Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 8 - Application of Integrals
Hochgeladen von
Sunil SinghOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 8 - Application of Integrals
Hochgeladen von
Sunil SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.
), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Book Name: NCERT Solutions
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
EXERCISE- 8.1
Question 1:
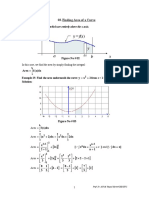
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y2 = x and the lines x = 1, x = 4 and the x-axis.
Solution 1:
HI S S
ES
NC A K' The area of the region bounded by the curve, y2 = x, the lines, x = 1 and x = 4, and the x-axis is
the area ABCD.
1
Area of ABCD =
1
ydx
RA C I
1
xdx
S
1
AL
4
32
x
3
L
2
ON M
1
2 23 3
4 1 2
3
WT .
2
8 1
3
K
14
units
3
R.
Question 2:
Find the area of the region bounded by y2 = 9x, x = 2, x = 4 and the x-axis in the first quadrant.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Solution 2:
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The area of the region bounded by the curve, y2 = 9x, x = 2, and x = 4, and the x-axis is the area
ABCD.
1
Area of ABCD =
2
ydx
1
3 xdx
HI S S
2
ES
4
NC A K' 23
x
3 3
2
2
RA C I
4
32
S
2 x
AL
2
3 3
2 4 2 2 2
L
ON M
2
8 2 2
3
16 4 2 units
WT .
K
Question 3:
Find the area of the region bounded by x2 = 4y, y = 2, y = 4 and the y-axis in the first quadrant.
Solution 3:
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The area of the region bounded by the curve, x2 = 4y, y = 2, and y = 4, and the y-axis is the area
ABCD.
1
Area of ABCD = 2
xdx
1
2 ydx
2
HI S S
1
2 ydx
2
ES
NC A K' 32
y
4
2 3
2
RA C I
2
S
4 32
2
AL
3
4 2
3
4
8 2 2
L
3
ON M
32 8 2
units
3
WT .
K
Question 4:
x2 y2
Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse 1
16 9
Solution 4:
R.
x2 y2
The given equation of the ellipse, 1 , can be represented as
16 9
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
It can be observed that the ellipse is symmetrical about x-axis and y-axis.
∴ Area bounded by ellipse = 4 × Area of OAB
4
Area of ABCD = ydx
HI S S
0
x2
ES
4
NC A K' 3 1 dx
0 16
3 4
4 0
16 x 2 dx
4
3 x 16 x
RA C I
16 x 2 sin 1
4 2 2 4 0
S
AL
3
2 16 16 8sin 1 1 0 8sin 1 0
4
3 8
L
4 2
ON M
3
4
4
3
WT .
Therefore, area bounded by the ellipse = 4 × 3π = 12π units
K
Question5:
x2 y 2
1
R.
Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse
4 9
Solution 5:
The given equation of the ellipse can be represented as
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
x2 y 2
1
4 9
x2
y 3 1 ... 1
HI S S
4
ES
NC A K' It can be observed that the ellipse is symmetrical about x-axis and y-axis.
∴ Area bounded by ellipse = 4 × Area OAB
2
Area of OAB= ydx
0
x2
Using (1)
2
3 1
RA C I
0 4
S
3 2
AL
2 0
4 x2
2
3x 4 1 x
4 x 2
sin
2 2 2 0
L
2
ON M
3 2
2 2
3
WT .
2
3
Therefore, area bounded by the ellipse = 4 6 units
K
2
R.
Question 6:
Find the area of the region in the first quadrant enclosed by x-axis, line x 3 y and the circle
x2 y 2 4
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Solution 6:
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The area of the region bounded by the circle, x2 y 2 4 , x 3 y , and the x-axis is the area
OAB.
The point of intersection of the line and the circle in the first quadrant is
3,1 .
Area OAB = Area ∆OCA + Area ACB
1 1 3
Area of OAC = OC AC 3 1 …
HI S S
2 2 2
ES
2
NC A K' Area of ABC = 3
ydx
2
4 x 2 dx
3
2
x 4 x
RA C I
4 x 2 sin 1
2 2 2
S
3
AL
3 3
2 4 3 2sin 1
2 2 2
3
L
2
ON M
2 3
3 2
2 3
WT .
3
…
3 2
K
Therefore, area enclosed by x-axis, the line x 3 y , and the circle x2 y 2 4 in the first
3 3
quadrant = units
2 3 2 3
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Question 7:
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
a
Find the area of the smaller part of the circle x2 + y2 = a2 cut off by the line, x .
2
Solution 7:
a
The area of the smaller part of the circle, x2 + y2 = a2, cut off by the line, x , is the area
2
ABCDA.
HI S S
ES
NC A K' It can be observed that the area ABCD is symmetrical about x-axis.
∴ Area ABCD = 2 × Area ABC
a
Area of ABC = ydx
RA C I
a
2
S
a
a a 2 x 2 dx
AL
2
a
x 2 a2 x
a x sin 1
2
L
2 2 a a
ON M
a2 a a2 a2 1
a2 sin 1
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
WT .
a 2 a a a2
.
4 2 2 2 2 4
K
a 2 a 2 a 2
4 4 8
a
2
1
R.
4 2
a
2
1
4 2
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
a2 a
2
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Area ABCD 2 1 1
4 2 2 2
a
Therefore, the area of smaller part of the circle, x2 + y2 = a2, cut off all the line, x , is
2
a2
1 units.
2 2
Question 8:
The area between x = y2 and x = 4 is divided into two equal parts by the line x = a, find the value
of a.
Solution 8:
The line, x = a, divides the area bounded by the parabola and x = 4 into two equal parts.
∴ Area OAD = Area ABCD
HI S S
ES
NC A K'
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
It can be observed that the given area is symmetrical about x-axis.
⇒ Area OED = Area EFCD
a
Area OED =
0
ydx
a
WT .
xdx
0
a
32
K
x
3
2
R.
0
3
2
a2 …(1)
3
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
4
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Area of EFCD = xdx
0
4
32
x
3
2
0
2 3
8 a 2
... 2
3
From (1) and (2), we obtain
a 2 8 a 2
3 3
2 2
3 3
3
2. a 2 8
3
HI S S
a2 4
ES
3
a 4 2
NC A K' 2
Therefore, the value of a is 4 3 .
RA C I
S
AL
Question 9:
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola y = x2 and y x
Solution 9:
L
ON M
The area bounded by the parabola, x2 = y, and the line, y x , can be represented as
WT .
K
R.
The given area is symmetrical about y-axis.
∴ Area OACO = Area ODBO
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
The point of intersection of parabola, x2 = y, and line, y = x, is A (1, 1).
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Area of OACO = Area ∆OAB – Area OBACO
1 1 1
Area of OAB= OB AB 11
2 2 2
1
1 1 x3 1
Area of OBACO = ydx x dx
2
0 0
3 0 3
⇒ Area of OACO = Area of ∆OAB – Area of OBACO
1 1
=
2 3
1
=
6
1 1
Therefore, required area = 2 units.
6 3
HI S S
ES
NC A K' Question 10:
Find the area bounded by the curve x2 = 4y and the line x = 4y – 2
Solution 10:
The area bounded by the curve, x2 = 4y, and line, x = 4y – 2, is represented by the shaded area
RA C I
OBAO.
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
K
Let A and B be the points of intersection of the line and parabola.
1
Coordinates of point A are 1, .
R.
4
Coordinates of point B are (2, 1).
We draw AL and BM perpendicular to x-axis.
NE
It can be observed that,
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Area OBAO = Area OBCO + Area OACO … (1)
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Then, Area OBCO = Area OMBC – Area OMBO
2 x2 2 x
2
dx dx
0 4 0 4
2 2
1 x2 1 x3
2x
4 2 0 4 3 0
2 4
1 1 8
4 4 3
3 2
2 3
5
6
Similarly, Area OACO = Area OLAC – Area OLAO
x2
0 0 x
2
dx
HI S S
dx
1 4 1 4
ES
0 0
NC A K' 1 x2 1 x3
2x
4 2 1 4 3 1
1 1 1 1
3
2 1
4 3
RA C I
4 2
S
1 1 1
2
AL
4 2 2
1 1 1
2 8 12
L
ON M
7
24
5 7 9
Therefore, required area = units
6 24 8
WT .
K
Question 11:
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y2 = 4x and the line x = 3
R.
Solution 11:
The region bounded by the parabola, y2 = 4x, and the line, x = 3, is the area OACO
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The area OACO is symmetrical about x-axis.
∴ Area of OACO = 2 (Area of OAB)
Area OACO = 2 ydx
3
0
2 2 xdx
3
HI S S
0
ES
3
NC A K' 23
x
3
4
2
RA C I
0
S
8 3
3 2
AL
3
8 3
L
Therefore, the required area is 8 3 units.
ON M
Question 12:
WT .
Area lying in the first quadrant and bounded by the circle x2 + y2 = 4 and the lines x = 0 and x =
2 is
K
A. π
B.
2
R.
C.
3
D.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Solution 12:
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The area bounded by the circle and the lines, x = 0 and x = 2, in the first quadrant is represented
as
2
Area OAB = ydx
0
2
4 x 2 dx
HI S S
0
ES
2
NC A K' x 4 x
4 x 2 sin 1
2 2 2 0
2
2
RA C I
units
S
Thus, the correct answer is A.
AL
L
Question 13:
ON M
Area of the region bounded by the curve y2 = 4x, y-axis and the line y = 3 is
A. 2
9
B.
WT .
4
9
C.
K
3
9
D.
2
Solution 13:
R.
The area bounded by the curve, y2 = 4x, y-axis, and y = 3 is represented as
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
3
Area OAB =
0
xdy
3 y2
HI S S
dy
0 4
ES
3
NC A K' 1 y3
4 4 0
1
27
12
RA C I
9
units
S
4
AL
Thus, the correct answer is B.
L
ON M
WT .
K
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
EXERCISE- 8.2
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Question 1:
Find the area of the circle 4x2 + 4y2 = 9 which is interior to the parabola x2 = 4y
Solution 1:
The required area is represented by the shaded area OBCDO.
HI S S
ES
NC A K'
Solving the given equation of circle, 4x2 + 4y2 = 9, and parabola, x2 = 4y, we obtain the point of
RA C I
1 1
intersection as B 2, and D 2, .
S
AL
2 2
It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical about y-axis.
∴ Area OBCDO = 2 × Area OBCO
L
We draw BM perpendicular to OA.
ON M
Therefore, the coordinates of M are 2,0 .
Therefore, Area OBCO = Area OMBCO – Area OMBO
9 4 x dx
2
x2
WT .
2 2
0 4 0 4
K
1 2 1 2
2 0
9 4 x 2 dx x 2 dx
4 0
2
1 x3
2
1 9 2x
x 9 4 x 2 sin 1
4 3 0 4 3 0
R.
2
1 9 1 2 2 1
2
3
2 9 8 sin
4 2 3 12
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
2 9 1 2 2 2
sin
4 8 3 6
2 9 1 2 2
sin
12 8 3
1 2 9 1 2 2
sin
2 6 4 3
Therefore, the required area OBCDO is
1 2 9 1 2 2 2 9 1 2 2
2 sin sin
2 6 4 3 6 4 3
units
Question 2:
Find the area bounded by curves (x – 1)2 + y2 = 1 and x2 + y2 = 1
HI S S
Solution 2:
ES
The area bounded by the curves, (x – 1)2 + y2 = 1 and x2 + y2 = 1, is represented by the shaded
NC A K' area as
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
On solving the equations, (x – 1)2 + y2 = 1 and x2 + y2 = 1, we obtain the point of intersection
1 3 1 3
as A , and B ,
WT .
2 2 2 2
K
It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical about x-axis.
∴ Area OBCAO = 2 × Area OCAO
We join AB, which intersects OC at M, such that AM is perpendicular to OC.
1
The coordinates of M are , 0
R.
2
Area OCAO Area OMAO Area MCAM
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
1
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
2 1 x 1 dx 1 1 x 2 dx
2 1
0
2
1
x 1
1
1 2 x 1
1 x 1 sin 1 x 1 1 x 2 sin 1 x
2
2 2 0 2 2 1
2
1 2
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2
1 sin 1 sin 1 sin 1
1
1 sin
4 2 2 2 2 2 4 2 2 2
3 1 1 1 3 1
8 2 6 2 2 2 2 8 2 6
3
4 12 4 4 12
3
HI S S
4 6 2
ES
NC A K' 2 3
6 4
2 3 2 3
Therefore, required area OBCAO = 2 units
2
RA C I
6 4 3
S
AL
Question 3:
L
Find the area of the region bounded by the curves y = x2 + 2, y = x, x = 0 and x = 3
ON M
Solution 3:
The area bounded by the curves, y = x2 + 2, y = x, x = 0, and x = 3, is represented by the shaded
area OCBAO as
WT .
K
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Then, Area OCBAO = Area ODBAO – Area ODCO
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
x 2 2 dx xdx
3 3
0 0
3 3
x3 x2
2x
3 0 2 0
9
9 6
2
9
15
2
21
units
2
Question 4:
HI S S
Using integration finds the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (–1, 0),
ES
NC A K' (1, 3) and (3, 2).
Solution 4:
BL and CM are drawn perpendicular to x-axis.
It can be observed in the following figure that,
RA C I
Area (∆ACB) = Area (ALBA) + Area (BLMCB) – Area (AMCA) … (1)
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
K
Equation of line segment AB is
30
y0 x 1
11
3
y x 1
R.
2
1
3 3 x2 3 1 1
Area ALBA x 1 dx x 1 1 3units
1
NE
1 2 2 2 1 2 2 2
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Equation of line segment BC is
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
23
y 3 x 1
3 1
1
y x 7
2
3
1 1 x2 1 9 1
Area BLMCB
3
x 7 dx 7 x 21 7 5units
1 2 2 2 1 2 2 2
Equation of line segment AC is
20
y0 x 1
3 1
1
y x 1
2
3
1 3 1 x2 1 9 1
Area AMCA x 1 dx x 3 1 4units
2 1 2 2 1 2 2 2
HI S S
Therefore, from equation (1), we obtain
ES
NC A K' Area (∆ABC) = (3 + 5 – 4) = 4 units
Question 5:
RA C I
Using integration find the area of the triangular region whose sides have the equations y = 2x
S
+1, y = 3x + 1 and x = 4.
AL
Solution 5:
The equations of sides of the triangle are y = 2x +1, y = 3x + 1, and x = 4.
On solving these equations, we obtain the vertices of triangle as A(0, 1), B(4, 13), and C (4, 9).
L
ON M
WT .
K
R.
It can be observed that,
Area (∆ACB) = Area (OLBAO) –Area (OLCAO)
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
3x 1 dx 2 x 1 dx
4 4
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
0 0
4 4
3x 2
2 x2
x x
2 0 2 0
24 4 16 4
28 20
8units
Question6:
Smaller area enclosed by the circle x2 + y2 = 4 and the line x + y = 2 is
A. 2 (π – 2)
B. π – 2
C. 2π – 1
D. 2 (π + 2)
HI S S
Solution 6:
ES
NC A K' The smaller area enclosed by the circle, x2 + y2 = 4, and the line, x + y = 2, is represented by the
shaded area ACBA as
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
It can be observed that,
Area ACBA = Area OACBO – Area (∆OAB)
4 x 2 dx 2 x dx
2 2
WT .
0 0
2 2
x 4 x x
4 x 2 sin 1 2 x
K
2 2 2 0 2 0
2. 4 2
2
2 units
R.
Thus, the correct answer is B.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Question 7:
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Area lying between the curve y2 = 4x and y = 2x is
2 1
A. C.
3 4
1 3
B. D.
3 4
Solution 7:
The area lying between the curve, y2 = 4x and y = 2x, is represented by the shaded area OBAO
as
HI S S
ES
NC A K'
The points of intersection of these curves are O (0, 0) and A (1, 2).
We draw AC perpendicular to x-axis such that the coordinates of C are (1, 0).
RA C I
∴ Area OBAO = Area (∆OCA) – Area (OCABO)
S
1 1
2 xdx 2 xdx
AL
0 0
1
3 1
x x2
2
2 2
3
L
2 0
ON M
2 0
4
1
3
1
WT .
3
K
1
units
3
Thus, the correct answer is B.
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Miscellaneous EXERCISE
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Question 1:
Find the area under the given curves and given lines:
(i) y = x2, x = 1, x = 2 and x-axis
(ii) y = x4, x = 1, x = 5 and x –axis
Solution 1:
i. The required area is represented by the shaded area ADCBA as
HI S S
2
Area ADCBA = ydx
ES
NC A K' 1
2
x 2 dx
1
2
x3
3 1
RA C I
8 1
S
AL
3 3
7
units
3
L
ii. The required area is represented by the shaded area ADCBA as
ON M
WT .
K
R.
5
Area of ADCBA =
1
x 4 dx
5
x5
NE
5 1
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
5
5
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
1
5 5
1
5
4
5
1
625
5
624.8 units
Question 2:
Find the area between the curves y = x and y = x2
Solution 2:
The required area is represented by the shaded area OBAO as
HI S S
ES
NC A K'
RA C I
S
AL
The points of intersection of the curves, y = x and y = x2, is A (1, 1).
L
ON M
We draw AC perpendicular to x-axis.
∴ Area (OBAO) = Area (∆OCA) – Area (OCABO) … (1)
1 1
xdx x 2 dx
0 0
1 1
WT .
x 2 x3
2 0 3 0
K
1 1
2 3
1
units
6
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Question 3:
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Find the area of the region lying in the first quadrant and bounded by y = 4x2, x = 0, y = 1 and y
=4
Solution 3:
The area in the first quadrant bounded by y = 4x2, x = 0, y = 1, and y = 4 is represented by the
shaded area ABCDA as
HI S S
ES
NC A K' Area ABCD= xdx
4
4 4
dx
1 2
RA C I
4
3
S
1 y2
AL
2 3
2 1
1 3
L
4 2 1
ON M
3
1
8 1
3
7
WT .
units
3
K
Question 4:
R.
0
Sketch the graph of y x 3 and evaluate 6
x 3 dx
Solution 4:
The given equation is y x 3
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
The corresponding values of x and y are given in the following table.
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
On plotting these points, we obtain the graph y x 3 of as follows.
HI S S
ES
NC A K'
It is known that, x 3 0 for -6 x -3 and x 3 0 for -3 x 0
RA C I
3
S
x 3 dx 6 x 3 dx 3 x 3 dx
0 0
AL
6
3 0
x2 x2
3x 3x
2 6 2 3
L
ON M
32 6 2 32
3 3 3 6 0 3 3
2
2 2
9 9
WT .
2 2
9
K
Question 5:
R.
Find the area bounded by the curve y = sin x between x = 0 and x = 2π
Solution 5:
NE
The graph of y = sin x can be drawn as
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
∴ Required area = Area OABO + Area BCDB
2
sin xdx sin xdx
0
cos x 0 cos x
2
HI S S
cos cos 0 cos 2 cos
ES
NC A K' 1 1 1 1
2 2
2 2 4 units
RA C I
S
AL
Question 6:
Find the area enclosed between the parabola y2 = 4ax and the line y = mx
L
Solution 6:
ON M
The area enclosed between the parabola, y2 = 4ax, and the line, y = mx, is represented by the
shaded area OABO as
WT .
K
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
4a 4a
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The points of intersection of both the curves are (0, 0) and 2 , .
m m
We draw AC perpendicular to x-axis.
∴ Area OABO = Area OCABO – Area (∆OCA)
4a 4a
m 2 axdx m mxdx
2 2
0 0
4a
3 m2 4a
x2 x 2 m2
2 a m
3 2 0
2 0
3
4 a 2 m 4a
2
4
a 2 2
3 m 2 m
32a 2 m 16a 2
3m3 2 m 2
HI S S
ES
32a 2 8a 2
NC A K'
3m3 m3
8a 2
units
3m3
RA C I
S
AL
Question 7:
Find the area enclosed by the parabola 4y = 3x2 and the line 2y = 3x + 12
L
ON M
Solution 7:
The area enclosed between the parabola, 4y = 3x2, and the line, 2y = 3x + 12, is represented by
the shaded area OBAO as
The points of intersection of the given curves are A (–2, 3) and (4, 12).
WT .
We draw AC and BD perpendicular to x-axis.
∴ Area OBAO = Area CDBA – (Area ODBO + Area OACO)
K
2
1 4 3x
3x 12 dx
1
dx
2 2 2 4
4 4
1 3x 2 3 x3
R.
12 x
2 2 2 4 3 2
1 1
24 48 6 24 64 8
NE
2 4
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
HI S S
ES
NC A K'
1 1
90 72
2 4
RA C I
45 18
S
27 units
AL
L
ON M
Question 8:
x2 y 2 x y
Find the area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse 1 and the line 1
9 4 3 2
Solution 8:
WT .
x2 y 2 x y
The area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse, 1 , and the line, 1 , is
K
9 4 3 2
represented by the shaded region BCAB as
∴ Area BCAB = Area (OBCAO) – Area (OBAO)
3 x2 3 x
2 1 dx 2 1 dx
R.
0 9 0
3
2 3
9 x 2 dx 3 1 dx
2 3
3 0
3 0
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
3
9 1 x 2 x2
3
2 x
9 x sin
2
3x
3 0 3
HI S S
3 2 2 2 0
ES
NC A K' 2 9 2 9
9
3 2 2 3 2
2 9 9
3 4 2
RA C I
2 9
2
S
3 4
AL
3
2 units
2
L
ON M
Question 9:
x2 y 2 x y
Find the area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse 2 1and the line 1
WT .
2
a b a b
Solution 9:
K
x2 y 2 x y
The area of the smaller region bounded by the ellipse, 2
2 1 , and the line, 1 , is
a b a b
represented by the shaded region BCAB as
R.
∴ Area BCAB = Area (OBCAO) – Area (OBAO)
a x2 a x
b 1 2 dx b 1 dx
0 a 0
a
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
b a 2 b a
a x dx
a 0 a 0
a x 2
dx
HI S S
b x 2 x2
a a
a2 1 x
ES
NC A K' a x sin
2
ax
a 2 2 a 0 2 0
b a 2 2 a 2
a
a 2 2 2
RA C I
b a 2 a 2
a 4
S
2
AL
ba 2
1
2a 2
L
ab
ON M
1
2 2
ab
2
4
WT .
K
Question 10:
Find the area of the region enclosed by the parabola x2 = y, the line y = x + 2 and x axis
Solution 10:
R.
The area of the region enclosed by the parabola, x2 = y, the line, y = x + 2, and x-axis is
represented by the shaded region OABCO as
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The point of intersection of the parabola, x2 = y, and the line, y = x + 2, is A (–1, 1).
∴ Area OABCO = Area (BCA) + Area COAC
HI S S
1
x 2 dx x 2 dx
0
ES
NC A K' 2 1
1 0
x2 x3
2x
2 2 3 1
12 2
2
13
RA C I
2 1 2 2
2 2 3
S
AL
1 1
224
2 3
5
L
units
ON M
6
WT .
Question 11:
Using the method of integration find the area bounded by the curve x y 1
K
[Hint: the required region is bounded by lines x + y = 1, x – y = 1, – x + y = 1 and – x – y = 11]
Solution 11:
The area bounded by the curve, x y 1 , is represented by the shaded region ADCB as
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The curve intersects the axes at points A (0, 1), B (1, 0), C (0, –1), and D (–1, 0).
It can be observed that the given curve is symmetrical about x-axis and y-axis.
∴ Area ADCB = 4 × Area OBAO
HI S S
4 1 x dx
1
ES
0
NC A K'
x2
4 x
2 0
1
1
4 1
RA C I
2
S
1
AL
4
2
2 units
L
ON M
Question 12:
Find the area bounded by curves x, y : y x 2
and y= x
WT .
Solution 12:
x, y : y x and y= x , is represented by the shaded region
K
2
The area bounded by the curves,
as
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical about y-axis.
Required area = 2 [ Area (OCAO) – Area (OCADO)]
2 xdx x 2 dx
1 1
0 0
HI S S
x 2 1 x3 1
2
ES
NC A K' 2 0 3 0
1 1
2
2 3
RA C I
1 1
2 units
6 3
S
AL
L
Question 13:
ON M
Using the method of integration find the area of the triangle ABC, coordinates of whose vertices
are A (2, 0), B (4, 5) and C (6, 3)
Solution 13:
The vertices of ∆ABC are A (2, 0), B (4, 5), and C (6, 3).
WT .
K
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
Equation of line segment AB is
HI S S
50
y0 x 2
ES
NC A K' 42
2 y 5 x 10
5
y x 2 ... 1
2
RA C I
Equation of line segment BC is
35
S
y 5 x 4
AL
64
2 y 10 2 x 8
2 y 2 x 18
L
y x 9 ... 2
ON M
Equation of line segment CA is
03
y 3 x 6
26
WT .
4 y 12 3 x 18
4 y 3x 6
K
3
y x 2 ... 3
4
Area (∆ABC) = Area (ABLA) + Area (BLMCB) – Area (ACMA)
R.
45 63
x 2 dx x 9 dx x 2 dx
6
2 2 4 2 4
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
4 6 6
5 x2 x2 3 x2
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
2x 9x 2x
2 2 2 2 4 4 2 2
5 3
8 8 2 4 18 54 8 36 18 12 2 4
2 4
3
5 8 8
4
13 6
7 units
Question 14:
Using the method of integration find the area of the region bounded by lines:
2x + y = 4, 3x – 2y = 6 and x – 3y + 5 = 0
HI S S
Solution 14:
The given equations of lines are
ES
NC A K' 2x + y = 4 … (1)
3x – 2y = 6 … (2)
And, x – 3y + 5 = 0 … (3)
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
K
The area of the region bounded by the lines is the area of ∆ABC. AL and CM are the
R.
perpendiculars on x-axis.
Area (∆ABC) = Area (ALMCA) – Area (ALB) – Area (CMB)
4 x 5 2 4 3x 6
dx 4 2 x dx dx
NE
1
3 1 2
2
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
4 4
1 x2 1 3x 2
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
2
5 x 4 x x 2 6x
3 2 1
1 2 2 2
1 1 1
8 20 5 8 4 4 1 24 24 6 12
3 2 2
1 45 1
1 6
3 2 2
15
1 3
2
15 15 8 7
4 units
2 2 2
Question 15:
HI S S
Find the area of the region x, y : y 2
4 x.4 x 2 4 y 2 9
ES
NC A K' Solution 15:
The area bounded by the curves, x, y : y 2
4 x.4 x 2 4 y 2 9 , is represented as
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
K
1 1
The points of intersection of both the curves are , 2 and , 2 .
2 2
R.
The required area is given by OABCO.
It can be observed that area OABCO is symmetrical about x-axis.
∴ Area OABCO = 2 × Area OBC
Area OBCO = Area OMC + Area MBC
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
1 3
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
1
2 2 xdx 12 9 4 x 2 dx
0
2 2
1 3
1
2 xdx 3 2 x
2 2
2 2
1 dx
0
2 2
Question 16:
Area bounded by the curve y = x3, the x-axis and the ordinates x = –2 and x = 1 is
A. – 9
15
B.
4
15
C.
4
HI S S
17
D.
4
ES
NC A K' Solution 16:
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
1
K
Required area = ydx
2
1
x3dx
2
1
x4
R.
4 2
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
1 (2) 4
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
4
4
1 15
4 units
4 4
Thus, the correct answer is B.
Question 17:
The area bounded by the curve y x x , x-axis and the ordinates x = –1 and x = 1 is given by
[Hint: y = x2 if x > 0 and y = –x2 if x < 0]
A.0
1
B.
3
HI S S
2
C.
ES
3
NC A K' D.
4
3
Solution 17:
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
1
Required area = ydx
K
1
1
x x dx
1
0 1
x 2 dx x 2 dx
1
R.
0
0 1
x3 x3
3 1 3 0
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
1 1
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
3 3
2
units
3
Thus, the correct answer is C.
Question 18:
The area of the circle x2 + y2 = 16 exterior to the parabola y2 = 6x is
A.
4
3
4 3
B.
4
3
4 3
C.
4
8 3
HI S S
3
ES
NC A K' D.
4
3
8 3
Solution 18:
The given equations are
x2 + y2 = 16 … (1)
RA C I
y2 = 6x … (2)
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
K
Area bounded by the circle and parabola
2 Area OADO Area ADBA
R.
2 16 xdx 16 x 2 dx
2 4
0 2
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
3 2
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
x2 x 16 x
4
2 6 2 16 x 2 sin 1
3 2 2 4 2
2 0
2
2 32 1
2 6 x 2 8. 16 4 8sin 1
3 0 2 2
4 6
3
2 2 2 4 12 8
6
16 3 8
8 4 3
3 3
4
4 3 6 3 3 2
3
4
3 4
HI S S
3
4
4 3 units
ES
NC A K' 3
Area of circle = π (r)2
= π (4)2
= 16π units
RA C I
4
Required area = 16 - 4 3
S
3
AL
4
4 3 4 3
3
4
8 3 units
L
ON M
3
Thus, the correct answer is C.
WT .
Question 19:
K
The area bounded by the y-axis, y = cos x and y = sin x when 0 x
2
A. 2 2 1
R.
B. 2 1
C. 2 1
D. 2
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
Solution 19:
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
The given equations are
y = cos x … (1)
And, y = sin x … (2)
Required area = Area (ABLA) + area (OBLO)
1
HI S S
1
1 xdy 2 xdy
0
ES
2
NC A K' 1 1
1 cos 1 ydy 1 sin 1 xdy
2 2
Integrating by parts, we obtain
1
RA C I
1
y cos 1 y 1 y 2 x sin 1 x 1 x 2 2
1 0
S
2
AL
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
cos 1 1 cos 1 1 sin 1 1
2 2 2 2 2 2
L
1 1
1
ON M
4 2 2 4 2 2
2
1
2
WT .
2 1units
K
Thus, the correct answer is B.
dt
Put 2x = t dx =
2
3 1
R.
When x = , t = 3 and when x = , t = 1
2 2
1
1 3
2 2 xdx 3 t
4 1
2 2
dt
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
R. K. MALIK’S JEE (MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL
NEWTON CLASSES + BOARD, NDA, FOUNDATION
Class XII Chapter 8 – Application of Integrals Maths
______________________________________________________________________________
1
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
R. K. MALIK'S NEWTON CLASSES, RANCHI
3 2
x2 1 t
3
9 1 t
2 9 t sin
2
3
4 2 2 3 1
2 0
3
2 1 1 3 9 3 1 9 1
2 9 3 sin 1 9 1 sin 1
2 2 2
3 2 4 2 2 3 2 2 3
2 1 9 1 9 1
0 sin 1 1 8 sin 1
3 2 4 2 2 2 3
2 1 9 9 1
2 sin 1
3 4 4 2 3
2 9 2 9 1 1
sin
3 16 4 8 3
HI S S
9 9 1 1 2
sin
ES
NC A K' 16 8 3 12
9 9 1 1 2 9 9 1 1 1
Therefore, the required area is 2 sin sin units
16 8 3 12 8 4 3 3 2
RA C I
S
AL
L
ON M
WT .
K
R.
NE
MAKE YOUR CONCEPTS CRYSTAL CLEAR
VISIT OUR YOU TUBE CHANNEL : MATHEMATICS MADE INTERESTING
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
th
Office.: 606 , 6 Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1, Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8228920542
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PIPESIMDokument286 SeitenPIPESIMPedro Antonio Mejia SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20Dokument23 Seiten19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20likhith chowdary25% (4)
- Emailing GR 11 - Maths - Step Ahead - Teacher Document - 2022 PDFDokument114 SeitenEmailing GR 11 - Maths - Step Ahead - Teacher Document - 2022 PDFMac Mawasha100% (1)
- C 89297 2698020354106393136Dokument7 SeitenC 89297 2698020354106393136mystery26Noch keine Bewertungen
- CS 500: Fundamentals of Databases: Midterm Exam SolutionsDokument13 SeitenCS 500: Fundamentals of Databases: Midterm Exam SolutionsMohamed KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18Mab102T-Advanced Calculus and Complex Analysis: Unit I - Double and Triple IntegralsDokument22 Seiten18Mab102T-Advanced Calculus and Complex Analysis: Unit I - Double and Triple Integralsraffiq85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ns Xii AoiDokument42 SeitenNs Xii Aoipathakjiji02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Radical ExpressionsDokument19 SeitenModule 3 Radical ExpressionsAthena Jane NapolisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integral CalculusDokument2 SeitenIntegral CalculusShubhenduGuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jabatan Pendidikan Negeri Kedah Majlis Pengetua Sekolah Malaysia Negeri Kedah Darul AmanDokument20 SeitenJabatan Pendidikan Negeri Kedah Majlis Pengetua Sekolah Malaysia Negeri Kedah Darul AmanazuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Ting 4 2010Dokument9 SeitenSoalan Ting 4 2010aziana ashaariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test2thursday1803 2015Dokument1 SeiteTest2thursday1803 2015eidalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test2thursday1803 2015Dokument1 SeiteTest2thursday1803 2015Azlin IdayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 Add Maths Trial Paper 2 PDFDokument15 Seiten2018 Add Maths Trial Paper 2 PDFChin VennNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.5 Applications of Integration (A) The Definite Integral and AreaDokument22 Seiten5.5 Applications of Integration (A) The Definite Integral and AreaMark LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi Public School Harni: Academic Session 2023 - 2024 Practice WorksheetDokument1 SeiteDelhi Public School Harni: Academic Session 2023 - 2024 Practice Worksheetsriramsonic007Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Cikgujep - Com) Kedah Add Maths P2 2017 PDFDokument18 Seiten(Cikgujep - Com) Kedah Add Maths P2 2017 PDFlim chui hongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Maths Iib Ipe Imp Q.bank 2023-2024Dokument14 SeitenSenior Maths Iib Ipe Imp Q.bank 2023-2024Satyavathi GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appl of IntDokument3 SeitenAppl of IntharshxzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 Sr2 Add MathsDokument11 Seiten2018 Sr2 Add MathsJia JiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Under Curve One Shot #BounceBackDokument84 SeitenArea Under Curve One Shot #BounceBackNirav VaghasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-EE009-3-2-EMTH3-VC1 Tutorial ProblemsDokument4 Seiten2-EE009-3-2-EMTH3-VC1 Tutorial ProblemsBrian WaithakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Applications of Integrals Important Questions 2022-23Dokument3 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Applications of Integrals Important Questions 2022-23adarsh awasthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centroids and Moment of InertiaDokument23 SeitenCentroids and Moment of InertiaAndrea Beatrice OroNoch keine Bewertungen
- hw1B4002Dokument1 Seitehw1B4002vaashuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cal2 Sem2 2021Dokument2 SeitenCal2 Sem2 2021Huynh Duong Ton LucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 5AN NGUYENNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS - SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions BNJC 2023-24Dokument6 SeitenTS - SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions BNJC 2023-24nanimuhirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centroids and Center of GravityDokument9 SeitenCentroids and Center of GravityJoash Normie DuldulaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Cikgujep - Com) Add Maths Pra SPM m2 - Sept 2017 - p2Dokument19 Seiten(Cikgujep - Com) Add Maths Pra SPM m2 - Sept 2017 - p2BtgPeiiYiingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Important QuestionDokument16 SeitenMaths Important QuestionSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level-1: X 1 F (X) X 1Dokument2 SeitenLevel-1: X 1 F (X) X 1Anonymous gC6zjrhQMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics-Iii (Transform & Discrete Mathematics) : R Xiyjzk R R RDokument2 SeitenMathematics-Iii (Transform & Discrete Mathematics) : R Xiyjzk R R RMortaza HaidarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper: MatrixDokument3 SeitenPaper: Matrixsanjay udhayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VC.07: Transforming 2D Integrals Literacy: y X Cos R X Sin R yDokument6 SeitenVC.07: Transforming 2D Integrals Literacy: y X Cos R X Sin R ySri RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review in Integral CalculusDokument2 SeitenReview in Integral CalculusRAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul SBP SPM 2014 Perfect Score Add Math PDFDokument83 SeitenModul SBP SPM 2014 Perfect Score Add Math PDFAiman JohariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0.0 Muka Depan Additional Mathematics Perfect ScoreDokument10 Seiten0.0 Muka Depan Additional Mathematics Perfect Score3014398Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths 1B - Chapter Wise Important Questions PDF - PDF - Line (Geometry) - TriangleDokument31 SeitenMaths 1B - Chapter Wise Important Questions PDF - PDF - Line (Geometry) - TriangleRaparthi PrithamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20Dokument22 Seiten19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20sai tejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geom B Midterm Rev PKT 08Dokument19 SeitenGeom B Midterm Rev PKT 08بستان المعرفةNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microproject MathsDokument12 SeitenMicroproject Mathsanimeshdorugade244Noch keine Bewertungen
- SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2024Dokument6 SeitenSR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2024ow123aisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30-05-21 Inc - Sr.iit Star Co-Sc Jee Adv 2015 P-II Cat-20 Key & SolDokument12 Seiten30-05-21 Inc - Sr.iit Star Co-Sc Jee Adv 2015 P-II Cat-20 Key & SolVijay RaghavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 9: Integral Calculus: Tan XDXDokument5 SeitenExam 9: Integral Calculus: Tan XDXElmarc CodenieraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Perlis P1Dokument19 SeitenTrial Perlis P1abNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5.5. Question BankDokument10 Seiten3.5.5. Question BankPrudhvi Raghu Teja100% (1)
- 19-02-22 JR - Iit Star Co-Sc (Model-A) Jee Adv 2020 (P-I) Wat-40 Key & SolDokument11 Seiten19-02-22 JR - Iit Star Co-Sc (Model-A) Jee Adv 2020 (P-I) Wat-40 Key & SolsdnishacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ii Pu Mathematics Work Sheet Application of Integrals - 8Dokument7 SeitenIi Pu Mathematics Work Sheet Application of Integrals - 8l53034001Noch keine Bewertungen
- BUM2123 Final 2021IDokument7 SeitenBUM2123 Final 2021Inabila hanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Sheet 2Dokument18 SeitenLecture Sheet 2SM Muntasir SarwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate Geometry and Calculus. TIME: 3hrs Max. Marks.75Dokument16 SeitenCoordinate Geometry and Calculus. TIME: 3hrs Max. Marks.75Tarigonda GiridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS Ipe 2023 7Dokument15 SeitenTS Ipe 2023 7bharathbharath6824Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crux v16n01 JanDokument39 SeitenCrux v16n01 JanhitlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Formula All Collection PDFDokument75 SeitenMath Formula All Collection PDFEr S Karthick AnnamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Calculus 3 June 2018Dokument2 SeitenDe Calculus 3 June 2018Hoàng VõNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiziks: (C) of Black Body Radiation (Classical Theory)Dokument2 SeitenFiziks: (C) of Black Body Radiation (Classical Theory)Jagvir SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sr.S60, ELITE, TARGET & LIIT - Jee-Main-GTM - PHYSICSDokument7 SeitenSr.S60, ELITE, TARGET & LIIT - Jee-Main-GTM - PHYSICSbaluduvamsi2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Area Under CurveDokument4 SeitenArea Under CurveDivyansh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Solving Quadratic Equations SolutionsDokument3 Seiten7 - Solving Quadratic Equations SolutionsNahuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ts SR Maths Iib Imp Questions-2023Dokument6 SeitenTs SR Maths Iib Imp Questions-2023Kota ๖ۣۜRαkͥesͣhͫNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Course of Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsVon EverandA Course of Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resolution of Singularities of Embedded Algebraic SurfacesVon EverandResolution of Singularities of Embedded Algebraic SurfacesNoch keine Bewertungen
- I.A. - Ll-Hindi OptDokument15 SeitenI.A. - Ll-Hindi OptSunil Singh100% (1)
- I.A. - MB - Alt - English CompDokument10 SeitenI.A. - MB - Alt - English CompSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sat Ntse 2019 Stage 1 Solutions KarnatakaDokument25 SeitenSat Ntse 2019 Stage 1 Solutions KarnatakaSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 111 KDDDokument3 Seiten111 KDDSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0086 0087Dokument2 Seiten0086 0087Sunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mat Ntse 2019 Stage 1 Solutions TelanganaDokument20 SeitenMat Ntse 2019 Stage 1 Solutions TelanganaSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Height - Distances PDFDokument3 SeitenHeight - Distances PDFSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- (1402) 02 07 2018 Yccp Time Table PDFDokument1 Seite(1402) 02 07 2018 Yccp Time Table PDFSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 1 - Daily Practice Problems (Mathematics) PDFDokument7 SeitenDPP 1 - Daily Practice Problems (Mathematics) PDFSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVI LIST - Northern - Region - 2018 PDFDokument94 SeitenAVI LIST - Northern - Region - 2018 PDFSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career Point: Faculty Selection TestDokument4 SeitenCareer Point: Faculty Selection TestSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution CBTDokument39 SeitenSolution CBTSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4811Dokument25 Seiten4811Sunil Singh100% (1)
- PT 2 MAT WithoutAnsDokument17 SeitenPT 2 MAT WithoutAnsSunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSA (Cryptosystem) : 1 HistoryDokument9 SeitenRSA (Cryptosystem) : 1 HistoryTanmay RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esoteric PhysicsDokument107 SeitenEsoteric PhysicsKelvins Momanyi100% (3)
- Unit-5 Residues and Its ApplicationsDokument39 SeitenUnit-5 Residues and Its ApplicationsChandradeep Reddy TeegalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMR PYQs 7-9Dokument6 SeitenSMR PYQs 7-9TRY UP GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Protection: Read Comtrade File DataDokument23 SeitenDifferential Protection: Read Comtrade File Datarian0201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methods, 9Th Edition: Theresa L. White and Donald H. McburneyDokument145 SeitenResearch Methods, 9Th Edition: Theresa L. White and Donald H. McburneyKassandra MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Point-Biserial Correlation CoefficientDokument3 SeitenPoint-Biserial Correlation Coefficientisabella343Noch keine Bewertungen
- S2 - TrigonometryDokument79 SeitenS2 - TrigonometryDylan OtteyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Time Delay Relay FunctionsDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding Time Delay Relay FunctionsAndrew BullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otake Hideo - Opening Theory Made EasyDokument87 SeitenOtake Hideo - Opening Theory Made Easyanon-505528100% (21)
- Lahore University of Management Sciences: Midterm Exam Schedule Fall 2012Dokument13 SeitenLahore University of Management Sciences: Midterm Exam Schedule Fall 2012Ahmad_Bilal_As_3566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matemática de BlockchainsDokument200 SeitenMatemática de BlockchainspedroNoch keine Bewertungen
- WNL Users GuideDokument852 SeitenWNL Users Guidemichael.jorge5307Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Problem ThermoDokument25 SeitenSample Problem ThermoJonnah Faye Mojares0% (1)
- Cost Volume Profit (CVP) AnalysisDokument40 SeitenCost Volume Profit (CVP) AnalysisAnne PrestosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrapbook Info GGGGDokument5 SeitenScrapbook Info GGGGDanstan Ferrolino Genova IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Seminar PresentationDokument48 SeitenProject Seminar PresentationGokulnath PillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyborgs: The ArchetypeDokument32 SeitenCyborgs: The ArchetypeMichał StojeckiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee 40Dokument4 SeitenFiitjee 40BHAAJI0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Book ProceedingsOfTheSecondInternatDokument385 Seiten2019 Book ProceedingsOfTheSecondInternatkishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code - Bright: User'S GuideDokument232 SeitenCode - Bright: User'S GuideEduardo Alemany PerretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-Linear Functions of Random VariablesDokument25 SeitenChapter 3-Linear Functions of Random VariablesStr.EngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tess ElationDokument7 SeitenTess ElationBoy ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Hybrid Simulation Approach For Quantitatively Analyzing The Impact ofDokument10 SeitenA Hybrid Simulation Approach For Quantitatively Analyzing The Impact ofjose_guerra_73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emgt5220 c9 TLDokument28 SeitenEmgt5220 c9 TLmike jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planbook AlgebraDokument15 SeitenPlanbook Algebraapi-233970614Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying Review NotesDokument7 SeitenSurveying Review Notessadon100% (1)