Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sweet & Karen Review and Tutorial Center No. 82 Zone 1, Estancia Malinao, Albay Cp. No. 09109436343
Hochgeladen von
Dominic Careo0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
22 Ansichten6 SeitenFundamental of mathematics LET review 2018
Originaltitel
Math Handout
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenFundamental of mathematics LET review 2018
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
22 Ansichten6 SeitenSweet & Karen Review and Tutorial Center No. 82 Zone 1, Estancia Malinao, Albay Cp. No. 09109436343
Hochgeladen von
Dominic CareoFundamental of mathematics LET review 2018
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
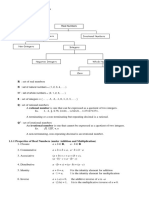
Sweet & Karen Review and Tutorial Center e.
Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition/ Subtraction- States that
No. 82 Zone 1, Estancia Malinao, Albay multiplication distributes over addition and subtraction
Cp. No. 09109436343 Eg. 5( 7+14)= (5)(7) + (8)(14)= 147
III. Operation on Integers
General Education : Mathematics a. Addition- Like signs: add the absolute values, and prefix the negative sign if the
May 11, 2018
addends are negative
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
Unlike signs: get the absolute values of the numbers and subtract the
Lecturer: Neil Dominic D. Careo
smaller absolute value from the other and prefix the negative sign if the
I. The Number System negative addend has the larger value
Eg. -12 + (-6)= -18 -3+11= 11-3= 8 5 + (-9)= -(9-5)= -4
Imaginary
Complex b. Subtraction- If the minuend and subtrahend are both positive and the minuend is
Irrational
greater than the subtrahend, proceed to subtract forthwith. Otherwise, change the
Real Non-integers Counting
sign of the supposed subtrahend and proceed as in addition
Rational
Eg. 12 – 7 = 5 4 – 11 = 4+ -(11)= -7
Integers Zero c. Multiplication (Division)- to multiply (or divide) two integers with
Like signs: get the product (or quotient) of their absolute values
Negative Unlike signs: get the negative of the product (or quotient) of their absolute values
II. Number Properties Eg. -9 x -12 = -108 -3 x 7 = -21 12/-4 = -3
a. Closure Property- When adding or multiplying any element in a set of numbers, IV. Divisibility Rules
the sum or product is a unique real number which belongs to that same set
Divisibility by Rule
Eg. 20+5+18+47= 90 18 x 21 x 10 = 3,780
b. Commutative Property- States that changing the positions of the addends or the 2 If the last number is an even number Eg. 2, 4, 6, 8…
factors does not affect the sum or the product 3 If the sum of all individual digits in the number is divisible by 3
Eg. 25+ 52= 52+25 7 x 8= 8 x 7 4 If the last two digits of the number is divisible by 4
c. Associative Property- States that changing the grouping of addends in a sum or
5 If the last digit of the number is 0 or 5
grouping of factors in a product does not change the resulting sum or product
Eg. (10+ 7) +3= 10+ (3+7) 3 x ( 4x 5 )= (3 x 4 ) x 5 6 If the number is even and divisible by 3
d. Identity Property 7 Double the last digit. Subtract the doubled last digit from the number without the
Addition: The sum of any number and zero is the same number. 0 is the identity last digit. If the difference is a multiple of 7, then it is divisible by 7
Eg. 100+0= 100 8 If the last three digits of the number is divisible by 8
Multiplication: The product of any number and one is the same number. 1 is the 9 If the sum of the individual digits in the number is divisible by 9
identity Eg. 50 x 1= 50
10 If the last digit of the number is 0
11 If after subtracting and adding the digits successively the result is divisible
by 11
Fractions- defined as a quotient or ratio of two numbers
Prime and Composite Numbers Kinds of Fractions
Prime Number- counting number that has exactly two factors, 1 and itself As to relation between the numerator and denominator
Eg. 2, 3, 5, 7, 13, 17, 19, … a. Proper Fraction- the numerator is less than the denominator eg. 5/9
