Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bibliografia
Hochgeladen von
Jose Gregorio Araujo Perez0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten2 Seitenxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Originaltitel
bibliografia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten2 SeitenBibliografia
Hochgeladen von
Jose Gregorio Araujo Perezxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
1. BOYLE P, SEVERI G.: Epidemiology of prostate cancer. Chemoprevention.
Eur Urol 1999;
35: 370-376.
2. ARRIZABALAGA M, NAVARRO M, MORAS J y cols.: Incidencia de los principales carcinomas
urológicos en el área sanitaria VII de Madrid. Actas Urológicas Españolas 1994: 145: 161.
3. Migowski A SG. Survival and prognostic factors of patients with clinically localized prostate
cancer. RevSaúde Pública 2010; 44(2): 344-52
4. Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Cáncer en las Américas. Perfiles de país, 2013.
Washington, D.C.: 2013.
5. Matiz, José Luis Poveda, et al. "Evolución de la mortalidad por cáncer de próstata en
Colombia: estudio ecológico." Urología Colombiana 23.1 (2014): 3-10.
6. Velásquez, Esteban. Cáncer de próstata continúa en aumento en Colombia. Redacción
Social 2015.
7. Guía práctica clínica. Diagnóstico y tratamiento del cáncer de próstata en el segundo y
tercer nivel de atención. Consejo de salubridad general 2009.
8. Ruiz J. Relación de la susceptibilidad genética y de las características anatomopatológicas
del cáncer de próstata con los polimorfismos de nucleótido simple. Universidad Autónoma
de Barcelona 2012.
9. American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. website. PSA testing for the
pretreatment staging and posttreatment management of prostate cancer: 2013 Revision
of 2009 Best Practice Statement. www.auanet.org/guidelines/prostate-specific-antigen-
(2009-amended-2013). Accessed October 9, 2017.
10. Leitzmann MF, Platz EA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Giovannucci E. "Ejaculation frequency
and subsequent risk of prostate cancer." Journal JAMA, 2004, páginas 1578-86, Vol. 291
PMID 15069045
11. Miller, DC, Hafez, KS, Stewart, A, et al. "Prostate carcinoma presentation, diagnosis, and
staging: an update form the National Cancer Data Base." Cancer 2003; 98:1169. PMID
12973840
12. Singh D, Febbo PG, Ross K, Jackson DG, Manola J, Ladd C, et al. Gene expression correlates
of clinical prostate cancer behavior. Cancer Cell. 2002;1(2):203-9.
13. Bubendorf L, Kolmer M, Kononen J, Koivisto P, Mousses S, Chen Y, et al. Hormone therapy
failure in human prostate cancer: analysis by complementary DNA and tissue microarrays.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999 20;91(20):1758-64.
14. Rubin MA, Zhou M, Dhanasekaran SM, Varambally S, Barrette TR, Sanda MG, et al. alpha-
Methylacyl coenzyme A racemase as a tissue biomarker for prostate cancer. JAMA. 2002
3;287(13):1662-70
15. Andriole GL, Crawford ED, Grubb RL, 3rd, Buys SS, Chia D, Church TR, et al. Mortality
results from a randomized prostate-cancer screening trial. N Engl J Med. 2009
26;360(13):1310-9.
16. De Marzo AM, Marchi VL, Epstein JI, Nelson WG. Proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the
prostate: implications for prostatic carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1999;155(6):1985-92.
17. Nupponen NN, Visakorpi T. Molecular cytogenetics of prostate cancer. Microsc Res Tech.
2000 1;51(5):456-63.
18. Yano S, Matsuyama H, Matsuda K, Matsumoto H, Yoshihiro S, Naito K. Accuracy of an array
comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) technique in detecting DNA copy number
aberrations: comparison with conventional CGH and loss of heterozygosity analysis in
prostate cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2004 15;150(2):122-7.
19. Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. The role of companion diagnostics in the
development and use of mutation-targeted cancer therapies. Nat Biotechnol.
