Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ans P2 Johor 2010
Hochgeladen von
Rozaini OthmanOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ans P2 Johor 2010
Hochgeladen von
Rozaini OthmanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SULIT 2
4551/2
Marking scheme
Section A
Question 1
Question Mark Scheme Mark
1(a) Able to state the types of solutions
Sample answers
Solution J: Hypotonic solution
Solution K: Isotonic solution
Solution L: Hypertonic solution 1+1+1 3
(b) Able to explain the difference in curvature
Sample answer
Solution J:
F1: The strip in solution J curved outwards/ towards the
epidermis/ epidermal layer
P1: (Cortex) cells/ (parenchyma) cells become turgid/ longer
because water diffuses into the cell/ protoplasm/ cytoplasm
by osmosis.
P2: Epidermal cells have a layer of cuticle on the outside
P3: which resist/ restrict the entry of water (and retain its normal
size)
Any 2 1+1
Solution L:
F2: The strip in solution L curved inward/ towards the cortex/
parenchyma layer
P4: Water diffuses out of the cytoplasm/ protoplasm of the
(cortex) cells/ (parenchyma) cells by osmosis
P5: The cytoplasm and/or the vacuole of the cells will shrink
Any 2
1+1 4
(c)(i) Able to state the solution isotonic to the cell sap
Sample answer
Solution K 1
Able to give reasons correctly
(c)(ii)
Sample answer
P1: The strip in solution K remain straight
P2: because the (cortex/ parenchyma) cells have not increase
turgidity/flaccidity// no change in size/ remain the same size
P3: Water diffuses in and out of the cells by osmosis at the
same rate// Rate of endosmosis equal rate of exosmosis
Any 2
1+1 3
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 3
4551/2
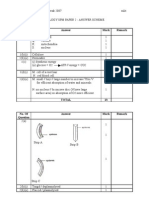
(d) Able to draw the labelled diagram
D: Correct drawing 1
with vacuole
doubled-line cell wall
plasma membrane pulled away with some parts attached to
the cell wall (totally detached from the cell wall is not accept)
L: Correct labels
plasma/ cell membrane 1
vacuole
Cell wall
Vacuole
Plasma/ Cell 2
membrane
Total 12
Question 2
No Mark Scheme Mark
2 (a)(i) Able to state the type of cell division involved in cell cycle in
Diagram 2
Answer :
Mitosis/Mitotic cell division 1
(a)(ii) Able to state one reason for answer in (a)(i)
Sample answer :
P1 : Produces 2 daughter cells
P2 : Occurs at root tip 1
Any 1 P
(a)(iii) Able to arrange the phases in Diagram 2 in correct 3
sequence by using the letters in Diagram 2
Answer :
QRTSP
1
(b) Able to explain why root tip is used for preparing slides to
show this cell cycle
Sample answer :
F : Root tip is growing region 1+1
P : the cells are actively divide 2
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 4
4551/2
(c)(i) Able to name stage Q
Answer :
Interphase 1
(c)(ii) Able to explain the importance of stage Q to this cell cycle
Sample answer :
F1: Replication of DNA occurs
P1: to produce two genetically identical daughter cells
F2 : Synthesis ATP//accumulate energy
P2 : Enable the cell to divide
Any 2 1+1 3
(d)(i) Able to define cloning
Sample answer :
P1: Process of producing genetically identical organisms 1+1
P2: through asexual reproduction
P3: by stem/leaf cutting/layering/grafting/any suitable example
Any 2
(d)(ii) Able to state one advantage and one disadvantage of cloning
Sample answer :
1
Advantage :
P1: Large numbers of offspring can be produced 4
P2: in a short time
P3: The good characteristic of parent can be maintained in the
offspring
Any 1 P 1
Disadvantages :
P3: The offspring produced do not show any genetic variation
P4: The offspring produced have same level of resistance to
certain diseases/pests
Any 1 P
TOTAL 12
Question 3
No Mark Scheme Mark
3 (a)(i) Able to state the process by which gaseous exchange takes
place across the alveolus.
