Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Che 125: Chemical Reaction Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Wendell Kim LlanetaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Che 125: Chemical Reaction Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Wendell Kim LlanetaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
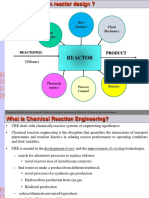
ChE 125: Chemical Reaction Engineering
Chemical Kinetics -
Chemical Reaction Engineering –
Typical Chemical Process
Physical Chemical Physical
Treatment Treatment Treatment
Steps Steps Steps
Table 1.1 Classification of Chemical Reactions Useful in Reactor Design
Noncatalytic Catalytic
Most gas-phase reactions Most liquid-phase reactions
Homogeneous
Fast reactions such as burning Reactions in colloidal systems
of a flame Enzyme and microbial reactions
Burning of coal Ammonia synthesis
Roasting of ores Oxidation of ammonia to produce
Attack of solids by acids nitric acid
Heterogeneous
Gas-liquid absorption with Cracking of crude oil
reaction Oxidation of SO2 and SO3
Reduction of iron ore to iron
and steel
Factors Affecting the Rate of Reaction
1. Nature of Reactants
- State of matter – Gases tend to react faster than solids and liquids
- Bond Type
- Bond Strength
2. Concentration of Reactants
3. Temperature
4. Catalyst
5. Surface Area
6. Pressure
7. Rate of mass and heat transfer
- for heterogeneous systems, they become rate controlling
8. Others
- pH
- viscosity
- external factors like stirring, agitating
Collision Theory
Note: Contact time does not affect the rate of reaction.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reactor: (Ethane) (Ethylene)Dokument48 SeitenReactor: (Ethane) (Ethylene)sameerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - Basic Considerations in Reactor DesignDokument9 Seiten01 - Basic Considerations in Reactor DesignsanelisofuturemoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 4Dokument418 SeitenPaper 4Ahmad asa100% (1)
- ChemistryDokument4 SeitenChemistryHabiba ElwaselyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 and 5: Introduction To Organic Chemistry and Alkanes/AlkenesDokument1 SeiteChapter 4 and 5: Introduction To Organic Chemistry and Alkanes/AlkenesRXNOFCHMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ate of Hemical Eactions: by StudentDokument17 SeitenAte of Hemical Eactions: by StudentDyah Ayu pramoda wardaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Checklist SPMDokument1 SeiteChemistry Checklist SPMIman100% (1)
- Science - Form 4 - Chapter 5Dokument12 SeitenScience - Form 4 - Chapter 5Marcia PattersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teknik Reaksi Kimia I: by HaryantoDokument23 SeitenTeknik Reaksi Kimia I: by HaryantoHarymsl MslNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus AnalysisDokument10 SeitenSyllabus Analysisimtiaz.aulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT - I - Chemical Process Technology: School of Bio and Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDokument78 SeitenUNIT - I - Chemical Process Technology: School of Bio and Chemical Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringVineet klNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics 2023: Prof. Dr. Sahar A. El-MollaDokument36 SeitenChemical Kinetics 2023: Prof. Dr. Sahar A. El-MollaMohamed KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Exam Style QuestionsDokument1 SeiteChemistry: Exam Style Questionsapi-199070930Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 ChemDokument1 SeiteChapter 1 ChemPranav SriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry NotesDokument2 SeitenChemistry Notesevelynkanuri86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry Lecture 1Dokument46 SeitenInorganic Chemistry Lecture 1Nate EducationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationDokument15 SeitenGrade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationBekki VanderlendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phoenix Curriculum - Science (Chemistry) .150899589Dokument2 SeitenPhoenix Curriculum - Science (Chemistry) .150899589CanioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem12 c06 6 2Dokument4 SeitenChem12 c06 6 2ehaxhaj2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry List of ExperimentDokument3 SeitenChemistry List of ExperimentKaiswan GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRE-II - Lecture 1Dokument14 SeitenCRE-II - Lecture 1bhavya.singh.che22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reaction Engineering: Prepared By: Ma. Junallie F. Pomperada Che, Mengr.,Phdt.MDokument24 SeitenChemical Reaction Engineering: Prepared By: Ma. Junallie F. Pomperada Che, Mengr.,Phdt.MReynaldo CalitinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Reactive ChemistryDokument4 SeitenModule 3 Reactive Chemistryisaheqq12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 Notes - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Lecture 3 NotessDokument12 SeitenLecture 3 Notes - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Lecture 3 NotessMack TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical ReactionDokument8 SeitenChemical ReactionShankar PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Test 1: Date: 27/08/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedDokument1 SeiteChemistry Test 1: Date: 27/08/2020 Day: Thursday Topics/Chapters InvolvedRXNOFCHMNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: AP Exam Study GuideVon EverandAP Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: AP Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASVAB Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 4 of 8: ASVAB Exam Study GuideVon EverandASVAB Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 4 of 8: ASVAB Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRAXIS II Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: PRAXIS II Exam Study GuideVon EverandPRAXIS II Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: PRAXIS II Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLEP Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: CLEP Exam Study GuideVon EverandCLEP Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: CLEP Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCAT Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 4 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideVon EverandPCAT Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 4 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAT Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: SAT II Exam Study GuideVon EverandSAT Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: SAT II Exam Study GuideBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (2)
- GED Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 13: GED Exam Study GuideVon EverandGED Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 13: GED Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: GCSE Exam Study GuideVon EverandGCSE Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: GCSE Exam Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- TEAS 6 Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 4 of 5: TEAS 6 Exam Study GuideVon EverandTEAS 6 Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 4 of 5: TEAS 6 Exam Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- NY Regents Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flashcards: New York Regents Exam Study GuideVon EverandNY Regents Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flashcards: New York Regents Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACT Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 12 of 13: ACT Exam Study GuideVon EverandACT Test Prep Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 12 of 13: ACT Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideVon EverandMCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- CatalystDokument22 SeitenCatalystAdan JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Edexcel Unit 4 - Extracting Metals and EquilibriumDokument15 SeitenChemistry Edexcel Unit 4 - Extracting Metals and Equilibriumshivensolanki31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Combustión y TermoquímicaDokument9 SeitenCombustión y TermoquímicaJesús Paz GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rahman S. Z. Saleem: Department of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, SBASSE Lahore University of Management SciencesDokument22 SeitenRahman S. Z. Saleem: Department of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, SBASSE Lahore University of Management Scienceshazyhazy9977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Term 1 XDokument247 SeitenScience Term 1 XKanchan Mishra50% (2)
- Ncjescoa 01Dokument39 SeitenNcjescoa 01Rajat Mittal 1815906Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and EquilibriumVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and EquilibriumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.1 2 Factors Affecting Rate of ReactionDokument15 Seiten6.1 2 Factors Affecting Rate of ReactionSho baconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Science - Hydrogen NotesDokument10 SeitenCombined Science - Hydrogen Notesanon_932738245Noch keine Bewertungen
- As Paper 2 2016Dokument343 SeitenAs Paper 2 2016JuanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyVon EverandPalladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Matsci B0656) E.T. Turkdogan-Fundamentals of Steel Making-Maney Materials Science (2010)Dokument346 Seiten(Matsci B0656) E.T. Turkdogan-Fundamentals of Steel Making-Maney Materials Science (2010)Isaac Jonathan Vargas Aviles100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Rate of Chemical ReactionDokument14 SeitenFactors Affecting Rate of Chemical ReactionMhilette Oweneal Francisco100% (1)
- Manuscript Predicting and Mitigating Corrosion in Amine UnitsDokument13 SeitenManuscript Predicting and Mitigating Corrosion in Amine UnitsSatria 'igin' Girindra NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 Physical and Chemical ChangesDokument17 Seiten5.1 Physical and Chemical ChangesElly EllynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDokument12 Seiten1.1 Rate of ReactionSiti Nur DanishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry: Title: Chemical KineticsDokument2 SeitenGeneral Chemistry: Title: Chemical KineticsLESLIE ANNE CARIASNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNİT 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Presentation SonDokument31 SeitenUNİT 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Presentation SonIskenderli FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Activity 1 (Ga1) General Inorganic Chemistry No. of Questions SubtopicsDokument2 SeitenGroup Activity 1 (Ga1) General Inorganic Chemistry No. of Questions SubtopicsZyrah Marri CamerinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Capsule Notes (EM) - All Chapters by Ravi Sir PDFDokument21 SeitenChemistry Capsule Notes (EM) - All Chapters by Ravi Sir PDFShibin AshiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warning! Warning! Warning! Warning!: Ifyouaskmeifyouneedalab Coat You Will Be Going Straight To Primera Vuelta!Dokument10 SeitenWarning! Warning! Warning! Warning!: Ifyouaskmeifyouneedalab Coat You Will Be Going Straight To Primera Vuelta!Battlefield ForeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading & Writing Money Values Through 100: Teacher WendellDokument15 SeitenReading & Writing Money Values Through 100: Teacher WendellWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 40 Problem Set #1Dokument1 SeiteChem 40 Problem Set #1Wendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table Review SheetDokument4 SeitenPeriodic Table Review SheetWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer For Chem 23 1st Long ExamDokument4 SeitenReviewer For Chem 23 1st Long ExamWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manly Plastics Inc. InfographicDokument2 SeitenManly Plastics Inc. InfographicWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review in Math 4Dokument6 SeitenReview in Math 4Wendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of Employment (Sulu Garden)Dokument1 SeiteCertificate of Employment (Sulu Garden)Wendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOck 2 ChemistryDokument4 SeitenMOck 2 ChemistryWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Tools 1219981524329718 9Dokument5 SeitenScience Tools 1219981524329718 9Wendell Kim Llaneta0% (1)
- Mock 2 IRDokument3 SeitenMock 2 IRWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemoglobin, Collagen & Elastin FilesDokument3 SeitenHemoglobin, Collagen & Elastin FilesWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESL Teacher Cover Letter - JobHeroDokument2 SeitenESL Teacher Cover Letter - JobHeroWendell Kim Llaneta0% (1)
- Experiment 5Dokument2 SeitenExperiment 5Wendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 Calibration of Bomb Calorimeter I. ObjectiveDokument4 SeitenExperiment 1 Calibration of Bomb Calorimeter I. ObjectiveWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Reactions (From Smith)Dokument2 SeitenSummary of Reactions (From Smith)Wendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of PercentDokument4 SeitenApplication of PercentWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JANUARY 2018: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDokument12 SeitenJANUARY 2018: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Questions Fo UPCATDokument4 SeitenChemistry Questions Fo UPCATWendell Kim LlanetaNoch keine Bewertungen