Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BACH2113 Kinetics, Mechanisms and Stereochemistry Tutorial 3 - Stereochemistry (Part 1)
Hochgeladen von
Anusia ThevendaranOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BACH2113 Kinetics, Mechanisms and Stereochemistry Tutorial 3 - Stereochemistry (Part 1)
Hochgeladen von
Anusia ThevendaranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
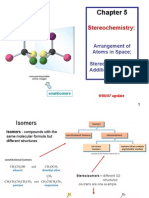
BACH2113 Kinetics, Mechanisms and Stereochemistry
Tutorial 3 – Stereochemistry (Part 1)
1. Important keys
-
- Absolute configuration
- Configurational isomers
- R and S configuration
- D and L configuration
- E and Z configuration
- Constitution isomers
- Stereoisomers
- Asymmetric/chiral/stereo-center
- Achiral
- Optically active
- Specific rotation
- Plane-polarized light
- Polarimeter
- Racemate
- Racemic mixture
- Fischer projection
- Enantionmers
- Geometric isomers
- Meso compounds
- Plane of symmetry
- Relative configuration
- Resolution of racemic mixture
- Regioselective and Stereoselective
- Stereospecific
- Syn- and anti-addition
2.
2. Which of the following objects are chiral:
(i) Screwdriver
(ii) A screw
(iii) A bean stalk
(iv) A shoe
(v) A hammer
3. Which of the following compounds are optically active?
CHBr2Cl, BHFCl, CH3CHCl2, CHFBrCl, BeHCl
4. Assign R or S configurations to each chiral center in an ascorbic acid.
5. Name each of the following compounds using R, S, E and Z designations where necessary.
6. A 1.50 g sample of caniine, the toxic extract of poison hemlock, was dissolved in 10 mL of ethanol
and placed in a sample cell with a 5.0 cm pathlength. The observed rotation at the sodium D line was
+1.21. Calculate []D for coniine.
7. A sample of pure (S)-2-butanol was placed in a 10.0 cm polarimeter tube. Using the D line of a
sodium lamp, the observed rotation at 20 C was α = +104. The density of this compound is 0.805
gmL-1. What is the specific rotation of (S)-2-butanol?
8. Calculate the observed rotation of a solution of 0.5245g of (S)-1-amino-1-phenylethane diluted to a
volume of 10.0 mL with methanol at 20 C, using the D line of a sodium lamp and a 1.00 dm tube.
Specific rotation of this material: [α]D23 = -30.0.
9. Draw a tetrahedral representation of (R)-2-chlorobutane.
Assign priorities to the following sets of substituents:
(i) –H, -Br, -CH2CH3, -CH2CH2OH
(ii) –COOH, -COOCH3, -CH2OH, -OH
(iii) –CN, -CH2NH2, -CH2NHCH3, -NH2
(iv) –Br, -CH2Br, -Cl, -CH2Cl
10. Draw structural formula for each of the following compound, clearly showing all aspects of the
stereochemistry.
(i) Z-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-ol
(ii) R-4-methyl-4-phenylcyclohex-2-enone
(iii) (7S, 8R)-7,8-epoxy-2-methyloctadecane
(iv) E-2-methyl-2-buten-1-ol
(v) (2Z, 4E)-2-chlorohexa-2,4-diene
11. Indicate whether each of the following pairs of compounds are identical or are enantiomers,
diastereomers or constitutional isomers:
12. Draw all possible stereoisomers of cyclobutane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid, and indicate the
interrelationships. Which, if any, are optically active? Do the same for cyclobutane-1,3-
dicarboxylic acid.
13. (i) With suitable examples differentiate between the terms “diastereoisomer” and “enantiomers”.