Sample answer :
(Simple) diffusion 1
(a)(ii) Able to explain how the process occur
Sample answer :
F: Partial pressure of oxygen in the air of alveolus is higher than 1+1
in blood capillary
P: (Gas diffuse) follow the concentration gradient 3
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 5
4551/2
(b)(i) Able to name blood vessel S
Answer :
Pulmonary artery
1
(b)(ii) Able to describe the role of blood vessel S in transporting
oxygen from alveolus to muscle cell
Sample answer :
P1: In the blood, oxygen from alveolus combine with respiratory 1+1
pigment / haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin / oxygenated
blood
P2: transport oxygenated blood // oxyhaemoglobin to heart
P3: the heart pump the oxygenated blood to muscle cells
Any 2 3
(c)(i) Able to name process P and process Q
Answer :
P : Aerobic respiration 1+1
Q : Anaerobic respiration
(c)(ii) Able to explain one difference between process P and
process Q
Sample answer :
P Q
D1 Complete breakdown Incomplete breakdown of
of glucose glucose
E1 Release large amount Release less amount of 1+1
of energy // 2898 kJ energy // 150 kJ per
per molecule glucose // molecule glucose // 2
38 molecules of ATP molecules of ATP
D2 Produce carbon Produce lactic acid
dioxide and water
E2 Produced as waste Caused muscular 4
product cramps/fatigue
D3 Occurs in the Occurs in the cytoplasm
mitochondria
E2 Oxygen is required Oxygen is not required
Any 2
(d) Able to explain the statement
Sample answer :
F1: (During the vigorous activity) the muscle cells are in a state 1+1
of oxygen deficiency / oxygen debt // the blood cannot
supply oxygen fast enough to meet the demand for energy /
ATP
P1: (The increase in heartbeat rate) is to deliver more oxygen /
glucose to muscle cells
P2: to obtain extra energy (from anaerobic respiration) // to
increase rate of cellular respiration
P3: to remove more carbon dioxide from the muscle cells
Any 2
2
TOTAL 12
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 6
4551/2
Question 4
No Mark Scheme Mark
4(a)(i) Able to state type of blood circulatory system shown by
organism P and organism Q.
Answer
Organism P :
Double circulatory system
Organism Q :
Single circulatory system 1+1 2
(a)(ii) Able to name one example of organism P and organism Q.
Sample answers
Organism P :
Human
Organism Q :
Fish
1+1 2
(b) Able to explain the importance of having the blood
circulatory system to organism P.
Sample answer
F : (double circulatory system ) is more efficient
P1: the heart pumps the blood twice / the blood flow into the heart
twice in a complete circulation.
P2 : higher pressure of blood can be maintained.
P3 : the blood travels more faster to organs
P4 : the organs get sufficient amount of glucose / oxygen /
nutrient // the waste product / carbon dioxide / urea can be
eliminated out of organ.
Any 3 1+1+ 3
1
(c) Able to explain one difference of heart structure between
organism P and organism Q.
Sample answer
F : heart of organism P has four chamber but organism Q has
two chamber
P1: organism P has right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle and left
ventricle but organism Q has ventricle and atrium. //
organism P has two atriums and two ventricles but organism
Q has one ventricle and one atrium.
P2 : in organism P , the heart receives both oxygenated blood
and deoxygenated blood while in organism Q , the heart only
receives deoxygenated blood.
Any 2
1+1 2
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 7
4551/2
(d) Able to explain why a person needs second injection to
maintain the level of immunity
Sample answer
F : booster dose
P1 : stimulate lymphocycte to produce more antibody
P2 : to achieve immunity level
P3 : that protect the person against disease
Any 3 1+1+1 3
Total 12
Question 5
No Mark Scheme Mark
5(a) Able to complete Diagram 5 to show the cross between the
plants
Sample Answer
1. RRTT
2. rrtt
3. Genotype F1 : RrTt
4. Phenotype F1 : Red, tall 1+1+1+ 3
1
(b)(i) Able to Use Punnett Square to show crossing of F1 generation
to produce F2 offspring.
