Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
HW9 Sum and Difference Identities
Hochgeladen von
Alice DwyerOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
HW9 Sum and Difference Identities
Hochgeladen von
Alice DwyerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
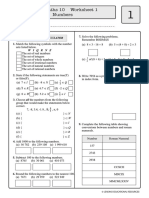
HW 9 Sum and Difference Identities (14.
4)
Name______________________________
I will be able to use sum and difference identities.
Sum and Difference Identities
sin( A B ) sin A cos B cos A sin B cos( A B ) cos A cos B sin A sin B
sin( A B ) sin A cos B cos A sin B cos( A B ) cos A cos B sin A sin B
Examples:
A.) Find sin (15°)
Find the exact value for each expression.
1.) sin (30° + 45°) 2.) sin (30° + 135°) 3.) cos (30°
+ 45°)
4.) sin (210° - 315 °) 5.) cos (150° - 45°) 6.) sin
(240° - 315°)
7.) sin (105°) 8.) sin (165°) 9.) sin (75°)
10.) cos (225°) 11.) cos (-235°) 12.) sin (285°)
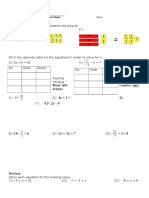
Double and Half-Angle Identities (14.5)
Name______________________________
I will be able to use sum and difference identities.
Double Angles Half Angles
A 1 cos A
sin
sin( 2 A) 2 sin( A) cos( A) 2 2
cos(2 A) cos 2 ( A) sin 2 ( A)
depends on value for
A 1 cos A
cos
2
2
sine or cosine
Examples:
Use the information to find the exact value of sin 2 and cos2.
3 1
A.) 90 180; sin B.) 0 90; cos
5 4
Use the information to find the exact value of sin ½ and cos ½.
1 5
C.) 0 90; cos D.) 90 180; sin
5 6
Use the information to find the exact value of sin 2 and cos2.
1 2
1.) 0 90; sin 2.) 270 360; sin
4 5
Use the information to find the exact value of sin ½ and cos ½.
5 5
3.) 90 180; cos 4.) 180 270; cos
6 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Maths WorksheetDokument15 SeitenBasic Maths WorksheetSubbukbalaji LakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Formulae - Trigo Formulae For LAKSHYA JEEDokument2 SeitenTrigonometry Formulae - Trigo Formulae For LAKSHYA JEEprekshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Trigonometry (I)Dokument1 SeiteBasic Trigonometry (I)Lok Lam SzetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2 Compound Angle FormulasDokument8 Seiten7.2 Compound Angle FormulasZion KeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides 5Dokument36 SeitenSlides 5Prof Samuel KashinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonomery - Basic ExerciseDokument11 SeitenTrigonomery - Basic ExerciseShashwat PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0267418d1ac7a-Trigonometry Ratio Zero Level - IDokument3 Seiten0267418d1ac7a-Trigonometry Ratio Zero Level - IRahul SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Notes (Revision) MathematicsDokument90 SeitenShort Notes (Revision) MathematicsjasleenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Concepts (Compound Angles) : (Mahindra Showroom), BSNL Office Lane, Jhalawar Road, Kota, Rajasthan (324005)Dokument1 SeiteKey Concepts (Compound Angles) : (Mahindra Showroom), BSNL Office Lane, Jhalawar Road, Kota, Rajasthan (324005)Yash ChaudhauryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-10 2H WDokument1 Seite3-10 2H WdevikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double-And Half-Angle Identities: Use A Double-Angle Identity To Find The Exact Value of Each ExpressionDokument10 SeitenDouble-And Half-Angle Identities: Use A Double-Angle Identity To Find The Exact Value of Each ExpressionAbas AcmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Chapter 4: Trigonometric Function: DAS10103 - NORAINDokument4 SeitenTutorial Chapter 4: Trigonometric Function: DAS10103 - NORAINSyafiq AimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tri 5 2Dokument3 SeitenTri 5 2Rishav SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotient Identities: Sin Tan Cos Cos Cot SinDokument55 SeitenQuotient Identities: Sin Tan Cos Cos Cot SinYoga SutresnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 2.2 Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle ApproachDokument40 SeitenSection 2.2 Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle ApproachNoob KidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brahm: AstraDokument10 SeitenBrahm: AstraKeshav JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1 - Trigonometric Identities Math 301Dokument14 Seiten7.1 - Trigonometric Identities Math 