Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Number Theory: Sets of Numbers
Hochgeladen von
melissaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Number Theory: Sets of Numbers
Hochgeladen von
melissaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NUMBER THEORY
SETS OF NUMBERS
Real Numbers
Rational Numbers
Natural Numbers ℕ
Natural numbers are the counting numbers {1, 2, 3, ...} Integers
Whole Numbers
Whole Numbers 𝕎 Natural Numbers
Whole numbers are the non-negative integers. {0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
Integers ℤ
Integers are the natural numbers and their negatives
{... −3, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...}.
Rational Numbers ℚ
Rational numbers are the ratios of integers, also called fractions, such as 1/2 = 0.5 or 4/3 = 1.333...
Rational decimal expansions end or repeat.
Real Numbers ℝ
Real numbers are all the numbers on the continuous number line. Real numbers may be rational or
irrational.
Imaginary Numbers
Imaginary numbers are numbers whose squares are negative. They are the square root of minus one,
i = √−1, and all real number multiples of i, such as 2i.
Other Types of Numbers
Factors and Multiples
Square Numbers
Even Numbers
Odd Numbers
Prime Numbers
Composite Numbers
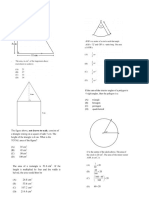
1) Identify the sets to which the following numbers belong by marking the appropriate boxes.
Natural Whole Integer Rational Irrational Real Imaginary
6
9.673
−4
√17
√625
9𝑖
7
2) Arrange the numbers: 1.1, 2, √2, 1.45, 𝜋 in ascending order
3) List the factors of a) 36 b) 100
4) List the multiples of a)7 b) 15
5) Identify the HCF of the following numbers: 6) Identify the LCM of the following numbers:
a) 4, 6, 8 a) 4, 6, 8
b) 16, 24, 96 b) 16, 24, 96
c) 30, 60, 225 c) 30, 60, 225
d) 13, 39, 131 d) 13, 39, 131
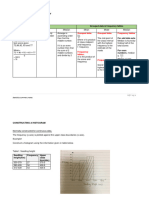
Bases
In mathematics, a base is the number of different digits that a system of counting uses to represent
numbers. For example, the most common base used today is base 10 - the decimal system. It uses the
10 digits from 0 to 9.
A number is formed by grouping the digits together.
● Each digit has a fixed position called its place.
● The face value of a digit is the value of the digit itself
● Place value of a digit = (face value of the digit) × (value of the place)
(You should be able to state the value of a digit of a numeral in base 2, 4, 8 and 10)
Base 10 Base 4
In the number 3702 In the number 1320
the place value of 3 is 3000 the place value of 1 is
the place value of 7 is 700 the place value of 3 is
the place value of 0 is 0 the place value of 2 is
the place value of 2 is 2 the place value of 0 is
Base 8 Base 2
In the number 3702 In the number 1101
the place value of 3 is the place value of the first 1 is
the place value of 7 is the place value of the second 1 is
the place value of 0 is the place value of 0 is
the place value of 2 is the place value of the last 1 is
Practice – Base 2 and Base 8
(1)1 in binary is equal to (12) 110 in binary is equal to Solutions
( 2 ) 2 in octal is equal to (13) 40 in octal is equal to
1) 1 11) 931
( 3 ) 3 in octal is equal to (14) 66 in octal is equal to
2) 2 12) 6
( 4 ) 7 in octal is equal to (15) 117 in octal is equal to 13) 32
3) 3
( 5 ) 11110 in binary is equal to (16) 421 in octal is equal to 4) 7 14) 54
( 6 ) 111010 in binary is equal to (17) 526 in octal is equal to 5) 30 15) 79
( 7 ) 110011000 in binary is equal to (18) 110000000 in binary is 6) 58 16) 273
7) 408 17) 342
( 8 ) 111001111 in binary is equal to (19) 111110101 in binary is
8) 463 18) 384
( 9 ) 1066 in octal is equal to (20) 1001100001 in binary is 19) 501
9) 566
(10) 1011111100 in binary is equal to (21) 1101011101 in binary is 10) 764 20) 609
(11) 1110100011 in binary is equal to 21) 861
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CSEC Additional Mathematics Specimen P2Dokument9 SeitenCSEC Additional Mathematics Specimen P2Naseeb AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Arithmetic: BillsDokument4 SeitenConsumer Arithmetic: Billsmelissa100% (2)
- Lesson 5-Consumer ArithmeticDokument12 SeitenLesson 5-Consumer Arithmeticalessse100% (1)
- Mathematics January 2020 Paper 2Dokument34 SeitenMathematics January 2020 Paper 2Tamera Green100% (1)
- Mathematics (2013) May Paper 2Dokument11 SeitenMathematics (2013) May Paper 2JewelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of MomentsDokument18 SeitenPrinciple of Momentsmelissa50% (2)
- Jamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideVon EverandJamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machines Physics CXCDokument5 SeitenMachines Physics CXCdemetri lanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC MATHEMATICS 2017 PAPER 1 (Solutions With Explanations)Dokument18 SeitenCSEC MATHEMATICS 2017 PAPER 1 (Solutions With Explanations)The MathematicianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec Chemistry Notes 7Dokument2 SeitenCsec Chemistry Notes 7debestieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Math Practice PDFDokument4 SeitenForm 4 Math Practice PDFAliyah wrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Programming Jan 2017Dokument4 SeitenLinear Programming Jan 2017melissa100% (1)
- CSEC Geography June 2014 P1Dokument14 SeitenCSEC Geography June 2014 P1Josh Hassanali100% (1)
- Circle Theorem Booklet PDFDokument16 SeitenCircle Theorem Booklet PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- Additional Mathematics Paper For PractiseDokument5 SeitenAdditional Mathematics Paper For PractiseaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Mathematics - Area of SectorDokument2 SeitenAdditional Mathematics - Area of SectorKatherine WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSB 2010 May-June P2 PDFDokument20 SeitenHSB 2010 May-June P2 PDFA GOJONoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors and MatricesDokument102 SeitenVectors and Matricespriya persaud100% (1)
- Benco 2021 Maths Test 3Dokument16 SeitenBenco 2021 Maths Test 3fecofyleNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC January 2013 Mathematics P1 PDFDokument9 SeitenCSEC January 2013 Mathematics P1 PDFTamera GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Mathematics - Circle TheoremsDokument30 SeitenCSEC Mathematics - Circle TheoremsCarl Agape DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- PU11 Computer Science Notes - Data RepresentationDokument12 SeitenPU11 Computer Science Notes - Data Representationgautham2850% (2)
- Integrated Science Mark Scheme CXCDokument9 SeitenIntegrated Science Mark Scheme CXCPeter MissoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Math Geometry - AnglesDokument11 SeitenCSEC Math Geometry - Anglesg100% (1)
- CSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDokument10 SeitenCSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDwayne DixonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBA GegraphyDokument13 SeitenSBA GegraphyShayn Ryan100% (1)
- Circuits Physic LabDokument5 SeitenCircuits Physic LabAaliyah SeniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Add Maths Study GuideDokument4 SeitenCSEC Add Maths Study Guider6hNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITN Module 5Dokument18 SeitenITN Module 5Paulo Alexandre Buinhas FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's Law Practice Questions PDFDokument3 SeitenHooke's Law Practice Questions PDFmelissa100% (1)
- CXC Geography CSEC - Practical Skills and Field Study ? ? NotesDokument64 SeitenCXC Geography CSEC - Practical Skills and Field Study ? ? NotesKevin RougierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 2013 June P1 PDFDokument11 SeitenMathematics 2013 June P1 PDFMichael TimsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prep For Success Hookes Law Letter SizeDokument7 SeitenPrep For Success Hookes Law Letter SizeRavin BoodhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch8 Cabook PDFDokument7 SeitenCh8 Cabook PDFThiruvenkata ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Information Technology January 2018 P2Dokument21 SeitenCSEC Information Technology January 2018 P2Tyrese SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletDokument8 SeitenSection A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletJoy BoehmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 May CSEC Physics Paper2 PDFDokument15 Seiten2014 May CSEC Physics Paper2 PDFCXC Dl1100% (1)
- CSEC Statistics Brief NotesDokument5 SeitenCSEC Statistics Brief NotesJosane WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSB Unit Test 2Dokument11 SeitenHSB Unit Test 2Jessica Kinney0% (1)
- CSEC January 2019 Mathematics P1Dokument14 SeitenCSEC January 2019 Mathematics P1Arianna Goodluck100% (1)
- Combined 2016 Ee PaperDokument30 SeitenCombined 2016 Ee Paperolvernejacobs9741Noch keine Bewertungen
- CXC Csec Mathematics 2016 January p1Dokument16 SeitenCXC Csec Mathematics 2016 January p1Janicea HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformations - SPQDokument10 SeitenTransformations - SPQAnthony BensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec Agricultural Science Syllabus With Specimen PapersDokument138 SeitenCsec Agricultural Science Syllabus With Specimen Papersapi-508592459Noch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC English B June 2013 P01Dokument6 SeitenCSEC English B June 2013 P01Sachin Bahadoorsingh100% (1)
