Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Variance
Hochgeladen von
Felix Ray DumaganCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Variance
Hochgeladen von
Felix Ray DumaganCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Variance (of a discrete random variable)
A measure of spread for a distribution of a random variable that determines the degree
to which the values of a random variable differ from the expected value, a measurement
of the spread between numbers in a data set.
The variance of random variable X is often written as Var(X) or σ2 or σ2x.
For a discrete random variable the variance is calculated by summing the product of the
square of the difference between the value of the random variable and the expected
value, and the associated probability of the value of the random variable, taken over all
of the values of the random variable.
In symbols, Var(X) = (x - µ)2 P(X = x)
An equivalent formula is, Var(X) = E(X2) – [E(X)]2
The square root of the variance is equal to the standard deviation.
Example
Random variable X has the following probability function:
x 0 1 2 3
P(X = x) 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.3
Using Var(X) = (x - µ)2 P(X = x)
µ = 0 x 0.1 + 1 x 0.2 + 2 x 0.4 + 3 x 0.3
= 1.9
Var(X) = (0 – 1.9)2x 0.1 + (1 – 1.9)2x 0.2 + (2 – 1.9)2x 0.4 + (3 – 1.9)2x 0.3
= 0.89
Using Var(X) = E(X2) – [E(X)]2
E(X) = 0 x 0.1 + 1 x 0.2 + 2 x 0.4 + 3 x 0.3
= 1.9
E(X2) = 02 × 0.1 + 12 × 0.2 + 22 × 0.4 + 32 × 0.3
= 4.5
Var(X) = 4.5 – 1.92
= 0.89
Variance is used in statistics for probability distribution. Since variance
measures the variability (volatility) from an average or mean and volatility is a
measure of risk, the variance statistic can help determine the risk an investor
might assume when purchasing a specific security. A variance value of zero
indicates that all values within a set of numbers are identical; all variances that
are non-zero will be positive numbers. A large variance indicates that
numbers in the set are far from the mean and each other, while a small
variance indicates the opposite.
Examples
1) Senior High Statistics test scores on Random Variables are described by the following
probability distribution.
Score 40 50 60 70 80
P(Score) .1 .2 .3 .3 .1
A) Determine the mean and variance of the scores.
B) Mrs. Burnett, in yet another act of benevolence, decides to scale the scores so her students
will not be denied admission to the college of their choice. She decides the actual grades will
become: Grade = 1.5 * Score – 20 .
Determine the mean and variance of the grades.
Which Score(s), if any, will not increase
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Weekly Home Learning Plan General Math q1 and q2Dokument19 SeitenWeekly Home Learning Plan General Math q1 and q2Felix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City Midterm Examination Nstp-Cwts NAME: - SCOREDokument5 SeitenPolytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City Midterm Examination Nstp-Cwts NAME: - SCOREFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Home Learning Plan UCSP q1 and q2Dokument15 SeitenWeekly Home Learning Plan UCSP q1 and q2Felix Ray Dumagan100% (2)
- English 9 Week 4 Module SummerDokument13 SeitenEnglish 9 Week 4 Module SummerFelix Ray Dumagan67% (3)
- Hypertext and IntertextDokument3 SeitenHypertext and IntertextFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omnibus Certification of Authenticity and VeracityelementaryDokument2 SeitenOmnibus Certification of Authenticity and VeracityelementaryFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City High School DepartmentDokument14 SeitenPolytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City High School DepartmentFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City High School DepartmentDokument1 SeitePolytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City High School DepartmentFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 10 Summer Week 4Dokument13 SeitenEnglish 10 Summer Week 4Felix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer LoadDokument1 SeiteSummer LoadFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key Capitalization QuizDokument2 SeitenAnswer Key Capitalization QuizFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diss Module For Summer Week 3Dokument11 SeitenDiss Module For Summer Week 3Felix Ray Dumagan75% (4)
- English 9 Summer Week 3Dokument18 SeitenEnglish 9 Summer Week 3Felix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam Contempo BSRT1Dokument3 SeitenMidterm Exam Contempo BSRT1Felix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Weeek 2 Module SummerDokument15 SeitenGrade 10 Weeek 2 Module SummerFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in Acquatics For Grade 12Dokument10 SeitenModule in Acquatics For Grade 12Felix Ray Dumagan100% (1)