301Math 30-1 EDGE Study Guide Workbook - by RTD LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Trigonometric Equations and IdentitesDokument64 Seiten7 - Trigonometric Equations and IdentitesMath 30-1 EDGE Study Guide Workbook - by RTD LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Review Part 5 Trig GeometryDokument8 SeitenExam Review Part 5 Trig Geometrystealthysky0129Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example 1 Chapter 10 Angles in All Four QuadrantsDokument3 SeitenExample 1 Chapter 10 Angles in All Four QuadrantsElisabeth PhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigoDokument1 SeiteTrigovaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fairfield Am 2 Prelim 2009Dokument11 SeitenFairfield Am 2 Prelim 2009JASON_INGHAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- 042 Trigonometry ReviewDokument6 Seiten042 Trigonometry Reviewefua.dhrNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC Sir SheetDokument17 SeitenMC Sir Sheetabhijeet100% (1)
- Maths Grade 12 MIP 2022Dokument51 SeitenMaths Grade 12 MIP 2022cvuthulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Exercuses For PH Trigonometric 1 PDFDokument2 Seiten01 Exercuses For PH Trigonometric 1 PDFShar 754Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics GR 12 P2 1 TrigonometryDokument140 SeitenMathematics GR 12 P2 1 TrigonometryphiwoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asm 4047Dokument1 SeiteAsm 4047studartzofficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Basic Maths and Vectors All DppsDokument23 Seiten01 Basic Maths and Vectors All DppsRevan SiddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlgebraDokument35 SeitenAlgebraShauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTH100Dokument3 SeitenMTH100Syed Abdul Mussaver ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - 2 Sum and Difference Formulas - BlitzerDokument32 SeitenChapter 5 - 2 Sum and Difference Formulas - BlitzerNoli NogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowen AM P2Dokument6 SeitenBowen AM P2ZeneonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios and IdentitiesDokument7 SeitenTrigonometric Ratios and IdentitiesUMANG BAJPAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Sum and Difference Identities HWDokument2 SeitenSum and Difference Identities HWapi-361405873Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Unit ExamDokument4 SeitenTrigonometry Unit Examapi-488757804Noch keine Bewertungen
- Find The Sine, Cosine, and Tangent of Angle TDokument2 SeitenFind The Sine, Cosine, and Tangent of Angle TAngela PeligroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 016 Sum and Difference IdentitiesDokument8 SeitenWeek 016 Sum and Difference IdentitiesCarsten HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathongo - Formula Sheet - Trig. Ratios & Equations: B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B ADokument4 SeitenMathongo - Formula Sheet - Trig. Ratios & Equations: B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B ADhananjay S MathekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry FormulaeDokument2 SeitenTrigonometry FormulaeabcNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Amkss My 4e5na Am p2Dokument15 Seiten2010 Amkss My 4e5na Am p2Timothy HandokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIGO FormulaeDokument10 SeitenTRIGO FormulaeSankalp JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ial Maths p3 Ex4c PDFDokument4 SeitenIal Maths p3 Ex4c PDFahmed ramadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Sample PaperDokument28 SeitenChemistry Sample Papercgdtgv hjghgNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2V1 Ch03 FS 01e EOpNIGJbDokument47 SeitenM2V1 Ch03 FS 01e EOpNIGJbAnthony ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH6 - Trig Identities and EquationsDokument34 SeitenCH6 - Trig Identities and Equationsmalik4164512095Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 2 Lesson 3 (Week 8)Dokument21 SeitenQuarter 2 Lesson 3 (Week 8)Angelo ResuelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 01-10 PHYSICS AbhimanyuDokument14 SeitenDPP 01-10 PHYSICS AbhimanyuRohan VayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry: All in One Formulas List !Dokument10 SeitenTrigonometry: All in One Formulas List !Rohit Ghere50% (2)