Composite number- counting numbers that has more than two factors b. Improper Fraction- the numerator is greater than the denominator eg. 12/7
Eg. 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15… As to relation of the denominators of two or more fractions
(1 is neither prime or composite and 2 is the only even prime) a. Similar Fraction- the denominators are equal eg. 2/5 and 4/5
Prime Factorization- is finding which prime factors if multiplied together will result to the b. Dissimilar Fraction- the denominators are not equal eg. 3/7 and 4/9
original number Other Classes
Methods: a. Equivalent Fraction- Fractions having the same value eg. 4/5 and 8/10
a. Repeated division by primes b. Mixed Fraction- composed of whole number and a proper fraction eg. 7 2/3
b. Factor tree Reducing Fractions to Lowest Terms
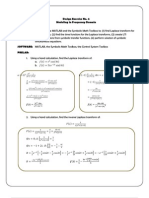
Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 2 numbers [a, b ] is the smallest number that is divisible Principle: Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same number
by a and b at the same time. The smallest number that is multiple of the given numbers. does not change the value of the fraction
Methods: Rule: To reduce fraction into lowest term , divide both the numerator and the
a. Intersection of sets method denominator by their GCF
Eg. 9: {9, 18, 27, 36} Eg.
13
÷
13 1
=
80
÷
10
=
8
24: {12, 24, 36, 48} 65 13 5 130 10 13
Operations on Fractions
b. Prime Factorization Method- write the prime factorization for each of the given
1. Addition (Subtraction) of Fractions
numbers so that common and only common factors are in the same column. The
Similar- Add (Subtract) their numerator and copy their denominator , then
LCM is the product of the highest powers occurring in a column of any of the prime
reduce the sum to its lowest term.
factorizations
13 5 18
Eg. 9: 32 Eg. + =
7 7 7
24: 3 x 22 Dissimilar- Change the dissimilar fractions to similar fractions by doing these
32 x 22= 36 (LCM) steps
Greatest Common Factor/Divisor (GCF or GCD) of two numbers (a , b ) is the largest a. Find the LCD( Least Common Denominator). The LCD is the LCM of the
factor or divisor common to both a and b Denominator
Eg. Find the GCF of 18 and 24 b. Divide the LCD by each denominator then multiply the quotient by the
a. Intersection of sets method numerator
18: {2, 3, 6, 9, 18} c. The resulting value in step b are the numerators of the similar fractions
24: {2, 3, 6, 8, 12, 24} and the LCD is the denominator
b. Prime Factorization d. Add (Subtract) the resulting fractions and reduce the result to its lowest
18: 2 x 32 term
24: 23x 3 4 8 28+40 68
Eg. + = =
2 x 3 = 6 (GCF) 5 7 35 (𝐿𝐶𝐷) 35
c. Euclidean Algorithm/ Division Method
2. Multiplication- Multiply the numerators together, and multiply the a. Terminating Decimals- Multiply by a fraction the numerator and
denominators together, then reduce the product to its lowest term denominator of which both are equal to such power of ten with as
Eg.
4 3
𝑥 =
4𝑥3
=
1 many zeroes as there are decimal places in a given decimal, and then
9 8 9𝑥8 6 1000 625 5
simplify. Eg. 0.625 x 1000= 1000 = 8
3. Division- the quotient of two fractions is the product of dividend and the
reciprocal of the divisor b. Repeating Decimals- The procedure is outlined below together with
9 1 9𝑥3 27 an example to illustrate each step. Eg. To convert x= 0.166
eg. ÷ = = 1. Multiply the number by such power of 10 as would move one
5 3 5𝑥1 5
repeating portion across the decimal point. 100x = 1.66
V. Power and Exponents 2. Multiply the number by such power of 10 as would move the
Important concepts involving powers and exponents repeating portion across the decimal point 10x = 1.66
1. 10 x 10 = 100 or 102 3. Subtract the result of step 2 from step 1 90x = 15
2. 10 x 10 x 10 = 1000 or 103 4. Simplify 90x = 15 x= 15/90= 1/6
3. 10 x 10 x 10 x10 10 000 or 104 VII. Ratio and Proportion
A shorter way of writing 10 x 10 is 102 , the exponential form Ratio- is a comparison of two numbers and is generally separated by a colon :
In the exponential form 102, the number 10 is called the base and the Eg. Grace has a bag with 3 videocassettes, 4 marbles, 7 books, and 1 orange.
number 2 on the upper right hand corner of the base is called the 1. What is the ratio of books to marbles?
exponent 2. What is the ratio of videocassettes to the total number of items in the
Rules: bag?
a. Any number raised to the first power is that number eg. 101 = 10 Proportion- is an equation with a ratio on each side. It is a statement that two
b. Any non-zero whole number raised to zeroth power is equal to 1 ratios are equal
Eg. 1000= 1 Format: a/b = c/d or a:b=c:d
c. In multiplying numbers having the same base, simply copy the base Kinds of Proportions
and then add the exponents eg. 34 + 32 = 3(4+2)= 36= 90 1. Direct Proportion- when one quantity increases/decreases the other
d. In dividing two numbers having the same base, simply copy the base quantity increases/decreases also
and then subtract the exponent eg. 25 ÷ 22= 2(5-2)= 23= 8 Eg. Mother uses 2 cans of milk to 5 glasses of water. How many cans of
VI. Conversions milk does she need if she has 15 glasses of water?
1. Fractions to Decimals Solution: 2 milk : 5 water = N : 15 water
Divide the numerator by the denominator eg. 5/8 = 0.625 5N = 30 , N= 6 cans of milk
2. Decimals to Percents 2. Inverse Proportion- when one quantity increases/decreases the other
Multiply by 100% or move the decimal point two places to the right and quantity will have an opposite change.
add the % sign. Eg. 0.625= 0.625 x 100 = 62.5% Eg. If 10 men can finish painting the building in 8 days, how many men are
3. Percent to Decimals needed to finish the same work in 5 days?
Divide by 100% or drop the % sign and move the decimal point two Solution:
places to the left. Eg. 62.5% = 0.625 1. Determine the large and small numbers
4. Decimals to Fractions (small) 10 men - 8 days (large)
(large) N men – 5 days ( small)
2. Equate the small as well as the large numbers IX. Elementary Algebra
𝑆𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑆𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙 Basic Terms
=
𝐿𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 𝐿𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 Variable- any symbol that is used to represent an element of a set e.g. x, y
10 5 80 Domain- the set of all elements represented by a particular variable
= 5𝑁 = 80 𝑁= = 16 𝑚𝑒𝑛
𝑁 8 5 Constant- a symbol with only one element in its domain eg. 3, -2, π
3. Partitive Proportion- a number is divided into parts proportional to the
Algebraic Expression- a constant, a variable, or any combination of constant and
ratio of the other numbers
variables involving indicated operation (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division,
Eg. I have 50 candies. I will give my candies to John, Brian, and
raising to a power, or extraction of a root) on them.
Dominick in the ratio of 2:3:5 . How many marbles will each of my
Eg. 25x2-1 , 2xy + y2, x-y((x-y)/4)
friends get?
Polynomial- an algebraic expression consisting only of non-negative integer powers
Solution: Step 1: Get one part of the ration, Let N be that one part
of variables, and with no variable in a denominator. Among the examples of the
2N be the share of John
algebraic expression above, only the last is not polynomial.
3N be the share of Brian
Term of a Polynomial- a constant or a constant multiplied by non- negative integer
5N be the share of Dominick
powers of variables. A polynomial with only 1 term is monomial, polynomial with 2
2N + 3N + 5N = 50
terms is binomial and polynomial with 3 terms is trinomial
10N= 50 , N= 5
Eg. -15x2y3z4 monomial
Step 2 : Get the share of each 2 2
X -3y + xy trinomial
John= 2(5)= 10 Brian = 3(5)= 15 Dominick= 5(5)= 25
Numerical Coefficient- that constant that is multiplied by the non negative powers of
VIII. Rate, Base, and Percentage
variables in a term
Eg. 35% of 50 = 17.5
Literal Coefficient- the non- negative powers of variables in a term
Percentage is a certain percent of a number, or part taken from a
Similar Terms- terms with the same literal coefficient. If the terms are not similar, they
whole
are said to be dissimilar
Base is a number from where a certain percent is to be taken out, or
Degree of Term- sum of exponents of all variable factors of a term
the total or whole quantity from where a part is taken. It usually
Evaluating Algebraic Expressions- refers to the process of finding the value of the
follows “ % of” or “percent of”.
expression upon substitution of the given values for the respective variables
Rate is a number with percent symbol (%) or percent to be taken from
Eg. Evaluate x2y3 -2y2 + 4 when x= -2 y= 3
the whole quantity. 2 3 2
(-2) (3) -2(3) +4 = 94
To find the rate, base and percentage
Equation- statement expressing in symbols the relationship of equality between two
1. Percentage= rate x base
quantities
Eg. 20% of 60 = N
Linear Equation in one variable- an equation that can be written in the form ax+b=0,
0.20 x 60 = 12
where a and b are constants and a<0 eg. 3x – 4 = 0 4 – 2x = 3x + 5
2. Rate= Percentage/ base
Addition and Subtraction Property of Equality (APE, SPE)
Eg. N% of 80 is 20
If a,b, and c are real numbers and a = b, then
20/80= 0.25= 25%
a+c=b+c
3.Base= Percentage/ rate
a–c=b–c
Eg. 25% of N = 30
= 30/0.25= 120
Multiplication and Division Property of Equality (MPE, DPE) X. Inequalities
If a, b, and c are real numbers and a=b , then Inequalities- a statement that says one quantity is less than (<) or greater than (>)
axb=bxc another. In some instances, one quantity may be less than or equal to (≤) or greater
a/b = b/c than or equal to (≥) another.
Solution of an Equation- refers to an element of the domain of the variables that Compound Inequality- a compound statement that says one quantity is less than (or
makes the equation true greater than) another but is greater than (or less than) a third eg. -4 < 2x -3 ≤9
Solving Linear Equations- refers to the process of finding, through the use of the Properties of Inequality
properties of equality, all solutions of the equation 1. Trichotomy- If a and b are real numbers, then a < b , and a = b, or a> b
Some pointers in solving linear equations 2. Transitive- if a< b and b < c , then a< c
1. Simplify each side of the equation by If a>b and b>c, then a> c
-Removing grouping symbols using the distributive law 3. Addition Property- If a ,b and c are real numbers and a<b, then a+c < b + c
-Removing fraction by multiplying both sides of the equation by the LCD of all Solution of a Linear Inequality- the process of finding, through the use of the
fractions properties of inequality, all the solution of the inequality.
2. Use the APE/SPE to have all variables only on one side of the equation and the Eg. -4 ≤ 2x – 3 ≤ 9
constants on the other eg. Simplify 3(5x + 2)= 2x-5 -4 + 3 ≤ 2x – 3 + 3 ≤ 9 + 3
Solving word problems involving linear Equations Steps -1 ≤ 2x ≤ 12 -1/2 ≤ x ≤ 6
1. Read the problem carefully Word Problems Involving Linear Inequalities
2. Determine what is to be found Example- Patrichia’s grades in the last four tests were 85, 89, 90, 93. What must be her
3. Choose a variable to represent an unknown, usually that which needs to be found grade in the fifth and last test to get an average of at least 90?
4. Translate word phrases to algebraic expression XI. Plane Geometry
5. Formulate the equation Basic Geometric Elements
6. Solve the equation 1. Point- a dimensionless geometric figure having no properties other than location
7. Solve the problem or space
Example: Four times the sum of a number and four is 24. What is the number 2. Line- the shortest distance between any two points
Let x= unknown number 4( x+4) = 24 3. Angle- the opening between two lines or two planes that meet. The point where
4x + 16= 24 the two lines meet is called the vertex.
