Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Summary of MIS
Hochgeladen von
Jagjeet SinghOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Summary of MIS
Hochgeladen von
Jagjeet SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Summary of MIS
The flow of material and cash in an organization is synchronized and coordinated
through the flow of information. The systematic flow of information in an
organization is managed through computer based or manual information systems.
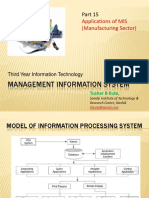
Inpu Proce Output
t ss
Correcti Feedbac
ve Unit k
MIS (Management Information System) is the system that provides information
support for managerial review and decision making. A good MIS should be capable
of:
1. Managing large amount of data
produced from day to day transactions.
2. Confirming that the data and
transactions are valid
3. Quickly searching for specific
information form data
4. Highlighting exceptions in the system
5. Regular communication of information to the users
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
1. Define the objectives and goals of the system.
2. Analyze existing system and assess its outcomes and limitations
3. Design new system concept, prototype and process
4. Install new hardware and software and test.
5. Implement and operate the new system
6. Evaluate, review and take corrective steps
Amit Goyal – Experiential Trainer – amitgoyal@tkws.co.in
Summary of ERP & BPR
ERP is a set of concepts and techniques employed for the integrated management
of business as a whole, from the viewpoint of effective use of management
resources, to improve the efficiency of an enterprise.
ERP Benefits
Reduction in Lead Times
On time Shipment
Reduction in cycle time
Improved Resource Utilization
Better customer satisfaction
Improved supplier performance
Increased flexibility
Reduced quality costs
Improved Information Accuracy
Decision Making Capability
Basic ERP Modules
• Business forecasting, planning and control
• Sales & Distribution
• Production Planning
• Material Management
• Finance
• Personnel
• Fixed Assets
• Quality Control
• Maintenance Management
Business Process Re-engineering(BPR): The fundamental rethinking and radical
redesign of business process to achieve dramatic improvements in the critical
contemporary measures of performance such as cost, quality, service and speed.
IT provides the versatility, speed, accuracy, storage & capability to processes to
achieve the desired improvements. IT acts as an enabler.
Amit Goyal – Experiential Trainer – amitgoyal@tkws.co.in
Hardware and Software
Hardware > Input Devices > Mouse, Keyboard, Trackball, Touch pad, tablet, joystick, etc
Hardware > Output Devices > Monitor (CRT, LCD, TFT), Printer, MMP, etc
Hardware > Central Processing Unit > RISC (Celeron, Netbook) CISC (Core 2 Duo, Via)
Hardware > Storage Device > Hard disk drive, Pen drive, Smartcards
Hardware > Optical Media > CD-R/RW DVD-R/RW
Hardware > Components > Motherboard, RAM, USB, SMPS, Expansion Slots, Graphics
Adapter, Port
Hardware > Networking > Modem, LAN, Router, Switch, Access Point, RJ45 Connector, CAT5
Software > Operating System > Ms Windows, MAC OS, UNIX, Linux, Solaris, Symbian
Software > Office Productivity > MS Office, Sun Office, Lotus Notes
Software > Utilities > Web Browser, Instant Messaging Software, Anti Virus, Media Player
Software > Database > MS SQL, My SQL, Foxpro, Oracle, Ms Access
Software > Application > Accounting, ERP, Payroll, PoS, Games, Graphic Editing, Animation
Software > Integrated Development Environment > Visual Studio, Dot Net, Java Studio
Software > Programming Language > Visual Basic, Java, C#, Assembly
Software > Scripting > Java Script, VB Script, CGI, ASP, CGI, HTML
Evaluation Criteria
1. Technical Evaluation
2. Operational Feasibility
3. Financial Considerations
4. Expansion Capability
• Memory and Cache
• Disk capacity
• CPU Speed, processing architecture and capabilities
• Servers
• Terminals
• Network and cabling, internet and intranet
• EDI, Email
• Network hardware
• Output Devices
• Operating systems
A database is an integrated collection of well defined data and information, centrally
controlled in all its aspects, created and stored in a typical structure for an organization.
Field Record File Database
Hierarchical Database Model (HDBM), Network Database Model (NDBM), Relational Database
Model (RDBM)
DBMS reduces redundancy and inconsistency of data, provides easy access and searching,
enables concurrent usage, ensures integrity and resolves security issues.
