Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Components of Balance of Payments
Hochgeladen von
Jeyaprabha Jeslin0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten2 SeitenBalance of Payments and the concepts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBalance of Payments and the concepts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten2 SeitenComponents of Balance of Payments
Hochgeladen von
Jeyaprabha JeslinBalance of Payments and the concepts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
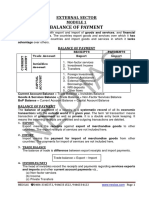
COMPONENTS OF BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
(1) Current Account:
Current account refers to an account which records all the transactions relating to export and
import of goods and services and unilateral transfers during a given period of time.
Current account contains the receipts and payments relating to all the transactions of visible
items, invisible items and unilateral transfers.
Components of Current Account:
The main components of Current Account are:
1. Export and Import of Goods (Merchandise Transactions or Visible Trade):
A major part of transactions in foreign trade is in the form of export and import of goods (visible
items). Payment for import of goods is written on the negative side (debit items) and receipt from
exports is shown on the positive side (credit items). Balance of these visible exports and imports
is known as balance of trade (or trade balance).
2. Export and Import of Services (Invisible Trade):
It includes a large variety of non- factor services (known as invisible items) sold and purchased
by the residents of a country, to and from the rest of the world. Payments are either received or
made to the other countries for use of these services.
Services are generally of three kinds:
(a) Shipping,
(b) Banking, and
(c) Insurance.
Payments for these services are recorded on the negative side and receipts on the positive side.
3. Unilateral or Unrequited Transfers to and from abroad (One sided Transactions):
Unilateral transfers include gifts, donations, personal remittances and other ‘one-way’
transactions. These refer to those receipts and payments, which take place without any service in
return. Receipt of unilateral transfers from rest of the world is shown on the credit side and
unilateral transfers to rest of the world on the debit side.
4. Income receipts and payments to and from abroad:
It includes investment income in the form of interest, rent and profits.
Current Account shows the Net Income:
Current Account records all the actual transactions of goods and services which affect the
income, output and employment of a country. So, it shows the net income generated in the
foreign sector.
Balance on Current Account:
In the current account, receipts from export of goods, services and unilateral receipts are entered
as credit or positive items and payments for import of goods, services and unilateral payments
are entered as debit or negative items. The net value of credit and debit balances is the balance
on current account.
1. Surplus in current account arises when credit items are more than debit items. It indicates net
inflow of foreign exchange.
2. Deficit in current account arises when debit items are more than credit items. It indicates net
outflow of foreign exchange.
(2) Capital Account:
Capital account of BOP records all those transactions, between the residents of a country and the
rest of the world, which cause a change in the assets or liabilities of the residents of the country
or its government. It is related to claims and liabilities of financial nature.
Capital Account is used to:
(i) Finance deficit in current account; or
(ii) Absorb surplus of current account.
Capital account is concerned with financial transfers. So, it does not have direct effect on
income, output and employment of the country.
Components of Capital Account:
The main components of capital account are:
1. Borrowings and landings to and from abroad: It includes:
A. All transactions relating to borrowings from abroad by private sector, government, etc.
Receipts of such loans and repayment of loans by foreigners are recorded on the positive (credit)
side.
B. All transactions of lending to abroad by private sector and government. Lending abroad and
repayment of loans to abroad is recorded as negative or debit item.
2. Investments to and from abroad: It includes:
A. Investments by rest of the world in shares of Indian companies, real estate in India, etc. Such
investments from abroad are recorded on the positive (credit) side as they bring in foreign
exchange.
B. Investments by Indian residents in shares of foreign companies, real estate abroad, etc. Such
investments to abroad be recorded on the negative (debit) side as they lead to outflow of foreign
exchange.
3. Change in Foreign Exchange Reserves:
The foreign exchange reserves are the financial assets of the government held in the central bank.
A change in reserves serves as the financing item in India’s BOP. So, any withdrawal from the
reserves is recorded on the positive (credit) side and any addition to these reserves is recorded on
the negative (debit) side. It must be noted that ‘change in reserves’ is recorded in the BOP
account and not ‘reserves’.
Balance on Capital Account:
The transactions, which lead to inflow of foreign exchange (like receipt of loan from abroad, sale
of assets or shares in foreign countries, etc.), are recorded on the credit or positive side of capital
account. Similarly, transactions, which lead to outflow of foreign exchange (like repayment of
loans, purchase of assets or shares in foreign countries, etc.), are recorded on the debit or
negative side. The net value of credit and debit balances is the balance on capital account.
A. Surplus in capital account arises when credit items are more than debit items. It indicates net
inflow of capital.
B. Deficit in capital account arises when debit items are more than credit items. It indicates net
outflow of capital.
In addition to current account and capital account, there is one more element in BOP, known as
‘Errors and Omissions’. It is the balancing item, which reflects the inability to record all
international transactions accurately.
Balance on Current Account Vs. Balance on Capital Account:
Balance on current account and balance on capital account are interrelated.
A. A deficit in the current account must be settled by a surplus on the capital account.
B. A surplus in the current account must be matched by a deficit on the capital account.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Unit-3 (BALANCE OF PAYMENTS)Dokument15 SeitenUnit-3 (BALANCE OF PAYMENTS)Shivam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Balance of PaymentsDokument8 SeitenComponents of Balance of PaymentsAnonymous dZpgL93UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On International Financial ManagementDokument7 SeitenAssignment On International Financial ManagementKiran NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Balance of PaymentDokument3 SeitenChapter 12 Balance of Paymentayushsingh7173Noch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payments: International FinanceDokument42 SeitenBalance of Payments: International FinanceSoniya Rht0% (1)
- Class 12 Notes - Balance of PaymentsDokument5 SeitenClass 12 Notes - Balance of PaymentsAryan ph vlogsNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEY's Balance of Payments PPTs As Per Revised Syllabus (Teaching Made EasierDokument325 SeitenDEY's Balance of Payments PPTs As Per Revised Syllabus (Teaching Made EasierAditya P NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Balance of Payments I: NtroductionDokument3 SeitenComponents of Balance of Payments I: NtroductionSamuel HranlehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payments Accounts: Structure, Classification and Measuring's!Dokument8 SeitenBalance of Payments Accounts: Structure, Classification and Measuring's!shahnasheitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7Dokument4 SeitenCH 7Aryan RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOP SlideDokument19 SeitenBOP SlidePrajesh CalicutNoch keine Bewertungen
- TERMS OF TRADE: BALANCE OF PAYMENTS AND CORRECTIVE MEASURESDokument34 SeitenTERMS OF TRADE: BALANCE OF PAYMENTS AND CORRECTIVE MEASURESvijiNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Bop - FinalDokument42 SeitenB. Bop - Finalsamy7541Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Economics IIDokument237 SeitenInternational Economics IImeghasunil24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Open EconomyDokument33 SeitenOpen EconomyLikith RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Balance of Payments AccountsDokument10 SeitenStructure of Balance of Payments Accountssruthi akulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument19 SeitenUnit 3karthik.bNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Bop-Fe 2021Dokument20 SeitenChapter 8 Bop-Fe 2021Sireen IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of PaymentsDokument8 SeitenBalance of PaymentsHaniya KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business SchoolDokument56 SeitenBalance of Payment: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business SchoolasifanisNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of BOPDokument4 SeitenHistory of BOPSanskriti JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibo-03 2020-21Dokument22 SeitenIbo-03 2020-21arun1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- BOP GUIDEDokument9 SeitenBOP GUIDESujataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 - Chapter 3Dokument30 Seiten12 - Chapter 3Karan KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment: Presentation OnDokument21 SeitenBalance of Payment: Presentation Ondeepak_67Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 2 - BoPDokument36 SeitenQuiz 2 - BoPGuneesh ChawlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ifm BopDokument18 SeitenIfm Bopsunil8255Noch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payments Causes of Disequilibrium Approaches To Bop Policy Traditional Absorption and Monetary Approach1678901130918Dokument42 SeitenBalance of Payments Causes of Disequilibrium Approaches To Bop Policy Traditional Absorption and Monetary Approach1678901130918UPSC 2022100% (1)
- Balance of Payments AccountingDokument6 SeitenBalance of Payments AccountingBini MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment (BOP) : DefinitionDokument2 SeitenBalance of Payment (BOP) : DefinitionvaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Trade and Balance of PaymentDokument16 SeitenBalance of Trade and Balance of PaymentDr-Shefali Garg100% (1)
- Balance of Payments Theory and AccountsDokument30 SeitenBalance of Payments Theory and AccountsRohanAwtani100% (1)
- International Accounts SummaryDokument7 SeitenInternational Accounts Summarynolissa100% (1)
- Composition of Balance of PaymentsDokument8 SeitenComposition of Balance of PaymentsYashonidhi ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payments Accounts - Docfiinal LecDokument15 SeitenBalance of Payments Accounts - Docfiinal LecDon Pelicio NgohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch. 7 Balance of PaymentsDokument6 SeitenCh. 7 Balance of PaymentsAneshak KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment: External SectorDokument6 SeitenBalance of Payment: External SectorVishnuvardhan RavichandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment: Meaning AndcomponenetsDokument5 SeitenBalance of Payment: Meaning AndcomponenetsBhawna MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment: Exports Imports Goods Servic Es Financial Capital Financial TransfersDokument15 SeitenBalance of Payment: Exports Imports Goods Servic Es Financial Capital Financial TransfersBharti GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of PaymentsDokument4 SeitenBalance of PaymentsAbhijit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of PaymentDokument6 SeitenBalance of Paymentbhagat103Noch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of PaymentsDokument17 SeitenBalance of PaymentsBhavya SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOP: Record of Economic TransactionsDokument11 SeitenBOP: Record of Economic Transactionsilerious ileriousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment SummaryDokument7 SeitenBalance of Payment Summaryjose luis simbineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payments Theory ExplainedDokument14 SeitenBalance of Payments Theory ExplainedArka DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of PaymentDokument28 SeitenBalance of PaymentRk BainsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payment Components ExplainedDokument6 SeitenBalance of Payment Components ExplainedForum DaghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of PaymentDokument58 SeitenBalance of PaymentRahul upadhayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of PaymentDokument4 SeitenBalance of PaymentTabish MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payments ExplainedDokument29 SeitenBalance of Payments ExplainedKaran KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Notes Unit 4Dokument19 SeitenMacroeconomics Notes Unit 4Eshaan GuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Trade and Exchange Rates ExplainedDokument6 SeitenInternational Trade and Exchange Rates ExplainedMinhaj TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 243 Lecture 1 - The New World EconomyDokument37 SeitenECON 243 Lecture 1 - The New World Economynitin_usmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTL FUNDS: BALANCE, TRADE, GROWTHDokument8 SeitenINTL FUNDS: BALANCE, TRADE, GROWTHRose Enor100% (1)
- Presentation On Balance of Payment (BOP)Dokument17 SeitenPresentation On Balance of Payment (BOP)Abdii Dhufeera100% (1)
- Balance of TradeDokument4 SeitenBalance of TradeFatema SultanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance of Payments (BoP)Dokument23 SeitenBalance of Payments (BoP)sathsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics - The Balance of Payments AccountsDokument11 SeitenEconomics - The Balance of Payments AccountsAshraf AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionVon EverandCPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideVon EverandIntermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Law Reviewer 1Dokument49 SeitenProperty Law Reviewer 1Pafra BariuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eed HND 1 SSDokument10 SeitenEed HND 1 SSAbanum Chuks100% (2)
- Emmanuel Kaluri's Resume: Sales, Business Development and Operations ExpertiseDokument5 SeitenEmmanuel Kaluri's Resume: Sales, Business Development and Operations ExpertiseEmmanuel KaluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Literature: Chapter-2Dokument29 SeitenReview of Literature: Chapter-2Gautam SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mar 102022 Smespd 02 eDokument83 SeitenMar 102022 Smespd 02 esalam ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Rating To Customers in Commercial Banks: Rationality and IssuesDokument40 SeitenCredit Rating To Customers in Commercial Banks: Rationality and IssuesMaiChi PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chery v. Conduent EducationDokument15 SeitenChery v. Conduent EducationMooreKuehnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gulf Capital: The Case For Middle Market Structured CapitalDokument8 SeitenGulf Capital: The Case For Middle Market Structured CapitalAgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Build-operate-transfer (BOT) project financing model explainedDokument7 SeitenBuild-operate-transfer (BOT) project financing model explainedUlrich Maria BaltzerNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Indian MoneyDokument9 SeitenHistory of Indian MoneyPoornima MathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar 3 2017Dokument85 SeitenSeminar 3 2017Stephanie XieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines Supreme Court upholds debt collection caseDokument4 SeitenPhilippines Supreme Court upholds debt collection caseMarco Miguel LozadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 06 2012sDokument20 Seiten16 06 2012sBounna PhoumalavongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Analysis of Banking SectorsDokument56 SeitenFundamental Analysis of Banking Sectorssidhant kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al-Abbas Sugar Mills LTD: Balance SheetDokument3 SeitenAl-Abbas Sugar Mills LTD: Balance SheetSamie ElahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Law ProjectDokument24 SeitenCompany Law ProjectAnonymous qFWInco8cNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleared OTC Interest Rate Swaps: Security. Neutrality. TransparencyDokument22 SeitenCleared OTC Interest Rate Swaps: Security. Neutrality. TransparencyAbhijit SenapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRD CaseDokument6 SeitenHRD CaseluqmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBP Vs CADokument5 SeitenDBP Vs CAVictoria EscobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSMEs BookletDokument72 SeitenMSMEs Bookletlucky_rishikNoch keine Bewertungen
- #16 DBP V Family Foods MNFG CoDokument7 Seiten#16 DBP V Family Foods MNFG CoAlynna SandatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Payable Chapter 2Dokument7 SeitenNotes Payable Chapter 2Herrah Joyce SalinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panlilio vs. Regional Trial Court, Branch 51, City of ManilaDokument10 SeitenPanlilio vs. Regional Trial Court, Branch 51, City of ManilaMaria Nicole VaneeteeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting For Developers 101Dokument7 SeitenAccounting For Developers 101farkasdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obligation & Contracts (2 Modes of ExtinguishmentDokument3 SeitenObligation & Contracts (2 Modes of ExtinguishmentRachel Almadin100% (4)
- Kerrisdale Capital Prime Office REIT AG ReportDokument19 SeitenKerrisdale Capital Prime Office REIT AG ReportCanadianValueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writ of Possession JurisDokument17 SeitenWrit of Possession JurisEdmond LorenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rise in Bank NPAs Due to External and Internal FactorsDokument10 SeitenRise in Bank NPAs Due to External and Internal FactorsRakesh KushwahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial AnalysisDokument116 SeitenFinancial AnalysisMahfuzulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence of Life Evidence of Person Entitled To PaymentDokument5 SeitenEvidence of Life Evidence of Person Entitled To Paymentjoe89% (9)