Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Bulk Reservoirs The The Able Áeaiurins P?.ro!jty The A Reservoir The
Hochgeladen von
Alfredo Junior0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten1 SeiteHidrocarburos
Originaltitel
Ejecicio
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenHidrocarburos
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten1 SeiteThe Bulk Reservoirs The The Able Áeaiurins P?.ro!jty The A Reservoir The
Hochgeladen von
Alfredo JuniorHidrocarburos
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
-!
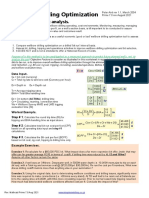
I PROBLI],I 2. 1
Pore volume a¡d average porosity calculati-ons
,s t-y'
Po-r9lity is the fraction of the bulk volume which is not
In hydroca¡bon reservoirs poro.siiy-;;p;;";;;u
the fracti-on of the total reservoirthe
?gIi{.
voiume rvhich is ávrfl-
able for occupancy by either liquios or-!áses. There are
several nethoás rór áeaiurins p?.ro!jty iñ tirá-r"táráio{,.
The- accuracy of any of these-méttroai áepánd.s upon the
and, quantitv of the data avail"i,i;;-uná-lrre"uni-
?lrLli{
rorm'rty or the reservoir. volume of tñe total porosity
in a reservoir is knor'¡r as The
the pore uoiu*u.
'1. Deten¡inu pore volume of an oil reservoir fro¡r the
follor¡ing lhg
data:
An isopachous trap has been planimetered
and porosity data has been óUtainea frora
]ogu and cores. These data has been tabu_
lated and follorvs:
Area Thlchness Average porosity productive
/i(
_
acres\ h ( f eet) -aGi- - -- -" Á;;;-i,ü;ü;.
) 720 20 11oó 1
6ro 20 c). ) 2.
405 20 IB.g
202 20 20.2 4
Pore Volune = 3x h x fr acre feet
-{ = ,1¡Ca in aCfeS (average area)
h = Thickness j.n feet
g = Poro si-ty
-'1I .!,. A^
T)t
(#¡ h.txfrt = (?2o ! 6tol x 20 x .zz}
= 3A32.1ñ acre feet
PV, =
(6lo + I¿oq') x20 ¡ .233
¿
= 2364.95 acre feet
plr (405 + 202) x 20 x .189
2
= 1147.23 acre feet
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Prehistory of Lake Athabasca: An Initial StatementVon EverandPrehistory of Lake Athabasca: An Initial StatementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Llil.L - T - LJ - RcoDokument20 SeitenLlil.L - T - LJ - RcoDHIVAKAR AppuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech Ce 7 Sem Water Resources Engineering Nce 702 2017Dokument4 SeitenBtech Ce 7 Sem Water Resources Engineering Nce 702 2017Saket RusiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Combined 1 QDokument6 SeitenExercise Combined 1 QАмина НабиеваNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE2303 AD2 Nov-Dec2010 QP With AnsDokument13 SeitenAE2303 AD2 Nov-Dec2010 QP With AnsVigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric DeterministicDokument15 SeitenVolumetric DeterministicAlameen GandelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yarn BLG - Soil Test ReportDokument29 SeitenYarn BLG - Soil Test ReportroniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isopach MapDokument7 SeitenIsopach MapPiyanan Chanchompoo100% (1)
- InterpretationDokument25 SeitenInterpretationmohamed_booksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postgraduate PG Mba Semester 3 2022 May Advanced Financial Management Pattern 2019Dokument4 SeitenPostgraduate PG Mba Semester 3 2022 May Advanced Financial Management Pattern 2019girishpawarudgirkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postgraduate PG Mba Semester 3 2022 March Advanced Financial Management Pattern 2019Dokument4 SeitenPostgraduate PG Mba Semester 3 2022 March Advanced Financial Management Pattern 2019Tushar ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering IIDokument2 SeitenEnvironmental Engineering IISakshi KumbhalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Structures & Irrigation Design Drawing Jan 2016 (2010 Scheme)Dokument2 SeitenHydraulic Structures & Irrigation Design Drawing Jan 2016 (2010 Scheme)Irfan IrfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Topic 8 - Site Location Impact On AirfieldsDokument99 Seiten1 - Topic 8 - Site Location Impact On Airfieldsejimenez6791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 - Hydrology 2 - STDDokument35 SeitenLecture 6 - Hydrology 2 - STDbelababyNoch keine Bewertungen
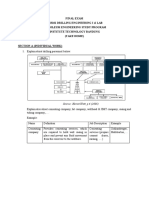
- FINAL EXAM - Drilling Engineering I + LabDokument6 SeitenFINAL EXAM - Drilling Engineering I + LabBaida Iqlima100% (2)