(ii) Compare and contrast the properties of optical and of geometric isomers.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NASA Facts Explorer XVI The Micrometeoroid SatelliteDokument4 SeitenNASA Facts Explorer XVI The Micrometeoroid SatelliteBob AndrepontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry Basic Concepts Useful Notes For StudentsDokument26 SeitenStereochemistry Basic Concepts Useful Notes For StudentsReddappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astron: MFL Testing Procedure For Tank FloorDokument16 SeitenAstron: MFL Testing Procedure For Tank FloorleonciomavarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry Arrangement of Atoms in SpaceDokument59 SeitenStereochemistry Arrangement of Atoms in SpaceNAGARAJUNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of IEC StandardsDokument12 SeitenList of IEC Standardsaravindeee08100% (1)
- Stereochemistry QustionsDokument43 SeitenStereochemistry QustionsSwaraj Paul100% (1)
- StereochemistryDokument44 SeitenStereochemistryraghav79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry PDFDokument3 SeitenStereochemistry PDFbencleese100% (1)
- Alkanes Cycloalkanes and AlkenesDokument3 SeitenAlkanes Cycloalkanes and AlkenesDorota ZębikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressor Anti-Surge ValveDokument2 SeitenCompressor Anti-Surge ValveMoralba SeijasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Year Chemistry The Gas LawsDokument31 Seiten6th Year Chemistry The Gas LawsAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm C97/C97M-09Dokument3 SeitenAstm C97/C97M-09Azuriak150% (2)
- 02-Stoichiometric CalculationsDokument47 Seiten02-Stoichiometric CalculationsHandayani KesumadewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Septic Tank - Components and Design of Septic Tank Based On PopulationDokument7 SeitenSeptic Tank - Components and Design of Septic Tank Based On Populationمنير أحمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning SchedulingDokument20 SeitenPlanning Schedulingvague100% (1)
- CHM 1321 Assignment 3 - : AnswersDokument5 SeitenCHM 1321 Assignment 3 - : AnswersSara YuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goc of ChemistryDokument3 SeitenGoc of ChemistryMohd DanishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereo ChemistryDokument57 SeitenStereo ChemistryAuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry (With Seatwork)Dokument18 SeitenStereochemistry (With Seatwork)Kate Lyle ParfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- StereoDokument15 SeitenStereoPrasann KatiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 8 Chirality (III) AtropisomerismDokument20 SeitenLecture 8 Chirality (III) AtropisomerismJasmar BenawraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereopg 1to27Dokument32 SeitenStereopg 1to27KunalSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2002 El-Mossalamy - Charge Transfer Complexes of Some Oxazolones With IodineDokument6 Seiten2002 El-Mossalamy - Charge Transfer Complexes of Some Oxazolones With IodineMerve İzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Exam 3 Answers, Organic ChemistrtDokument6 SeitenWeb Exam 3 Answers, Organic ChemistrtAshish Manatosh BarikNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH105 - (O) - Tutorial3 (Q) PDFDokument2 SeitenCH105 - (O) - Tutorial3 (Q) PDFShivansh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2425 Chapt 13Dokument10 Seiten2425 Chapt 13Ivan Alberto NinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis & Determination of Isomeric Form of "2 - ( (3 - Bromophenyl) Hydrazono) 3 - Oxo - Butanoic Acid"Dokument5 SeitenSynthesis & Determination of Isomeric Form of "2 - ( (3 - Bromophenyl) Hydrazono) 3 - Oxo - Butanoic Acid"IOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Carbamoyl-2,2-Dimethylcyclopentane-1,1-Dicarboxylic Acid: Organic CompoundsDokument7 Seiten3-Carbamoyl-2,2-Dimethylcyclopentane-1,1-Dicarboxylic Acid: Organic CompoundsJarrett RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry: Chemistry in Three Dimensions (Chiral Compound)Dokument54 SeitenStereochemistry: Chemistry in Three Dimensions (Chiral Compound)yolandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination MCQDokument11 SeitenCoordination MCQSubhasish Sau100% (2)
- 4 - (Sec-Butylamino) - 3-Nitrobenzoic Acid: Organic CompoundsDokument13 Seiten4 - (Sec-Butylamino) - 3-Nitrobenzoic Acid: Organic Compoundsshafida hamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios - QO I T3Dokument5 SeitenEjercicios - QO I T3dddddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ronald J. Hrynchuk Et Al - The Crystal Structure of Free Base Cocaine, C17HZ1N04Dokument7 SeitenRonald J. Hrynchuk Et Al - The Crystal Structure of Free Base Cocaine, C17HZ1N04GummyColaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isomerism PDFDokument48 SeitenIsomerism PDFBhavesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICT BHB Sem 2 2Dokument59 SeitenICT BHB Sem 2 2Ayushmaan TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- G 044028042Dokument15 SeitenG 044028042IOSR Journal of PharmacyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques Shobhit NirwanDokument43 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques Shobhit NirwanTanmoy GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ssa CH 5 StereochemistryDokument51 SeitenSsa CH 5 StereochemistryHilmi IrsyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 2105 Tutorial Sheet 1 - 2023Dokument6 SeitenCHE 2105 Tutorial Sheet 1 - 2023Kankomba MuleyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallabenzenes: An Expert ViewVon EverandMetallabenzenes: An Expert ViewL. James WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Structural Analysis of Spiropyran and Spirooxazine Compounds and Their PolymorphsDokument12 SeitenA Structural Analysis of Spiropyran and Spirooxazine Compounds and Their PolymorphsXuyên NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal Chemistry I Drاجابة-1Dokument6 SeitenMedicinal Chemistry I Drاجابة-1حسام الدين الحيفيNoch keine Bewertungen
- StereochemistryDokument57 SeitenStereochemistrycisna ambarwatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 討厭的有機作業Dokument1 Seite討厭的有機作業曾詠靖Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Questions - Chapter 25Dokument6 SeitenSample Questions - Chapter 25Glenn Farah Faye RausaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StereochemistryDokument53 SeitenStereochemistryalyssa_marie_ke100% (17)
- StereochemistryDokument8 SeitenStereochemistryAmalVijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Janczak 1994Dokument7 SeitenJanczak 1994Dr. Luis Angel Garza RdzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 Intro Organic Chem Tutorial (Teachers)Dokument14 Seiten2009 Intro Organic Chem Tutorial (Teachers)Tommy Jing Jie NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.SEETARAM SWAMY, M.Pharm.,: Asst. Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Chilkur Balaji College of PharmacyDokument46 SeitenS.SEETARAM SWAMY, M.Pharm.,: Asst. Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Chilkur Balaji College of PharmacyAli Akbar JamshaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions Chapter 1-10Dokument107 SeitenQuestions Chapter 1-10PriyaranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis and Structure of Optically Active 3-Amino-2H-azirinesDokument6 SeitenSynthesis and Structure of Optically Active 3-Amino-2H-azirinesdelfin000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 3Dokument4 SeitenHomework 3Ahmad DulfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makeup Test RevisionDokument3 SeitenMakeup Test RevisionNondumiso MavundlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 3Utkarsh Bansal0% (1)
- 低氧化态化合物合成方法Dokument12 Seiten低氧化态化合物合成方法Zixuan ZhengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 5 Solution PDFDokument3 SeitenProblem Set 5 Solution PDFLouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMN ProblemsDokument7 SeitenRMN ProblemsAnonymous llSDP0tNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 (Optical Isomers)Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 1 (Optical Isomers)Ahmed ZakyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM1280 2011 Midterm Exam PDFDokument3 SeitenCHEM1280 2011 Midterm Exam PDFLouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem3053 Exam2, 2007Dokument7 SeitenChem3053 Exam2, 2007Cameron PearceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Paper I SuggestedAnswerDokument10 SeitenMock Paper I SuggestedAnswerIndrik WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Organik - 4Dokument63 SeitenKimia Organik - 4Gung AriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Unit 4 Goodie BagDokument29 SeitenChemistry Unit 4 Goodie BagJacob Salkin100% (2)
- KOT121 Answer Sem2 2008 2009Dokument8 SeitenKOT121 Answer Sem2 2008 2009Ren Liew Jia QingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Pinewood International Senior Secondary School Class - 11Dokument2 SeitenThe Pinewood International Senior Secondary School Class - 11k6n6mgmrmnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 3Dokument25 SeitenMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 3ridwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationVon EverandInfrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pillared Metal-Organic Frameworks: Properties and ApplicationsVon EverandPillared Metal-Organic Frameworks: Properties and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water: Determination of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity For Urban RunoDokument15 SeitenWater: Determination of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity For Urban RunoAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer SampleDokument14 SeitenPolymer SampleAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resources 06 00064 v2 PDFDokument16 SeitenResources 06 00064 v2 PDFAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- BABS2213 TutorialDokument12 SeitenBABS2213 TutorialAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Statistical EstimationDokument12 Seiten8 Statistical EstimationAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scan QR Code at Autogate or Checkpoint Counter: Payment Type Public EbankDokument1 SeiteScan QR Code at Autogate or Checkpoint Counter: Payment Type Public EbankAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- BABS2213 TutorialDokument12 SeitenBABS2213 TutorialAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Skill Cert RD 201709Dokument5 SeitenSoft Skill Cert RD 201709Anusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karyotyping LabDokument16 SeitenKaryotyping LabAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRT 140 Physical Chemistry Programme Industrial Chemical Process SEM 1 2013/2014Dokument72 SeitenPRT 140 Physical Chemistry Programme Industrial Chemical Process SEM 1 2013/2014Anusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diamond Science & TechnologyDokument54 SeitenDiamond Science & TechnologyAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linkage Map Worksheet Genetics 2017Dokument2 SeitenLinkage Map Worksheet Genetics 2017Anusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- T6 ProbDokument3 SeitenT6 ProbAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Org Exp7Dokument5 SeitenOrg Exp7Anusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Report CarbohydratesDokument4 SeitenFormal Report CarbohydratesAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quo p1384 Posco-MkpcDokument1 SeiteQuo p1384 Posco-MkpcAnusia ThevendaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- HNBR Material TestDokument16 SeitenHNBR Material TestskyerfreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- List NotesDokument27 SeitenList NotesMohit MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astrophysics QuestionsDokument19 SeitenAstrophysics QuestionsMauzoom AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bituminus Material PDFDokument196 SeitenBituminus Material PDFSubramanian BalakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cree CGH40006pDokument15 SeitenCree CGH40006pQazi KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weebly ReportDokument15 SeitenWeebly Reportapi-316004735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Friction Stir Additive ReviewDokument34 SeitenFriction Stir Additive ReviewpeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- BGP Tutorial SimplifiedDokument41 SeitenBGP Tutorial SimplifiedAashish ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Empirical Study On The Nexus Between The Emotional Intelligence of Top Managers and Their Assessment of Intellectual CapitalDokument30 SeitenAn Empirical Study On The Nexus Between The Emotional Intelligence of Top Managers and Their Assessment of Intellectual Capitalmaher76Noch keine Bewertungen
- T60 Transformer Management Relay: UR Series Instruction ManualDokument404 SeitenT60 Transformer Management Relay: UR Series Instruction Manualeng amadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication Module 4Dokument34 SeitenSatellite Communication Module 4JKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stars and Galaxies 9th Edition Seeds Test BankDokument20 SeitenStars and Galaxies 9th Edition Seeds Test Bankngocalmai0236h100% (32)
- Lab 9: Standard Plate Count: How Do We Know How Many Bacteria Are in A Liquid?Dokument4 SeitenLab 9: Standard Plate Count: How Do We Know How Many Bacteria Are in A Liquid?Penelope MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guar Gum: Product Data Sheet (PDS)Dokument1 SeiteGuar Gum: Product Data Sheet (PDS)Moatz HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual B-Tronic SystemDokument35 SeitenInstruction Manual B-Tronic SystemYipper ShnipperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibration Procedure On ML-D5, D6 (ZERO-SPAN Adjustment)Dokument2 SeitenCalibration Procedure On ML-D5, D6 (ZERO-SPAN Adjustment)Haytham RedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SeqP&D GPL Met enDokument52 SeitenSeqP&D GPL Met enSriram ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mazda 3Dokument5 SeitenMazda 3Jhony GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cronje Chemical 2010 PDFDokument569 SeitenCronje Chemical 2010 PDFPara MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2210 w18 Ms 12Dokument12 Seiten2210 w18 Ms 12Fiyazul HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laplace TransformDokument2 SeitenLaplace TransformumangNoch keine Bewertungen
- FluidsDokument10 SeitenFluidslara alghamdiNoch keine Bewertungen