2006;24(8):985-95.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Voca C IonalDokument16 SeitenVoca C IonalJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DoctorDokument2 SeitenDoctorJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DD125 CP CO Esp v2r0 UnlockedDokument4 SeitenDD125 CP CO Esp v2r0 UnlockedJose Gregorio Araujo Perez0% (1)
- Prospect IvaDokument2 SeitenProspect IvaJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DD154 CP CO Esp v0r0 UnlockedDokument4 SeitenDD154 CP CO Esp v0r0 UnlockedJose Gregorio Araujo Perez0% (2)
- Funciones Exponenciales y LogaritmicasDokument11 SeitenFunciones Exponenciales y LogaritmicasJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentación 111Dokument3 SeitenPresentación 111Jose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resumen InfoDokument3 SeitenResumen InfoJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- De-Muerte-En-Colombia-Articulo-730249.: Redacción Nacional (2017)Dokument4 SeitenDe-Muerte-En-Colombia-Articulo-730249.: Redacción Nacional (2017)Jose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presupuesto Material Publicitario y Material PDokument1 SeitePresupuesto Material Publicitario y Material PJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIBLIOGRAFI1Dokument3 SeitenBIBLIOGRAFI1Jose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- De-Muerte-En-Colombia-Articulo-730249.: Redacción Nacional (2017)Dokument4 SeitenDe-Muerte-En-Colombia-Articulo-730249.: Redacción Nacional (2017)Jose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocumentoDokument2 SeitenDocumentoJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presupuesto Material Publicitario y Material PDokument1 SeitePresupuesto Material Publicitario y Material PJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encuesta Estudiantes y Docentes de Septimo GradoDokument1 SeiteEncuesta Estudiantes y Docentes de Septimo GradoJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentacion de La Reina Popular Del Carnaval Del Barrio Los CedrosDokument1 SeitePresentacion de La Reina Popular Del Carnaval Del Barrio Los CedrosJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contrato de Arrendamiento ComercialDokument8 SeitenContrato de Arrendamiento ComercialJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carlos DelgadoDokument6 SeitenCarlos DelgadoJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cuenta de CobroDokument1 SeiteCuenta de CobroJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENCUESTADokument1 SeiteENCUESTAJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morin, Potter y FreireDokument6 SeitenMorin, Potter y FreireJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentación 1Dokument1 SeitePresentación 1Jose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tercera EntregaDokument22 SeitenTercera EntregaJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derecho de PticionDokument2 SeitenDerecho de PticionJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carlos DelgadoDokument6 SeitenCarlos DelgadoJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cuento SDokument22 SeitenCuento SJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentacion de La Reina Popular Del Carnaval Del Barrio Los CedrosDokument1 SeitePresentacion de La Reina Popular Del Carnaval Del Barrio Los CedrosJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esca Rape LasDokument2 SeitenEsca Rape LasJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cuenta de CobroDokument1 SeiteCuenta de CobroJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cuento SDokument22 SeitenCuento SJose Gregorio Araujo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnsayoDokument4 SeitenEnsayoValentina Solano ramirezNoch keine Bewertungen
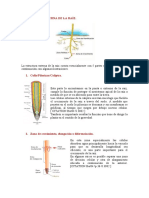
- Estructura Externa de La RaízDokument7 SeitenEstructura Externa de La RaízJUAN CAMILO FRANCO PENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamariz Angeles Carmen Del RosarioDokument2 SeitenTamariz Angeles Carmen Del RosarioJose AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Densidad Volumetrica Teorica y LinealDokument7 SeitenDensidad Volumetrica Teorica y LinealLuis SolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psicologia Oscura ST 287029 Downloadable 3532195Dokument127 SeitenPsicologia Oscura ST 287029 Downloadable 3532195Enoc Martinez TrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrada German Devesa ManualDokument195 SeitenIntegrada German Devesa ManualDomingo GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relacion Del Sistema Nervioso Con El ComportamientoDokument8 SeitenRelacion Del Sistema Nervioso Con El ComportamientoGloria Soto100% (1)
- Diodos EspecialesDokument14 SeitenDiodos EspecialesAnibal VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informe Practico 6 Tallo y HojaDokument10 SeitenInforme Practico 6 Tallo y HojaMERCEDES GUTIERREZ CERNA100% (2)
- Reglamento de Internado Minsa EssaludDokument8 SeitenReglamento de Internado Minsa EssaludYahirOneloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caso Práctico Higiene 4Dokument4 SeitenCaso Práctico Higiene 4Victor RodrigesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autoevaluacion Acreditacion SUA Bajo - 5095 PDFDokument20 SeitenAutoevaluacion Acreditacion SUA Bajo - 5095 PDFAngela Maria Ortiz UribeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LudopatiaDokument10 SeitenLudopatiamarlen valeria amaya villamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproducción de MMS y MMLDokument3 SeitenReproducción de MMS y MMLEnrique Llano BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesis Samuel Ok EmpastarDokument88 SeitenTesis Samuel Ok EmpastarSuárez DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estructura Agregacion y Porosidad en Suelos ForestDokument7 SeitenEstructura Agregacion y Porosidad en Suelos ForestTrifon Barnet ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamenDokument9 SeitenExamenjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- MV2 Plan de Mantenimiento de Infraestructura y EquipamientoDokument10 SeitenMV2 Plan de Mantenimiento de Infraestructura y Equipamientojosecarlos.linaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ciclos Del AguaDokument3 SeitenCiclos Del AguaYaseniMoreno100% (1)
- XYPEX - APLICACION SISTEMA ImpermeabilizanteDokument8 SeitenXYPEX - APLICACION SISTEMA Impermeabilizantechristian paul santur cunyaracheNoch keine Bewertungen
- DISEÑO HUERTO ESCOLAR Ecoauditorias BiodiversidadDokument6 SeitenDISEÑO HUERTO ESCOLAR Ecoauditorias BiodiversidadSoni Gonzales0% (1)
- Guia de Analisis SensorialDokument6 SeitenGuia de Analisis SensorialJohana Acosta CuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Métodos de Mejora Genética de AlógamasDokument11 SeitenMétodos de Mejora Genética de AlógamasAndrea YumboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia Inguinal 2.Dokument10 SeitenHernia Inguinal 2.Nathaly MontoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducción A La BioéticaDokument238 SeitenIntroducción A La BioéticaDarío Moreira100% (2)
- Huella HidricaDokument24 SeitenHuella HidricaValeria FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desarrollo Actividad 2 PasteleriaDokument4 SeitenDesarrollo Actividad 2 PasteleriaCarlos Adonnai CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vasculitis ResumenDokument24 SeitenVasculitis ResumenErick GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapa Conceptual Aparato CardiocirculatorioDokument1 SeiteMapa Conceptual Aparato CardiocirculatorioraquelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proyecto Division CuartosDokument42 SeitenProyecto Division CuartosArturoNoch keine Bewertungen