4x= 8 x= 2 Types:
Example: Cardo is twice as old as Joaquin. Two years ago, Cardo is three times as old a. Null or zero angle- equal to zero
as Joaquin. Find their ages now. b. Acute Angle- greater than 0 but less than 90○
Let c= age of Cardo j= age of Joaquin c. Right Angle- equal to 90○
c = 2j d. Obtuse Triangle- greater than 90○ but less than 180○
c – 2 = 3 ( j – 2) e. Straight Angle- equal to 180○
2j – 2 = 3( j – 2) f. Reflex Angle- greater than 180○ but less than 360○
4= j= present age of joaquin g. Full Angle or Perigon- equal to 360○
4(2)= 8 present age of Cardo Other Types of Angles
a. Adjacent angles- two angles with a common leg
b.Complementary Angle- two angles whose sum is a right angle (90○)
c.Supplementary Angles- two angles whose sum is a straight angle (180○)
d.Explementary Angles- two angles whose sum is a perigon (360○)
e.Vertical Angles- angles formed by two intersecting lines. Vertical angles are
equal.
Perimeter- is the distance around the outside of a polygon or any closed curve
Area- of a simple, closed , planar curve is the amount of space inside
Volume- of a solid 3D shape is the amount of space displayed by it.
References:
1. 1001 Solved Problems in Mathematics, 3rd ed., Excel Council,
2008
2. www. Varsitytutors.com
3. www.mathisfun.com
4. Cayago, Ma. Jessa V., “Fundamentals of Mathematics”, 2017
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellDokument14 SeitenChapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellAveen ShabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Manual Principles of Highway Engineering and Traffic Analysis Mannering Fred L 4th EdnDokument344 SeitenSolutions Manual Principles of Highway Engineering and Traffic Analysis Mannering Fred L 4th EdnMalik Zain50% (2)
- SST6Dokument12 SeitenSST6JT3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter OverviewDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Chapter OverviewJun ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- SST 6 Chapter 4 OutlineDokument13 SeitenSST 6 Chapter 4 OutlineGail AidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Concepts and CalculationDokument46 SeitenMathematics Concepts and CalculationNoemi Rosario SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Math Concepts ACTDokument17 Seiten100 Math Concepts ACTAyushGourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book For CBRCDokument76 SeitenBook For CBRCMonica Grace P. Guia100% (1)
- Numbers and Basic Operation in MathDokument29 SeitenNumbers and Basic Operation in MathAndang RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 3 Geometric SequencesDokument19 SeitenMathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 3 Geometric SequencesLyle Isaac L. IllagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary Algebra EducationDokument73 SeitenSecondary Algebra EducationDjuwita PekanbaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Gened Reviewer 1Dokument17 SeitenMath Gened Reviewer 1Julybee Latog Ines100% (2)
- DC 2Dokument97 SeitenDC 2mushagraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Vocabulary and Common SymbolsDokument11 SeitenMath Vocabulary and Common SymbolsMd Mohiyul Islam100% (1)
- Math8 Summative Test Q1 wk3 4 2021 2022Dokument2 SeitenMath8 Summative Test Q1 wk3 4 2021 2022sdasdasd123aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan for Geometry BasicsDokument8 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan for Geometry BasicsGlenn ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Information::: Form 1 - Embv - SWM - MRFDokument3 SeitenBasic Information::: Form 1 - Embv - SWM - MRFDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Locked Loops For Wireless CommunicationsDokument434 SeitenPhase Locked Loops For Wireless Communicationscnt2ssk100% (1)
- Novmeber 2018 ChE Licensure ExamDokument9 SeitenNovmeber 2018 ChE Licensure ExamDominic Careo100% (1)
- Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Math ExamDokument4 SeitenRepublic of the Philippines Department of Education Math ExamChristine Joy E. Sanchez-CasteloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book For CBRCDokument76 SeitenBook For CBRCFrelen Lequinan100% (1)
