Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Compact Sections Ratio Check PDF
Hochgeladen von
jtai1983Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Compact Sections Ratio Check PDF
Hochgeladen von
jtai1983Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
AISC_PART 16_Spec.1_A:14th Ed.
_ 2/17/12 2:34 PM Page 16
16.1–16 MEMBER PROPERTIES [Sect. B4.
See also Structural Steel Design by Jack McCormac 5th Ed. Table 5-2
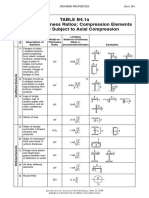
TABLE B4.1a
Width-to-Thickness Ratios: Compression Elements
Members Subject to Axial Compression
Limiting
Case
Width-to- Width-to-Thickness
Description of Thickness Ratio r
Element Ratio (nonslender/slender) Examples
1 Flanges of rolled
I-shaped sections,
plates projecting
from rolled I-shaped
sections; outstanding
E
legs of pairs of b/t 0.56
angles connected Fy
with continuous
contact, flanges of
channels, and
flanges of tees
Unstiffened Elements
2 Flanges of built-up [a]
I-shaped sections
and plates or angle kcE
b/t 0.64
legs projecting from Fy
built-up I-shaped
sections
3 Legs of single
angles, legs of
double angles with
separators, and all E
b/t 0.45
other unstiffened Fy
elements
4 Stems of tees E
d/t 0.75
Fy
5 Webs of doubly-
symmetric I-shaped E
h/tw 1.49
sections and Fy
channels
6 Walls of rectangular
HSS and boxes of E
b/t 1.40
uniform thickness Fy
Stiffened Elements
7 Flange cover plates
and diaphragm E
plates between lines b/t 1.40
Fy
of fasteners or welds
8 All other stiffened
elements E
b/t 1.49
Fy
9 Round HSS
E
D/t 0.11
Fy
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, June 22, 2010
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
AISC_PART 16_Spec.1_A:14th Ed._ 2/17/12 2:18 PM Page 17
Sect. B4.] MEMBER PROPERTIES 16.1–17
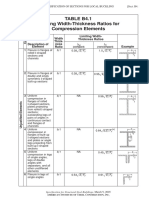
TABLE B4.1b
Width-to-Thickness Ratios: Compression Elements
Members Subject to Flexure
Limiting
Width-to-Thickness Ratio
Case
Width-to- p r
Description of Thickness (compact/ (noncompact/
Element Ratio noncompact) slender) Examples
10 Flanges of rolled
I-shaped sections, E E
channels, and tees b/t 0.38 1.0
Fy Fy
11 Flanges of doubly [a] [b]
and singly symmet- E k E
Unstiffened Elements
ric I-shaped built-up b/t 0.38 0.95 c
sections Fy FL
12 Legs of single
angles E E
b/t 0.54 0.91
Fy Fy
13 Flanges of all
I-shaped sections E E
and channels in b/t 0.38 1.0
flexure about the Fy Fy
weak axis
14 Stems of tees E E
d/t 0.84 1.03
Fy Fy
15 Webs of doubly-
symmetric I-shaped E E
h/tw 3.76 5.70
sections and Fy Fy
channels
16 Webs of singly- hc E [c]
symmetric I-shaped hp Fy E
hc /tw ⎛ ⎞
2
≤ λr 5.70
sections Mp
⎜ 0.54 M − 0.09⎟
Fy
⎝ y ⎠
17 Flanges of
Stiffened Elements
rectangular HSS E E
b/t 1.12 1.40
and boxes of Fy Fy
uniform thickness
18 Flange cover plates
and diaphragm E E
plates between b/t 1.12 1.40
Fy Fy
lines of fasteners
or welds
19 Webs of rectangular
E E
HSS and boxes h/t 2.42 5.70
Fy Fy
20 Round HSS
E E
D/t 0.07 0.31
Fy Fy
[a] kc = 4兾 h / t w but shall not be taken less than 0.35 nor greater than 0.76 for calculation purposes.
[b] FL = 0.7Fy for major axis bending of compact and noncompact web built-up I-shaped members with Sxt /Sxc ≥ 0.7;
FL = Fy Sxt /Sxc ≥ 0.5Fy for major-axis bending of compact and noncompact web built-up I-shaped members with Sxt /Sxc < 0.7.
