when you come next Saturday.
GRAMMATICAL RULES (REGLAS GRAMATICALES)
I. (+) AFIRMATIVE FORM (forma afirmativa)
Para conjugar el presente simple usamos el infinitivo para los sujetos “I”, “you”, “we”
y “they” y para las terceras personas “he”, “she” y “it”, añadimos una “-s” al final del
verbo.
Structure (Estructura)
[SUJETO] + [VERBO] (en infinitivo sin to) + [COMPLEMENTO]
Ejemplos:
I talk. (Yo hablo.)
They learn. (Ellos aprenden.)
He eats vegetables. (Él come vegetales.)
Alice dances at the theatre. (Alice baila en el teatro.)
The dog breaks the fence. (El perro rompe la cerca.)
She lives in Tingo Maria city.(ella vive en la ciudad de Tingo María)
Caso especial: "-es" para la 3ª persona
Para los verbos acabados en "-o","-sh", "-ch”, "-ss", "-x”, "-z", "-y" se añade "-
es" en lugar de "-s para la 3ª persona del singular".
Veamos a continuación algunos ejemplos:
Verbo Tercera persona Significado
to go he goes él va
to wish he wishes él desea
to reach he reaches él alcanza
to express he expresses él expresa
to fix he fixes él arregla
to kiss he kisses él besa
Caso especial: "-ies" para la 3ª persona
Adicionalmente, los verbos acabados en "-y" cuando la "y" no es precedida de
una vocal, forman la tercera persona en "-ies".
Verbo Tercera persona Significado
to occupy he occupies él ocupa
to study he studies él estudia
For verbs that end in a vowel + Y, we just add -S.
Pero cuidado si la "-y" es precedida por una vocal, la tercera persona se forma
con una "-s" (desinencia estándar)
Verbo Tercera persona Significado
to buy he buys él compra
to play she plays ella juega
II. (-) NEGATIVE FORM (forma negativa)
Para hacer una oración negativa en inglés normalmente usamos Do not o Does not
con todos los verbos, EXCEPTO los verbos To Be y Modal (can, might, should, etc.).
"DO" se utiliza con "I, you, we, they" y " DOES" se utiliza con la tercera persona
singular "he, she, it".
Structure (Estructura)
[SUJETO] + do (es) + not + [VERBO] + [COMPLEMENTO]
El verbo principal va en el infinitivo.
Negative Contractions (contracciones negativas)
Don't = Do not
Doesn't = Does not
I don't like meat = I do not like meat.
Ejemplos:
I do not [don’t] talk. (Yo no hablo.)
He does not [doesn’t] eat. (Él no come.)
They do not [don’t] learn. (Ellos no aprenden.)
I don’t play tennis. (Yo no juego al tenis.)
He doesn’t work in an office. (Él no trabaja en una oficina.)
They don’t travel to Madrid. (Ellos no viajan a Madrid.)
III. (?) INTERROGATIVE FORM (forma interrogativa)
En las oraciones interrogativas también se hace uso del verbo auxiliar to do.
Anteponiéndolo al sujeto.
El verbo principal va en el infinitivo.
Structure (Estructura)
La estructura de las preguntas cerradas o de yes/no (es decir aquellas que
no tienen partícula interrogativa) es:
Do / Does + [SUJETO] + [VERBO] + [COMPLEMENTO]?
Ejemplo:
Do you like music? ¿Te gusta la música?
Does he speak English? ¿Él habla inglés?
La estructura de las preguntas abiertas (es decir aquellas que tienen
partícula interrogativa) es:
[WH - QUESTIONS] + Do/Does + [SUJETO] + [VERBO] ?
Ejemplo:
Why do you like music? ¿Por qué te gusta la música?
