Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Formula Sheet PDF
Hochgeladen von
crazyAss GamerOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Formula Sheet PDF
Hochgeladen von
crazyAss GamerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
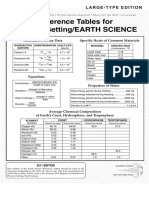
Chemistry Reference Tables
Name Value
Avogadro’s number 6.022 1023 particles/mole
0.0821 L atm
mole K
L mmHg
Gas constant (R) 62.4
mole K
8.314 L kPa
mole K
1.00 atm = 101.3 kPa =
Standard pressure
760. mmHg = 760. torr
Standard temperature 0C or 273K
Volume of 1 mole of any gas at STP 22.4 L
Thermodynamic Constants Symbol Value
Heat of fusion of water H f (water) 334 J/g
Heat of vaporization of water Hv (water) 2,260 J/g
2.05 J for ice, 2.02 J
g°C g°C
Specific heat of water C p (water) for steam,
4.18 J for liquid
g°C
Specific Heat J Density
Metal g°C Melting Point (°C)
(g/cm3)
Aluminum 0.897 2.702 660
Copper 0.385 8.92 1083
Gold 0.129 19.31 1064
Iron 0.449 7.86 1535
Lead 0.129 11.3437 328
Magnesium 1.023 1.74 649
Mercury 0.140 13.5939 –39
Nickel 0.444 8.90 1455
Titanium 0.523 4.5 1660
Zinc 0.388 7.14 420
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 1
Organic Substances
Name Density Melting Point (°C) Boiling Point (°C)
Ethanol
0.7893 g/cm3 114 79
(CH3CH2OH)
Glucose
1.56 g/cm3 146 Decomposes
(C 6H12O6)
Hexane
0.6603 g/cm3 95 69
(C 6H14)
Methane
0.716 g/L 182 161
(CH4)
Methanol
0.7914 g/cm3 98 65
(CH3OH)
Sucrose
1.58 g/cm3 86 Decomposes
(C12H22O11)
Inorganic Substances
Name *Density @ STP Melting Point (°C) Boiling Point (°C)
Chlorine 3.21 g/L 101 35
Hydrogen 0.0899 g/L 259 253
Hydrogen
1.640 g/L 115 85
chloride
Hydrogen sulfide 1.54 g/L 85 61
Nitrogen 1.25 g/L 210 196
Nitrogen monoxide 1.34 g/L 164 152
Oxygen 1.43 g/L 218 183
Sodium
2.532 g/cm3 851 Decomposes
carbonate
Sodium chloride 2.165 g/cm3 801 1413
Sulfur dioxide 2.92 g/L 73 10
*Water (at 4°C) 1.00 g/cm3 0 100
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 2
Formulas
D m D = density
V
K C 273 m = mass
P1V1 PV
2 2 V = volume
T1 T2
Pt P1 P2 P3 ... K = Kelvin
M1V1 M2V2 P = pressure
PV nRT R = gas constant
M moles of solute T = temperature
liter of solution
q mC pT M = molarity
q mHv n = number of moles
q mHf q = quantity of heat energy
pH pOH 14 C p = specific heat
pH log[H] Hv = heat of vaporization
pOH log[OH] H f = heat of fusion
K w = equilibrium constant for
Kw [H][OH] 1 10 14
the ionization of water
[H] 10 pH
[OH] 10 pOH
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 3
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 4
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 5
SOLUBILITY RULES
Soluble: Insoluble (0.10 M or greater):
All Nitrates, Acetates, Ammonium, All Carbonates and Phosphates
and Group 1 (IA) salts except Group 1 (IA) and
All Chlorides, Bromides, and Ammonium
Iodides, All Hydroxides except
except Silver, Lead, and Group 1 (IA), Strontium, Barium,
Mercury(I) and Ammonium
All Fluorides except Group 2 (IIA), All Sulfides except Group 1 (IA),
Lead(II), and Iron(III) 2 (IIA), and Ammonium
All Sulfates except Calcium, All Oxides except Group 1 (IA)
Strontium, Barium, Mercury,
Lead(II), and Silver
Guidelines for Predicting the Products of Selected Types of Chemical Reactions
Key: M = Metal
NM = Nonmetal
1. SYNTHESIS:
a. Formation of binary compound: A + B AB
b. Metal oxide and water: MO + H2O base
c. Nonmetal oxide and water: (NM)O + H2O acid
2. DECOMPOSITION:
a. Binary compounds: AB A + B
b. Metallic carbonates: MCO3 MO + CO2
c. Metallic hydrogen carbonates: MHCO3 MCO3 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
d. Metallic hydroxides: MOH MO + H2O
e. Metallic chlorates: MClO3 MCl + O2
f. Oxyacids decompose to nonmetal oxides and water: acid (NM)O + H2O
3. SINGLE REPLACEMENT:
a. Metal-Metal replacement: A + BC AC + B
b. Active metal replaces H from water: M + H2O MOH + H2
c. Active metal replaces H from acid: M + HX MX + H2
d. Halide-Halide replacement: D + BC BD + C
4. DOUBLE REPLACEMENT: AB + CD AD + CB
a. Formation of a precipitate from solution
b. Acid-Base neutralization
5. COMBUSTION REACTION
Hydrocarbon + oxygen carbon dioxide + water
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 6
ACTIVITY SERIES of Halogens: Polyatomic Ions
+
F2 NH 4 Ammonium
Cl2 BrO 3 Bromate
Br2 CN
Cyanide
I2 C 2H3O2
Acetate
(CH3COO )
ClO 4 Perchlorate
ACTIVITY SERIES of Metals ClO3 Chlorate
Li ClO2 Chlorite
Rb
ClO Hypochlorite
K
Ba IO3 Iodate
Sr MnO 4 Permanganate
Replace hydrogen
Ca NO
from cold water 3 Nitrate
Na
Mg NO 2 Nitrite
Al OH Hydroxide
Mn Hydrogen
Zn HCO3
carbonate
Cr Replace hydrogen from HSO 4 Hydrogen sulfate
Fe steam
Cd SCN Thiocyanate
Co CO23 Carbonate
Ni Cr2O72 Dichromate
Sn 2
Replace hydrogen from CrO Chromate
Pb acids
4
2
[ H2 ] SO 4 Sulfate
Sb SO23 Sulfite
Bi PO34
React with oxygen to form Phosphate
Cu oxides
Hg
Ag
Pt
Au
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 7
NCDPI Reference Tables for Chemistry (2012) Page 8
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- (PDF) Reference Sheet - Chemistry PDFDokument8 Seiten(PDF) Reference Sheet - Chemistry PDFRastateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Balance Kiln & Cooler P 6: InstructionsDokument32 SeitenHeat Balance Kiln & Cooler P 6: Instructionstika100% (1)
- Calculation of Flow From PinholeDokument6 SeitenCalculation of Flow From PinholeSubrata MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Data: Table 1: Basic Crude Oil Analysis For Sample Collected From Well # H-18 Experiment Method ResultDokument2 SeitenAnalytical Data: Table 1: Basic Crude Oil Analysis For Sample Collected From Well # H-18 Experiment Method ResultYousef Adel HassanenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry School Center by SlidesgoDokument48 SeitenChemistry School Center by SlidesgoRoy JekriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 11th Edition PetrucciDokument36 SeitenSolution Manual For General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 11th Edition Petruccisoupydjereedxd3on0100% (24)
- Rob's Energy Mustknows v1.0Dokument24 SeitenRob's Energy Mustknows v1.0Rob100% (7)
- Full Download Solution Manual For General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 11th Edition Petrucci PDF Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenFull Download Solution Manual For General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 11th Edition Petrucci PDF Full Chapterclick.blindehdu1y100% (19)
- Heat Exchanger Area & Boilup Rate CalculationDokument19 SeitenHeat Exchanger Area & Boilup Rate CalculationNitin KurupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation Form CombustionDokument2 SeitenCalculation Form CombustionKrishna KameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SG of Gas at NTP PDFDokument1 SeiteSG of Gas at NTP PDFDilnesa EjiguNoch keine Bewertungen
- T5 Heats of Fusion and VaporizationDokument1 SeiteT5 Heats of Fusion and VaporizationDương HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Specification SheetDokument4 SeitenHeat Exchanger Specification SheetAnita PanthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Density of Gases at STP Density of Some Common SolidsDokument2 SeitenDensity of Gases at STP Density of Some Common Solids김동주Noch keine Bewertungen
- Helical Super Heater DesignDokument13 SeitenHelical Super Heater DesignG S DeshpandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Process Inputs Fluid Flow Rate (Kg/hr) Density (gm/cc) Sp.Heat (Kcal/kg.°C) λ (Kcal/kg) Inlet Temperature °CDokument12 SeitenA. Process Inputs Fluid Flow Rate (Kg/hr) Density (gm/cc) Sp.Heat (Kcal/kg.°C) λ (Kcal/kg) Inlet Temperature °CPrad1979100% (1)
- Properties by Correlation For Process SimulationDokument4 SeitenProperties by Correlation For Process SimulationSuryakant RanderiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Dependence of Entropy, Standard State ForDokument12 SeitenTemperature Dependence of Entropy, Standard State ForSaleha SohailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Diameter For Methanol-IPA System (Continuous) - Top Boil Up PropertiesDokument3 SeitenCalculation of Diameter For Methanol-IPA System (Continuous) - Top Boil Up PropertiesBagadi AvinashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Largetype Earth Sci Reference Tables 2011Dokument16 SeitenLargetype Earth Sci Reference Tables 2011whiterun05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Tube Boiler DesignDokument3 SeitenFire Tube Boiler DesignRajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeneralData Lavan NewDokument1 SeiteGeneralData Lavan NewRos Neftegaz TransitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat CalcDokument7 SeitenHeat CalcasdfghjkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sk0014 Physical & Inorganic Chemistry Tutorial 9 ThermochemistryDokument2 SeitenSk0014 Physical & Inorganic Chemistry Tutorial 9 ThermochemistryNeil8353 GgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 3 and 4Dokument8 SeitenTask 3 and 4tlsandiaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Org 2 Exp 2 MSDSDokument1 SeiteOrg 2 Exp 2 MSDSChristian RV EscosarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcetaldehydeDokument98 SeitenAcetaldehydeKrishna DangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of WaterDokument3 SeitenProperties of WatertaylorknoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-TEXANOL Ester AlcoholDokument2 Seiten3-TEXANOL Ester AlcoholS.MadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satish - Weight To Volume2Dokument40 SeitenSatish - Weight To Volume2mesattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat DutyDokument7 SeitenHeat Dutyingegnere1234Noch keine Bewertungen
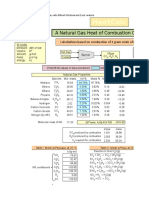
- Heatcalc: A Natural Gas Heat of Combustion CalculatorDokument7 SeitenHeatcalc: A Natural Gas Heat of Combustion CalculatorMuzzamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- He 1061Dokument12 SeitenHe 1061vijay88666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Heat CapacitiesDokument1 SeiteSpecific Heat CapacitiesAnderson MayobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KE RT: Kinetic EnergyDokument3 SeitenKE RT: Kinetic EnergyROBINSON ALEXIS PINEROS PENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Garbage IncineratorDokument59 SeitenGarbage IncineratorgsdaundhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lee2014 Ie500110v Si 001Dokument3 SeitenLee2014 Ie500110v Si 001Bidesh M KirtaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condensate Specs and TBP 1Dokument1 SeiteCondensate Specs and TBP 1asad razaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Heat CalcDokument7 Seiten3 Heat CalcNITINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methane Properties: Erty Value Unit Value Unit Value UnitDokument6 SeitenMethane Properties: Erty Value Unit Value Unit Value UnitdNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO2 Capture & CompressionDokument22 SeitenCO2 Capture & Compressionchen junwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Liquid Separator DesignDokument3 SeitenGas Liquid Separator DesignSoheil MoradiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melting Point - Wikipedia PDFDokument51 SeitenMelting Point - Wikipedia PDFKishore KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Gas Ratio - SwapnilDokument33 SeitenSpecific Gas Ratio - SwapnilYhane100% (1)
- FormalinDokument27 SeitenFormalinAdeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoilerDokument29 SeitenBoilerhonchoabhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Ethyl 2520hexanol Properties&UsesDokument11 Seiten2 Ethyl 2520hexanol Properties&UsesRisa Dev100% (1)
- Resultados Sotfware-4Dokument1 SeiteResultados Sotfware-4Luis Fernando Castrillón MadrigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- N-Propanol: Petrochemicals Technical InformationDokument4 SeitenN-Propanol: Petrochemicals Technical Informationsharmi2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- GeneralData Siri NewDokument1 SeiteGeneralData Siri NewRos Neftegaz TransitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factores de Conversion Gas NaturalDokument10 SeitenFactores de Conversion Gas NaturalIvan SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Phase Separator SpreadsheetDokument4 Seiten3 Phase Separator SpreadsheetToyinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiling and Melting Points of Some MetalsDokument5 SeitenBoiling and Melting Points of Some MetalsAshia GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix (SI) (9th. Editon) - A1-A14 - 220329Dokument25 SeitenAppendix (SI) (9th. Editon) - A1-A14 - 220329찬양Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermophysical Properties of Carbon DioxideDokument4 SeitenThermophysical Properties of Carbon DioxideAnonymous 6cQRWqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line 1 Calculation REV 1 PDFDokument6 SeitenLine 1 Calculation REV 1 PDFYYON KYNN KOHNoch keine Bewertungen
- AppendixDokument51 SeitenAppendixgemilang perdikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maersk Olie Og Gas AS Esplanaden 50 DK-1263 Copenhagen K. Denmark Attn. Mr. L. AnderssonDokument21 SeitenMaersk Olie Og Gas AS Esplanaden 50 DK-1263 Copenhagen K. Denmark Attn. Mr. L. AnderssonFatih FıratNoch keine Bewertungen
- GC1-chapter 01Dokument70 SeitenGC1-chapter 01Heidi CotillionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions Test Yourself 3Dokument2 SeitenChemical Reactions Test Yourself 3Nizar MTechNoch keine Bewertungen
- VCS STD 5711 102 09 2005 Method Statement PDFDokument4 SeitenVCS STD 5711 102 09 2005 Method Statement PDFFadi MagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sand Cone Set (T-061) ASTM D1556 - AASHTO T-191Dokument2 SeitenSand Cone Set (T-061) ASTM D1556 - AASHTO T-191Oth'is WatngarninyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Taefdxtoht 4 Oo 8 ADokument16 Seiten2 Taefdxtoht 4 Oo 8 AmelsabaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument36 SeitenLiterature Reviewprakush_prakush0% (1)
- Kera Awak Product CatalogueDokument22 SeitenKera Awak Product CatalogueAnis TaboubiNoch keine Bewertungen
- +worked Examples For Eurocode 2 Final - DeF080723 (SL 16 09 08) - Potporni Zidovi+Dokument11 Seiten+worked Examples For Eurocode 2 Final - DeF080723 (SL 16 09 08) - Potporni Zidovi+Mile GorgievskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Green ConcreteDokument18 SeitenCivil Green Concretesharukh88% (8)
- Phenol: Carboxylation of Phenol: Kolb-Schmitt ReactionDokument9 SeitenPhenol: Carboxylation of Phenol: Kolb-Schmitt ReactionAkhilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : A F P A Decreases, Therefore The Pressure Exerted On The Floor Will IncreaseDokument2 Seiten7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : A F P A Decreases, Therefore The Pressure Exerted On The Floor Will IncreaseRuby Chong100% (1)
- Preformulasi RifaximinDokument19 SeitenPreformulasi RifaximinVilza Dwiki YuvitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Steel Structures - Courses - 2013Dokument253 SeitenSpecial Steel Structures - Courses - 2013Largu George DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- STP 538-1973Dokument239 SeitenSTP 538-1973Tim SchouwNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE Engineering Thermoplastics Design GuideDokument292 SeitenGE Engineering Thermoplastics Design GuideLoke Fong67% (3)
- Thawing 1 RACUDokument66 SeitenThawing 1 RACURfsdjr AceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 - Janjuhah Et Al., - Carbonates and Evaporites1Dokument19 Seiten2017 - Janjuhah Et Al., - Carbonates and Evaporites1Waleed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12th Chemistry Chapter 9 (Coordination Compounds) Important Unsolved QuestionsDokument6 SeitenClass 12th Chemistry Chapter 9 (Coordination Compounds) Important Unsolved Questionsanuragk.kumar2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- GS AFES 3 Pond-ChimneyDokument52 SeitenGS AFES 3 Pond-ChimneyHabibz ZarnuJi100% (1)
- Brochure Antifoams Defoamers Tego AntifoamDokument8 SeitenBrochure Antifoams Defoamers Tego AntifoamAmilaLakmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap-5 Framed StructuresDokument12 SeitenChap-5 Framed StructurestekalignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleaning Pig Designs and ApplicationsDokument24 SeitenCleaning Pig Designs and ApplicationsChristopher BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arun Sir JoCP PaperDokument50 SeitenArun Sir JoCP PaperAmrit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 568 RR Thulasi - CMS Agro Madurai BOQDokument30 Seiten568 RR Thulasi - CMS Agro Madurai BOQEr S Thirumarai NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral RecitationDokument2 SeitenOral RecitationEarl Cris RiggsNoch keine Bewertungen
- JKM550 570N 72HL4 BDV F1 enDokument2 SeitenJKM550 570N 72HL4 BDV F1 enSai LaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron - Carbon SystemDokument21 SeitenIron - Carbon SystemYavana KeerthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 PDFDokument20 SeitenChapter 4 PDFSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bohler - w302 SuperiorDokument8 SeitenBohler - w302 SuperiorHugo Mario Ariza Palacio100% (1)