Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
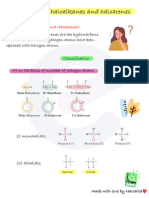
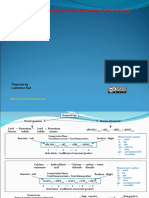
Trans Vicinal: Halogenation Dihalides
Hochgeladen von
Karla PereraOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trans Vicinal: Halogenation Dihalides
Hochgeladen von
Karla PereraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
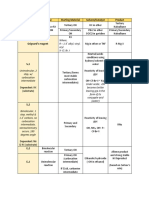
Chapter 8 Reactions and Mechanisms
Mechanism Reactants & reagents Substituents of Stereochemistry Intermediate? Rearrange Regiospecific? Addition type
product ments? Syn/Anti Relevant
Inorganic
Cis/Trans products?
Halogenation Alkene + Br2/Cl2 Trans vicinal 2nd part of the reaction Bromonium No Anti Anti
(Chlorination + dihalides is SN2 resulting in a Cation (+) Markovnikov
Bromination) pair of enantiomers
in CCl4 racemic m.) (Looks like a
cyclopropane)
(or meso compound)
Halohydrin Alkene + Br2/Cl2 Trans Halide on less 2nd part of the reaction Bromonium No Anti Anti
substituted carbon is SN2 resulting in a Cation (+)
in H2Oor aqueous agent and OH on more pair of enantiomers
( OH + something with substituted carbon (racemic m.) if (Looks like a
hydrogen) reactant is cis cyclopropane)
X + OH
(or meso compound if
substrate is trans)
Carbene Alkene + carbene (:CX2) Cyclopropane ring Pair of enantiomers No No Trans Anti
addition with X & X attached (racemic mixture) f Cyclo-
to same carbon reactant is cis propane
(or meso compound if
substrate is trans)
Simmons-Smith ZnI2 (driving
reaction force
Option A: Two adjacent OH Starting material cis = Yes No Cis – diol Syn addition
SYN OsO4 on Sulfur & groups (vicinal dial) meso compound
Dihydroxylation Hydrogen compound Cyclic Syn
Cis-diol Starting material trans intermediate
Option B: = racemic mixture
KMnO4 [COLD]/+
0- b-
OH- & H2O
Dihydroxylation 1. KMnO4 [HOT] Unsubstituted = CO2 Yes
+ basic conditions + H3O (Important) Monosubstituted =
Carboxylic acid
0- b-
Disubstituted =
Ketone
Mechanism Reactants & reagents Substituents of Stereochemistry Intermediate? Rearrange Cis/Trans Addition Type Inorganic
product ments? product Regiospecific? products?
Acid catalyzed A Hydrogen on the Carbocation YES Acid reforms
hydration of an Alkene + water in less substituted intermediate Carbocatio at the end
alkene presence of carbon and an OH on n may (catalyst)
the more substituted rearrange H3O+
Dilute acid carbon
(H3O+/H2SO4) (H + OH)
Ozonolysis (1) O3 Unsubstituted = formaldehyde
Monsubstituted = aldehyde
Reductive vs. Reductive (Lots of Disubtituted = ketone
Oxidation Hydrogens):
conditions
(2)
Zn/HOAC or DMS or
Zn/H2O or
(CH3)2S
Hydrohalogenati Alkene + H-X Racemic Mixture produced Achiral YES Markovnikov
on Intermediate addition
carbocation
Addition of Alkene + H2SO4 Carbocation Markovnikov
Sulfuric Acid to intermediate addition
Alkenes
Oxymercuration no free NO Markovnikov
/Demercuration carbocation addition
(partial
carbocation)
Hydroboration- no Syn addition ANTI
Oxidation Markovnikov
addition
Alkene Alkane
Halogenation (chlorination +
bromination)
Halohydrin formation
Acid catalyzed hydration
Reactions with water that end
up with an alcohol
Halohydrin formation
Acid Catalyzed hydration
Oxymercuration
demercuration
Reaction Reagents
Syn 1,2-Dihydroxylation Either OsO4
or KMnO4 (COLD)
OXIDATIVE CLEAVAGE
Oxidation of alkene KMnO4 (HOT)
Ozonolysis (1) O3 in CH2Cl2 -78 degrees Celcius
Workup with Zinc in acetic acid
(2) Zn/HOAc
Markovikov Addition Anti-Markovikov Addition
Acid Catalyzed Hydration of an alkene Halogenation
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 12th - Genral - Named Organic Reaction Sheet Class NotesDokument5 Seiten12th - Genral - Named Organic Reaction Sheet Class Notesaaravtrivedi313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Organic ReactionsDokument6 SeitenSummary of Organic ReactionsAbudi Alsagoff100% (5)
- CH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanDokument58 SeitenCH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanpujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crux and Reagents of Organic ChemDokument4 SeitenCrux and Reagents of Organic ChemBILL RUSSO100% (5)
- Dynamics 2 D Multiple Choice 2014-06-10Dokument10 SeitenDynamics 2 D Multiple Choice 2014-06-10Karla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Sufanilic AcidDokument4 SeitenSynthesis of Sufanilic AcidWinston Jake Gerolaga0% (1)