Sample answers
Gametes RT Rt rT rt
RT RRTT RRTt RrTT RrTt
Rt RRTt RRtt RrTt Rrtt
rT RrTT RrTt rrTT rrTt
rt RrTt Rrtt rrTt rrtt
G : all gametes correct = 1 mark
C : 14 to 16 genotype correct = 2 marks
4 to 13 genotype correct = 1 mark 1+2 4
(b) Able to calculate phenotype ratio of the offspring produced in F2
(ii) generation
Sample answer
Phenotype: Red, Tall Red, dwarf White, tall White, dwarf
Calculation 9 3 3 1
: 16 16 16 16
Ratio: 9 3 3 1
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 8
4551/2
All phenotype correct = 1 mark
All calculation correct = 1 mark
All ratio correct = 1 mark
1+1+1 3
(c) Able to explain why some of the offspring produced do not have
same phenotype as their parents.
Sample answer
P1: The dominant allele / R / T will mask/cover the effect of the
recessive allele / r / t //any suitable explanation
P2: a recessive allele / r / t only expresses itself when dominant
allele / R / T is absent
P3: RrTt represent red flowered tall plant while white flowered dwarf
plant are not expressed // any suitable example of genotype and
phenotype
Any 2 1 + 1 2
Total 12
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 9
4551/2
Section B
Question 6
No Mark Scheme Marks
6(a) Able to describe the differences between light reaction and
dark reaction
Sample answers:
Light reaction Dark reaction
D1. Occurs in granum Occurs in stroma
D2. Requires light Does not require light
D3. Involves photolysis of Involves reduction/fixation
water of carbon dioxide
D4. Materials required is Materials required is
water carbon dioxide
D5. Produces oxygen and Produces glucose
water Max
Any 4 4m
(b) Able to explain how plants grown in greenhouses can
ensure the production of crops throughout the year.
Sample answer:
F: In temperate countries light intensity / temperature changes
throughout the year.
P1: In winter , temperature is very low
P2: In autumn, the plants shed their leaves // Light intensity/
temperature is low
P3: Rate of photosynthesis is very low
P4: In spring and summer, the light intensity/temperature are
optimum for photosynthesis.
P5: So the rate of photosynthesis is maximum / highest.
P6: In the greenhouse, light intensity/concentration of carbon
dioxide/temperature are maintained at optimum level (for
photosynthesis ) throughout the year.
P7: So the rate of photosynthesis is maintained at maximum
level throughout the year (regardless of changes in light
intensity or temperature).
P8: The plants are able to increase yields / increase the crops Max
production throughout the years. 6m
Any 6
(c) Able to explain the rate of photosynthesis in plant
throughout the day
Sample answer:
F1: From 0000 to 0600, the rate of photosynthesis is very low
P1: The light intensity / temperature is (very) low
P2: ( At low temperature,) photosynthetic enzymes are inactive.
F2: From 0600 to 1200 , the rate of photosynthesis increase
(rapidly)
P3: Light intensity / Temperature also increases
P4: Enzyme for photosynthesis become more active.
P5: Stomata open wider to allow absorption of more carbon
dioxide
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 10
4551/2
F3: The rate of photosynthesis is maximum / the highest at 1200
P6: The light intensity / temperature is optimum (for
photosynthesis).
P7: Enzymes are the most active.
F4: From 1200 to 1800, the rate of photosynthesis decreases
P8: Light intensity / temperature decreases
P9: Photosynthetic enzyme are less active
P10: Stomatal openings/pores become smaller
P11 : Less carbon dioxide is absorbed
F5: From 1800 to 2300 , the rate of photosynthesis become very
low/stopped/ceased
P12 : Light intensity / temperature is very low
P13: Photosynthetic enzymes are not active
P14: Stomata closed Max
P15: Very little / no carbon dioxide is absorbed 10m
Any 10
Total 20
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 11
4551/2
Question 7
No Mark Scheme Sub Total
mark mark
7 (a) Able to describe how the structures of kidney are adapted 4
to enable them to carry out homeostasis process.
Sample answer
F1 : (each kidney) contains hundreds of thousand / a large
number of nephrones
P1 : to filter substances from the blood efficiently.