- MATH14 - Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Formulas - Doruan - MidtermDokument9 SeitenMATH14 - Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Formulas - Doruan - MidtermCaimar DoruanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigo IIT JEEDokument3 SeitenTrigo IIT JEEPujan100% (1)
- Trigonometrie - Voorbeelde en Oefeninge ENGDokument7 SeitenTrigonometrie - Voorbeelde en Oefeninge ENGClarise van ZylNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 - TrigonometryDokument10 SeitenTopic 3 - Trigonometryapi-25887606100% (1)
- 02 Compound Angle - Sheet (Trig. - Ph-1)Dokument45 Seiten02 Compound Angle - Sheet (Trig. - Ph-1)Keshav JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S4 05-06 Amath YearlyDokument4 SeitenS4 05-06 Amath YearlyHedia LhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIGONOMETRYDokument28 SeitenTRIGONOMETRYJesus Iii ObutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry 1 DPPDokument12 SeitenTrigonometry 1 DPPI'M ANSARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Candy Corn Roll and ColorDokument4 SeitenCandy Corn Roll and ColorAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- GardeningDokument2 SeitenGardeningAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shark Family SH Digraph Activity PDFDokument8 SeitenShark Family SH Digraph Activity PDFAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processed To Unprocessed Ana, Cindy SantaDokument27 SeitenProcessed To Unprocessed Ana, Cindy SantaAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Activities PacketDokument14 SeitenSummer Activities PacketAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winter PhonicsDokument27 SeitenWinter PhonicsAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- YEAR 1 CHECKLIST 2PP WebDokument2 SeitenYEAR 1 CHECKLIST 2PP WebAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Learning Pack PrepDokument75 SeitenHome Learning Pack PrepAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Independent Work Weeks 1Dokument27 SeitenIndependent Work Weeks 1Alice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Festival ReadsDokument4 SeitenYour Festival ReadsAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle The Like TermsDokument5 SeitenCircle The Like TermsAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backpack2 LittlebooksDokument16 SeitenBackpack2 LittlebooksAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- At Home Learning Week 7Dokument24 SeitenAt Home Learning Week 7Alice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Maths Year 10Dokument76 SeitenMaster Maths Year 10Alice Dwyer100% (3)
- What Is 364 To The Nearest 100?Dokument17 SeitenWhat Is 364 To The Nearest 100?Alice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- May Flowers Abcs PDFDokument10 SeitenMay Flowers Abcs PDFAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yr9 InequalitiesDokument22 SeitenYr9 InequalitiesAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 Steer Report Lessons LearnedDokument202 Seiten2009 Steer Report Lessons LearnedAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems of Linear Inequalities Card Sort PreviewDokument10 SeitenSystems of Linear Inequalities Card Sort PreviewAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW11 Two Step EquationsDokument2 SeitenHW11 Two Step EquationsAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework WS #6Dokument3 SeitenHomework WS #6Alice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW14 Slope From Two PointsDokument2 SeitenHW14 Slope From Two PointsAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Topics Review - : Name PerDokument2 SeitenAlgebra Topics Review - : Name PerAlice DwyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting A Number From A Textbox: Computer Programming 1 Inputting From TextboxesDokument1 SeiteGetting A Number From A Textbox: Computer Programming 1 Inputting From TextboxesZarif ZulkafliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remotivation Therapy (Sammm)Dokument4 SeitenRemotivation Therapy (Sammm)Sam Venezuelȧ100% (3)
