Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tripartite Synapse
Hochgeladen von
Yusuf JunetCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tripartite Synapse
Hochgeladen von
Yusuf JunetCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
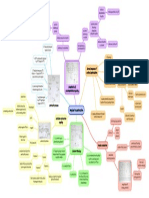
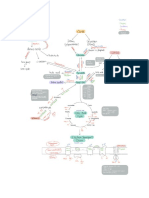
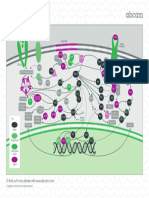
The Tripartite Synapse III.
Glial Cell
I. Presynaptic Neuron A. Astrocyte
Nerve Ending Releases Transmitter
reuptake
Myhea
S
reuptake
eli th
n
blockade
Glutamate
uptake by transporter
+ (GFAP)
Illustration by: Kendra Scouten
Na
Glial
Glutamate Growth Fibrillary
Factors Acidic
Kainate
Transmitter Receptor Protect Glucose Protein
a marker of
Nourish glia activation
Modulate
AMPA Receptor Neurosteroid
Na+ Biosynthesis
Mg++
II. Post Synaptic B.
PSD NMDA Receptor Micro-Glia
Neuron with
Glutamate ↑ Ca++
Receptors
CaMKII
Bz
Second Receptor
Messengers GABA receptor
Ca++
Golgi release synapse formation
Kinases
Cl- sprouting
Transcription
Transcription Factors
Factors
ea s .
Mitochondria
mRNA
ll d l v
th
C.
ce viva
DNA
r
Oligo-
su
Endoplasmic
Reticulum dendrocyte
Endoplasmic
Reticulum
for new myelin
Peptides
Protein
CRH vs.TRH
Synthesis Axon of
Neuron II
Legend:
The Tripartite (three-part) Synapse involves: I) a presynaptic axon of neuron I (orange, top left) releasing transmitters to activate
(glutamate) or inhibit (GABA-Bz) activity of the II) post-synaptic neuron (yellow, middle). The third critical component is III) the glial
cell (pink, top right), an (A) astrocyte which protects cells by taking up glutamate to prevent overexcitation and secretes growth
factors; provides energy via glucose; and modulates receptor (R) function with the generation of neurosteroids (which interact
with Bz-GABA receptors and NMDA receptors. Other (B) microglia secrete cytokines and scavenge cellular debris; while (C)
oligodendrocytes make the myelin necessary to insulate the axons of neurons to insure good conductivity. The myelin sheath
breaks down in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and now there is evidence of oligodendroglia dysfunction in bipolar illness and failure in
late stages of schizophrenia. CaMK-II is the major calcium ion (Ca++) sensor of the neuron involved in up or down regulation of
synaptic excitability necessary for short and long term memory. It is decreased in bipolar illness.
The neurons (I and II) and glia (III) of parts of the prefrontal cortex appear deficient in number and function. Lithium increases the
survival and production (neuro-glia genesis) of both cell types!
Abbreviations:
Na++, sodium ion; Mg++, magnesium; NMDA, AMPA, and kainate are three types of glutamate receptors in the postsynaptic
density (PSD); Ca++, calcium ion; CaMKII, calcium calmodulin kinase-II; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; Bz, benzodiazepine;
Cl-, chloride ion; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AMPKDokument2 SeitenAMPKDavid Robin100% (1)
- NHB SuppoDokument11 SeitenNHB SuppoAna-Roberta NitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Pain and OpioidsDokument38 Seiten2019 Pain and Opioidsgowod86101Noch keine Bewertungen
- T Cell Receptor Signaling: F-A CtinDokument2 SeitenT Cell Receptor Signaling: F-A CtinOlgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Https - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 16 Fly DLB 00061 Eng Notch PW Handout SMDokument2 SeitenHttps - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 16 Fly DLB 00061 Eng Notch PW Handout SMtamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnenolone Trial in Autism-A Neurosteroid Approach 2016Dokument23 SeitenPregnenolone Trial in Autism-A Neurosteroid Approach 2016redmi karimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notch SignalingDokument2 SeitenNotch SignalingMelanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 6Dokument16 SeitenSession 6Stella ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- View Large - AccessMedicine - McGraw-Hill MedicalDokument3 SeitenView Large - AccessMedicine - McGraw-Hill Medicalمحمد ضياءNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akt PKBDokument1 SeiteAkt PKBCarl DonaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ticagrelor - Changing Paradigm in ACS ManagementDokument42 SeitenTicagrelor - Changing Paradigm in ACS ManagementBudi WirawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ViruzhinkiDokument20 SeitenViruzhinkiЕгор ЧудовскийNoch keine Bewertungen
- Https - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 15 Fly Alzh Ref m096 Eng 00 Alzheimers PW Handout DigitalDokument2 SeitenHttps - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 15 Fly Alzh Ref m096 Eng 00 Alzheimers PW Handout DigitaltamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kasus Soca CitraDokument4 SeitenKasus Soca CitraPentolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akt PKBDokument1 SeiteAkt PKBmilenerato2240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry by DR - AzamDokument98 SeitenBiochemistry by DR - AzamArrya DSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument11 SeitenUnit 3s17010324Noch keine Bewertungen