F2 : (each kidney) has ureter
P2 : to carry away the urine / solution of wastes dissolved in
water / creatinine/toxin and drugs
F3 : (each kidney) received blood (that already) under
relatively high pressure.
P3 : ultrafiltration can take place efficiently
F4 : the kidney is controlled by negative feedback
mechanisms
Any 4
(b) Able to describe how the machine used to remove waste 6
product such as urea from person with kidney failure .
Sample answer
P1 : blood from the patient’s artery is passed through a
machine
P2 : which contains a dialyser / dialysis solution
P3 : dialysis tubing has a semi-permeable membrane
P4 : concentration of waste molecules / urea in blood is
higher than in the dialysis solution // there is concentration
gradient between the blood and dialysis solution
P5 : waste molecules / urea / excess salts diffuse through
membrane from blood to dialysis solution.
P6 : dialysis solution is continuously being replaced //
essential substances remain in the blood.
P7 : plasma protein / red blood cells are not able to diffuse
through membrane of dialysis tubing
P8 : because the size is bigger/too big
P9 : the direction of the flow of blood is opposite to the
direction of dialysis solution
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 12
4551/2
P10 : to ensure the waste molecule / urea is continuously
being remove from blood to dialysis solution.
P11 : the filtered blood re-enters the patients blood vessel
Any 6
(c) Able to explain the differences between the percentage of 10
chemical substances in blood and urine.
Sample answer
F1 : percentage of water in blood is higher than in urine.
P1 : In the proximal convoluted tubule
P2 : The Na+ are pumped into the capillary //
some salts are reabsorbed by a active transport
P3 : The movement of solutes into the capillary network
decreases the solute concentration of the filtrate but
increases the solute concentration in the capillary
network.
P4 : As a result, water diffuses into blood capillaries by
osmosis from the proximal convoluted tubule / Loop of
Henle / distal convoluted tubule / collecting duct
F2 : Percentage of plasma protein is higher in blood compared
to urine // percentage of plasma protein is nil in urine
P5 : size of plasma proteins are larger/too large which cannot
be filtered out/diffused out during ultrafiltration.
F3 : percentage of glucose is high in blood but nil in urine
P6 : All glucose are reabsorbed by active transport at proximal
convoluted tubule.
F4 : percentage of urea is higher in urine than in blood
P7 : Urea is actively transported from the blood capillary to the
distal convoluted tubule.
P8 : by secretion process
Any 10
Total 20
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 13
4551/2
Question 8
No Mark Scheme Sub Total
Mark Mark
8 (a)(i) Able to explain the cause of the phenomenon and its
effect on the environment
C: Causes of the phenomenon
E: Effects of the phenomenon
Sample answers
F : This phenomenon is called green house effect
C1: Combustion of fossil fuels from vehicles/ factories/
forest burning / coal-fired power station
C2: excessive deforestation
C3: increase carbon dioxide concentration in the
atmosphere
C4: pollutants/CFC/methane
E1: carbon dioxide traps heat/ infra-red light/ long-wave
radiation
E2: increase in global/ world atmospheric temperature/
cause a rise in Earth’s temperature/ global warming.
E3: melting of polar ice/ rise in the sea levels
F with any 5 points 1+5 6
(a)(ii) Able to suggest measures to overcome the
phenomenon
Sample answers
P1: use alternative source of energy to reduce the usage of
fossil fuels/energy generated from wind / water/ solar
P2: restrict open burning/ forest burning/ use incinerator
P3: reduce deforestation for farming/other development
projects
P4: Selective harvesting/logging/cut matured tree only
P5: replanting more trees which have been cut down
P6: the use of technology / unleaded petrol / catalytic
converter
Any 4 4 4
(b) Able to discuss the effects of the phenomenon on the
lives on Earth.