Amit Goyal – Experiential Trainer – amitgoyal@tkws.co.in
Applications of MIS
Personnel Management
Inputs Outputs
Attendance & Leave Statutory Reports like Muster, PF, ESI Returns, IT
Form 16, 24A
Manpower details Employee details, Accident reports
Salary / Wages, statutory Daily Attendance Reports, Joining and transfer
deductions reports
Loans and deductions Manpower cost as per department, job or product
Accidents Overtime, absenteeism and distribution or
workload
Production data Analysis of attendance by season, festival, etc
Skills Report of job scheduling and workload distribution
Bio data Training and development needs and calendars
Family data Manpower hierarchy and recruitment plans
Financial Management
Inputs Outputs
Sales Tax Returns, TDS, Sales Tax, Excise register
Purchase Declaration of financial results to public every 6
months
Salary Cash flow, Trial Balance, Balance Sheet, P&L
Inventory Stock Valuation
Expenses Account receivables, payables and aging
Capital Purchases Expense summary, cash position
Shareholder Funds ROI, Break even analysis and price decision
Duties and taxes
Budgets
Investments
Production Management
Inputs Outputs
Production quantity Production plan and job schedule
Material requirement and usage Job order status, load status on machines
Rejection quantity at Material availability status
intermediate and final stage
Breakdown incidence Make, buy or subcontract
Labor hours Excessive product rejection
Use of power, fuel and Hold up of key jobs beyond limit
consumables
Machine and facilities utilization Excessive work in process inventory or backlogs
Continued breakdown of manufacturing facility
Utilization of key facilities below a limit
Amit Goyal – Experiential Trainer – amitgoyal@tkws.co.in
Material Management
Inputs Outputs
Purchase quantity Stock ledger
Issue quantity Valued stock statement, value of non moving
inventory
Stocks Octroi, MODVAT, RG1, RT12, customs bond
registers, etc
Goods returns Price fluctuations and trend
Rejections Daily goods received, floor rejections, overruns
Performance Reliability of suppliers, vendor performance
Value of purchase Material performance
Average of standard rate of Statement of supplies due but not yet received
accounting
Marketing Management
Inputs Outputs
Product Sale Product sales ledger, sales summaries
Dealer, distributor, customer Account receivables
Zone, Area Sales analysis, order bool, market and competition
analysis
Inventory Ageing of receivables
Receivables Sales versus budget
Market segment Complaints versus closed complaints
Exports market Orders received and accepted
Returns Dispatch report
Complaints
Amit Goyal – Experiential Trainer – amitgoyal@tkws.co.in
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Agile Procurement: Volume II: Designing and Implementing a Digital TransformationVon EverandAgile Procurement: Volume II: Designing and Implementing a Digital TransformationNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIS Ch-2Dokument7 SeitenAIS Ch-2Rabbumaa KabbadaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIS-1 - Module On Topic 2Dokument8 SeitenAIS-1 - Module On Topic 2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is An ERP?Dokument53 SeitenWhat Is An ERP?aatayyab100% (12)
- Bestow ERP General 2Dokument14 SeitenBestow ERP General 2M. MUBASHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Information SystemDokument13 SeitenManagement Information SystemJinal Bhanushali0% (1)
- Management Information SystemDokument13 SeitenManagement Information SystemJinal BhanushaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIS 1 Conceptual Foundations of Accounting Information Systems (ALREADY DISCUSSED)Dokument43 SeitenAIS 1 Conceptual Foundations of Accounting Information Systems (ALREADY DISCUSSED)TAETAE50% (2)
- Sap FicoDokument10 SeitenSap FicoKamal Kumar RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neron Informatics Decelopment PlanDokument10 SeitenNeron Informatics Decelopment PlanSujeet KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of The World's Leading ERP System JR Batek, IT Audit Manager - Cooper Industries Tim Guerinot, Sr. SAP Staffing Consultant - Whitaker ITDokument33 SeitenAn Overview of The World's Leading ERP System JR Batek, IT Audit Manager - Cooper Industries Tim Guerinot, Sr. SAP Staffing Consultant - Whitaker ITsethu_bala1Noch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FioriAppDokument16 SeitenSAP FioriAppManikandan VijayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument42 SeitenChapter 1yonas bezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Mis in Manufacturing SectorDokument66 SeitenApplication of Mis in Manufacturing SectorHimanshu DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7Dokument69 SeitenLecture 7yuzlubahadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managementinformationsystem15 110316025755 Phpapp02Dokument66 SeitenManagementinformationsystem15 110316025755 Phpapp02sneha kotawadekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Softhub ERPDokument28 SeitenSofthub ERPSofthub TecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations ManagementDokument22 SeitenOperations ManagementJean TampelicNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCD Job DescriptionDokument29 SeitenCCD Job Descriptionkunzle1Noch keine Bewertungen
- AIS - Chapter 2 Overview of The Business ProcessesDokument24 SeitenAIS - Chapter 2 Overview of The Business ProcessesErmias GuragawNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument29 SeitenCH 1Arbi ChaimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERP - Enterprise Resource PlanningDokument38 SeitenERP - Enterprise Resource Planningnehank17100% (3)
- 01 Business Process and Business FunctionDokument4 Seiten01 Business Process and Business FunctionArwin SomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management: General Ledger Basic BudgetingDokument8 SeitenFinancial Management: General Ledger Basic BudgetingSajid IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Too MDokument32 SeitenIntroduction Too MgiovananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 1 Om - Dwi PriyantoDokument58 SeitenPertemuan 1 Om - Dwi PriyantoDwi P RiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations and Production ManagementDokument18 SeitenOperations and Production ManagementagreiantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Support ProcessDokument34 SeitenSupport ProcessRachmad AriefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epm ReviseDokument61 SeitenEpm ReviseOliver LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Intelligence in Competitive AdvantageDokument22 SeitenBusiness Intelligence in Competitive Advantageaxxaan4097Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operations ManagementDokument22 SeitenOperations ManagementUmair SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To OperationsDokument37 SeitenIntroduction To OperationsSage MainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 DEVELOPING A COMPETITIVE STRATEGYDokument9 SeitenModule 4 DEVELOPING A COMPETITIVE STRATEGYitsdaloveshot naNANAnanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL # Module Name Requirements DetailsDokument10 SeitenSL # Module Name Requirements DetailsAsif Reman ArmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transaction Processing SystemsDokument13 SeitenTransaction Processing Systemsvinit PatidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Management I: 3º Gadi-5º Dg-Adi-DerDokument27 SeitenOperations Management I: 3º Gadi-5º Dg-Adi-DerAlem Abebe AryoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCMChapter 4Dokument28 SeitenSCMChapter 4Aryle VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEAN Manufacturing & ERP: How To Leverage ERP To Get LeanDokument26 SeitenLEAN Manufacturing & ERP: How To Leverage ERP To Get LeanDeepak D OjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Industry and MIS - SlidesDokument14 SeitenManufacturing Industry and MIS - SlidesSanath Fernando100% (1)
- 1 Introduction To OMDokument25 Seiten1 Introduction To OMrajaraghuramvarma1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDokument29 SeitenIntroduction To Operations ManagementPiyush SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Code: COM-O306: Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyDokument51 SeitenSubject Code: COM-O306: Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyshadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- POG Software ProposalDokument16 SeitenPOG Software Proposalsourabh.verma9770Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acyitm2 - Unit 1Dokument14 SeitenAcyitm2 - Unit 1Gian Carlo RamonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- E2. ENM (ML) Solution CMA May-2023 Exam.Dokument7 SeitenE2. ENM (ML) Solution CMA May-2023 Exam.Sharif MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Information System: Functional Areas of ManagementDokument38 SeitenManagement Information System: Functional Areas of ManagementSethulekshmi mohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSCM5 - 01 - Technology in SCMDokument74 SeitenLSCM5 - 01 - Technology in SCMRoma KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 2 - IS Application at Operational LevelDokument68 SeitenGROUP 2 - IS Application at Operational LevelBayu Widhi RespatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Identification/ Screening of Project IdeasDokument12 SeitenProject Identification/ Screening of Project IdeasHarsh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Org & SystemDokument38 SeitenUnit 1 - Introduction To Org & Systemmano ranjithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass IIDokument12 SeitenAss IIBeza AbrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heizer 01Dokument107 SeitenHeizer 01sabinaa20Noch keine Bewertungen
- It Infrastructure For A Manufacturing CompanyDokument29 SeitenIt Infrastructure For A Manufacturing CompanyamolpumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise Resource Planning: MPC 6 Edition Chapter 1aDokument25 SeitenEnterprise Resource Planning: MPC 6 Edition Chapter 1aKhaled ToffahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter01and02 (Street08spring)Dokument67 SeitenChapter01and02 (Street08spring)dheeraj_raj_jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)Von EverandWiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)Noch keine Bewertungen
- STR Mpa-MpmDokument8 SeitenSTR Mpa-MpmBANGGANoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumeDokument3 SeitenResumeabreddy2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sanjay ProjectDokument41 SeitenSanjay ProjectPrynka RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Tank Seat Slab DesignDokument2 SeitenWater Tank Seat Slab DesignMesfin Derbew100% (2)
- ID 2051814.1 Oracle Support Sample SetupDokument9 SeitenID 2051814.1 Oracle Support Sample SetupFerasHamdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Configure A Wi-Fi Network How To Configure A RADIUS/EAP ServerDokument7 SeitenHow To Configure A Wi-Fi Network How To Configure A RADIUS/EAP ServerSeluuunnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCash OrientationDokument27 SeitenGCash OrientationArmiel SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project Miguel Santana GallegoDokument44 SeitenFinal Project Miguel Santana GallegoDaniel PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Water TreatmentDokument7 SeitenHVAC Water TreatmentDuxToyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Cardiac Catheters - 2012-2018Dokument4 SeitenGlobal Cardiac Catheters - 2012-2018Axis Research MindNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Wireless Communications For Mining OperationsDokument38 SeitenABB Wireless Communications For Mining OperationsAymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Management 07Dokument8 SeitenPrinciples of Management 07knockdwnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat 15Dokument2 SeitenCat 15Gustavo Vargas0% (1)
- Tutorial Joint Push Pull - English - V1.1 - 20 Feb 08Dokument31 SeitenTutorial Joint Push Pull - English - V1.1 - 20 Feb 08shadownrunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobil Pyrotec™ HFD 46Dokument2 SeitenMobil Pyrotec™ HFD 46ABDUL REHMAN PIPRANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Viola - David Tudor - The Delicate Art of FallingDokument9 SeitenViola - David Tudor - The Delicate Art of FallingRobin ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sapthagiri College of Engineering: Tracing Manufacturing Processes Using Blockchain Based Token CompositionsDokument19 SeitenSapthagiri College of Engineering: Tracing Manufacturing Processes Using Blockchain Based Token CompositionsYashi FakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMDokument36 SeitenSMharan2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Decision Making and LoopingDokument94 SeitenChapter 5 - Decision Making and LoopingAcapSuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canalta Parts CatalogueDokument25 SeitenCanalta Parts Cataloguellando1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adirondack Life Media KitDokument8 SeitenAdirondack Life Media KitJohnny LibitzNoch keine Bewertungen
- TG-5 Relay SettingDokument10 SeitenTG-5 Relay Settingbasil100% (1)
- Richard Feynman BiographyDokument5 SeitenRichard Feynman Biographyapi-284725456100% (1)
- 100124119Dokument175 Seiten100124119mkeiwuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK 116403 Ge File. Performance TestsDokument54 SeitenGEK 116403 Ge File. Performance TestsSulaiman JafferyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plunger Pump Service Manual: Installation and Start-Up InformationDokument6 SeitenPlunger Pump Service Manual: Installation and Start-Up InformationDark CenobiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glenair Connector Terms - SummaryDokument4 SeitenGlenair Connector Terms - SummarybenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORF Issue Brief 309 SpaceLawDokument12 SeitenORF Issue Brief 309 SpaceLawNitish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansi C29.2aDokument22 SeitenAnsi C29.2afecasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step-By-Step Guide - Sensors Alarms1Dokument14 SeitenStep-By-Step Guide - Sensors Alarms1Andy_kokoNoch keine Bewertungen