- Cape Applied Mathematics Cheat SheetDokument6 SeitenCape Applied Mathematics Cheat SheetNobody JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- London Examinations GCE: Human Biology Ordinary LevelDokument20 SeitenLondon Examinations GCE: Human Biology Ordinary Levelwilsky05Noch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Physics Past Papers Jan 2017 Q5 Logic GatesDokument4 SeitenCSEC Physics Past Papers Jan 2017 Q5 Logic GatesjoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Jan CSEC Math Paper2Dokument34 Seiten2021 Jan CSEC Math Paper2Marie HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math May-June 2015Dokument32 SeitenMath May-June 2015shaniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sets - SPQDokument10 SeitenSets - SPQAnthony BensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesDokument20 SeitenCanadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesTrevor G. SamarooNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Physics January 2007 P1Dokument12 SeitenCSEC Physics January 2007 P1Sachin MarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- May June 2019 032Dokument16 SeitenMay June 2019 032Jarome BrathwaiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Physics June 2010 P032Dokument11 SeitenCSEC Physics June 2010 P032aidan kamrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra, Relations, Functions and Graphs IIDokument27 SeitenAlgebra, Relations, Functions and Graphs IIAnthony Benson100% (2)
- A Process of Testing Language Arts: Maharaj Publishers LimitedDokument19 SeitenA Process of Testing Language Arts: Maharaj Publishers LimitedShaRonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 4Dokument6 SeitenMatrices - Lessons - Part 4Anthony BensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Chemistry January 2009 P032Dokument7 SeitenCSEC Chemistry January 2009 P032AshleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBA 2 ModifiedDokument3 SeitenSBA 2 Modifiedannmarie100% (1)
- PhysicsDokument11 SeitenPhysicsdeondremorris56Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Practical Booklet Updated-4th-Form-CsecDokument17 SeitenBiology Practical Booklet Updated-4th-Form-CsecSashanna Morgan100% (1)
- Understanding Base Quantities and Derived QuantitiesDokument14 SeitenUnderstanding Base Quantities and Derived QuantitiesKogeela Vani VeerasingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CXC Jan 2000 p2Dokument7 SeitenCXC Jan 2000 p2omar_oj_40% (1)
- Form 4 Math Practice ExamDokument13 SeitenForm 4 Math Practice ExamOsayande OronsayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbols As Used in Circuit DiagramsDokument2 SeitenSymbols As Used in Circuit DiagramsmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and BatteriesDokument3 SeitenCells and BatteriesmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Interest HomeworkDokument1 SeiteSimple Interest HomeworkmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity MCDokument11 SeitenElectricity MCmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enthalpy 2Dokument8 SeitenEnthalpy 2melissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conserving Electrical EnergyDokument1 SeiteConserving Electrical EnergymelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionDokument10 SeitenTransfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Taking MeasurementsDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To Taking MeasurementsmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
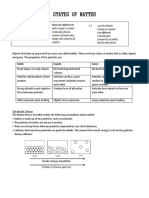
- 02 States of Matter + ExpansionDokument5 Seiten02 States of Matter + ExpansionmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrostaticsDokument6 SeitenElectrostaticsmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Gas LawsDokument12 Seiten04 Gas LawsmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrices: A - (3 4 5) B - C. DDokument5 SeitenMatrices: A - (3 4 5) B - C. DmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 The Nature of HeatDokument2 Seiten01 The Nature of HeatmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
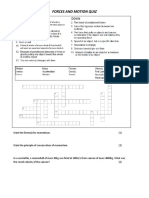
- Forces and Motion Crossword PDFDokument1 SeiteForces and Motion Crossword PDFmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Density: Density Is The Mass Per Unit Volume of A SubstanceDokument4 SeitenDensity: Density Is The Mass Per Unit Volume of A SubstancemelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Book of RevelationDokument1 SeiteThe Book of RevelationmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table WorksheetDokument2 SeitenPeriodic Table WorksheetmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces Test PDFDokument3 SeitenForces Test PDFmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Programming PDFDokument3 SeitenLinear Programming PDFmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Algebra Quiz 2015Dokument4 SeitenForm 4 Algebra Quiz 2015melissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratics 2016tcDokument9 SeitenQuadratics 2016tcmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Notes and PPQDokument13 SeitenElectricity Notes and PPQmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factorization: Ab A B n+12m N 6 M NDokument5 SeitenFactorization: Ab A B n+12m N 6 M NmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Mathematics Quiz-Sets: NameDokument1 SeiteForm 4 Mathematics Quiz-Sets: NamemelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transposing Equations: S T+a (T) V X T X) PV T (V)Dokument4 SeitenTransposing Equations: S T+a (T) V X T X) PV T (V)melissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Algebra Quiz 2017Dokument4 SeitenForm 4 Algebra Quiz 2017melissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 4 DLL q2 Week 10Dokument7 SeitenMath 4 DLL q2 Week 10Misha Madeleine GacadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Architecture and Organization Unit1 &,2.Dokument23 SeitenComputer Architecture and Organization Unit1 &,2.Mishra ArjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Science 1 ReviewerDokument5 SeitenMath Science 1 Reviewermichelle manliguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnderstandingdecimalsfoldableDokument6 SeitenUnderstandingdecimalsfoldableapi-242351866Noch keine Bewertungen
- Huraian Sukatan Pelajaran Matematik Tahun 6Dokument43 SeitenHuraian Sukatan Pelajaran Matematik Tahun 6Mat Jang100% (26)
- Toaz - Info Busmath 11 q1 Module 2 PRDokument33 SeitenToaz - Info Busmath 11 q1 Module 2 PRJomark RebolledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathDokument5 SeitenMathjanel marquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NumberDokument102 SeitenNumberZaimin Yaz MarchessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Number SystemDokument39 SeitenThe Number SystemRomel SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numeration EssayDokument4 SeitenNumeration Essayapi-277969008Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 02Dokument10 SeitenCH 02Mrs. Vasanthi MuniasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ComputersDokument72 SeitenIntroduction To ComputersSonny SabianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook PDF Calculating Dosages Safely A Dimensional Analysis Approach PDFDokument41 SeitenEbook PDF Calculating Dosages Safely A Dimensional Analysis Approach PDFsandra.putnam416100% (31)
- Digits and Place ValueDokument8 SeitenDigits and Place ValueRizky DestyniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number SystemDokument22 SeitenNumber Systemabir 911554Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods For EngineersDokument217 SeitenNumerical Methods For EngineersCIVIL ENGINEERINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Title: Computer Programming Language: Department of Naval Architecture & Marine EngineeringDokument38 SeitenCourse Title: Computer Programming Language: Department of Naval Architecture & Marine EngineeringA'raf Bin Islam SwapnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics For Junior High Schools: September 2012Dokument121 SeitenMathematics For Junior High Schools: September 2012Humble GeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtap g5s1 StudentDokument2 SeitenMtap g5s1 StudentLuis SalengaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A LESSON PLAN IN MATHEMATICS IV EXPLICIT TEACHIng Place Value and Value of DecimalsDokument4 SeitenA LESSON PLAN IN MATHEMATICS IV EXPLICIT TEACHIng Place Value and Value of DecimalsJulius VillafuerteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class-4 Handouts of Unit-1Dokument6 SeitenClass-4 Handouts of Unit-1Priyansh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing and Ordering DecimalsDokument15 SeitenComparing and Ordering DecimalsJulie IsmaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5: Number Systems: Instructor MaterialsDokument23 SeitenModule 5: Number Systems: Instructor MaterialsArief Wahyu HidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5: Number Systems: Instructor MaterialsDokument23 SeitenModule 5: Number Systems: Instructor MaterialspauaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Q PaperDokument2 SeitenMaths Q PaperamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMU8086 TutorialDokument81 SeitenEMU8086 TutorialGaurav Arora50% (4)
- Quarter 2 Mathematics IV Summative TestDokument4 SeitenQuarter 2 Mathematics IV Summative TestJenny Rose GloriosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Decimals UnitDokument12 SeitenTeaching Decimals UnitbrunerteachNoch keine Bewertungen