- Linear Programming IDokument42 SeitenLinear Programming IBong NepoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Middle School Number Theory TermsDokument10 SeitenMiddle School Number Theory TermsGaluh JgsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fraction Cheat Sheet Math 8Dokument1 SeiteThe Fraction Cheat Sheet Math 8txcrudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FractionsDokument2 SeitenFractionsapi-259421821Noch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Bits of Life 1Dokument1 Seite100 Bits of Life 1Jennifer CollinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- SST6Chapter23outline PDFDokument28 SeitenSST6Chapter23outline PDFBee BeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unlike Denominators OrganizerDokument2 SeitenUnlike Denominators OrganizerdburrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- FractionsnotessheetDokument2 SeitenFractionsnotessheetapi-293306021Noch keine Bewertungen
- 101 Golden PointsDokument27 Seiten101 Golden PointsSudheer AravapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYLLABUS For MAT091 Basic Math SkillsDokument9 SeitenSYLLABUS For MAT091 Basic Math SkillsIan Bernales OrigNoch keine Bewertungen
- SST6Chapter25outline PDFDokument17 SeitenSST6Chapter25outline PDFRosemarie CatanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Tips For IV SolutionsDokument1 SeiteQuick Tips For IV Solutionsjames baeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Numbers PDFDokument18 SeitenClassification of Numbers PDFAmarnadh100% (2)
- Word Families Building PossibilitiesDokument13 SeitenWord Families Building PossibilitiesHoàng Anh DũngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Between Improper Fractions and Mixed NumbersDokument6 SeitenConverting Between Improper Fractions and Mixed NumbersAbdelnasir HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Dokument3 SeitenFind + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Pherngy CadanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEMathDokument140 SeitenGEMathAlvin NaagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2Dokument7 SeitenLesson 2Saalivaahanan BaskaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Fundamental Concepts in AlgebraDokument32 SeitenModule 1 Fundamental Concepts in AlgebraquigaojoanneNoch keine Bewertungen
- LET Mathematics Refresher Course on Number Properties and TheoryDokument28 SeitenLET Mathematics Refresher Course on Number Properties and TheoryVe Jay Angela Guimte0% (1)
- Integers - Definition, Rules, Properties and ExamplesDokument10 SeitenIntegers - Definition, Rules, Properties and ExamplesAyaan Ali FayyazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Class 2022 Handouts (Elem)Dokument16 SeitenSummer Class 2022 Handouts (Elem)Jeremy B. MotusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numbers and Basic Operation in MathDokument29 SeitenNumbers and Basic Operation in MathASYAFANoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiplication and Division RulesDokument14 SeitenMultiplication and Division RulesodylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integer Operations: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and DivisionDokument33 SeitenInteger Operations: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and DivisionggvgrrrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5 Math 7Dokument13 SeitenWeek 5 Math 7Jomar GregorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Materials - Gen MathDokument28 SeitenReviewer Materials - Gen MathJuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math7 Q1 SLM WK4Dokument11 SeitenMath7 Q1 SLM WK4RheaMaeDeLeonAntiguaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integer OperationsDokument16 SeitenInteger OperationsNico ValeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Louis College Project Explores Fractions, Integers and Real NumbersDokument10 SeitenSt. Louis College Project Explores Fractions, Integers and Real NumbersFrancisca DankwahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numbers and PropertiesDokument7 SeitenNumbers and PropertiesPOke wOrlDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 7 Week 4 KURT CLARENCE REPALDADokument15 SeitenMath 7 Week 4 KURT CLARENCE REPALDAJubs codesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Calc Review of Fundamentals Part 1 2018-07-30Dokument397 SeitenPre Calc Review of Fundamentals Part 1 2018-07-30reynandcpcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Bridging TransesL1Dokument6 SeitenMath Bridging TransesL1Ara Belle PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 - All Chapter Notes - Math ByjuDokument136 SeitenGrade 7 - All Chapter Notes - Math ByjuArnav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DISCUSSDokument4 