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043Dokument4 SeitenInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043mahesh babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises Advanced Seismic ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenExercises Advanced Seismic ApplicationsKatrina CourtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working: ComprehensiveDokument10 SeitenWorking: Comprehensiveapi-253275095Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes SanidhyaDokument19 SeitenNotes SanidhyaPravishya ChukkalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WT Feb2012PastPaper WithA PDFDokument8 SeitenWT Feb2012PastPaper WithA PDFGuluzada UlviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predimensionamiento de Equipo (Métodos Cortos)Dokument24 SeitenPredimensionamiento de Equipo (Métodos Cortos)DianaMenchacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 5-10: A and Same Prooucers Tnen Precesses B IsDokument4 SeitenChapters 5-10: A and Same Prooucers Tnen Precesses B Islala arNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMSSF ACC003 Topic 4 Additional HandoutsDokument2 SeitenDMSSF ACC003 Topic 4 Additional HandoutsJosh lamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM PracticalsDokument4 SeitenSM PracticalsBikash ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Collection: Offset Well SelectionDokument20 SeitenData Collection: Offset Well SelectionHernandez CitlalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIGURE P7.30: (A) Use Dimensional Analysis With The Assumption That The WingbeatDokument6 SeitenFIGURE P7.30: (A) Use Dimensional Analysis With The Assumption That The Wingbeatmohamed ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability Test For Fine-Grained and Granular SoilDokument10 SeitenPermeability Test For Fine-Grained and Granular SoilEdeouz EsmilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentacion Bulk Solid HandlingDokument62 SeitenPresentacion Bulk Solid HandlingMiguel Prada100% (1)
- HW-1 - Stress in Soils 2 2 2Dokument15 SeitenHW-1 - Stress in Soils 2 2 2Umair AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detention Volume Estimating Workbook (PDF) - 201404301105510967Dokument300 SeitenDetention Volume Estimating Workbook (PDF) - 201404301105510967Sunil DakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Owolabi 1994Dokument6 SeitenOwolabi 1994AbassyacoubouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ponds 3.2 T M: Echnical EMODokument10 SeitenPonds 3.2 T M: Echnical EMOMohamed Amine ZemouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sediment Basin Design Example PDFDokument8 SeitenSediment Basin Design Example PDFAgus FirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 IrrigationDokument8 Seiten2016 Irrigationsita ram JatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG Reservoir Rock Typing 4Q14Dokument5 SeitenENG Reservoir Rock Typing 4Q14Vanesita SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 - Depletion of Mineral ResourcesDokument3 SeitenChapter 17 - Depletion of Mineral ResourcesXiena50% (2)
- Mill Power SAG MillsDokument7 SeitenMill Power SAG MillsJheny MattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 23 PDFDokument1 SeiteForm 23 PDFPila OnmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indicated Troublesome: - and KaskadeDokument10 SeitenIndicated Troublesome: - and KaskadecopiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question For Exam in BUETDokument8 SeitenQuestion For Exam in BUETShaibal Ahmed0% (1)
- فاينل ميكانيك التربه ثالث مدني 10 11Dokument4 Seitenفاينل ميكانيك التربه ثالث مدني 10 11Samer al sadikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cet307 Hwre Dec 2022Dokument4 SeitenCet307 Hwre Dec 2022hakih95814Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raw Materials: (RC - RP - C) TGDokument4 SeitenRaw Materials: (RC - RP - C) TGBee PshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culvert DesignDokument41 SeitenCulvert Designkolopen andrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mba1 QT Dec07Dokument2 SeitenMba1 QT Dec07Gurkirat Singh TiwanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wells Subsurface Tutorials BabsDokument12 SeitenWells Subsurface Tutorials BabsMaría MarquinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34 Btechce 1Dokument11 Seiten34 Btechce 1aadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric SDokument54 SeitenVolumetric SMohamed SadekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book 27 Nov 2023Dokument11 SeitenBook 27 Nov 2023maulivora310Noch keine Bewertungen
- RBF 5Dokument19 SeitenRBF 5SM ConsultantsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accountant Sample PaperDokument10 SeitenAccountant Sample PaperAgastya KarnwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equipment Hire RateDokument2 SeitenEquipment Hire RateMd. Shiraz JinnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economico-Mathematical Analysis of Transition From Open-Pit To Underground MiningDokument8 SeitenEconomico-Mathematical Analysis of Transition From Open-Pit To Underground MiningYudiAristaYulandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ei - 401Dokument7 SeitenEi - 401HirokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework2 PDFDokument2 SeitenHomework2 PDFcdracularocket0% (1)