Sample answers
F: The phenomenon is known as the thinning/ depletion of
the ozone layer
P1: More ultraviolet ray reaches the Earth’s surface
P2: Ultra-violet ray will deteriorate human’s body immune
system
P3: An increase in the number of people suffering from skin
cancer/ melanoma / cataract
P4: High ultraviolet rays destroy phytoplanktons
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 14
4551/2
P5: break the food chain of marine life / the aquatic
ecosystem
P6: the number of stomata / chlorophyll of the leaves will be
reduced
P7: Rate of photosynthesis decreases
F with any 5P 1+5 6
(c) Able to explain the concept of sustainable and its need
to protect our environment.
Sample answers
F: (Sustainable development refers to) the measures
undertaken to ensure that human activity optimally
utilize Earth’s natural resources such that they can be
replenished naturally//suitable explanation
P1: Sustainable development is necessary as the rate at
which man is using the finite natural resources will
compromise future generation’s demands//suitable
explanation
P2: Ultimately, the natural resources, if continued to be
depleted, will no longer be able to sustain human
society//suitable explanation
P3: Sustainable development involves the protection of
air/land/water
P4: which make up the surrounding we live in and survive
upon.
P5: (It is intimately linked) to the protection of wildlife as well
P6: in order to maintain a stable/balanced ecosystem
F + any 3P 1+3 4
Total 20
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 15
4551/2
Question 9
No. Mark Scheme Marks
9(a) Able to state what fertilisation is
(i)
Sample Answer
Fertilisation occurs when the nucleus of a sperm and the nucleus 1
of an ovum fuse to form zygote
(a)(ii) Able to describe the early development after the formation of
a zygote from process I to IV
Sample Answer
Process I
P1 : Fertilisation occurs at the fallopian tube to form a zygote
Process II
P2 : the zygote begins to divide by mitosis
P3 : known as an embryo
P4 : The zygote is divided successively into a solid mass of cell
P5 : At this stage, a morula is formed
Process III
P6 : the morula then divides to form a hollow ball with fluid-filled
cavity
P7: called blastocyst//blastula
Process IV
P8 : (seven day after fertilisation) the blastocyst implants itself into
the endometrium
P9 : The blastocyst/blastula formed has an inner cell mass which
will develop into an embryo
Any 7 7
(iii) Able to predict what might happen if the corpus luteum fails
to develop after fertilisation.
Sample answer:
P1 : the level of progesterone drops / decrease
P2 : the foetus will be aborted
P3 : because the function of progesterone is to maintain
thickening / vascularisation of the endometrium wall
Any 2
2
(b) Able to describe the in vitro fertilisation technique
Sample answer:
F : In-vitro fertilisation (IVF) is the fertilisation of the egg that
occurs outside the human body
P1 : the wife was injected with hormone to stimulate the
development of the secondary oocyte / ovum in ovaries
P2 : secondary oocyte / immature ova are collected by using a
laparoscope (from ovary before ovulation)
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
SULIT 16
4551/2
P3 : The immature ova are placed in culture solution to mature
P4 : Sperms are collected/placed in the culture solution
P5 : sperms from husband fertilise with the secondary oocyte in a
Petri dish (contains culture medium)
P6 : (after fertilization) zygote will divide by mitosis
P7 : (after 2 days) formed embryo are at eight celled stage
P8 : Afew embryos/fertilised ova are transferred into the
endometrium wall of uterus by using catheter
P9 : embryos/fertilised ova are implanted into endometrium wall
of uterus and start to develop
P10 : baby that is delivered is called test tube baby
P11 : This technique is complicated / expensive/the
probability to success is low
F with any 9 Ps 10
TOTAL MARK 20
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN TAMAT
4551/2 © 2010 Hak Cipta JPNJ SULIT
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bio PPT T4 2021 SkemaDokument4 SeitenBio PPT T4 2021 SkemaHaslinda SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Paper 2 Marking SchemeDokument15 SeitenBiology Paper 2 Marking Schemeveronica francisNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Spmsoalan) Skema Biologi K2 Terengganu 2014Dokument12 Seiten(Spmsoalan) Skema Biologi K2 Terengganu 2014zaihassniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melaka Marking Scheme Biology Paper 2 & 3Dokument29 SeitenMelaka Marking Scheme Biology Paper 2 & 3smtsp0% (1)
- Section A No. of Answer Mark Remark: EpidermisDokument11 SeitenSection A No. of Answer Mark Remark: EpidermisFerguson TehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Perak 2007 BIOLOGY SPM PAPERDokument11 SeitenMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Perak 2007 BIOLOGY SPM PAPERhasimahazitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Scheme of P2Dokument15 SeitenAnswer Scheme of P2hasimahazitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema f4Dokument11 SeitenSkema f4HAMIRAH ABD HAMIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Scheme Bio Paper 2 PPT f4 2017Dokument7 SeitenAnswer Scheme Bio Paper 2 PPT f4 2017Norfaezah RomliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulit 4551/2: Reject: Provide Reject: AbsorbDokument17 SeitenSulit 4551/2: Reject: Provide Reject: AbsorbYatihanna MrodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Jawapan StrukturDokument7 SeitenSkema Jawapan Strukturmarwani mat nasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peraturan Pemarkahan Biologi K2 4551/2: Tingkatan 5Dokument28 SeitenPeraturan Pemarkahan Biologi K2 4551/2: Tingkatan 5Kah Lok OoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Paper 2 Mark SchemeDokument14 SeitenBiology Paper 2 Mark SchemeMeiyien YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP k2 Percubaan SBP 2007Dokument3 SeitenPP k2 Percubaan SBP 2007kamil muhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio2 Marking SBPDokument17 SeitenBio2 Marking SBPSimPorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retest Answer Scheme BiologyDokument7 SeitenRetest Answer Scheme Biologyg-16355677Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007Dokument17 SeitenMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007hasimahazitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2Dokument2 SeitenWeek 2ahmedpadela84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P2 (Structure)Dokument5 SeitenMark Scheme P2 (Structure)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W AnsDokument93 Seiten2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W Ansjee2kk100% (1)
- Skema Pemarkahan Kertas 2 Biologi PPT 2016, PPD Hulu SelangorDokument15 SeitenSkema Pemarkahan Kertas 2 Biologi PPT 2016, PPD Hulu SelangorFerguson TehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4551 Biologi Skema Pemarkahan 2018Dokument15 Seiten4551 Biologi Skema Pemarkahan 2018danialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Sciences P1 GR 10 Exemplar Memo EngDokument8 SeitenLife Sciences P1 GR 10 Exemplar Memo EngstephanseggsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2 Biologi Trial SB PPDokument12 SeitenP2 Biologi Trial SB PPFerguson TehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Biologi Kertas 1 Mid Year 2007Dokument21 SeitenAnswers Biologi Kertas 1 Mid Year 2007BtgPeiiYiingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology N5 Past Paper Questions Cell Biology1Dokument46 SeitenBiology N5 Past Paper Questions Cell Biology1moizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Trial 2014 Batu PahatDokument25 SeitenSkema Trial 2014 Batu PahatKavinesh GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SkemaDokument21 SeitenSkemaMarch H AHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial SPM SBP 2010 Biology Marking SchemeDokument29 SeitenTrial SPM SBP 2010 Biology Marking SchememarwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans Bio 2010Dokument15 SeitenAns Bio 2010bendthedicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Num. Scoring Criteria MarksDokument12 SeitenNum. Scoring Criteria MarkswhitneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme, BIOLOGY Paper 2, Trial SBP 2007: AnswerDokument14 SeitenMark Scheme, BIOLOGY Paper 2, Trial SBP 2007: Answerhuixin1017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Worksheet Answerkey Grade 9Dokument5 SeitenRevision Worksheet Answerkey Grade 9lenora.fernandes-smchsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument4 SeitenBiologyAbanggi k sangmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Kertas 1&2 N9 2020Dokument25 SeitenSkema Kertas 1&2 N9 2020Azween SabtuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 6 June 2000Dokument3 SeitenPaper 6 June 2000MSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Dokument0 SeitenAnswer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Thuran NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Tganu k2 (Skema)Dokument13 SeitenTrial Tganu k2 (Skema)Maizla IzmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokument65 SeitenCell Structure and FunctionIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans Paper 2 SelangorDokument12 SeitenAns Paper 2 SelangorRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10: National Senior CertificateDokument13 SeitenGrade 10: National Senior CertificateMalerh VVE Marlon 223100% (1)