SeitenDISCUSSNorsaifah AbduljalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALGEBRA 1: 1.4-Numerical Properties & ExpressionsDokument4 SeitenALGEBRA 1: 1.4-Numerical Properties & ExpressionsCaty LiesekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeaP Math G4 Week 5 Q3Dokument4 SeitenLeaP Math G4 Week 5 Q3Imats MulintapangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer For Mathematics 7 1st Quarter Examination 1Dokument1 SeiteReviewer For Mathematics 7 1st Quarter Examination 1Giana ClouieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dealing Down ProjectDokument4 SeitenDealing Down Projectapi-254467161Noch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidated Learner Guide - Mathematics in The Modern WorldDokument109 SeitenConsolidated Learner Guide - Mathematics in The Modern WorldPutang InaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Unit 1A PreCalc ConceptsDokument9 SeitenModule 1 Unit 1A PreCalc Conceptskorleon gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: Integers: Here's My Notes Aha Aha:dDokument7 SeitenMathematics: Integers: Here's My Notes Aha Aha:dMyst EryNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Education SummaryDokument24 SeitenGeneral Education SummaryJenna Marie TolosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INSTRUCTIONS: Solve The Problems by Finding The Product of The Following IntegersDokument6 SeitenINSTRUCTIONS: Solve The Problems by Finding The Product of The Following IntegersGenevieve MelgazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sifat Operasi Bilangan BulatDokument15 SeitenSifat Operasi Bilangan BulatNadila IntsaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlgebraDokument9 SeitenAlgebraJulpritz DecenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 - ch01 - l6.ppt (Donea)Dokument25 SeitenA1 - ch01 - l6.ppt (Donea)Luan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math ReviewerDokument4 SeitenMath ReviewerRhian Mae SibuganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sakit Sa EyesDokument8 SeitenSakit Sa EyesJohn Ray BacaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 NotesDokument2 SeitenLesson 5 NotesDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERM EXAM 2020 - MS BEM - Oct 17, 2020Dokument1 SeiteMIDTERM EXAM 2020 - MS BEM - Oct 17, 2020Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAREO, Neil DominicDokument1 SeiteCAREO, Neil DominicDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Technology and Human ValuesDokument44 Seiten9 Technology and Human ValuesDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS BEM 208 Environmental Impact AssessmentDokument12 SeitenMS BEM 208 Environmental Impact AssessmentDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concept of Waste and Waste ManagementDokument9 SeitenThe Concept of Waste and Waste ManagementMaJakobsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Critical ReviewsDokument2 SeitenWriting Critical ReviewsDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can You Tell Fake News From Real News?Dokument7 SeitenCan You Tell Fake News From Real News?Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 - Information AgeDokument26 SeitenLesson 5 - Information AgeDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Article: Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste Management System in A Developing CountryDokument12 SeitenResearch Article: Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste Management System in A Developing CountryDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TourismDokument41 SeitenTourismDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Phi EiaDokument82 Seiten01 Phi EiaChilleMae100% (1)
- Writing Critical ReviewsDokument2 SeitenWriting Critical ReviewsDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esp LogoDokument1 SeiteEsp LogoDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Guide - Res - CVCJRDokument6 SeitenCourse Guide - Res - CVCJRDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS BEM 208 Midterm EIA Process ComparisonDokument8 SeitenMS BEM 208 Midterm EIA Process ComparisonDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 ODCD (LGU LEGAZPI)Dokument7 SeitenForm 2 ODCD (LGU LEGAZPI)Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERM EXAM 2020 - MS BEM - Oct 17, 2020Dokument1 SeiteMIDTERM EXAM 2020 - MS BEM - Oct 17, 2020Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 - EMBV SWM ODCD DetailsDokument3 SeitenForm 