- Organic Chemical Reactions (ALKANES-ALKYNES)Dokument9 SeitenOrganic Chemical Reactions (ALKANES-ALKYNES)Kayla Andrea CalibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OxidationDokument18 SeitenOxidationKamal RankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.AcidBases FinalDokument35 Seiten3.AcidBases FinalSoham RaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations IIDokument1.209 SeitenComprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations IIHello World100% (1)
- Competency Exam in Organic ChemistryDokument3 SeitenCompetency Exam in Organic ChemistryWinsletJoyDauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 BiomoleculesDokument24 Seiten9 BiomoleculesCBSE123.CO.NR100% (3)
- Coterminal Angles and Reference Angles PDFDokument4 SeitenCoterminal Angles and Reference Angles PDFMark Abion ValladolidNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLB SeriesDokument3 SeitenHLB SeriesDownload AppsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Edition Nelson Test BankDokument14 SeitenLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Edition Nelson Test BankDonnaHalloend100% (35)
- 1000 Mcqs ChemistryDokument113 Seiten1000 Mcqs ChemistryMariam IshtiaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antoine CoefficientsDokument26 SeitenAntoine CoefficientsAndikaSeptianSitanggangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Carboxylic Acids and Its Derivatives (Booklet-1)Dokument16 Seiten4 - Carboxylic Acids and Its Derivatives (Booklet-1)kraken monsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Intermediates: Types of Bond CleavagesDokument31 SeitenReaction Intermediates: Types of Bond CleavagesB Sai SidharthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-NaphtholDokument6 SeitenSynthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-NaphtholdatUPstudentdoeNoch keine Bewertungen
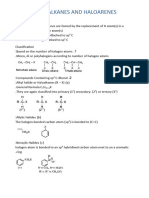
- CBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFDokument18 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFhehe11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDokument2 SeitenAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesGAMEPORIUMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalyst Note: (PT, Ni, PD)Dokument8 SeitenCatalyst Note: (PT, Ni, PD)Justin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- HALOALKENES AND HALO ARENES - Chemistry NotesDokument24 SeitenHALOALKENES AND HALO ARENES - Chemistry Notesrahul SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Organic Chemistry (Brahmastra) Part 2Dokument763 SeitenComplete Organic Chemistry (Brahmastra) Part 2mohdamaankhan74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Reaction Stoichiometric CalculationsDokument49 SeitenTypes of Reaction Stoichiometric CalculationsJohn Milen Garvida FabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plij Gib Me BookDokument16 SeitenPlij Gib Me BookDarsheel AmbasthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Study Material: IIT-JAM ChemistryDokument74 SeitenSample Study Material: IIT-JAM ChemistryPradeep PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winstein: Concept of Ion Pairs: Contact or Tight Ion PairDokument14 SeitenWinstein: Concept of Ion Pairs: Contact or Tight Ion PairAnil Kumar100% (1)
- CHEM F311 Lecture 2 Oxiding and Reducing AgentsDokument16 SeitenCHEM F311 Lecture 2 Oxiding and Reducing AgentsSAYAN RAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reagent ListDokument9 SeitenReagent ListArka MukhopadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions Icse Class 9thDokument4 SeitenChemical Reactions Icse Class 9thAniket SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSE Chem Last MinuteDokument61 SeitenDSE Chem Last Minute何卓函Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ChemistryDokument7 SeitenOrganic ChemistryABDULLAH SHAHZADNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12a Alkena Dan Reaksinya Bagian 2Dokument91 Seiten12a Alkena Dan Reaksinya Bagian 2ElisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dhoom # 9 Haloalkane & Haloarene in One Shot (10.6.2020)Dokument156 SeitenDhoom # 9 Haloalkane & Haloarene in One Shot (10.6.2020)Jeet RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Boron (III) - Catalyzed Amide and Ester Condensation ReactionsDokument13 SeitenNew Boron (III) - Catalyzed Amide and Ester Condensation ReactionsAngélica Andrea SalinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full NCERT Organic Reactions ch10 to ch14 - इसे करके जाओगे तो 65+ Score पक्का (25.2.2021)Dokument89 SeitenFull NCERT Organic Reactions ch10 to ch14 - इसे करके जाओगे तो 65+ Score पक्का (25.2.2021)Sameer Narula100% (1)