- Trial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaDokument14 SeitenTrial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaFarah Shafiqah AmiruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Set-2 KeyDokument14 SeitenBiology Set-2 Keyroyal ghostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme 2017Dokument10 SeitenMark Scheme 2017Millie DanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Practise Answers To Practise Questions Not On Test Topic 2 Cells 1 HourDokument7 SeitenExtra Practise Answers To Practise Questions Not On Test Topic 2 Cells 1 HouremmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gr.11 Life Sciences Remote learning workbook term 2_RevisionDokument29 SeitenGr.11 Life Sciences Remote learning workbook term 2_Revisionbonolomasemola68Noch keine Bewertungen
- LFSC March QP & Memo 2020 Gr10Dokument14 SeitenLFSC March QP & Memo 2020 Gr10wanyanemosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 10th 1st Half Final OkDokument2 SeitenBio 10th 1st Half Final OkAyyaz ShadNoch keine Bewertungen
- TERHAD Plant Excretion Mark SchemeDokument4 SeitenTERHAD Plant Excretion Mark SchemeaminahNoch keine Bewertungen
- FHSC1234 Tutorial 9S 202210Dokument5 SeitenFHSC1234 Tutorial 9S 202210Zhi YongNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biochemistry of Development: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyVon EverandThe Biochemistry of Development: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyVon EverandThe Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zika Virus and Diseases: From Molecular Biology to EpidemiologyVon EverandZika Virus and Diseases: From Molecular Biology to EpidemiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification and Guide to the LiteratureVon EverandThe Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification and Guide to the LiteratureBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research in ProtozoologyVon EverandResearch in ProtozoologyTze-Tuan ChenBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemical Transmission of Nerve Impulses: A Historical SketchVon EverandChemical Transmission of Nerve Impulses: A Historical SketchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P2 (Kedah)Dokument11 SeitenMark Scheme P2 (Kedah)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P1 (Kedah)Dokument2 SeitenMark Scheme P1 (Kedah)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biologi Kertas 3 1 Jam 30 Minit: Program Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2010Dokument10 SeitenBiologi Kertas 3 1 Jam 30 Minit: Program Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2010Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2010Dokument30 SeitenProgram Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2010Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking Scheme (Kedah)Dokument15 SeitenMarking Scheme (Kedah)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Dokument24 SeitenPerfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Set 3Dokument36 SeitenAnswer Set 3Rozaini Othman0% (2)
- Program Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Biologi STPM Kedah 2012 (Paper 1)Dokument33 SeitenProgram Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Biologi STPM Kedah 2012 (Paper 1)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To BiologyDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To BiologyRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme: Program Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2010Dokument14 SeitenMark Scheme: Program Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2010Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biologi: Program Peningkatan Prestasi AkademikDokument16 SeitenBiologi: Program Peningkatan Prestasi AkademikRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans Paper 2 SelangorDokument12 SeitenAns Paper 2 SelangorRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SET 2 AnswerDokument55 SeitenSET 2 AnswerRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Set 3Dokument36 SeitenAnswer Set 3Rozaini Othman0% (2)
- Set 1Dokument16 SeitenSet 1Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SET 1 AnswerDokument17 SeitenSET 1 AnswerRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P3 Melaka (SPM)Dokument10 SeitenMark Scheme P3 Melaka (SPM)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Perfect Score Biology 2010-Set-2Dokument39 SeitenSPM Perfect Score Biology 2010-Set-2Fikri ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P2 Melaka (SPM)Dokument9 SeitenMark Scheme P2 Melaka (SPM)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P2 Pahang (STPM)Dokument16 SeitenMark Scheme P2 Pahang (STPM)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P1 and P2 KedahDokument20 SeitenMark Scheme P1 and P2 KedahRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P1 Pahang (STPM)Dokument2 SeitenMark Scheme P1 Pahang (STPM)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item No. Suggested Answers: Marks: Skema Trial Biology 2010Dokument10 SeitenItem No. Suggested Answers: Marks: Skema Trial Biology 2010scribd_lostandfoundNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 Pahang (STPM)Dokument11 SeitenPaper 2 Pahang (STPM)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1 Kedah (STPM)Dokument36 SeitenPaper 1 Kedah (STPM)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- P3Q2 KedahDokument1 SeiteP3Q2 KedahRozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1 Pahang (STPM)Dokument21 SeitenPaper 1 Pahang (STPM)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking Scheme: Paper Three - Trial Biology 2010 Question 1: 1 (A)Dokument6 SeitenMarking Scheme: Paper Three - Trial Biology 2010 Question 1: 1 (A)Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2 Perlis 2010Dokument20 SeitenP2 Perlis 2010Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme P3Q2Dokument6 SeitenMark Scheme P3Q2Rozaini OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)Dokument3 SeitenUT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daughters of The Storm by Kim Wilkins - Chapter SamplerDokument32 SeitenDaughters of The Storm by Kim Wilkins - Chapter SamplerHarlequinAustraliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chetan Bhagat's "Half GirlfriendDokument4 SeitenChetan Bhagat's "Half GirlfriendDR Sultan Ali AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDokument62 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsTeds TV89% (84)
- Bethany Getz ResumeDokument2 SeitenBethany Getz Resumeapi-256325830Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Dokument51 SeitenTrove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Ceren ArkancanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeDokument44 SeitenThe Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeYiğit KılıçNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHB 2Dokument15 SeitenCHB 2Dr. Guruprasad Yashwant GadgilNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Life and Works of Jose RizalDokument20 SeitenThe Life and Works of Jose RizalBemtot Blanquig100% (1)
- Febrile SeizureDokument3 SeitenFebrile SeizureClyxille GiradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AJK Newslet-1Dokument28 SeitenAJK Newslet-1Syed Raza Ali RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masonry Brickwork 230 MMDokument1 SeiteMasonry Brickwork 230 MMrohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Information Technology and Innovation To Improve Business Performance Through Marketing Capabilities in Online Businesses by Young GenerationsDokument10 SeitenThe Impact of Information Technology and Innovation To Improve Business Performance Through Marketing Capabilities in Online Businesses by Young GenerationsLanta KhairunisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFDokument6 Seiten3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFPablo MatrakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MKT-case StudyDokument7 SeitenMKT-case StudyJoe Thampi KuruppumadhomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panasonic TC-P42X5 Service ManualDokument74 SeitenPanasonic TC-P42X5 Service ManualManager iDClaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ne 01 20 09 2018Dokument436 SeitenNe 01 20 09 2018VaradrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wika Type 111.11Dokument2 SeitenWika Type 111.11warehouse cikalongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Castel - From Dangerousness To RiskDokument10 SeitenCastel - From Dangerousness To Riskregmatar100% (2)
- Kastanakis 2014Dokument8 SeitenKastanakis 2014Andreea Georgiana MocanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM206 Answers 1Dokument3 SeitenCHEM206 Answers 1Shiro UchihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color Codes and Irregular Marking-SampleDokument23 SeitenColor Codes and Irregular Marking-Samplemahrez laabidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectDokument16 SeitenFuture Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectsulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Useful Coaching Questions: Questions To Create A State Change Questions To Ask When Something Goes WrongDokument2 SeitenUseful Coaching Questions: Questions To Create A State Change Questions To Ask When Something Goes WrongAntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'Dokument5 SeitenMark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'bhaskkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Attendance Management SystemDokument54 SeitenAndroid Attendance Management Systemskpetks75% (12)
- STEM Spring 2023 SyllabusDokument5 SeitenSTEM Spring 2023 SyllabusRollins MAKUWANoch keine Bewertungen
- COT EnglishDokument4 SeitenCOT EnglishTypie ZapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nqs PLP E-Newsletter No68Dokument5 SeitenNqs PLP E-Newsletter No68api-243291083Noch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesDokument126 Seiten01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesSreeja Sadanandan100% (1)