- Diss Week 2 Soc Sci ModudleDokument14 SeitenDiss Week 2 Soc Sci ModudleFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay RubricDokument1 SeiteEssay RubricFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
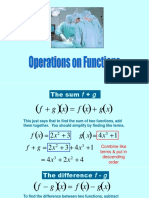
- Operations On FunctionsDokument17 SeitenOperations On FunctionsFelix Ray DumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Part 6 - Hypothesis TestsDokument3 SeitenPart 6 - Hypothesis Testsapi-339771906Noch keine Bewertungen
- You Are Given The Following Information About An Invertible ARMA Time-Series Model: 0 4 0 2 3 4 - , ,, ,..Dokument40 SeitenYou Are Given The Following Information About An Invertible ARMA Time-Series Model: 0 4 0 2 3 4 - , ,, ,..Andrew GoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 5 - Measures of Central Tendency and VariabilityDokument5 SeitenActivity 5 - Measures of Central Tendency and VariabilityGWYNETTE CAMIDCHOLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis TestingDokument6 SeitenHypothesis TestingYuan GaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Chapter 11Dokument9 SeitenSolutions Chapter 11Denzil D'SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA301 - Statistics and Probability Solved 301Dokument15 SeitenSTA301 - Statistics and Probability Solved 301Ali HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 GCE A Level Solution H1 MathDokument2 Seiten2013 GCE A Level Solution H1 MathNgo Duy VuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walpole Chapter 10Dokument13 SeitenWalpole Chapter 10Mehmet PolatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data ProcessingDokument112 SeitenData ProcessingJay Lester E. DapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sta301 Finalterm Mcqs With Reference Solved by ArslanDokument45 SeitenSta301 Finalterm Mcqs With Reference Solved by ArslanAbd Ul AahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Linear Regression Part 1Dokument63 SeitenSimple Linear Regression Part 1_vanitykNoch keine Bewertungen
- n i=1 α/2 i σ n nDokument4 Seitenn i=1 α/2 i σ n nAlexander CTO100% (1)
- KPIDokument10 SeitenKPImehak rajdevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nama: Retna Maryuhayavia NIM: 312020023 Kelas: B/S1 Keperawatan Lintas JalurDokument8 SeitenNama: Retna Maryuhayavia NIM: 312020023 Kelas: B/S1 Keperawatan Lintas Jalurretna maryuhayaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.chapter 3 Demand ForecastingDokument43 Seiten4.chapter 3 Demand Forecastingopio jamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efektivitas Model Pembelajaran Problem Solving Dan Problem Based Learning Ditinjau Dari Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematika SDDokument14 SeitenEfektivitas Model Pembelajaran Problem Solving Dan Problem Based Learning Ditinjau Dari Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematika SDwebotre netNoch keine Bewertungen
- APA TablesDokument7 SeitenAPA TablesYet Barreda BasbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16BT40405 - Probability and Stochastic ProcessesDokument2 Seiten16BT40405 - Probability and Stochastic ProcessesSiva GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Black Belt ProgramDokument10 SeitenMaster Black Belt ProgramBoo BalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OM-1 Question PaperDokument10 SeitenOM-1 Question PaperNohan JoemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Book - Methodology and Theory For The BootstrapDokument41 SeitenE-Book - Methodology and Theory For The BootstrapazwansurotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pruebas de Dickey - Fuller Aumentada (ADF) : Ho: La Serie Presenta Raiz UnitariaDokument7 SeitenPruebas de Dickey - Fuller Aumentada (ADF) : Ho: La Serie Presenta Raiz UnitariasergioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2. Relaxing The Assumptions of CLRM - 0Dokument17 SeitenLecture 2. Relaxing The Assumptions of CLRM - 0Javohir VahobovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 4 FinalDokument10 SeitenHomework 4 Finalapi-624134741Noch keine Bewertungen
- 41 3 Tests Two SamplesDokument22 Seiten41 3 Tests Two SamplesvignanarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Factor Structure of The System Usability Scale: July 2009Dokument11 SeitenThe Factor Structure of The System Usability Scale: July 2009difaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression With StataDokument108 SeitenRegression With Stataapi-373702575% (4)
- STA 2023 Unit 3 Shell Notes (Chapter 6 - 7)Dokument36 SeitenSTA 2023 Unit 3 Shell Notes (Chapter 6 - 7)UyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Sol Mcd2080-Fat-2Dokument4 SeitenSample Sol Mcd2080-Fat-2Dennys TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correspondence AnalysisDokument19 SeitenCorrespondence AnalysisCART11Noch keine Bewertungen