- BioBiochem Lesson 1 in CC 1 Student May 2 12 (Dragged)Dokument1 SeiteBioBiochem Lesson 1 in CC 1 Student May 2 12 (Dragged)DSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amyloid Plaque and Neurofibrillary Tangle Formation in Alzheimer's DiseaseDokument2 SeitenAmyloid Plaque and Neurofibrillary Tangle Formation in Alzheimer's DiseaseMelanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) : S. V. MakeshDokument22 SeitenATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) : S. V. MakeshAnonymous jdC36sKP57Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notch Signaling - Cell Signaling TechnologyDokument3 SeitenNotch Signaling - Cell Signaling Technologyasadbiotech4Noch keine Bewertungen
- mTOR Signaling PathwayDokument1 SeitemTOR Signaling PathwayRichard WooliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- USFDA Approved PKIsDokument19 SeitenUSFDA Approved PKIsAnamaria IuoraşNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Metabolic Map Lipids Part Two Illustration AtfDokument1 SeiteThe Metabolic Map Lipids Part Two Illustration AtfJoax Wayne SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Points For DigestionDokument2 SeitenImportant Points For Digestionaaravrshah14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Urea CycleDokument10 SeitenUrea CycleSragwin ThridhamnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - 3 - Impulse To ContractionDokument1 Seite1 - 3 - Impulse To ContractionislisnovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism MapDokument1 SeiteMetabolism Mapyinose7198Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Respiration FlowchartDokument1 SeiteCellular Respiration FlowchartAndrew100% (5)
- Alfonzo 2006Dokument29 SeitenAlfonzo 2006Walid HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geological Map of KliripanDokument1 SeiteGeological Map of KliripanSi GoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaplan AnatomyDokument1 SeiteKaplan AnatomyBeto RendonNoch keine Bewertungen
- G Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Adenylyl Cyclase: Ligand BindingDokument3 SeitenG Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Adenylyl Cyclase: Ligand BindingPanda DaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Receptorial Signaling Pathway of InsulinDokument1 SeiteReceptorial Signaling Pathway of InsulinsdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current MI Rabies MapDokument1 SeiteCurrent MI Rabies MapWDIV/ClickOnDetroitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current MI Rabies MapDokument1 SeiteCurrent MI Rabies MapWDIV/ClickOnDetroitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 4-2. Mechanism of Action of Selected Nonpeptide NeurotransmittersDokument1 SeiteTable 4-2. Mechanism of Action of Selected Nonpeptide NeurotransmittersaustinchenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Semester Important Answers !!Dokument16 Seiten1st Semester Important Answers !!Dikshant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutagenesis AB PAB ALAZ AHMDokument5 SeitenMutagenesis AB PAB ALAZ AHMAsdada Adsad CdfdsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Glycine and Applied ExamplesDokument1 Seite18 Glycine and Applied Examplestaryn.ballard21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sympathetic Vs Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDokument23 SeitenSympathetic Vs Parasympathetic Nervous SystemG4min6 M45t3rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media 823904 SMXXDokument26 SeitenMedia 823904 SMXXДемьян МатченкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lansoprazole 2Dokument1 SeiteLansoprazole 2Ilham AchtzehnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current MI Rabies MapDokument1 SeiteCurrent MI Rabies MapWDIV/ClickOnDetroitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 Protein 1Dokument45 SeitenCh2 Protein 1Loay Abu ZahraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiologic Effects: B6M2 Case 5 4/ 26/ 2019 GROUP 15Dokument1 SeitePhysiologic Effects: B6M2 Case 5 4/ 26/ 2019 GROUP 15Group15Nikki Louise PaquibotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Plan On InsurgencyDokument31 SeitenAction Plan On InsurgencyMary Rose BenipayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurology: CindyDokument32 SeitenNeurology: CindyTaschiro YuliarthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current MI Rabies Map in MichiganDokument1 SeiteCurrent MI Rabies Map in MichiganElizabeth WashingtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Gastronomy: Introduction ToDokument12 SeitenMolecular Gastronomy: Introduction ToTatiana100% (2)
- CTTN BiokimiaDokument1 SeiteCTTN BiokimiaAlicya BriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGSPAA Group Accounts 31 Dec 2018 Signed PDFDokument68 SeitenSGSPAA Group Accounts 31 Dec 2018 Signed PDFVinod VaradanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mineral Nutrition L1 PDFDokument38 SeitenMineral Nutrition L1 PDFANKITA MANDAVINoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument1 SeiteCarbohydrate MetabolismdaefaegagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled NotebookDokument1 SeiteUntitled NotebooknandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.lipid Metabolism - Catabolism Oct 16,2019 - For StudentsDokument1 Seite1.lipid Metabolism - Catabolism Oct 16,2019 - For StudentsAlif BaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Map of St. KittsDokument1 SeiteMap of St. KittsZidane KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOP 50 BIO Questipns by TetriDokument56 SeitenTOP 50 BIO Questipns by TetritetriofficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument59 SeitenCarbohydrate MetabolismSragwin ThridhamnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCP-027 VectraLCPDesignGuideTG AM 0613Dokument80 SeitenLCP-027 VectraLCPDesignGuideTG AM 0613Evert100% (1)
- ISP SFD PDFDokument73 SeitenISP SFD PDFNamo SlimanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA 2nd Sem SyllabusDokument6 SeitenMBA 2nd Sem SyllabusMohammad Ameen Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actara (5 24 01) PDFDokument12 SeitenActara (5 24 01) PDFBand Dvesto Plus CrepajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uxc01387a PDFDokument16 SeitenUxc01387a PDFmahesh123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages of The CapmDokument3 SeitenAdvantages of The Capmdeeparaghu6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics (Pythagorean Theorem)Dokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics (Pythagorean Theorem)Carlo DascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Temperature PDFDokument56 SeitenBody Temperature PDFBanupriya-Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Direct and Indirect Pulp CappingDokument9 SeitenJurnal Direct and Indirect Pulp Cappingninis anisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week1 TutorialsDokument1 SeiteWeek1 TutorialsAhmet Bahadır ŞimşekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Ms-Dos 6.22Dokument1.053 SeitenUsing Ms-Dos 6.22lorimer78100% (3)
- YS1700 Drum Level ControlDokument2 SeitenYS1700 Drum Level ControlIdriss BarçaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F. Moyra Allen: A Life in Nursing, 1921-1996: Meryn Stuart, R.N., PH.DDokument9 SeitenF. Moyra Allen: A Life in Nursing, 1921-1996: Meryn Stuart, R.N., PH.DRose Nirwana HandayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnkitKumar InternshalaResume PDFDokument2 SeitenAnkitKumar InternshalaResume PDFkusha010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric DefectsDokument30 SeitenFabric Defectsaparna_ftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creativity Triggers 2017Dokument43 SeitenCreativity Triggers 2017Seth Sulman77% (13)
- 20 Ijrerd-C153Dokument9 Seiten20 Ijrerd-C153Akmaruddin Bin JofriNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Wicked Game by Kate BatemanDokument239 SeitenA Wicked Game by Kate BatemanNevena Nikolic100% (1)
- TM9-1904 - Ammunition Inspection Guide - 1944 PDFDokument414 SeitenTM9-1904 - Ammunition Inspection Guide - 1944 PDFhodhodhodsribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 17 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum BADARANDokument10 SeitenModule 17 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum BADARANLance AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science HandbookDokument50 SeitenComputer Science HandbookdivineamunegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al-Farabi Fusul Al MadaniDokument107 SeitenAl-Farabi Fusul Al MadaniDaniel G.G.100% (1)
- Protected PCM USB Memory Sticks For Pa3X.Dokument1 SeiteProtected PCM USB Memory Sticks For Pa3X.mariuspantera100% (2)
- Invenio Flyer enDokument2 SeitenInvenio Flyer enErcx Hijo de AlgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Module 2 Combined-1Dokument14 SeitenUnit 2 Module 2 Combined-1api-2930012170% (2)
- Simple Past and Past Perfect TensesDokument13 SeitenSimple Past and Past Perfect TensesSincerly RevellameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language EducationDokument33 SeitenLanguage EducationLaarni Airalyn CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EffectivenessDokument13 SeitenEffectivenessPhillip MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rfis On Formliners, Cover, and EmbedmentsDokument36 SeitenRfis On Formliners, Cover, and Embedmentsali tahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D2E133AM4701 Operating Instruction UsDokument9 SeitenD2E133AM4701 Operating Instruction UsMohamed AlkharashyNoch keine Bewertungen