[c] My is the moment at yielding of the extreme fiber. Mp = plastic bending moment, kip-in. (N-mm)
E = modulus of elasticity of steel = 29,000 ksi (200 000 MPa)
Fy = specified minimum yield stress, ksi (MPa)
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, June 22, 2010
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 15 The Peripheral Vascular System and Lymphatic SystemDokument4 SeitenChapter 15 The Peripheral Vascular System and Lymphatic SystemKhanh Hoang100% (1)
- Breaking Bad News: An Evidence-Based Review of Communication Models For Oncology NursesDokument8 SeitenBreaking Bad News: An Evidence-Based Review of Communication Models For Oncology NursesDaniela Lepărdă100% (1)
- HomelessDokument14 SeitenHomelessapi-318293414Noch keine Bewertungen
- CommunityReadinessHandbook PDFDokument70 SeitenCommunityReadinessHandbook PDFSari Uswatun ChasanahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work-Life Wellness: Redefining SuccessDokument5 SeitenWork-Life Wellness: Redefining SuccessScottDixon01100% (1)
- Simple and Good Career Objectives: Sample Objectives of Resume For FreshersDokument2 SeitenSimple and Good Career Objectives: Sample Objectives of Resume For FreshersSonia LawsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Letter of RecommendationDokument1 SeiteCritical Care Letter of Recommendationapi-5082668670% (1)
- Golden Hour of Neonatal Life - Need of The HourDokument21 SeitenGolden Hour of Neonatal Life - Need of The HourEdwin AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stres NurseDokument137 SeitenStres NursesbjnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Towards Wellness WEFDokument39 SeitenWorking Towards Wellness WEFaudreevee100% (1)
- Bowling Alley Marketing PlanDokument20 SeitenBowling Alley Marketing PlanPalo Alto Software100% (5)
- Piel Et Al - Understanding The Global Dimensions of Health (2005)Dokument303 SeitenPiel Et Al - Understanding The Global Dimensions of Health (2005)Jaime Fernández-Aguirrebengoa100% (1)
- Axially Loaded Compression Member - Table B4.1aDokument1 SeiteAxially Loaded Compression Member - Table B4.1aRamces SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TablasDokument13 SeitenTablashector tudonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tablas de Clasificacion de PerfilesDokument2 SeitenTablas de Clasificacion de PerfilesJuan David MejíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Width-to-Thickness Ratios TableDokument1 SeiteWidth-to-Thickness Ratios TableAljon Maglalang JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit With Thicnkess For Compression ElementsDokument3 SeitenLimit With Thicnkess For Compression ElementsJocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Especificacion - para - Construcciones - de - Acero - Aisc - 360-16 - 0Dokument4 Seiten3 Especificacion - para - Construcciones - de - Acero - Aisc - 360-16 - 0marcelo galarzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Aisc 341 10 Seismically Compact Check CompressDokument2 SeitenPDF Aisc 341 10 Seismically Compact Check CompressSalwa Agita50% (2)
- Ansi Aisc 341-10 Pags58-59Dokument2 SeitenAnsi Aisc 341-10 Pags58-59Jhonny GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Member and Connection Design Requirements: Chapter DDokument3 SeitenGeneral Member and Connection Design Requirements: Chapter DElias Fienco LoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- I-UK Hydro Fitting EODokument43 SeitenI-UK Hydro Fitting EOGutha Giribabu NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Width-to-thickness ratios for steel membersDokument2 SeitenWidth-to-thickness ratios for steel membersbryamdv23100% (1)
- Midterm Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenMidterm Cheat SheetAndrew WatsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech PropertiesDokument14 SeitenMech PropertiesYELLAMANDA SANKATINoch keine Bewertungen