- 100kva DG Set - 100kva Koel GensetDokument3 Seiten100kva DG Set - 100kva Koel GensetMothilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Wifi CrakDokument12 SeitenProject Wifi CrakZain ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 What Is Data Engineering PDFDokument79 SeitenChapter 1 What Is Data Engineering PDFChandra PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.K. Anand Contempt Delhi HC JudgementDokument112 SeitenR.K. Anand Contempt Delhi HC JudgementSampath BulusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Phragmanthera Capitata (Sprenge.) Balle On Pod and Beans Production of Two Cocoa Clones in Nkoemvone Seed Fields (South Cameroun) - JBES @scribdDokument9 SeitenImpact of Phragmanthera Capitata (Sprenge.) Balle On Pod and Beans Production of Two Cocoa Clones in Nkoemvone Seed Fields (South Cameroun) - JBES @scribdInternational Network For Natural SciencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The Internet of Things Definition, Potentials, and Societal Role of A FasDokument19 SeitenUnderstanding The Internet of Things Definition, Potentials, and Societal Role of A FasSteven GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Needs Analysis PDFDokument11 SeitenNeeds Analysis PDFRobertMaldiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQF Edition 8 Quick Start GuideDokument27 SeitenSQF Edition 8 Quick Start Guidefourat.zarkounaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Deparment Computer Science Information TechnologyDokument19 SeitenMirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Deparment Computer Science Information TechnologySeharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tài liệu tiếng Trung HSK5Dokument1 SeiteTài liệu tiếng Trung HSK5Nguyễn Ngọc Xuân NghiêmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Design and Construction of Geosynthetic Reinforced Embankments On Soft FoundationsDokument40 SeitenGuidelines For Design and Construction of Geosynthetic Reinforced Embankments On Soft FoundationsManish Kumar Singh100% (1)
- El Lenguaje Del YogaDokument149 SeitenEl Lenguaje Del YogaMax AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of America Before Columbus According To Documents and Approved Authors PDFDokument878 SeitenHistory of America Before Columbus According To Documents and Approved Authors PDFTy0072100% (3)
- 2012 Nike Football Clinic 4Dokument2 Seiten2012 Nike Football Clinic 4Bruno ChuNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write Master Thesis AbstractDokument8 SeitenHow To Write Master Thesis Abstractidmcgzbaf100% (2)
- Goodman and Gilman's Sample ChapterDokument17 SeitenGoodman and Gilman's Sample Chapteradnankhan20221984Noch keine Bewertungen
- HVAKR Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenHVAKR Cheat SheetandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rise of Robot Friendship: Ethical Dilemmas in Science and TechnologyDokument10 SeitenThe Rise of Robot Friendship: Ethical Dilemmas in Science and TechnologyStephen VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authentic Listening X-Rays - ScriptDokument2 SeitenAuthentic Listening X-Rays - Scriptenfa.work.confNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adp w2 2019 TemplateDokument1 SeiteAdp w2 2019 Templatetokahontas85Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCT Grade 5 LANGUAGE ARTS 2017 (1)Dokument16 SeitenMCT Grade 5 LANGUAGE ARTS 2017 (1)Boppy VevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Financial Regulation Seminar QuestionsDokument2 SeitenInternational Financial Regulation Seminar QuestionsNicu BotnariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sediment Gravity FlowDokument38 SeitenSediment Gravity FlowkorewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Optimisation of Water Tanks Designed According To The Aci and Euro CodesDokument25 SeitenCost Optimisation of Water Tanks Designed According To The Aci and Euro CodesandysupaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air ConditionerDokument131 SeitenAir ConditionerRahul AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity-2: Ramsar Convention On WetlandsDokument9 SeitenBiodiversity-2: Ramsar Convention On WetlandsAhmad NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Marketing & Pricing SummariesDokument30 SeitenAll Marketing & Pricing SummariesTolulope OlajideNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 421-Digital System Design-Dr. Shahid Masud-Updated PDFDokument4 SeitenEE 421-Digital System Design-Dr. Shahid Masud-Updated PDFUbaid UmarNoch keine Bewertungen