Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ph2 JEE ADV P2-1
Hochgeladen von
Ashish Ranjan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten4 SeitenZzzzxxzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzxxxxxx zzzzxxxxxxxx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenZzzzxxzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzxxxxxx zzzzxxxxxxxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten4 SeitenPh2 JEE ADV P2-1
Hochgeladen von
Ashish RanjanZzzzxxzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzxxxxxx zzzzxxxxxxxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
COIT168A01; AO2PH2.P2.JEE ADV-300916
Section —| (Physics)
PART-A
q ice Type)
This section contains 8 mu (Multi Correct Choice AOA
multiph has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (0)
of which ONE OR MORE tive ake) questions, Each question ha:
1 Three particle A,B and C of equal masses move with equal
am v along the medians of an equilateral triangle After
Collision A comes to rest while B retraces its path with speed v.
The velocity of C is then
(AV (B) direction OA
(C)av () direction BO
2. Two balls, having linear moment j =pi and, = -pi, undergo a collision in free space. There
is no external force acting on the balls. Let 6; and p, be their final momenta. The following
option(s) is (are) NOT ALLOWED for any non-zero value of p, @1, 82, Dr, Ba, C1 and ca.
= aitbj+ek
(A) e ae (8)
By = ai + by}
Bl=ai+bj+ok
(Cas header (0) Be
By = ai +b,)-c,k B, = ai +b)
3. Acar anda truck, are moving with same K.E. or same momentum or same velocity and
applying same retarding force. Their stopping distances are S, and S, respectively
(A) S, = S, if kinetic energy and retarding force are equal
(B) S, = S, if momentum and retarding force are equal
(C) S, <5; if velocity and retarding force are equal
(D) S, > S, if momentum and retarding force are equal.
A curve between force and displacement is drawn for a particle moving in x — axis.
%
attraction
Y
repulsion
(A) At x; & x3 particle in stable equilibrium —(B) At x; & Xs particle in unstable equilitrium
(C) At x; & % particle in stable equilibrium _(D) At x, & Xs particle in unstable equilibrium
‘space for rough work
2JEE ADV.3009:
ce of a force field. Now it is taken
i
A particle is taken from point A to point B under the influence oF ice Tea, LOW itis tak
back from B to A and it is observed that the work or and We is the work done by non
not equal to the work done in taking it from B to retain reer
conservative forces and conservative forces present ai Pectvely.AU Is the
change in potential energy, k is the change is kinetic energy, ter)
(A) Wye AU= AK (B) W, = -AU (©) Whe + We = AK (O) We “
are sitting on a frictionless platform some
jatform towards B which B catches,
Two friends A and B (each weighting 40 kg)
all keeps on moving back and forth
distance d apart. A rolls a ball of mass 4 kg on the pl
Then B rolls the ball towards A and A catches it. The be atform.
between A and B. The ball has a fixed speed of 8 mis on the platferm.
.. 10
(A) speed of A after he catches the ball for the first time Is > mis.
(B) speed of A after he catches the ball for the first time is “> m/s.
(C) The centre of mass of the system will remain stationary irrespectively of the direction of
motion of the ball
(D) A can rolls the ball for 6 times.
A ball is projected with velocity v at angle @ at t = 0 with horizontal. It strikes a wall at a
distance L from it. Coefficient of restitution is ‘e’ then
sind
(A) Ball will return to ground at t = 2 a
v? sin? @
2
(B)d=eR “ofr is
2 sin?
(C) maximum height during motion = “8 = 8
9
(D) it will return to ground at t < 2%a8in"@
A ball of mass m is attached to the lower end of light vertical spring of force constant k. The
upper end of the spring is fixed. The ball is released form rest with the spring at its normal
(un- stretched ) length, and comes to rest again after descending through a distance x
(A) x= mgik
(B) x = 2mgik
(C) The ball will have no acceleration at the position where it has descended through x/2.
(D) The ball will have an upward acceleration equal to g at its lowermost position
‘space for rough work
coIr1s8Ao},
Comprehension Type
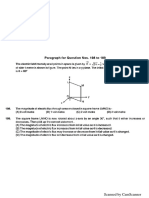
Paragraph for question nos. 9- 10
A small block of mass m ~ 1kg is placed over a wedge of
mass M = 4 kg as shown. Mass m is released from rest.
MI Surfaces are smooth. Origin O is as shown. 4a w
(a=10m/s*) an
9. Final velocity of the wedge is (in m/s)
ws V2 ©)
) (c) Ba
10. The block will strike the x — axis at x m
(A) 4.2 (B) 7.6 (C) 5.6 (0) 6.8
Paragraph for question nos. 11 — 12
The figure, shows a man of mass m standing
at the end A of a trolley of mass M placed at
rest on a smooth horizontal surface. The man M
Starts moving towards the end B with a A ae)
velocity urs with respect to the trolley. The
length of the trolley is L. ‘
When the man starts moving, then the velocity of the trolley v, with respect to ground will be
11.
Mu, mu, m M
Mee a a ©) Mu
eM eM (©) gts m
12, The distance moved by the man with respect to ground is.
mL ML m
p) ML co) ML
nem ® eM Om
PART-C
(Numerical Based)
This section contains 08 multiple choice questions. The answer to each question is a single digit integer,
ranging from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
My .
4. The mass per unit length of a rod varies as m= (M)x where Mo is a constant and x is the
distance of any point on rod measured from one end. Centre of mass of the rod from the
given end is at a distance * on the rod. Find the value of K.
‘space for rough work
iI. The 7
A simple pendulum is suspended from a peg On 2 verical wah Tre J.
pendulum’ is pulled away from the wall to @ horizon -
released. The ball his the wal, the coefficient of restitution PeInd 5
which the amplitude of 4
What is the minimum number of collisions after
oscillation becomes less than 60°?
peed of 4m sis
jered by it to
is moving with a s
The distance covered by a body to come to rest when it is movnd Pee
S when a retarding force F is applied. Ifthe KE is doubled, the distanc
‘come to rest for the same retarding force F is xS, Find *.
Figure shows a small block of mass m which is started with a
block of mass M
speed v on the horizontal part of the bigger
placed on a horizontal floor. The curved part of the surface
shown is semicircular. All the surfaces are frictionless. Find the
speed of the bigger block when the smaller block reaches the
Point A of the surface. (m = 1 kg M = 2kg, v = 3 m/sec )
A ball is allowed to fall from a height of 10 m. If there is 40% loss of energy due to impact,
then after one impact ball will go upto. m.
A particle of mass 1 gm having velocity (31 +2])ms™* has a glued impact with another particle
of mass 2 gm and velocity as (2j-3k) ms”. Find the speed of formed particle v(ms*)
Two particles A and B of equal mass “m” each are attached by a string
of length °2¢° and initially placed over a smooth horizontal table in the
position shown in figure. Particle B is projected across the table with
speed “u" perpendicular to AB as shown in figure. Find the velocities
of particle A after the string becomes taut (U = = 4V3).
A ball of mass m = 4kg collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary
wedge with a speed of Vp = 10 m/s. The mass of the wedge is M = 9kg,
which is kept on a smooth horizontal plane. The angle of incline is
6 = 30°. If the coefficient of restitution of collision is e = 0.5, then the
velocity of the wedge immediately after collision is ms
‘space for rough work
Physics
Part-A
1. AD 2 AD 3. ACD 4. BC
ABC 6 ACD 7. ABC 8 BCD
B i=. 1. B 12° «=B
Part-C
(tia. 2 4 oo 2 4 °°4
5 6 3 7 3 8 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NEET PhysicsDokument36 SeitenNEET PhysicsAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IITJEE 2014 Advanced Paper II & SolutionDokument39 SeitenIITJEE 2014 Advanced Paper II & SolutionPradeep RavichandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- JP XII Organic ChemistryDokument8 SeitenJP XII Organic ChemistryAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer SolutionDokument9 SeitenAnswer SolutionChennaiSuperkingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mont 2Dokument47 SeitenMont 2Ashish Ranjan0% (1)
- JEE Advanced Full Test I Paper 2 AnswersDokument12 SeitenJEE Advanced Full Test I Paper 2 AnswersYash ShanbhagNoch keine Bewertungen
- JA XI Physical Chemistry (06) - Introduction To Chemistry & Atomic Structure PDFDokument14 SeitenJA XI Physical Chemistry (06) - Introduction To Chemistry & Atomic Structure PDFAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mont 3 STD 12Dokument37 SeitenMont 3 STD 12Ashish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JP XII Organic Chemistry PDFDokument6 SeitenJP XII Organic Chemistry PDFAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JA XI Physical Chemistry (04) - Introduction To Chemistry & Atomic Structure PDFDokument12 SeitenJA XI Physical Chemistry (04) - Introduction To Chemistry & Atomic Structure PDFAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adva PI SolDokument6 SeitenAdva PI SolAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetalsDokument20 SeitenMetalsAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FiitjeeDokument11 SeitenFiitjeeApjodhpur100% (1)
- JEE Advanced Full Test I Paper 1Dokument23 SeitenJEE Advanced Full Test I Paper 1Sachin DhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calander 2018Dokument3 SeitenCalander 2018Ashish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric FluxDokument14 SeitenElectric FluxAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charges N ForcesDokument1 SeiteCharges N ForcesAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Emi-1Dokument29 SeitenBasics of Emi-1Ashish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th CRP Adv2 PDFDokument23 Seiten12th CRP Adv2 PDFdipanshu gayakwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 EL - Capacitance (Single Correct)Dokument8 Seiten05 EL - Capacitance (Single Correct)Ashish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TT PDFDokument1 SeiteTT PDFAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irodov EDY PDFDokument9 SeitenIrodov EDY PDFAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Faraday Law-1Dokument1 Seite02 Faraday Law-1Ashish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIITJEE PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY & MATHEMATICS PAPER - 2 MCQ SECTIONDokument17 SeitenFIITJEE PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY & MATHEMATICS PAPER - 2 MCQ SECTIONAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WRT Wep PDFDokument7 SeitenWRT Wep PDFAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XI Physics DPP Set (06) - Mathematical Tools & KinematicsDokument15 SeitenClass XI Physics DPP Set (06) - Mathematical Tools & KinematicsAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenAnswer KeyAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XII Physics DPP Set (01) - Previous Class XI Chapters-2Dokument11 SeitenClass XII Physics DPP Set (01) - Previous Class XI Chapters-2Ashish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XI Physics DPP Set (22) - Previous Chaps - Rotational Motionb.Dokument13 SeitenClass XI Physics DPP Set (22) - Previous Chaps - Rotational Motionb.Ashish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)