- LRFD Dimensions&Properties FuDokument8 SeitenLRFD Dimensions&Properties FuEngDbtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan Sep 06, 2021Dokument10 SeitenAdobe Scan Sep 06, 2021burhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jiashan Epen Bearing Co., LTDDokument76 SeitenJiashan Epen Bearing Co., LTDifl.iflNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-Compression MembersDokument41 SeitenChapter 3-Compression MembersGamtesa EjetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tsukuba, J 1994 Architects: Naito Architects & Ass., Tokyo Hiroshi Naito, Tatsuo Yoshida º Detail 4/1996Dokument1 SeiteTsukuba, J 1994 Architects: Naito Architects & Ass., Tokyo Hiroshi Naito, Tatsuo Yoshida º Detail 4/1996Stefan JakovljevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Fittings PipeDokument8 SeitenWeld Fittings PipeJavier AffifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assembly Instructions - Tube CouplingsDokument1 SeiteAssembly Instructions - Tube CouplingsEr.Amritpal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawings: Model ZR202G - L Integrated Type Zirconia Oxygen / High Temperature Humidity AnalyzerDokument3 SeitenDrawings: Model ZR202G - L Integrated Type Zirconia Oxygen / High Temperature Humidity AnalyzerRam KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03-Tension MembersDokument35 Seiten03-Tension Memberssherif IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- TC PartnumberDokument1 SeiteTC Partnumbernemi90Noch keine Bewertungen
- TX Topper Bi FilarDokument1 SeiteTX Topper Bi Filarfox7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermocouple With Flange Thermowell Tapered & Adjustable Compensation FittingDokument1 SeiteThermocouple With Flange Thermowell Tapered & Adjustable Compensation Fittingmohan babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Introdution To BJT v1.0 PDFDokument43 Seiten5 - Introdution To BJT v1.0 PDFJames DulangonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module 43 Slab Usd November 2020Dokument4 SeitenReview Module 43 Slab Usd November 2020Ma Ella Mae LogronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolt Torque SpreadsheetDokument1 SeiteBolt Torque Spreadsheetboo huNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slrsebp: Mason Industries, IncDokument2 SeitenSlrsebp: Mason Industries, Incgenas7265Noch keine Bewertungen
- Part Tree-052016Dokument1 SeitePart Tree-052016Siddharth GhorpadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3. T1 TT 31Thrs Famyoy: (Conventional Representation of External and Internal Threads)Dokument3 Seiten2.3. T1 TT 31Thrs Famyoy: (Conventional Representation of External and Internal Threads)Akash VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three: Compression Members: Y.Boopathi - Civil EnggDokument51 SeitenChapter Three: Compression Members: Y.Boopathi - Civil EnggBoopathi YoganathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- R3 Shell Tube HEDokument5 SeitenR3 Shell Tube HEDalber VazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubeside Calculation DetailsDokument1 SeiteTubeside Calculation DetailsTIPAZONoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 6 - (Laterally Supported Beams)Dokument31 SeitenMODULE 6 - (Laterally Supported Beams)Tobi100% (1)
- PTV/PTT Series - 12 MM Potentiometer: FeaturesDokument6 SeitenPTV/PTT Series - 12 MM Potentiometer: FeaturesFrankJoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dull Grading ChartDokument1 SeiteDull Grading Chartkenan192Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-6a Bolt Connection CENG417Dokument35 SeitenChapter-6a Bolt Connection CENG417zakai zakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suffix ListDokument69 SeitenSuffix Listsylvain croteauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tri ConeDokument2 SeitenTri ConeANoch keine Bewertungen
- A D B O M C - P II: Chieving Uctile Ehavior F Oment Onnections ARTDokument5 SeitenA D B O M C - P II: Chieving Uctile Ehavior F Oment Onnections ARTengkjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baseplate Anchor Bolt Is800 SSM VerificationDokument5 SeitenBaseplate Anchor Bolt Is800 SSM VerificationsundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Design of Noncompact and Slender Concrete-Filled Steel Tube (CFT) Beam-ColumnsDokument20 SeitenAnalysis and Design of Noncompact and Slender Concrete-Filled Steel Tube (CFT) Beam-Columnsclam2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Osciloscopio Portatil Mini Micro Dso138Dokument9 SeitenManual Osciloscopio Portatil Mini Micro Dso138tandre111Noch keine Bewertungen
- cp4 ConnectionDokument127 Seitencp4 Connectionznyaphotmail.com100% (1)
- Design of 8-Bolt Stiffened Moment End Plates: Overview of Analytical and Experimental StudiesDokument8 SeitenDesign of 8-Bolt Stiffened Moment End Plates: Overview of Analytical and Experimental StudieswajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet - Burndy - YA4CDokument2 SeitenDatasheet - Burndy - YA4CAriel MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection: NYLIGN Light Duty Flexible CouplingsDokument1 SeiteSelection: NYLIGN Light Duty Flexible Couplingsdragon_ecuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AISC structural steel design guide table for width-to-thickness ratiosDokument2 SeitenAISC structural steel design guide table for width-to-thickness ratiosjtai1983100% (1)
- Propiedades ÁreasDokument13 SeitenPropiedades ÁreasJack BerkampNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarginDokument4 SeitenMarginZeon GeidlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Fitting Symbol Guide Under 40 CharactersDokument5 SeitenPipe Fitting Symbol Guide Under 40 CharactersErnalyn ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME Acceptance WorldwideDokument1 SeiteASME Acceptance Worldwidejtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carber Testing CatalogDokument32 SeitenCarber Testing Catalogjtai1983100% (1)
- Engineering Example CalculationDokument78 SeitenEngineering Example Calculationkae kaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact Testing Enigma: A Review of ASME Section VIII, Division 1, Subsection C, Part UCS, Impact Testing RequirementsDokument13 SeitenThe Impact Testing Enigma: A Review of ASME Section VIII, Division 1, Subsection C, Part UCS, Impact Testing Requirementssanjaypatel25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Oxygen Service PDFDokument4 SeitenGuidelines For Oxygen Service PDFjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrostatic Test Pressure (Psig) For B16.5 Flanges PDFDokument1 SeiteHydrostatic Test Pressure (Psig) For B16.5 Flanges PDFjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Storage, Operation & Maintenance of Heat Exchangers PDFDokument8 SeitenStorage, Operation & Maintenance of Heat Exchangers PDFjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Nozzle Loading Reference TableDokument1 SeitePump Nozzle Loading Reference Tablejtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of ASME Section VIII Division 1 Appendices 1-9 and 1-10Dokument3 SeitenInterpretation of ASME Section VIII Division 1 Appendices 1-9 and 1-10sumedh444Noch keine Bewertungen
- EXAMPLE Nozzle Calculations Using ASME VIII Div 2 Appendix 1-10Dokument16 SeitenEXAMPLE Nozzle Calculations Using ASME VIII Div 2 Appendix 1-10jtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Welding DefectDokument17 SeitenWelding DefectAna Hidayah Syuhada100% (1)
- UG-37 F FactorDokument7 SeitenUG-37 F FactorjamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-Spectacle Blinds - RF 150lbDokument1 Seite13-Spectacle Blinds - RF 150lbDidit SusantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trim Number Chart API ValveDokument2 SeitenTrim Number Chart API Valvemoorthymech1979Noch keine Bewertungen
- NEWCO Cast Steel Bolted Bonnet GGCA CatalogDokument64 SeitenNEWCO Cast Steel Bolted Bonnet GGCA Catalogmcschuster6879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kent Introl Control Valve Cross Section PDFDokument1 SeiteKent Introl Control Valve Cross Section PDFjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Codes and Standards for High-Pressure Vessel DesignDokument6 SeitenInternational Codes and Standards for High-Pressure Vessel DesignkylenilsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Durco Plug Valve Dimensions PDFDokument28 SeitenDurco Plug Valve Dimensions PDFjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Fitting Symbol Guide Under 40 CharactersDokument5 SeitenPipe Fitting Symbol Guide Under 40 CharactersErnalyn ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Valve Twin Seal Brochure PDFDokument28 SeitenGeneral Valve Twin Seal Brochure PDFtogentongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrostatic Test Pressure (Psig) For B16.5 FlangesDokument1 SeiteHydrostatic Test Pressure (Psig) For B16.5 Flangesjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bs 01 904b PDFDokument19 SeitenBs 01 904b PDFRoo FaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Oxygen Service PDFDokument4 SeitenGuidelines For Oxygen Service PDFjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kent Introl Control Valve Cross SectionDokument1 SeiteKent Introl Control Valve Cross Sectionjtai1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- CIVL-365 Tutorial 8 SolutionDokument3 SeitenCIVL-365 Tutorial 8 SolutionIvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dcom QuestionDokument3 SeitenDcom Questionsushant sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterDokument18 SeitenFeatures General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterAntonioNobregaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horizontal Projectile WSDokument3 SeitenHorizontal Projectile WSForsbergPhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arihant 40 Days Crash Course For JEE Main Physics (Crackjee - Xyz)Dokument464 SeitenArihant 40 Days Crash Course For JEE Main Physics (Crackjee - Xyz)Milan Dai50% (4)
- Grammarism Ed Ing Adjectives Test 4 1189424Dokument2 SeitenGrammarism Ed Ing Adjectives Test 4 1189424Royal Stars Drama AcademyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDDokument6 SeitenLab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDLee-Ann LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monsterology Activity KitDokument2 SeitenMonsterology Activity KitCandlewick PressNoch keine Bewertungen
- JCB 532-120 PDFDokument4 SeitenJCB 532-120 PDFSyazrur Syazmir0% (1)
- Artikel Ilmiah FikriDokument6 SeitenArtikel Ilmiah FikriViola Mei DamayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Algebra by A.S.HadiDokument4 SeitenMatrix Algebra by A.S.HadiHevantBhojaram0% (1)
- Capacity and Safety Analysis of Hard Shoulder Running HSR A Motorway Case Study 2016 Transportation Research Part A Policy and PracticeDokument22 SeitenCapacity and Safety Analysis of Hard Shoulder Running HSR A Motorway Case Study 2016 Transportation Research Part A Policy and PracticeZen ZeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDokument6 SeitenType 2 Diabetes MellitusJoy NisoladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gold Grade of Epithermal Gold Ore at Lamuntet, Brang Rea, West Sumbawa District, West Nusa Tenggara Province, IndonesiaDokument10 SeitenGold Grade of Epithermal Gold Ore at Lamuntet, Brang Rea, West Sumbawa District, West Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesiasukri arjunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operator Manual T2100-ST2 - ST1Dokument50 SeitenOperator Manual T2100-ST2 - ST1Nurul FathiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 01 Breather Filters GBDokument8 Seiten10 01 Breather Filters GBosuengNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Qualification TestDokument5 SeitenEnglish Qualification TestMoh FaisolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapid Communication: Spontaneous Abortions and Policies On COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Use During PregnancyDokument14 SeitenRapid Communication: Spontaneous Abortions and Policies On COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Use During PregnancyStéphane BoucherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Risna YantiDokument14 SeitenJurnal Risna YantiRisnayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABYIPDokument18 SeitenABYIP千住 マリエルNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Subjects (1st - 5th Year) - 1Dokument5 SeitenCivil Engineering Subjects (1st - 5th Year) - 1Vincent TayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 5 Q1 W10Dokument31 SeitenMathematics 5 Q1 W10Aices Jasmin Melgar BongaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LutensolxpDokument11 SeitenLutensolxppkh29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1Dokument32 SeitenAustralian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1binoyrajcrNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongDokument3 SeitenI Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongAndréia E NiltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Computing 14) A. Aguilera, D. Ayala (Auth.), Professor Dr. Guido Brunnett, Dr. Hanspeter Bieri, Professor Dr. Gerald Farin (Eds.) - Geometric Modelling-Springer-Verlag Wien (2001)Dokument356 Seiten(Computing 14) A. Aguilera, D. Ayala (Auth.), Professor Dr. Guido Brunnett, Dr. Hanspeter Bieri, Professor Dr. Gerald Farin (Eds.) - Geometric Modelling-Springer-Verlag Wien (2001)ANDRES Fernando Mosquera DIAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coley A4Dokument49 SeitenColey A4mfiarkeeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDokument45 Seiten2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDaondy Friarsa SoehartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perioperative HypothermiaDokument4 SeitenPerioperative Hypothermiasri utari masyitahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Sense Mechanics 9Dokument9 SeitenCommon Sense Mechanics 9Vikas VatsNoch keine Bewertungen