When do you come back? ¿Cuándo vuelves?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- El Presente Simple Es Un Tiempo VerbalDokument8 SeitenEl Presente Simple Es Un Tiempo VerbalgabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles para Preparar La MateriaDokument4 SeitenIngles para Preparar La MateriaCoSqUiLLiTaS eN La PaNzA ( EMILY PALAU )Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conjugación Del Presente SimpleDokument4 SeitenConjugación Del Presente SimpleCelso Samuel Duran JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente SimpleDokument5 SeitenPresente SimpleJhoan AgamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inglés Modulo 01, Grado 8°Dokument5 SeitenInglés Modulo 01, Grado 8°BallatyMarcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Más InglesDokument6 SeitenMás Ingleskitchen coolNoch keine Bewertungen
- EL PRESENTE SIMPLE EN INGLÉS ValeriaDokument10 SeitenEL PRESENTE SIMPLE EN INGLÉS Valeriaval8val100% (2)
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument6 SeitenEl Presente Simple en InglésManuelANaupayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjugación Del Presente SimpleDokument10 SeitenConjugación Del Presente SimpleCmilla Montoya BalbínNoch keine Bewertungen
- Que Es El Verbo To Be Presente SimpleDokument10 SeitenQue Es El Verbo To Be Presente SimpleJusto Oliver GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clase 3 Simple Present TenseDokument8 SeitenClase 3 Simple Present Tensedjpolhn17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presente SimpleDokument3 SeitenPresente SimplePablo Emanuel MansillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Presente y Pasado Simple en InglésDokument11 SeitenEl Presente y Pasado Simple en InglésJHIMMY QUISPE AGUIRRENoch keine Bewertungen
- Taller de Los Esquemas Oracionales Con El Presente Simple en Inglés Del 15 de Abril de 2020 ClaveDokument7 SeitenTaller de Los Esquemas Oracionales Con El Presente Simple en Inglés Del 15 de Abril de 2020 ClaveYurasit OvallosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resumen de InglesDokument45 SeitenResumen de InglesLuciferGnu SudogroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente Simple en InglésDokument15 SeitenPresente Simple en InglésSantiago Vittorino OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affirmative Sentence2Dokument44 SeitenAffirmative Sentence2Jessica Johanna Carpio BernitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia Didáctica #1 (3° Año) Santo Domingo de Guzman PDFDokument10 SeitenGuia Didáctica #1 (3° Año) Santo Domingo de Guzman PDFAnacaroferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjugación Del Presente SimpleDokument6 SeitenConjugación Del Presente SimpleJuan Domingo García EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retroalimentacion de La Tarea 1 de Ingles 3Dokument2 SeitenRetroalimentacion de La Tarea 1 de Ingles 3Evelin Núñez DilonéNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente SimpleDokument9 SeitenPresente SimpleAlvarez Antonio100% (2)
- Present Simple GuideDokument5 SeitenPresent Simple GuideKAREN DANIELA BERRIO ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument5 SeitenEl Presente Simple en InglésLizandro VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument6 SeitenEl Presente Simple en Ingléssol IzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InglesDokument14 SeitenInglesOrii BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Construcción Del Presente SimpleDokument8 SeitenLa Construcción Del Presente Simplemaria fernanda100% (1)
- Conjugación Del Presente SimpleDokument5 SeitenConjugación Del Presente SimpleEstrélla GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LOS PRONOMBRES PERSONALES Se Usan para Sustituir A Sustantivos de PersonalesDokument8 SeitenLOS PRONOMBRES PERSONALES Se Usan para Sustituir A Sustantivos de PersonalesyomismaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument6 SeitenEl Presente Simple en InglésFelix cuba taipe100% (2)
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument7 SeitenEl Presente Simple en InglésJuan LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presenté SimpleDokument5 SeitenPresenté SimpleJoseRafaelRondonSosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Presente SimpleDokument6 SeitenEl Presente SimplebenjamindomadorxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente SimpleDokument4 SeitenPresente SimpleArturo CasYopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente Simple ExplicaciónDokument4 SeitenPresente Simple Explicaciónfernando gomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- InglesDokument19 SeitenInglesadolfo marinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present SimpleDokument2 SeitenPresent SimplePalito Ortega100% (1)
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument95 SeitenEl Presente Simple en InglésSandoval RoberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tag QuestionsDokument12 SeitenTag QuestionsEduardo CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Simple Present in EnglishDokument6 SeitenThe Simple Present in EnglishAntonio Gil AdrianzenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present PDFDokument6 SeitenSimple Present PDFPablo HanccoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trabajo ColaborativoDokument4 SeitenTrabajo ColaborativolilianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiempos Verbales en InglesDokument40 SeitenTiempos Verbales en InglesCam CamilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gramatica Completa Todos Los TiemposDokument72 SeitenGramatica Completa Todos Los TiemposAna FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente SimpleDokument8 SeitenPresente SimpleSantitos Elvis0% (1)
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument8 SeitenEl Presente Simple en InglésNerelis BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present SimpleDokument6 SeitenPresent SimpleOrqm OscarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pasos para Hacer Una Pagina Web Con Dream WeaverDokument20 SeitenPasos para Hacer Una Pagina Web Con Dream WeaverJavier Cajahuaman MallccoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desarrollo Cognitivo de 2 A 3 AñosDokument5 SeitenDesarrollo Cognitivo de 2 A 3 AñosRodrigo Sucari RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- INGLESDokument15 SeitenINGLESVeronica GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2 (Num. List) - (Nombre de Alumno) - (Grado y Grupo)Dokument9 Seiten4.2 (Num. List) - (Nombre de Alumno) - (Grado y Grupo)evolution123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aspectos Gramaticales - I QuizDokument9 SeitenAspectos Gramaticales - I QuizGeraldine GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Presente Simple en Inglés FacilDokument96 SeitenEl Presente Simple en Inglés FacilHectorDiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiempos VerbalesDokument43 SeitenTiempos Verbalesestrella luja nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles Presente SimpleDokument12 SeitenIngles Presente Simplejqjkyqz4mnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente Simple InglesDokument4 SeitenPresente Simple Inglescamauro10Noch keine Bewertungen
- El Presente Simple en InglésDokument10 SeitenEl Presente Simple en InglésJhonar MagallanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Los Tiempos Verbales en InglésDokument13 SeitenLos Tiempos Verbales en InglésAndreina QuiñonezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjugación Del Pasado, Presente y FuturoDokument6 SeitenConjugación Del Pasado, Presente y FuturoOmarToledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ONPEDokument31 SeitenONPEЛиз Магали0% (1)
- FoncodesDokument11 SeitenFoncodesЛиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reniec - MonografiasDokument27 SeitenReniec - MonografiasЛиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- LA PROVINCIA DE DOS DE MAYO (Autoguardado)Dokument20 SeitenLA PROVINCIA DE DOS DE MAYO (Autoguardado)Лиз Магали100% (1)
- INRENADokument8 SeitenINRENAЛиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles - Presente ProgresivoDokument9 SeitenIngles - Presente ProgresivoЛиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestion de Exportación-Exporta FácilDokument35 SeitenGestion de Exportación-Exporta FácilЛиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acta de Compromiso2Dokument1 SeiteActa de Compromiso2Лиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolución Del Comercio Internacional PDFDokument35 SeitenEvolución Del Comercio Internacional PDFЛиз Магали100% (3)
- La Investigacion MonograficaDokument22 SeitenLa Investigacion MonograficaЛиз Магали100% (1)
- Psicofarmacos y PsicoterapiaDokument31 SeitenPsicofarmacos y PsicoterapiaЛиз Магали100% (6)
- Modalidades de Trabajo en EquipoDokument21 SeitenModalidades de Trabajo en EquipoЛиз Магали0% (1)
- RCP en EmbarazadaDokument21 SeitenRCP en EmbarazadaЛиз Магали100% (3)
- Ingles - Presente ProgresivoDokument9 SeitenIngles - Presente ProgresivoЛиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farmacología Del Dolor y La Inflamación Aines y OpiaceosDokument41 SeitenFarmacología Del Dolor y La Inflamación Aines y OpiaceosЛиз Магали100% (1)
- Pronostico de La DemandaDokument6 SeitenPronostico de La DemandaЛиз МагалиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohidratos MonografiaDokument20 SeitenCarbohidratos MonografiaЛиз Магали67% (12)
- El Fragmento Se Compone de Dos Proposiciones Coordinadas Copulativas Que Forman Una Oración CompuestaDokument2 SeitenEl Fragmento Se Compone de Dos Proposiciones Coordinadas Copulativas Que Forman Una Oración CompuestaFranciscoJoseManasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estadìstica Fútbol - 200Dokument3 SeitenEstadìstica Fútbol - 200miguel henaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trabajo de Ingles IDokument17 SeitenTrabajo de Ingles IKevin VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles 1-4 Possessive Pronouns & AdjectivesDokument5 SeitenIngles 1-4 Possessive Pronouns & AdjectivesRomán FletesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan de Unidades InglesDokument33 SeitenPlan de Unidades InglesFreddy Flores ÁvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (A) Distribución y Estructura Interna de Los Clíticos Del Español Análisis de Cuatro Fenómenos Desde La Morfología Distribuida (Jorge Pérez)Dokument23 Seiten(A) Distribución y Estructura Interna de Los Clíticos Del Español Análisis de Cuatro Fenómenos Desde La Morfología Distribuida (Jorge Pérez)Carlos Alvarado OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles HeidiDokument9 SeitenIngles HeidiVioleta AlguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gramática EspañolaDokument23 SeitenGramática EspañolaGutiérrez Sosa Adolfo CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFRACCIONESDokument19 SeitenINFRACCIONESAbraham LiconaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deportes Alternativos 2018Dokument8 SeitenDeportes Alternativos 2018javimormon1828100% (1)
- Los Sustantivos en AlemanDokument11 SeitenLos Sustantivos en Alemanthyd2lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perífrasis VerbalesDokument1 SeitePerífrasis VerbalesRafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resumen Del Contrato de Leasing - SoriaDokument6 SeitenResumen Del Contrato de Leasing - SoriaGRACIELA ANDREA HUERTA ROJASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicas Comunicacion Semanas 1 Al 6Dokument6 SeitenPracticas Comunicacion Semanas 1 Al 6Stefanny Cárdenas PríncipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verbos en EspanolDokument18 SeitenVerbos en EspanolAnonymous eynRrXPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar 3º BisDokument61 SeitenGrammar 3º BisMapi Canet LlidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Uso Del GerundioDokument9 SeitenEl Uso Del GerundioFacundo Rodriguez CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trivia Regla 12Dokument26 SeitenTrivia Regla 12Yury Rai Carrion Acuña100% (2)
- BALONCESTODokument3 SeitenBALONCESTOFermin PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contrato Bodega de Almacenamiento Con Otro Si MamparaDokument6 SeitenContrato Bodega de Almacenamiento Con Otro Si MamparaNicole EscobarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gramática de Yokot'anDokument63 SeitenGramática de Yokot'anGenaro Israel Ab'äj Vot'an100% (6)
- Verbos Modales en Inglés May y MightDokument2 SeitenVerbos Modales en Inglés May y MightDiany AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 El Sintagma NominalDokument5 Seiten14 El Sintagma NominalChrisi FernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia Ingles Unit 10 11 12 New American Inside Out Pre Intermediate PDFDokument50 SeitenGuia Ingles Unit 10 11 12 New American Inside Out Pre Intermediate PDFDaniel RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Articulo Indeterminativo - ItalianaDokument4 SeitenArticulo Indeterminativo - ItalianaEdna Deyanira Cruz JuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taller 3 Gramatica SextoDokument8 SeitenTaller 3 Gramatica SextoDubier Armando Chamorro Ramirez0% (1)
- Futasal 2Dokument4 SeitenFutasal 2JuanitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puntuación y TildaciónDokument10 SeitenPuntuación y TildaciónJhair OlaveNoch keine Bewertungen