Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
V Sem 20 Electrical Engineering Export Export
Hochgeladen von
navneet0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
49 Ansichten1 SeiteVjjh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenVjjh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
49 Ansichten1 SeiteV Sem 20 Electrical Engineering Export Export
Hochgeladen von
navneetVjjh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
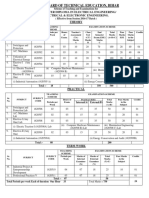
Three Phase Alternator
2.1 Definition and construction of three phase Alternator
a) Armature
b) Rotor- smooth cylindrical & projecting type
2.2 Derivation of e.m.f. equation of Alternator which includes
a) Chording factor
b) Distribution factor
2.3 Factors affecting the terminal voltage of Alternator
Unit-02 12 14
a) Armature resistive drop
b) Leakage reactance drop
c) Armature reaction at various power factors & concept of
Synchronous impedance
2.4 Regulation of three phase Alternator by
a) Synchronous impedance method
b) mmf method
(Numerical on all above)
Synchronous Motor
Unit-03 3.1 Principle of working/operation 10 10
3.2 Synchronous Motor on load with constant excitation
3.3 Effect of excitation at constant load
3.4 V curve & inverted V curve
3.5 Hunting & phase swinging
3.6 Applications
3.7 Starting of Synchronous Motor
3.8 Comparison between IM & Synchronous Motor
(Numerical on all above )
Single phase Motors
4.1 Double field revolving theory
4.2 Types of Single phase IM
4.3 Split phasing principle of starting
a) Resistance start induction run
Unit-04 b) Capacitor start induction run 06 06
c) Capacitor start Capacitor run
d) Double value Capacitor applications motor
4.4 Shaded pole IM
4.5 Applications
Special machines
5.1 Introduction to Induction Generator
Unit-05 06 04
5.2 Introduction to Linear Induction Motor
5.3 AC series motor
Total 64 70
Text / Reference Books:
Titles of the Book Name of Authors Name of the Publisher
Electrical Machines S. K. Bhattacharya TTTI, Chandigarh
Electrical Technology Vol. II B. L. Theraja S chand & Co.
Electrical engineering C.L.Dawes T. M. G. H.
Electrical Machinery Dr.P.S. Bimbra Khanna Publishers, New Delhi.
Electrical Machines M.V.Deshpande PHI Learning Pvt.Ltd, New Delhi.
Electrical Machines D.P.Kothari, I.J.Nagrath Tata McGraw Hill
A.C. Machines Shalini Verma Foundation Publishing
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Engagement of Apprentice 2023 Advertisement CRPD Appr 2023-24-17 Sbi Apprentice Recruitment 2023 Notification PDF 3Dokument12 SeitenEngagement of Apprentice 2023 Advertisement CRPD Appr 2023-24-17 Sbi Apprentice Recruitment 2023 Notification PDF 3navneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- SH2 - Field JB Detail-RECTIFeededDokument1 SeiteSH2 - Field JB Detail-RECTIFeedednavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notifications: Usha Martin Round Steel Wire Ropes For General Engineering Purposes-IS:2266, Length 700 Meter Usha MartinDokument3 SeitenNotifications: Usha Martin Round Steel Wire Ropes For General Engineering Purposes-IS:2266, Length 700 Meter Usha MartinnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cir 573 - Scheme of Mobile Phone Facility For Employees - Revision in EntitlementDokument1 SeiteCir 573 - Scheme of Mobile Phone Facility For Employees - Revision in EntitlementnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notifications: Usha Martin Round Steel Wire Ropes For General Engineering Purposes-IS:2266, Length 400 Meter Usha MartinDokument3 SeitenNotifications: Usha Martin Round Steel Wire Ropes For General Engineering Purposes-IS:2266, Length 400 Meter Usha MartinnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 Fiscal Policy in Keynesian Model: 6.0 ObjectivesDokument24 SeitenUnit 6 Fiscal Policy in Keynesian Model: 6.0 ObjectivesnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Title: Transmission Line O&M and Safety Practice: From: 11-13 Oct'18 Pre-TestDokument3 SeitenProgram Title: Transmission Line O&M and Safety Practice: From: 11-13 Oct'18 Pre-TestnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Becc-134 emDokument32 SeitenBecc-134 emnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical QuizDokument4 SeitenElectrical QuiznavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Part - A. Answer To Any Five Questions: Section 1Dokument34 SeitenI. Part - A. Answer To Any Five Questions: Section 1navneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Textbook of Electrical Technology by R.K.rajput (1) ExportDokument8 SeitenA Textbook of Electrical Technology by R.K.rajput (1) ExportnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Title: Transmission Line O&M and Safety Practice: From: 01-03 Nov'18 Post-TrainingDokument3 SeitenProgram Title: Transmission Line O&M and Safety Practice: From: 01-03 Nov'18 Post-TrainingnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- BECC-134 EM Block-500Dokument34 SeitenBECC-134 EM Block-500navneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curri Culum-Vi TAE: AmankumarDokument1 SeiteCurri Culum-Vi TAE: AmankumarnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- BECC-134 EM Block-4Dokument54 SeitenBECC-134 EM Block-4navneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Curriculum Diploma Electrical Engineering 310812.PDF-Copy ExportDokument24 SeitenModel Curriculum Diploma Electrical Engineering 310812.PDF-Copy ExportnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- North Bihar Power Distribution Company LTD.: Electric Supply Division (Muzaffarpur (R) )Dokument3 SeitenNorth Bihar Power Distribution Company LTD.: Electric Supply Division (Muzaffarpur (R) )navneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Receipt For State Bank Collect Payment: Govt Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur DateDokument1 SeiteE-Receipt For State Bank Collect Payment: Govt Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur DatenavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- V Sem 20 Electrical Engineering ExportDokument19 SeitenV Sem 20 Electrical Engineering ExportnavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Orkot® TLM & TXM Marine Bearings: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionsDokument7 SeitenOrkot® TLM & TXM Marine Bearings: Trelleborg Se Aling Solutionsprodn123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6CS6.2 Unit 5 LearningDokument41 Seiten6CS6.2 Unit 5 LearningAayush AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Universe - Rogues Testament by Steve MillerDokument281 SeitenX-Universe - Rogues Testament by Steve MillerRoccoGranataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitac 6120N ManualDokument141 SeitenMitac 6120N ManualLiviu LiviuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multilin 369Dokument5 SeitenMultilin 369Edo RossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Europa Universalis IV CheatsDokument7 SeitenEuropa Universalis IV CheatsZamri Bin RadzaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Øyvind H. Johansen Et Al - Qualification of An Enhanced Blast Explosive (DPX-6) : According To STANAG 4170Dokument25 SeitenØyvind H. Johansen Et Al - Qualification of An Enhanced Blast Explosive (DPX-6) : According To STANAG 4170MallamaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culminating Activity: (A Proposal)Dokument3 SeitenCulminating Activity: (A Proposal)Landice Myoui100% (1)
- Darcy Friction Loss Calculator For Pipes, Fittings & Valves: Given DataDokument2 SeitenDarcy Friction Loss Calculator For Pipes, Fittings & Valves: Given DataMSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact List For All NWGDokument22 SeitenContact List For All NWGKarthickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 11b ViewsDokument26 SeitenWeek 11b ViewsKenanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Pinnipedvibrissae To AeropropulsionDokument31 SeitenApplication of Pinnipedvibrissae To AeropropulsionShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV hll3220cw Uke PSGDokument17 SeitenCV hll3220cw Uke PSGczarownikivanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCTN Lsqmdocu63774Dokument21 SeitenDCTN Lsqmdocu63774Bharani KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSPDokument27 SeitenGSPVirgil Titimeaua100% (1)
- Firearms in America 1600 - 1899Dokument310 SeitenFirearms in America 1600 - 1899Mike100% (3)
- ISO9001 2008certDokument2 SeitenISO9001 2008certGina Moron MoronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation & Service Manual: Murzan IncDokument38 SeitenOperation & Service Manual: Murzan IncgokulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python - Tutorial: #!/usr/bin/python Print "Hello, Python!"Dokument174 SeitenPython - Tutorial: #!/usr/bin/python Print "Hello, Python!"ankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensus WP Dynamic Cold Water Meter (DN40-300)Dokument4 SeitenSensus WP Dynamic Cold Water Meter (DN40-300)Roderikus Rendy MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centaour 50 Solar TurbineDokument2 SeitenCentaour 50 Solar TurbineTifano KhristiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 01 IntroductionDokument4 SeitenLab 01 IntroductiontsikboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yugo m59 - 66 RifleDokument8 SeitenYugo m59 - 66 Riflestraightshooter100% (1)
- Customers at SurveyDokument10 SeitenCustomers at Surveynaren000Noch keine Bewertungen
- ES Service Transition PlanDokument7 SeitenES Service Transition PlanShamsher Singh BainsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CATALO VetivDokument240 SeitenCATALO VetivHữu CôngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applichem Case-SCM Sec B Group-2Dokument11 SeitenApplichem Case-SCM Sec B Group-2Ayush RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Notes On Building ConstructionDokument20 SeitenShort Notes On Building Constructionlarnz0% (1)
- Manual Hardware Lenovo Yoga BookDokument68 SeitenManual Hardware Lenovo Yoga BookRADU OCTAVIAN100% (2)