2 - EMBV SWM ODCD DetailsDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Japan's Environmental Impact AssessmentsDokument1 SeiteJapan's Environmental Impact AssessmentsDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Impact Assessment in Japan PresentationDokument22 SeitenEnvironmental Impact Assessment in Japan PresentationDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 – EMBV – SWM – SLFDokument5 SeitenForm 4 – EMBV – SWM – SLFDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 3 TRCA (LGU Legazpi)Dokument2 SeitenForm 3 TRCA (LGU Legazpi)Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Consuming Equipment/Tools, Etc.: List of City Property/Plant/Equipment Serviceable/Operational For Cy 2018Dokument1 SeiteElectric Consuming Equipment/Tools, Etc.: List of City Property/Plant/Equipment Serviceable/Operational For Cy 2018Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entity Level GHG Survey (2019)Dokument2 SeitenEntity Level GHG Survey (2019)Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sagumayon River Annual Assesment 2014 TNRDokument8 SeitenSagumayon River Annual Assesment 2014 TNRDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Sample ProblemsDokument1 SeitePhysics Sample ProblemsDominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Philippine Petrochemical Industry Profile: H.S. Code Description MFN Rate (%) ATIGA (%)Dokument6 SeitenThe Philippine Petrochemical Industry Profile: H.S. Code Description MFN Rate (%) ATIGA (%)Dominic CareoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Instructional MaterialsDokument4 SeitenFinal Instructional MaterialsMharaTootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Structure Systems With Sliding ModesDokument11 SeitenVariable Structure Systems With Sliding ModesNguyen Quang VinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cubic EquationsDokument2 SeitenCubic EquationsPaula FanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1 Derivation and Exact Solution of Heat Conduction EquationDokument2 SeitenExercise 1 Derivation and Exact Solution of Heat Conduction Equationprashant_salima6377Noch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Equations The Algebra That Almost Kills CalculusDokument71 Seiten100 Equations The Algebra That Almost Kills CalculussmeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math g5 m6 Full ModuleDokument496 SeitenMath g5 m6 Full ModuleLynor PeregrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Pharmacy IY - R17 - Remedial Maths PDFDokument2 SeitenB.Pharmacy IY - R17 - Remedial Maths PDFrajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical modeling: An introductionDokument8 SeitenNumerical modeling: An introductionCorey HeffernanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Mathematics - SyllabusDokument3 SeitenBusiness Mathematics - SyllabusTashfeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3 Linear Equations X Maths 2021Dokument30 SeitenCH 3 Linear Equations X Maths 2021Kavya YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- University Department of Mathematics Sido Kanhu Murmu University DumkaDokument20 SeitenUniversity Department of Mathematics Sido Kanhu Murmu University Dumkaanahh ramakNoch keine Bewertungen
- En Cours 2018 Lepl1102Dokument2 SeitenEn Cours 2018 Lepl1102Airton MotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isc Test Paper 1 Dated 06.01.2024Dokument4 SeitenIsc Test Paper 1 Dated 06.01.2024bangcash138Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Equation JEE MAINDokument6 SeitenQuadratic Equation JEE MAINAnshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulike Maths PDF 4Dokument25 SeitenUlike Maths PDF 419sharmaharsh80Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDESoranUniversity PDFDokument24 SeitenPDESoranUniversity PDFAram Nasih MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 6Dokument8 SeitenExercise 6Trixie CamachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer All Questions in This Section.: Pra Pentaksiran Mathematics T Semester 2 954/2 2019 RestrictedDokument2 SeitenAnswer All Questions in This Section.: Pra Pentaksiran Mathematics T Semester 2 954/2 2019 RestrictedRex KalNoch keine Bewertungen
- WMA01 01 Que 20150113 PDFDokument44 SeitenWMA01 01 Que 20150113 PDFmunzarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Ostwald Ripening and Their ApplicationsDokument32 SeitenTheories of Ostwald Ripening and Their ApplicationsElla AwaltanovaNoch keine Bewertungen