- Assignment 1 (2018)Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 1 (2018)Nthabeleng GaringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad Drilling Cost Per Foot Analysis Worksheet-1Dokument2 SeitenMathcad Drilling Cost Per Foot Analysis Worksheet-1berrouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - + - : - 47.suu:ooDokument9 Seiten1 - + - : - 47.suu:ooRAJORAJI CO.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics PYQsDokument12 SeitenFluid Mechanics PYQsHelp hellouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption and Diffusion of Hydrogen in SteelsDokument12 SeitenAbsorption and Diffusion of Hydrogen in SteelsadipanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteAssignment 2 PDFManojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressibility RubberDokument11 SeitenCompressibility Rubber2007rlwjdtnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review in Science 7Dokument2 SeitenReview in Science 7Concepcion Jasmin JodlomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 MT Mollecular NALLADokument45 Seiten2015 MT Mollecular NALLADeni haryadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gamma Titanium Aluminide Alloys Science andDokument5 SeitenGamma Titanium Aluminide Alloys Science andkorkmazmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Capacity of Sodium Silicate Liquids: Pascal RichetDokument3 SeitenHeat Capacity of Sodium Silicate Liquids: Pascal RichetDaniel SetyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Theoretics: Viscosity and Cohesion PressureDokument5 SeitenJournal of Theoretics: Viscosity and Cohesion PressureandraaaaapmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extended Surfaces LabDokument9 SeitenExtended Surfaces LabCaleb HerupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying & Curing of Paint FilmsDokument5 SeitenDrying & Curing of Paint FilmsOmar DhiebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Field Analysis of Tunnel Kiln For Brick ProductionDokument6 SeitenTemperature Field Analysis of Tunnel Kiln For Brick ProductionDWWillsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 22-Electric FieldDokument38 SeitenChapter 22-Electric Field0000003294 : Rawan Abdul Hakim SabhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm E140-2012Dokument25 SeitenAstm E140-2012Alessio MercataliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2E4B BucklingDokument4 Seiten2E4B BucklingMohd Ridzuan Ahmad100% (1)
- Cavity Writeup ExpDokument7 SeitenCavity Writeup ExpKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS2752 C60 Neoprene RubberDokument1 SeiteBS2752 C60 Neoprene RubberMohit JangidNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Perfromance Floor CoatingDokument9 SeitenHigh Perfromance Floor Coatinghis shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2 Cussler PDFDokument37 SeitenC2 Cussler PDFGil PinheiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ANSYS Mechanical: Workshop 5.1 Linear Structural AnalysisDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To ANSYS Mechanical: Workshop 5.1 Linear Structural AnalysisAjay Chacko100% (1)
- Zahn Cup-Type Viscosimeter Operating InstructionsDokument2 SeitenZahn Cup-Type Viscosimeter Operating InstructionsEran LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation of Transistor Characteristics of N-P-N and P-N-PDokument9 SeitenInvestigation of Transistor Characteristics of N-P-N and P-N-PMOKAYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Properties of Polymers 11Dokument22 SeitenStructure and Properties of Polymers 11aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch12 Free Energy and ThermodynamicsDokument8 SeitenCh12 Free Energy and ThermodynamicsCitrus_EscapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS 1Dokument7 SeitenSS 1xanshahNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Paperhub - Ir) 10.1134 s2070205119020187Dokument10 Seiten(Paperhub - Ir) 10.1134 s2070205119020187Mohammad FouladiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reseach Project On Zircnonia Doped AluminaDokument2 SeitenReseach Project On Zircnonia Doped Aluminatushargoelrkl1131Noch keine Bewertungen
- POLIMAXX P901BK TDS New 2016Dokument1 SeitePOLIMAXX P901BK TDS New 2016Yusuf Wahyu PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 27 Ef - Fluid Mechanics/Hydraulics: W V m γ= mg ρg mDokument67 SeitenMe 27 Ef - Fluid Mechanics/Hydraulics: W V m γ= mg ρg mJoseph NjugunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Revision Test Oct 2010Dokument6 SeitenSample Revision Test Oct 2010Karn ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- NG22 280 Cat SPD 000019 - 00Dokument20 SeitenNG22 280 Cat SPD 000019 - 00Theophilus OrupaboNoch keine Bewertungen