Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
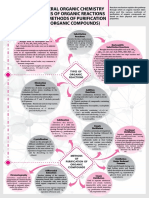
Concept Map - Chemistry - 2018 - June
Hochgeladen von
Rahique ShuaibOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Concept Map - Chemistry - 2018 - June
Hochgeladen von
Rahique ShuaibCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
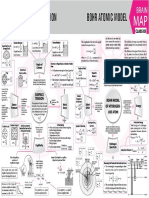
Electron A set of four
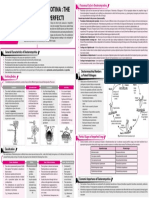
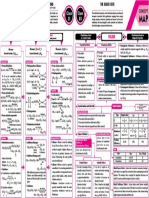
STRUCTURE OF ATOM
~10–16 cm members
Proton
FUNDA- (neutron) Quark which helps
MENTAL <10–17cm to determine
Niels Henrik David Bohr (Niels Bohr), a Danish physicist who QUANTUM
PARTICLES the complete
is generally regarded as one of the foremost physicists of the 20th Nucleus NUMBERS information
century. He was the first to apply the quantum concept, to the problem Atom ~10–12cm ~10–13cm
~10–8cm about all the e–
of atomic and molecular structure. For that work he received the
in an atom.
Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. His manifold roles in the origins and
development of quantum physics is his most important contribution.
Symbol Quantum Values Role
Numbers
Rules for Assigning Electrons
n Principal 1, 2, 3,..... Determines the energy (size).
Aufbau principle : e– occupy lowest energy orbital available.
Electromagnetic Wave Theory l Angular 0, 1, 2, .... Special distribution Pauli exclusion principle : Maximum 2 electrons per
n–1 of electron cloud and orbital must have opposite spins.
James Maxwell (1870) suggested that when electrically charged particles
angular momentum.
move under acceleration, alternating electrical and magnetic fields are Hund’s rule : If two or more orbitals of equal energy are
ATOMIC produced and transmitted. These fields are transmitted in the forms of waves, ml Magnetic 0, ±1, ±2, Determines the available, electrons will occupy them singly before filling
MODELS called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiations. .... ±l orientation in space. in pairs.
Electric field
ms Spin ±1/2 Describes the electron
x component spin (magnetic moment).
Energy Level
l 0 1 2 3
Direction of
propagation Sub-shell s p d f
z
4) Orbital present 1 3 5 7
n’s Mo del (190
Thomso y
Magnetic field
Plum pudding model
component
An atom was a sphere
Electromagnetic Spectrum : The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuum
Bohr’s
of positive electricity in of all electromagnetic waves arranged according to frequency and wavelength.
Model
which number of electrons Cosmic rays < g-rays < X-rays < Ultra-violet rays < Visible < Infrared < First energy level
Energy shells or
were embedded, Micro waves < Radio waves orbitals
sufficient to e
e +e + e An atom consist of a
Second Electron
neutralize the small heavy positively energy
positive charge. + e
+e +
level
Hydrogen Spectrum
e + e charged nucleus. According to Bohr’s theory, an electron neither emits nor absorbs
K
+ e Th
e electrons revolve n=1 M
e n=3 energy as long as it stays in a particular orbit.
only in those orbits Nucleus L
n=2 N However, an electron in an atom may jump from normal energy
which have a fixed n=4
level, to some higher energy level. During each such jump, energy
value of energy.
1) is emitted in the form of a photon (hv).
rd’s Mo del (191 E2 – E1 = hν = hc/l
Rutherfo For hydrogen like atoms :
Different excited electrons adopts different routes to return to
Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiations
The atom consists of two parts : −1312 Z 2 Z2 various lower energy levels.
Planck’s Quantum Theory : A body can emit or absorb energy only in terms
En = kJ mol–1 = –13.6 eV/atom Lyman series : From n = 2, 3, 4 ........ to n = 1
Nucleus : Very small in size,
n2 n2
carries positive charge. of integral multiple of a quantum/photon. Balmer series : From n = 3, 4, 5 ........ to n = 2
n2
Extra-nuclear part,
– E = nhv; Radius : rn = 52.9 pm Paschen series : From n = 4, 5, 6 ........ to n = 3
– Z
i.e., orbit : Space where,n = 1, 2, 3,.... Z Brackett series : From n = 5, 6, 7 ........ to n = 4
around the nucleus in –
+
– Velocity of electrons : vn = 2.188 × 108 cm s–1
n Pfund series : From n = 6, 7, 8 ........ to n = 5
–
which electrons were
distributed. Quantum Mechanical Model
Photoelectric Towards Quantum Mechanical Model
Effect The electrons in an atom have only quantized values of
Black Body Dual nature of matter : Every material particle in motion
energy.
Radiation When radiations with has dual nature (particle and wave nature).
These quantized values of energy are obtained from the
T2 If the substance being frequency greater than a certain h h
de-Broglie wavelength, λ = = solution of Schrodinger wave equation.
heated is a black body (which minimum frequency (v0) strike the mv P
T2 > T1 surface of a metal, the electrons d2Ψ d2Ψ d2Ψ 8 π2m
Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle : It is impossible
Intensity
T1
can emit and absorb all + + + (E – V)Ψ = 0
frequencies), the radiation are ejected from the surface of to measure simultaneously the exact position and dx 2 dy 2 dz 2 h2
emitted is called black the metal. This phenomenon momentum of an electron. By finding Ψ2 at different points around the nucleus in an atom,
body radiation. is called photoelectric h we can predict the region of space around the nucleus within
effect. ∆x × ∆p ≥ which the probability of finding the electron is maximum.
Wavelength 4π
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Using The Periodic TableDokument42 SeitenUsing The Periodic Tablecharlesc5746Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Class X Chemistry 086 TheoryDokument12 SeitenCbse Class X Chemistry 086 TheoryBara' HammadehNoch keine Bewertungen
- S For The Mon Ught TH T HoDokument110 SeitenS For The Mon Ught TH T Hoysreddy8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isc 100% Success in ChemistryDokument114 SeitenIsc 100% Success in ChemistryAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISC 2014 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperDokument23 SeitenISC 2014 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperMd Saif UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii ChemistryDokument119 SeitenXii ChemistryAftab AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 Atoms&Molecules MolesDokument23 SeitenCh2 Atoms&Molecules MolesFlorinel BaietelNoch keine Bewertungen
- (19th of 19 Chapters) Organic Chemistry Part 1 of 3 - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureDokument37 Seiten(19th of 19 Chapters) Organic Chemistry Part 1 of 3 - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureChengeto MatandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maharashtra-HSC-d & F Paper-2 TargetDokument39 SeitenMaharashtra-HSC-d & F Paper-2 TargetkrritikksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classnote 548fee8d37792Dokument46 SeitenClassnote 548fee8d37792vinay guttNoch keine Bewertungen
- MLL Study Materials Science Class X 2020-21-1Dokument223 SeitenMLL Study Materials Science Class X 2020-21-1Ajit Mote100% (1)
- Gcesoln 2Dokument3 SeitenGcesoln 2api-3734333100% (1)
- Periodic Table of ElementsDokument32 SeitenPeriodic Table of ElementsJodell BuensalidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The S-Block ElementsDokument34 SeitenThe S-Block ElementsPrakhar TandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDokument23 SeitenSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Contents for Hydrogen DocumentDokument14 SeitenTable of Contents for Hydrogen DocumentDipin Preet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRY XII Model Test PaperDokument68 SeitenCHEMISTRY XII Model Test PaperAman KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii Chemistry NotesDokument157 SeitenXii Chemistry NotesksvvijNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISC 2016 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved Paper PDFDokument23 SeitenISC 2016 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved Paper PDFAbhishek VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa Science Igcse Chemistry SowDokument103 SeitenAqa Science Igcse Chemistry SowAnthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas LawDokument6 SeitenGas LawrambabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3Dokument24 SeitenAqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3David AdigboNoch keine Bewertungen
- KVS Chemistry Class 11 Term 2 Revision NotesDokument64 SeitenKVS Chemistry Class 11 Term 2 Revision NotesAshish TiwaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.SC - Chemistry - 2016Dokument20 SeitenM.SC - Chemistry - 2016rmsh301Noch keine Bewertungen
- Xii Chemistry Patna RegionDokument235 SeitenXii Chemistry Patna RegionPrashant Jain100% (1)
- Acids Bases and SaltsDokument22 SeitenAcids Bases and Saltsd anjilappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table - 14th JuneDokument20 SeitenPeriodic Table - 14th JuneMD. ARIFUL ISLAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT JAM Chemistry: Books, Preparation Tips, Syllabus!Dokument14 SeitenIIT JAM Chemistry: Books, Preparation Tips, Syllabus!Kadamb SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Dokument4 SeitenO Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Kugan KishurNoch keine Bewertungen
- (3335) DPP 17 Chemical Bonding BDokument2 Seiten(3335) DPP 17 Chemical Bonding BRAJDEEP DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balancing EqueationsDokument6 SeitenBalancing EqueationsSurendra ZirpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon and Its Compounds: One Mark QuestionsDokument17 SeitenCarbon and Its Compounds: One Mark QuestionsPhone experimentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language of Chemistry - ICSEDokument15 SeitenLanguage of Chemistry - ICSEnitikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 13-Nitrogen Containing Organic CompoundsDokument5 SeitenUnit 13-Nitrogen Containing Organic CompoundsDeva RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 12 6Dokument130 SeitenUnit 12 6Lai BryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Chemistry Answer BookDokument30 SeitenAs Chemistry Answer Booksaviochow80% (5)
- Detailed Notes For ch4Dokument24 SeitenDetailed Notes For ch4Jemima KaishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Support Material 1Dokument207 SeitenScience Support Material 1yajurv Trivedi officialNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Paper 2 2016Dokument343 SeitenAs Paper 2 2016JuanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equilibrium: Acids, Bases and pHDokument10 SeitenIonic Equilibrium: Acids, Bases and pHKhushi RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PUC Chemistry Question BankDokument214 SeitenPUC Chemistry Question BankSathish Kumar100% (1)
- Class 12 ChemistryDokument164 SeitenClass 12 ChemistryAbhishek Dalmia81% (26)
- Atomic Structure IITDokument16 SeitenAtomic Structure IITAdiChemAdi69% (13)
- FREETESTPAPER.com - Your Source for Free Papers OnlineDokument42 SeitenFREETESTPAPER.com - Your Source for Free Papers OnlineUZAIR MAHBUB BHUYAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of The Atom Class IxDokument3 SeitenStructure of The Atom Class Ixfarooquima5327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemsheets GCSE 1147 General Electrolysis 3 1Dokument1 SeiteChemsheets GCSE 1147 General Electrolysis 3 1Sumaiya Iqbal78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Net PyqDokument537 SeitenOrganic Net Pyqpranjal jangid100% (1)
- Chemistry Unit 3 Student GuideDokument28 SeitenChemistry Unit 3 Student GuideApollo WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Material Ix Science - 2Dokument150 SeitenStudy Material Ix Science - 2Tantra Path100% (1)
- Mole-Concept Final PDFDokument57 SeitenMole-Concept Final PDFSatyanshu JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemsheets A2 1024 Naming Aromatic CompoundsDokument2 SeitenChemsheets A2 1024 Naming Aromatic Compoundsxl:D cNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsVon EverandOrganometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Problems of Chemical Kinetics and Reactivity: Volume 1Von EverandSome Problems of Chemical Kinetics and Reactivity: Volume 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkDokument28 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - October 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - October 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nums FLPDokument27 SeitenNums FLPRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkDokument28 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - September 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - September 2016Rahique Shuaib0% (1)
- Biology - October 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - October 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - November 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - November 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - September 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - September 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - April 2018Dokument1 SeitePhysics - April 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2014Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2014Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - September 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - September 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - November 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - November 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - November 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2018Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - October 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - October 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2018Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - May 2016Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - May 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - November 2017Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - November 2015Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - November 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESSENTIALS OF CHEMISTRYDokument1 SeiteESSENTIALS OF CHEMISTRYRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - July 2015Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - July 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alicyclic Hydrocarbons + Solid StatesDokument1 SeiteAlicyclic Hydrocarbons + Solid StatesSantanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - March 2016Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - March 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - June 2015Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Homework AssignmetDokument4 SeitenHeat Transfer Homework Assignmetedison navarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Lecture 14Dokument86 SeitenPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Lecture 14jwebbster4141Noch keine Bewertungen
- QuizDokument3 SeitenQuizabc75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rapidly Varied Flow CharacteristicsDokument8 SeitenRapidly Varied Flow CharacteristicsAbdulrasheed BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal and Axial Flow Pumps. Theory, Design and ApplicationDokument249 SeitenCentrifugal and Axial Flow Pumps. Theory, Design and ApplicationNuno Neves100% (1)
- 1688804054767.BP CB X Science PT1 BDokument1 Seite1688804054767.BP CB X Science PT1 Bgamingsm0047Noch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion ExplainedDokument16 SeitenProjectile Motion Explainedaries mandy floresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condenser CalculatorDokument17 SeitenCondenser CalculatorSaurav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics (Phys 1011) FinalDokument5 SeitenGeneral Physics (Phys 1011) FinalAby n100% (1)
- Causes and Effects of LighteningDokument7 SeitenCauses and Effects of LighteningLAMIA LATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Aids HomeworkDokument12 SeitenRadio Aids HomeworkAnand PanditNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument15 SeitenPhysicsKim Al-Gin Rayos ManongsongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound Generation and Propagation in DuctsDokument260 SeitenSound Generation and Propagation in DuctsJomer J SimpsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Vibrations Review QuestionsDokument4 SeitenMechanical Vibrations Review QuestionsInkedInqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Handbook of Organic Compounds. NIR, IR, Raman, and UV-Vis Spectra Featuring Polymers and Surfactants (A 3-Volume Set) (PDFDrive)Dokument1.490 SeitenThe Handbook of Organic Compounds. NIR, IR, Raman, and UV-Vis Spectra Featuring Polymers and Surfactants (A 3-Volume Set) (PDFDrive)Muhammad Jawad Ul RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derive The Radar Equation For An Isolated TargetDokument43 SeitenDerive The Radar Equation For An Isolated TargetalemuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrations ME400Dokument32 SeitenVibrations ME400Nick MezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elder 1967Dokument15 SeitenElder 1967ALEJANDRO GANCEDO TORALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1 - NewDokument8 SeitenLec 1 - NewAhmed RamadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Syllabus in 40 CharactersDokument3 SeitenPhysics Syllabus in 40 CharactersAmit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part I. Puzzle Word. Find The Answer in The BoxDokument1 SeitePart I. Puzzle Word. Find The Answer in The BoxDeana Gabato Camama-PormaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otdr EngDokument8 SeitenOtdr Engరాజా రావు చామర్తిNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Introduction To SpectrosDokument75 SeitenChapter 6 Introduction To SpectrosAkmal J. PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Light WavelengthDokument7 SeitenMeasuring Light WavelengthVAIBHAV KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dungtse Cluster Trial Examination 2018 Paper I PhysicsDokument17 SeitenDungtse Cluster Trial Examination 2018 Paper I PhysicsRigzean Thinley Lhendrup100% (1)
- Antenna Efficiency, Gain and Input ImpedanceDokument17 SeitenAntenna Efficiency, Gain and Input ImpedanceSaqib SherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate - The Given ConditionsDokument35 SeitenClimate - The Given ConditionsKAMAL S. TOMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Convection (ENSC 14a)Dokument43 Seiten3 Convection (ENSC 14a)Aldwin Angelo Culing MontañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling A Control System-Transfer Function Approach 23Dokument4 SeitenModelling A Control System-Transfer Function Approach 23Đạt Lê Quý QuốcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Theory and The AtomDokument18 SeitenQuantum Theory and The AtomIrish de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen