Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
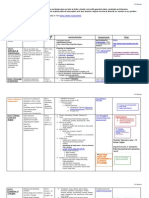
(D5) Proof Cheat Sheet
Hochgeladen von
Shrimp100%(3)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (3 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten2 Seitenno
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenno
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(3)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (3 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten2 Seiten(D5) Proof Cheat Sheet
Hochgeladen von
Shrimpno
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Proof Cheat Sheet Name ________________________
Date ____________ Period ______
Postulate/Theorem /Property/Term What it states
Addition Property of Equality If 3x – 7 = 14 then 3x = 21
Subtraction Property of Equality IF 5x + 5 = 10, then 5x = 5
Multiplication Property of Equality If ½ x = 3 then x = 6
Division Property of Equality If 5x = 20, then x = 4.
Substitution Property of Equality If a = b, then a may be replaced by b in any equation
or expression.
If AB + CD = EF and AB = 10, then 10 + CD = EF by
substitution
Transitive Property of Equality If a = b and b=c, then a=c.
If m<1 = m<2 and m<2 = m<3, then m<1 = m<3
Transitive Property of Congruence If a b, and b c, then a c.
If m<1 m<2 and m<2 m<3, then m<1 m<3
Reflexive Property of Equality a=a
Reflexive Property of Congruence
AB AB
Symmetric Property of Equality If a=b then b = a.
Symmetric Property of Congruence If CD , then CD AB
AB
ANGLES
Acute Angle An angle whose measure is less than 90
Obtuse Angle An angle whose measure is greater than 90 but less
than 180
Right Angle An angle whose measure is exactly 90
Straight Angle An angles whose measure is exactly 180
Complementary Angles The sum of two angle measures is 90
Supplementary Angles The sum of two angle measures is 180
Congruent Angles Angles that have the same measure
If <1 <2, then m<1 = m<2 (measures are equal)
Angle Bisector Divides an angle into two angles
Vertical Angle Theorem Vertical angles are
Linear Pair Postulate If two angles form a linear pair, then they are
a) supplementary
b) sum of their measures is 180
Angle Addition Postulate If C is in the interior of <AOD, then
m<AOC + m<COD = m<AOD
LINES & SEGMENTS
Parallel lines Coplanar lines that do not intersect
Perpendicular lines Two lines that intersect to form right angles
Congruent Segments Segments that have the same length
If AB ,
CD then AB = CD (lengths are equal)
Midpoint Point that divides a segment into two segments
Segment Bisector A segments, ray, or line that intersects a segment at
its midpoint.
Segment Addition Postulate If three points A, B, and C are collinear and B is
between A and C, then AB + BC = AC.
TRIANGLES
Acute Triangle A triangle with 3 acute angles
Obtuse Triangle A triangle with one obtuse angle
Right Tringle A triangle with one right angle
Isosceles Triangle A triangle with at least two sides
Scalene Triangle A triangle with no sides
Equilateral Triangle A triangle with three sides
PARALLEL LINES & ANGLE RELATIONSHIPS
Corresponding Angles Postulate If two lines are parallel, then corresponding angles
are
Corresponding Angles Converse If corresponding angles are , then the lines are
parallel.
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem If two lines are parallel, then alternate interior
angles are
Alternate Interior Angles Converse If alternate interior angles are , then the lines are
parallel.
Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem If two lines are parallel, then the alternate exterior
angles are
Alternate Exterior Angles Converse If alternate exterior angles are , then the lines are
parallel.
Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem or If two lines are parallel, then the same-side interior
Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem angles are supplementary.
Same-Side Interior Angles Converse or If same-side interior angles are supplementary, then
Consecutive Interior Angles Converse the lines are parallel.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Geometry Justification Tool KitDokument5 SeitenGeometry Justification Tool KitChristopher Charles100% (1)
- FileDokument11 SeitenFileJulianna Kaye PerrerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postulates and Theorems ListDokument12 SeitenPostulates and Theorems ListTerry McClintic100% (2)
- Properties Postulate Theorem Cheat SheetDokument3 SeitenProperties Postulate Theorem Cheat SheetRey PalapocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postulates and TheoremsDokument6 SeitenPostulates and TheoremsAngelique E. RanocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theorems and Postulates For GeometryDokument11 SeitenTheorems and Postulates For Geometrymajji satish100% (2)
- Geometry Theorems and Proofs SummaryDokument27 SeitenGeometry Theorems and Proofs SummaryAnna Chen100% (1)
- Lesson 2.6 Parallel Lines and TransversalsDokument18 SeitenLesson 2.6 Parallel Lines and TransversalsDaisyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postulates, Defs, and TheoremsDokument4 SeitenPostulates, Defs, and TheoremsacciofabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Bisectors: LearnDokument4 SeitenAngle Bisectors: LearnHasan Eser100% (2)
- Golden Sheet For Proofs With Triangle TheoremsDokument3 SeitenGolden Sheet For Proofs With Triangle TheoremseunhaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry ReviewDokument2 SeitenGeometry ReviewJesuv Cristian CleteNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC35 Geometry Ch01 Handout-209Dokument8 SeitenMC35 Geometry Ch01 Handout-209SCARLETT CARSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation Geometric Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteTransformation Geometric Cheat Sheetapi-292786124100% (1)
- Chapter Test8Dokument14 SeitenChapter Test8Liwliwa SuguitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Linear Equations NotesDokument2 SeitenWriting Linear Equations Notesapi-307475527Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDokument1 SeiteParallel Lines Cut by A Transversalapi-292786124100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Congruence and Similar TrianglesDokument51 SeitenChapter 10 Congruence and Similar TrianglesOsim AbesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Unit 3 QuadrilateralsDokument8 SeitenGeometry Unit 3 Quadrilateralsapi-287816312Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometryfor SSC Exams (WWW - Freeupscmaterials.wordpress - Com)Dokument62 SeitenGeometryfor SSC Exams (WWW - Freeupscmaterials.wordpress - Com)k.palraj100% (1)
- Presentation Triangle Midpoint TheoremDokument28 SeitenPresentation Triangle Midpoint Theorempriya86240100% (1)
- 7-4 Parallel Lines and Proportional PartsDokument34 Seiten7-4 Parallel Lines and Proportional PartsKenneth MadroñalNoch keine Bewertungen
- TheoremsDokument8 SeitenTheoremsanjustic25Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 Triangle Congruence-KeyDokument31 SeitenCH 4 Triangle Congruence-KeyNap DoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slope of A Line MathematicsDokument15 SeitenSlope of A Line Mathematicsvishesh redhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 1Dokument15 SeitenWorksheet 1Char GalvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taboo CH 1-3Dokument4 SeitenTaboo CH 1-3tina_cardone1100% (2)
- Solving One-Step EquationsDokument10 SeitenSolving One-Step EquationsMr. Peterson100% (1)
- Linear Equations Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteLinear Equations Cheat SheetAnthea ClarkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Angle RelationshipsDokument42 Seiten5 Angle Relationshipsaienne peraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Lines and TransversalDokument54 SeitenParallel Lines and TransversalLaarni Mae AureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoints CongruenceDokument104 SeitenPowerpoints CongruenceGlen GayagayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Eoc Review PacketDokument41 SeitenGeometry Eoc Review PacketCeline Loh100% (1)
- Geometry CurriculumDokument5 SeitenGeometry CurriculumWendy Millheiser MenardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theorems and PropertiesDokument6 SeitenTheorems and PropertiesA CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Guided Notes Student Copy - Parallel-Lines-Amp-TransversalsEditedDokument18 SeitenGeometry Guided Notes Student Copy - Parallel-Lines-Amp-TransversalsEditedyyoiz100% (1)
- Choice ADokument1 SeiteChoice Aapi-295097927Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry DefinitionsDokument27 SeitenGeometry DefinitionsEidref Nuaj100% (1)
- Flowchart and Paragraph ProofsDokument25 SeitenFlowchart and Paragraph ProofsVexegicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Squares, Square Roots and Perfect SquaresDokument6 SeitenSquares, Square Roots and Perfect SquaresAmee MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties Postulate Theorem Cheat SheetDokument5 SeitenProperties Postulate Theorem Cheat SheetAndreaNicoleBanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lines &angles: EmailDokument28 SeitenLines &angles: EmailGilbert Guzman Turaray100% (1)
- Angle VocabularyDokument1 SeiteAngle Vocabularyapi-327041524100% (1)
- List of Proof Reasons - REVISEDDokument4 SeitenList of Proof Reasons - REVISEDJayRRomeo75% (4)
- Unit Lessons On TransformationsDokument29 SeitenUnit Lessons On TransformationsmagdammNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area and Volume of Similar Shapes Worksheet 1 PDFDokument4 SeitenArea and Volume of Similar Shapes Worksheet 1 PDFTaha Yousaf100% (1)
- Write Down The Six Pairs of Congruent Corresponding PartsDokument2 SeitenWrite Down The Six Pairs of Congruent Corresponding PartsRuth MatrianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutDokument15 SeitenTopic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutShine100% (1)
- Angles Complementary Supplementary Vertical Adjacent Coloring ActivityDokument7 SeitenAngles Complementary Supplementary Vertical Adjacent Coloring Activityapi-294079637100% (1)
- 4.2 Congruence of Triangles (Reflexive, Symetric, Transitive)Dokument22 Seiten4.2 Congruence of Triangles (Reflexive, Symetric, Transitive)MiiMii Imperial Ayuste100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Gleancoe BookDokument84 SeitenChapter 5 Gleancoe BookPablo UlisesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 几何 Part 1(AMC10)Dokument24 SeitenChapter 3 几何 Part 1(AMC10)Xuemei zhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry PostulatesTheorems-ListDokument11 SeitenGeometry PostulatesTheorems-ListGeorge FanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jnb21 Postulate and TheoremsDokument8 SeitenJnb21 Postulate and Theoremssakurano_aj_saharon_21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch1 Geometry 2Dokument47 SeitenCh1 Geometry 2trantuanan123Noch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Dokument24 SeitenINTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Jama abdi ibraahim100% (1)
- AnGLES N Triang.sDokument11 SeitenAnGLES N Triang.sjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Note Summary Theorems1Dokument11 SeitenGeometry Note Summary Theorems1Jiane ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theorems Theorems: AB AB. AB CD, Then CD AB. AB CD and CD EF, Then AB EFDokument1 SeiteTheorems Theorems: AB AB. AB CD, Then CD AB. AB CD and CD EF, Then AB EFAmy DoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- High School Math NotesDokument24 SeitenHigh School Math NotesaoeusnthidNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITC Full Ensemble TrumpetDokument21 SeitenITC Full Ensemble TrumpetShrimp100% (1)
- Intercept Form Get The Equation Into That FormDokument1 SeiteIntercept Form Get The Equation Into That FormShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chemistry: Combustion AnalysisDokument4 SeitenAP Chemistry: Combustion AnalysisShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Always Like: Squared Negative NegativeDokument2 SeitenAlways Like: Squared Negative NegativeShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020-21 Vocation Wheel With InstructionsDokument1 Seite2020-21 Vocation Wheel With InstructionsShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Namesake Disc SimplifiedDokument2 Seiten2019 Namesake Disc SimplifiedShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valence Electrons PDFDokument1 SeiteValence Electrons PDFKrystel Monica ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 PacketDokument10 Seiten2019 PacketShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civics 101 The Declaration Revisited: Black Americans: Nick CapodiceDokument6 SeitenCivics 101 The Declaration Revisited: Black Americans: Nick CapodiceShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civics 101 The Declaration Revisited: Black Americans: Nick CapodiceDokument6 SeitenCivics 101 The Declaration Revisited: Black Americans: Nick CapodiceShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Namesake Disc SimplifiedDokument2 Seiten2019 Namesake Disc SimplifiedShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Classof2021) Today's Announcements 2Dokument2 Seiten(Classof2021) Today's Announcements 2ShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Just Want My Aria Con Variazioni OmgDokument2 SeitenI Just Want My Aria Con Variazioni OmgShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5 Square Roots, Integers CompletedDokument2 Seiten1.5 Square Roots, Integers CompletedShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra I Lesson 2.4 - Solving Equations With Variables On Both Sides Mrs. Snow, InstructorDokument2 SeitenAlgebra I Lesson 2.4 - Solving Equations With Variables On Both Sides Mrs. Snow, InstructorShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- AinEHYkiu1j5mvax4pD4T PDFDokument1 SeiteAinEHYkiu1j5mvax4pD4T PDFShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boooooboose: Algebra I Lesson2.3 Solving Multi-Step Equations Mrs. Snow, InstructorDokument2 SeitenBoooooboose: Algebra I Lesson2.3 Solving Multi-Step Equations Mrs. Snow, InstructorShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ain EHYkiu 1 J 5 Mvax 4 P D4 TDokument1 SeiteAin EHYkiu 1 J 5 Mvax 4 P D4 TShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW Lesson 6Dokument2 SeitenHW Lesson 6ShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUTI 2020 Cancelation InformationDokument1 SeiteBUTI 2020 Cancelation InformationShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- SampleCompareContrastEssay PDFDokument3 SeitenSampleCompareContrastEssay PDFShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dagger - Google SearchDokument1 SeiteDagger - Google SearchShrimpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Browse The AMS BookstoreDokument7 SeitenBrowse The AMS BookstorexpgongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths 11 3Dokument17 SeitenMaths 11 3api-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upsc Mathematics Optional PapersDokument17 SeitenUpsc Mathematics Optional PapersmanishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shapes and FormsDokument22 SeitenShapes and FormsROMMEL III ARGUELLESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of MachinesDokument18 SeitenTheory of MachinesVishal PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Mod 1-5Dokument19 SeitenAssessment Mod 1-5ARLENE CENITANoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Lab Manual FullDokument325 SeitenStructure Lab Manual FullAbraham Alejandro Arana Vilca100% (1)
- Chapter 4: Mensuration: WorksheetDokument2 SeitenChapter 4: Mensuration: WorksheetKhan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1923 - (Einstein) The Theory of The Affine FieldDokument2 Seiten1923 - (Einstein) The Theory of The Affine Fieldfaudzi5505Noch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Out in SurveyingDokument30 SeitenSetting Out in SurveyingAkankwasa Ronald100% (2)
- PDFDokument629 SeitenPDFSandra EcheverriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key Cat-1Dokument2 SeitenAnswer Key Cat-1adityaemmanuel1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- CRMO-2015 Questions and SolutionsDokument3 SeitenCRMO-2015 Questions and SolutionssaswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3Dokument10 SeitenModule 3Niño YbañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry: Review Exercise QuestionsDokument10 SeitenGeometry: Review Exercise QuestionsMustafa AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 9Dokument3 SeitenHomework 9Luis EduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensitivity Analysis of A Class of Serial ManipulatorsDokument6 SeitenSensitivity Analysis of A Class of Serial ManipulatorsIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeogebraDokument14 SeitenGeogebradominic lumberioNoch keine Bewertungen
- If You Underestimated Yourself To Do Mathematics, Then There's No Room For You To Improve. Mr. Louie A. CarlosDokument23 SeitenIf You Underestimated Yourself To Do Mathematics, Then There's No Room For You To Improve. Mr. Louie A. CarlosRusty GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Thin Curved BarsDokument18 SeitenStrength of Materials Thin Curved Barshamza100% (1)
- Tensor Calculus Tensor Calculus Ucde Absos Ali Shaikh Joydeep Sengupta AlphaDokument4 SeitenTensor Calculus Tensor Calculus Ucde Absos Ali Shaikh Joydeep Sengupta AlphaRakesh Debbarma0% (1)
- Limb Volume CalculatorDokument6 SeitenLimb Volume CalculatorYudhi HuseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Markscheme: Trigonometry Worksheet 3 With Mark Scheme (Graphs of Trig. Functions) 1a. (2 Marks)Dokument11 SeitenMarkscheme: Trigonometry Worksheet 3 With Mark Scheme (Graphs of Trig. Functions) 1a. (2 Marks)Ella JonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Bisector Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenLine Bisector Lesson Planapi-258989443Noch keine Bewertungen
- Periyar University: B.Sc. MathematicsDokument64 SeitenPeriyar University: B.Sc. MathematicsSiva SankaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Theory 12Dokument15 Seiten1 Theory 12Ranveer GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIS Class 9 Test PaperDokument4 SeitenMIS Class 9 Test PaperVishal BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cars Traveling Around A Banked Curve : W/ FrictionDokument3 SeitenCars Traveling Around A Banked Curve : W/ FrictionSalman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centre of Mass - (Step-2 - 3) - JEE 22-FinalDokument36 SeitenCentre of Mass - (Step-2 - 3) - JEE 22-FinalAditya PahujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsDokument6 SeitenTrigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsJulie Ailene AsuncionNoch keine Bewertungen