- Summary of Organic ChemistryDokument36 SeitenSummary of Organic Chemistrysyaz lianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatic ReactionsDokument40 SeitenAromatic ReactionsDharmadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Aromatik1Dokument40 Seiten11 Aromatik1Andre Anusta BarusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - Ionic Polymerization-2Dokument22 SeitenLecture 4 - Ionic Polymerization-2Lester John VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbons.Dokument70 SeitenHydrocarbons.Mandar Sheth100% (1)
- Bab Benzene and Aromaticity+ (II)Dokument48 SeitenBab Benzene and Aromaticity+ (II)ghaida farmasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase-Transfer CatalysisDokument16 SeitenPhase-Transfer CatalysisSIMARAN JAISWAL 41 M3SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Named ReactionsDokument5 SeitenNamed Reactionsgoodvp05Noch keine Bewertungen
- B001 Arihant PDFDokument12 SeitenB001 Arihant PDFmathclubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallics and Catalysis - IVDokument36 SeitenOrganometallics and Catalysis - IVankit guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument12 SeitenPDFJhonsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lone Pair DelocalizationDokument6 SeitenLone Pair DelocalizationGIORGIA MERIEN ILAONoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactive Intermediates - LecturesDokument24 SeitenReactive Intermediates - Lecturesapi-3771395100% (1)
- Haloalkanes MADDokument31 SeitenHaloalkanes MADggdfjkkvvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Reactions chm2120Dokument4 SeitenSummary of Reactions chm2120sabrinasameja75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbenes 170512195843Dokument38 SeitenCarbenes 170512195843ajayyashpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substitusi NukleofilikDokument38 SeitenSubstitusi NukleofilikAde FadilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaloalkanesDokument2 SeitenHaloalkanesGAMEPORIUMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymers PPSXDokument46 SeitenPolymers PPSXaleena'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Halogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackDokument23 SeitenHalogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackBritney PattersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackDokument23 SeitenHalogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackBritney PattersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Group Structural Reactivity General Formula Bond Type Polar/ Non-PolarDokument2 SeitenFunctional Group Structural Reactivity General Formula Bond Type Polar/ Non-PolarhydeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Chemistry On Limiting, Excess, Percentage Yield and Ionic EquationsDokument26 SeitenIB Chemistry On Limiting, Excess, Percentage Yield and Ionic EquationsoscarbecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes: FJ / Chemistry Unit, KMPK / Mac 2006 1Dokument46 SeitenHaloalkanes: FJ / Chemistry Unit, KMPK / Mac 2006 1Syaza NuramirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Organic Chemistry Chapter ThreeDokument40 SeitenPhysical Organic Chemistry Chapter ThreeMULUKEN TILAHUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering Industrial WaterDokument25 SeitenEnvironmental Engineering Industrial WaterTowfiq AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument6 SeitenChapter 10 - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesRitvik RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Chemistry Conversion TricksDokument7 SeitenBest Chemistry Conversion TricksShiglu Habibti100% (1)
- 3 2 (Aq) (Aq) 2(s) 3 (Aq)Dokument24 Seiten3 2 (Aq) (Aq) 2(s) 3 (Aq)oscarbecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Test 3Dokument4 SeitenSolutions Test 3roorayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-32 Elimination 1, 9th April, 2019 - TanmayDokument27 SeitenLecture-32 Elimination 1, 9th April, 2019 - TanmayAnkurNoch keine Bewertungen
- The University of Zambia School of Natural Sciences: Chemistry DepartmentDokument48 SeitenThe University of Zambia School of Natural Sciences: Chemistry Departmentmartin mulengaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUMBERLINEDokument12 SeitenNUMBERLINEDUHA GORASHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12Dokument46 SeitenChapter 12Eshita SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971Von EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Coordination Catalysis in Organic ChemistryVon EverandHandbook of Coordination Catalysis in Organic ChemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 116winter18 L16 Thin Lenses-Ray Tracing PDFDokument24 Seiten116winter18 L16 Thin Lenses-Ray Tracing PDFKarla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Sat/Act Math Book: Karla Perera 1st EditionDokument5 SeitenMy Sat/Act Math Book: Karla Perera 1st EditionKarla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Resonance Structures 343 Ans PDFDokument2 Seiten02 Resonance Structures 343 Ans PDFKarla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Syllabus Forensic Psychology Spring 2016Dokument6 SeitenFinal Syllabus Forensic Psychology Spring 2016Karla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebrate Central Nervous Systems Are Encased in The Bony Skull and Vertebral Invertebrate Nervous Systems Are Built Around The Digestive TractDokument1 SeiteVertebrate Central Nervous Systems Are Encased in The Bony Skull and Vertebral Invertebrate Nervous Systems Are Built Around The Digestive TractKarla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1a Floating EggDokument3 SeitenExp 1a Floating EggKarla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB2 - Topic 10.1 - Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDokument21 SeitenIB2 - Topic 10.1 - Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryIqra NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fischer and Schrock CarbenesDokument8 SeitenFischer and Schrock Carbenesharmanpreet kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaDokument1 SeiteOrganic Chemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaKunsovann KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- G10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekDokument4 SeitenG10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekSheela BatterywalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Daun PandanDokument4 SeitenKimia Daun Pandanlutfi_alhayathullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- For More Important Question's Visit:: Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDokument9 SeitenFor More Important Question's Visit:: Alcohols, Phenols and EthersrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetate, Mevalonate and Shikimic Acid PathwaysDokument19 SeitenAcetate, Mevalonate and Shikimic Acid Pathwaysamitaggarwal7888% (8)
- Sulfonation Mechanism of Benzene With SO3 in Sulfuric Acid or Oleum PDFDokument37 SeitenSulfonation Mechanism of Benzene With SO3 in Sulfuric Acid or Oleum PDFLaely Dian MarlindawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDokument2 SeitenRelative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionMatthew ColeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 - HydrocarbonsDokument3 Seiten1.2 - HydrocarbonskiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Compounds ScienceDokument2 SeitenCarbon Compounds ScienceVidgezxc LoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAS Scheme of Work IB Chem DP1!2!2018-19Dokument10 SeitenCAS Scheme of Work IB Chem DP1!2!2018-19Cicy IrnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOC PYQsDokument15 SeitenGOC PYQsshafique khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDokument20 Seiten12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123Noch keine Bewertungen
- PMR v19 I1 012 014Dokument3 SeitenPMR v19 I1 012 014Arianne Jayne G. GubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Wade 7th - 2Dokument27 SeitenChapter 10 Wade 7th - 2Afra FitrianitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Para Red Dye LR - 2022-10-0182Dokument18 SeitenPara Red Dye LR - 2022-10-0182moaz ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- EASR Vinay KumarDokument36 SeitenEASR Vinay KumarPRIYANSHU KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen