Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Philippine Financial System: Banking Institutions Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas Non-Bank Financial Institutions (Nbfi)
Hochgeladen von
Joyelle Kristen TamayoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Philippine Financial System: Banking Institutions Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas Non-Bank Financial Institutions (Nbfi)
Hochgeladen von
Joyelle Kristen TamayoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
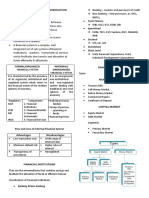
CAPITAL MARKET 2.
The mortgage market
Deals with loans on residential, commercial, and industrial
that portion of the financial market which deals with longer-term real estate, and on farmland
loanable funds (Money Market – short-term funds) 3. The stock market
loans obtained are used by industry and commerce mainly for fixed Common and preferred stocks are issued by corporations
investment. are traded.
Consists of all institutions that canalize the supply and demand for TWO COMPONENTS:
long-term capital and claims on capital o The organized exchanges
Comprises the entire structure of the Philippine financial system o The less formal over-the-counter markets
THE COST OF CAPITAL
PHILIPPINE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
CAPITAL FUNDING
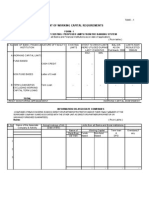
GROSS COMBINATION COST OF NET
ALTER
INCOME CAPITAL PROFIT
NATIVE SHORT LONG
BANKING (000,000) PREFERRED (000,000) (000,000)
BANGKO NON-BANK FINANCIAL TERM TERM
STOCKS
INSTITUTIONS SENTRAL NG INSTITUTIONS (NBFI) DEBT DEBT
PILIPINAS
1 P170 100% - - P20 P10
PRIVATE
BANKS 2 170 - 100% - 17 13
PRIVATE NBFI
3 170 - - 100% 10 20
COMMERCIAL
BANKS GOVERNMENT NBFI 4 170 33% 33% 34% 16 14
THRIFT BANKS
*Assuming other relevant costs of P40 million were deducted from the
gross income.
GOVERNMENT
BANKS
COMPONENTS OF THE CAPITAL MARKET:
1. The bond market
Done over-the-counter
Owned by and traded among the large financial institutions
like life insurance companies, mutual funds, and pension
funds
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Philequity Fund: Fund Fact Sheet As of Jan 31, 2020Dokument1 SeitePhilequity Fund: Fund Fact Sheet As of Jan 31, 2020JeanneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment Presentation V1Dokument45 SeitenRecruitment Presentation V1Akshay keerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Construction Equipment and Infra Finance Sector OverviewDokument60 SeitenIndian Construction Equipment and Infra Finance Sector Overviewsunleon31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mutual FundDokument43 SeitenMutual FundSachi LunechiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 1Dokument62 SeitenSession 1Sam NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview: Treasury Operations in BanksDokument61 SeitenAn Overview: Treasury Operations in BanksManipal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFBR Apac Capital Markets PhilippinesDokument8 SeitenRFBR Apac Capital Markets PhilippinesJheiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edgereport Abslamc Iponotes 28-09-2021 285Dokument20 SeitenEdgereport Abslamc Iponotes 28-09-2021 285sudhansumail102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Map Financial MarketesDokument3 SeitenMap Financial MarketesBryan Ivann MacasinagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Seventeen: Mutual Funds and Hedge FundsDokument30 SeitenChapter Seventeen: Mutual Funds and Hedge FundsAhmed El KhateebNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMSL REVISION NOTES DECEMBER 2020 AMENDED-Executive-RevisionDokument332 SeitenCMSL REVISION NOTES DECEMBER 2020 AMENDED-Executive-RevisionT.V.B.M CHAITANYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Finance Market Assessment KenyaDokument18 SeitenSupply Chain Finance Market Assessment Kenyaetebark h/michaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orange Modern Marketing Company Business ReportDokument8 SeitenOrange Modern Marketing Company Business ReportJessel TagalogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Financial SystemDokument41 SeitenIndian Financial SystemKaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 003.DTI Region 1 Webinar On Investments PromotionDokument99 Seiten003.DTI Region 1 Webinar On Investments Promotionminari myouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottomline JulyDokument26 SeitenBottomline JulygreeshmapashamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Map Financial MarketesDokument3 SeitenMap Financial MarketesBryan Ivann MacasinagNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Financial Markets and Institutions": Macasinag, Bryan Ivann S. Bsma-4B FM 321-13840 9/23/2021Dokument3 Seiten"Financial Markets and Institutions": Macasinag, Bryan Ivann S. Bsma-4B FM 321-13840 9/23/2021Bryan Ivann MacasinagNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIM K's financial newsletter explores mutual funds and market volatilityDokument4 SeitenIIM K's financial newsletter explores mutual funds and market volatilityABHISHEK DALAL 23Noch keine Bewertungen
- DaziaCSCPart1Chapters1 5Dokument29 SeitenDaziaCSCPart1Chapters1 5carlNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBI reportDokument35 SeitenRBI reportrudraanalytics1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two The Financial System2 - Eco551Dokument25 SeitenChapter Two The Financial System2 - Eco551Hafiz akbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rbi Allowed Banks To Increase Limit From 10 To 15 PercentDokument10 SeitenRbi Allowed Banks To Increase Limit From 10 To 15 PercentdidwaniasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Studies Class 12Dokument28 SeitenBusiness Studies Class 12Yashvi ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- NBFC - Vinay Kumar MouryaDokument8 SeitenNBFC - Vinay Kumar Mouryamadhurkj1512Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial SystemDokument35 Seiten1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial SystemShambhavi JNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFDokument35 Seiten1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFLohithashva Nanjesh Gowda100% (5)
- 1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFDokument35 Seiten1 SEM BCOM - Indian Financial System PDFShambhavi JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Financial System An IntroductionDokument4 SeitenIndian Financial System An IntroductionRonan FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 30 - PFRS For SEs, PFRS For SEs and Reporting For MicroenterprisesDokument6 SeitenChapter 30 - PFRS For SEs, PFRS For SEs and Reporting For MicroenterprisesNoella Marie BaronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Requirement by BNMDokument5 SeitenCapital Requirement by BNMlakhani.kamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- BankingDokument614 SeitenBankingSuvankar NandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Solutions - Intesa Sanpaolo CorporateDokument1 SeiteOur Solutions - Intesa Sanpaolo CorporateJake joseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 731 - 740 Fa-6Dokument17 Seiten731 - 740 Fa-6738 Lavanya JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Institute of Banking & FinanceDokument157 SeitenIndian Institute of Banking & FinanceSupriyaRongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 40 - Copy of 42 - Cma Format For BankDokument20 Seiten40 - Copy of 42 - Cma Format For Bankcvrao04100% (4)
- Topic1 Overview of The Financial SystemDokument26 SeitenTopic1 Overview of The Financial SystemNeekita NeetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Financial MarketsDokument29 SeitenNcert Financial Marketsjyoti singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets ExplainedDokument29 SeitenFinancial Markets Explainedlekha1997Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prudential Financial: Securities Investment Trust Enterprise (Patricia Tsai)Dokument27 SeitenPrudential Financial: Securities Investment Trust Enterprise (Patricia Tsai)National Press FoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investor PresentationDokument28 SeitenInvestor Presentationok2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Canadian Securities Exam PreparationDokument14 SeitenChapter 2 Canadian Securities Exam PreparationPRUTHVIRAJSINH ZALANoch keine Bewertungen
- Apalancamiento Financiero A Través de La Bursatilización de ActivosDokument54 SeitenApalancamiento Financiero A Través de La Bursatilización de ActivosMiguel RevillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISJ005Dokument99 SeitenISJ0052imediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investor PresentationDokument28 SeitenInvestor Presentationagral BrothersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Legal Framework of BankingDokument153 Seiten2016 Legal Framework of BankingLynn PalisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equity KIM - April 19 - 2011Dokument32 SeitenEquity KIM - April 19 - 2011rajivr_18Noch keine Bewertungen
- AP Preweek (B44)Dokument62 SeitenAP Preweek (B44)LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial InstituitonDokument35 SeitenFinancial InstituitonMayuri YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICICI Prudential Nifty Financial Services Ex Bank ETF - FinalDokument13 SeitenICICI Prudential Nifty Financial Services Ex Bank ETF - FinalSiddhant GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Register NBFC in India - NBFC Registration OnlineDokument26 SeitenHow To Register NBFC in India - NBFC Registration OnlineEnter sliceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 1 - Income Tax On CorporationsDokument12 SeitenSession 1 - Income Tax On CorporationsMitzi WamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amit Talda NotesDokument235 SeitenAmit Talda Notesewrgt4rtg4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structure OF External Commercial BorrowingDokument15 SeitenStructure OF External Commercial BorrowingNitesh TanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBA EMBA Class - Security Market & MF - Aug 28 2023 - FinalDokument66 SeitenIBA EMBA Class - Security Market & MF - Aug 28 2023 - FinalAbhinandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horizon Kinetics INFL DeckDokument34 SeitenHorizon Kinetics INFL DeckTodd SullivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PML Fixed Income Fund Jun 22 - enDokument1 SeitePML Fixed Income Fund Jun 22 - enAndy ArestiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shriram Transport Presentation December 2020Dokument50 SeitenShriram Transport Presentation December 2020Gaurav BorseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to NBFCs and Shadow BankingDokument26 SeitenIntroduction to NBFCs and Shadow BankingMaunil OzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of Acts of LasciviousnessDokument2 SeitenElements of Acts of LasciviousnessJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- People vs. SchneckenburgerDokument2 SeitenPeople vs. SchneckenburgerJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- XXX v. PeopleDokument2 SeitenXXX v. PeopleJoyelle Kristen Tamayo100% (1)
- 37 Rustan Vs IAC - Conditional ObligationsDokument2 Seiten37 Rustan Vs IAC - Conditional ObligationsJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No3Dokument2 SeitenAssignment No3Felip MatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lease Contract For Apartment or Condominum Unit Sample PDFDokument2 SeitenLease Contract For Apartment or Condominum Unit Sample PDFEduardo Anerdez83% (6)
- Assignment No. 2Dokument2 SeitenAssignment No. 2Joyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34 Smith Vs Sotelo - Conditional ObligationDokument3 Seiten34 Smith Vs Sotelo - Conditional ObligationJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 5 PDFDokument1 SeiteAssignment No. 5 PDFJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No 4Dokument2 SeitenAssignment No 4Felip MatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No3Dokument2 SeitenAssignment No3Felip MatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 62 Khe Hong vs. CA - Subsidiary RemediesDokument4 Seiten62 Khe Hong vs. CA - Subsidiary RemediesJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No3Dokument2 SeitenAssignment No3Felip MatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDokument16 SeitenBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssemblednashyachillesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estoppel CommentDokument1 SeiteEstoppel CommentJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RapeDokument7 SeitenRapeJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Memo SampleDokument5 SeitenTrial Memo SampleJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claudia's OBLICON Reviewer For BalaneDokument214 SeitenClaudia's OBLICON Reviewer For BalaneNenzo Cruz100% (4)
- CONSTI-Sept13-State ImmunityDokument42 SeitenCONSTI-Sept13-State ImmunityJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No3Dokument2 SeitenAssignment No3Felip MatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Memorandum For RespondentsDokument6 SeitenTrial Memorandum For RespondentsJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPDATED Case AssignmentDokument2 SeitenUPDATED Case AssignmentJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Memorandum For RespondentsDokument6 SeitenTrial Memorandum For RespondentsJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magallona VS ErmitaDokument7 SeitenMagallona VS ErmitaJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.R. No. 142840 May 7, 2001 ANTONIO BENGSON III, Petitioner, vs. House of Representatives Electoral Tribunal and Teodoro C. CruzDokument6 SeitenG.R. No. 142840 May 7, 2001 ANTONIO BENGSON III, Petitioner, vs. House of Representatives Electoral Tribunal and Teodoro C. CruzSar FifthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand LetterDokument2 SeitenDemand LetterJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poe-Llamanzares vs. COMELEC (March 8, 2016)Dokument28 SeitenPoe-Llamanzares vs. COMELEC (March 8, 2016)Vince LeidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PreambleDokument2 SeitenPreambleJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lease ContractDokument4 SeitenLease ContractJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noli Me Tangere Takes Place in The Philippines During The Time of SpanishDokument4 SeitenNoli Me Tangere Takes Place in The Philippines During The Time of SpanishJoyelle Kristen TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions on Finacle Core Banking SolutionDokument76 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions on Finacle Core Banking Solutionbalraj0% (1)
- G.R. No. 119729 January 21, 1997 Ace-Agro Development Corporation, PetitionerDokument130 SeitenG.R. No. 119729 January 21, 1997 Ace-Agro Development Corporation, PetitionerJaja GkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Little Life Champ Plan BrochureDokument16 SeitenLittle Life Champ Plan BrochureParteekKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4190512-Banking & InsuranceDokument4 Seiten4190512-Banking & InsurancejinalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divestment ReportDokument180 SeitenDivestment ReportLa Tía Eulogia RosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amagara MY - AG - 201701 - en - USDokument40 SeitenAmagara MY - AG - 201701 - en - USVenkat NiranchanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merchant Banking SyllabusDokument4 SeitenMerchant Banking SyllabusjeganrajrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment Banking Generic Cover LetterDokument1 SeiteInvestment Banking Generic Cover LetterbreakintobankingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 transaction cycle in VisionPLUS banking systemDokument7 Seiten100 transaction cycle in VisionPLUS banking systemGoushik Balakrishnan100% (1)
- حل الكتابDokument12 Seitenحل الكتابايهاب غزالةNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP7 Final Programme WebDokument99 SeitenEP7 Final Programme WebSara Loureiro da LuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lawful Money Defined: What It Is and How It Differs From Fiat CurrencyDokument4 SeitenLawful Money Defined: What It Is and How It Differs From Fiat CurrencyLedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tink - The Future of Payments Is OpenDokument46 SeitenTink - The Future of Payments Is OpenDavid HelmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment AnalysisDokument8 SeitenInvestment AnalysisTalha AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFM Program Profile International ProgramDokument8 SeitenPFM Program Profile International ProgramAditya Barmen SaragihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trust NewsDokument8 SeitenTrust NewsJRHT_FacebookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand Awareness Study of Equitas Small Finance Bank in BengaluruDokument112 SeitenBrand Awareness Study of Equitas Small Finance Bank in BengaluruAkshay K RNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDX Fact Book 2006 PDFDokument57 SeitenIDX Fact Book 2006 PDFdavidwijaya1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- AIA Philam Life Policy Fund Withdrawal FormDokument2 SeitenAIA Philam Life Policy Fund Withdrawal Formippon_osotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument86 SeitenChapter 2Allison StewartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Banking: Paradigm ShiftDokument80 SeitenIndian Banking: Paradigm ShiftJayesh Gawade100% (1)
- Van Twest V CaDokument8 SeitenVan Twest V CaJerano Paulo PulidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unlock Your Business Potential with 4 Keys to Profit GrowthDokument28 SeitenUnlock Your Business Potential with 4 Keys to Profit GrowthPratiiek Mor100% (6)
- Case Study On Letter of CreditDokument9 SeitenCase Study On Letter of CreditPrahant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Audit ProgramDokument9 SeitenSample Audit ProgramDanErwinMayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foreign Currency TransactionsDokument40 SeitenForeign Currency TransactionsJuliaMaiLeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank Statement SampleDokument3 SeitenBank Statement SampleJer Emy JoerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets and Institutions: Abridged 10 EditionDokument45 SeitenFinancial Markets and Institutions: Abridged 10 EditionNajmul Joy100% (1)
- Board Resolution Sample FormatDokument2 SeitenBoard Resolution Sample FormatShaswat JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Nam: Electronic National Agriculture MarketingDokument18 SeitenE-Nam: Electronic National Agriculture MarketingGeetha PravallikaNoch keine Bewertungen