Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Body
Hochgeladen von
api-422807700Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Body
Hochgeladen von
api-422807700Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
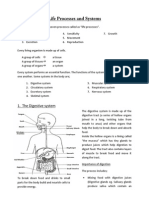
Body System Checklist
Circulatory System
• Major functions of circulatory system
• Diagram that includes the major parts - heart, artery, vein, capillary - and list the function(s) of
each.
• Describe each of the components of blood- red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, &
plasma
• Describe the path blood travels through your body
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. Use 2 examples.
• Describe two diseases associated with your body system
Digestive System
• Major functions of digestive system
• Diagram that includes the major parts - mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver,
pancreas, and large intestine - and list the function(s) of each.
• Describe the path food travels throughout the digestive system.
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. Use 2 examples.
Endocrine System
• Major functions of endocrine system
• Describe what hormones are and what they do
• Diagram that includes the major parts - hypothalamus, pituitary, thymus, thyroid, parathyroid,
adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, and testes - and list the function(s) of each.
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. Use at least 2 examples.
• Describe 2 diseases associated with your body system.
Excretory System
• Major functions of excretory system
• Diagram that includes the major parts - lungs, kidneys, urinary bladder, ureter, urethra, liver,
and skin - and list the function(s) of each.
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. You will need at least 2
examples.
• Find 5 fun facts about your body system.
• Describe 2 diseases associated with your body system.
Muscular System
• Major functions of muscular system
• Describe the function and locations of each type of muscle – skeletal muscle, smooth muscle,
and cardiac muscle
• Diagram that includes the major muscles in the body - biceps, oblique abdominis, sartorius,
deltoid, orbicularis oculi, sternomastoid, gastrocnemius, pectoral, temporalis, gluteus maximus,
quadriceps, tibialis, masseter, rectus abdominis, and triceps
• Describe how muscles work in pairs to make parts of the body move using the biceps and triceps
as an example.
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. You will need at least 2
examples.
• Describe 2 diseases associated with your body system.
Nervous System
• Description and major functions of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
• Diagram that includes the major parts - brain, spinal cord, nerves, and neurons - and list the
function(s) of each.
• Describe the path a nerve impulse travels throughout your body from stimulus to response.
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. You will need at least 2
examples.
• Describe 2 diseases associated with your body system.
Respiratory System
• Major functions of respiratory system
• Diagram that includes the major parts - trachea, lungs, diaphragm, epiglottis, larynx, vocal cords
- and list the function(s) of each.
• Describe the “breathing” process.
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. You will need at least 2
examples.
• Describe 2 diseases associated with your body system.
Skeletal System
• Major functions of skeletal system
• Diagram that includes the major parts -bones, ligaments, and tendon - and list the function(s) of
each. NOTE: Your diagram should also include the following bones in the body: cranium, clavicle,
humerus, scapula, sternum, rib, vertebra, ulna, radius, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges, pelvis (may list
parts), femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, and metatarsals.
• Describe each of the following joints and where they are located: hinge, pivot, and ball-and-
socket. You may include other joints as well.
• Explain how your body system works with other systems in the body. You will need at least 2
examples.
• Describe 2 diseases associated with your body system.
1. What is homeostasis? Why is it important?
Answer: Humans' internal body temperature is a great example of homeostasis. When an individual is
healthy, his or her body temperature retains a temperature 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit. Cells
depend on the body environment to live and function. Homeostasis keeps the body
environment under control and keeps the conditions right for cells to live and function. Without
the right body conditions, certain processes (eg osmosis) and proteins (eg enzymes) will not
function properly.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- REAL BABY FOOD: Easy All-Natural Recipes For Your Baby and Toddler by Jenna HelwigDokument8 SeitenREAL BABY FOOD: Easy All-Natural Recipes For Your Baby and Toddler by Jenna HelwigHoughton Mifflin Harcourt Cookbooks50% (2)
- Public Access - The GauntletDokument1 SeitePublic Access - The GauntletTesting0% (2)
- AFAR - 07 - New Version No AnswerDokument7 SeitenAFAR - 07 - New Version No AnswerjonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body System ChecklistDokument4 SeitenBody System Checklistapi-421863843Noch keine Bewertungen
- BodyDokument5 SeitenBodyapi-421876236Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body System Checklist 1Dokument6 SeitenBody System Checklist 1api-421876825Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body System Checklist 282 29Dokument6 SeitenBody System Checklist 282 29api-422811891Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body System ChecklistDokument6 SeitenBody System Checklistapi-422967453Noch keine Bewertungen
- BodyDokument8 SeitenBodyapi-422810721Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body System Checklist WWDokument11 SeitenBody System Checklist WWapi-421876727Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body Systems ProjectDokument5 SeitenBody Systems Projectapi-240312017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body System ChecklistDokument8 SeitenBody System Checklistapi-421876369Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body System ChecklistDokument6 SeitenBody System Checklistapi-422855075Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 (Anatomy)Dokument63 SeitenChapter 1 (Anatomy)Phan Sokkheang100% (1)
- Javan and Bryces Human Body ProjectDokument9 SeitenJavan and Bryces Human Body Projectapi-347432027Noch keine Bewertungen
- AP1HumanBodyOrientationDokument83 SeitenAP1HumanBodyOrientationPamela EmpasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Pop Video - Human Body SystemsDokument54 SeitenBrain Pop Video - Human Body SystemsDemiana MouradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Physiology: Santosh Dev Lecturer Department of Physiology Birat Medical CollegeDokument36 SeitenIntroduction To Physiology: Santosh Dev Lecturer Department of Physiology Birat Medical CollegedevdsantoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana&Physio 1 - The Human Body - An OrientationDokument59 SeitenAna&Physio 1 - The Human Body - An OrientationShery Han Bint HindawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Body: Anatomy and Function of Body SystemsDokument18 SeitenThe Human Body: Anatomy and Function of Body SystemsbrentupdegraffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4Dokument10 SeitenCo2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4accfor everythingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ota Go 730857Dokument9 SeitenOta Go 730857Super sonicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elijah Ryan HumanbodysystemsprojectDokument9 SeitenElijah Ryan Humanbodysystemsprojectapi-347114998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Body SystemsDokument40 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction To Body Systemsdonibung 007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionDokument51 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionNgoc TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Body Systems Test Review Body System Function Major Organs/Structures & Their Functions Specialized Cells (If Any)Dokument8 SeitenHuman Body Systems Test Review Body System Function Major Organs/Structures & Their Functions Specialized Cells (If Any)Christine Megan YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Organization and General Plan of TheDokument64 SeitenChapter 1 Organization and General Plan of TheLoverna Abella0% (1)
- Chapter 04Dokument52 SeitenChapter 04api-3743202Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument35 SeitenIntroduction in Human Anatomy and Physiologyraul nino MoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finished Evan Drew Human Body SystemDokument9 SeitenFinished Evan Drew Human Body Systemapi-347109807Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology & Anatomy (Introduction)Dokument18 SeitenPhysiology & Anatomy (Introduction)em2200139Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Body: An OrientationDokument44 SeitenThe Human Body: An OrientationMica Bernardo100% (1)
- Dentistry Stydent (Physiology) Second Year - by Hashim Gazo - Slide # 1Dokument17 SeitenDentistry Stydent (Physiology) Second Year - by Hashim Gazo - Slide # 1Hashim GhazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forelæsning 1Dokument19 SeitenForelæsning 1natashathelinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToAesthethic finds100% (1)
- Health TuteDokument6 SeitenHealth TuteN GunaratneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLS224-lecture 1Dokument50 SeitenCLS224-lecture 1Abdulelah BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomical Terms, Etc.Dokument40 SeitenAnatomical Terms, Etc.Karen Cayse EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human BodyDokument47 SeitenThe Human BodyAngelica RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blue and Cream Vintage General ProposalDokument12 SeitenBlue and Cream Vintage General ProposalKimberly Jane MitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology: Overview of Organ SystemsDokument40 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology: Overview of Organ SystemsGeorge KoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT I: The Human Body: 1.0 Intended Learning OutcomesDokument22 SeitenUNIT I: The Human Body: 1.0 Intended Learning Outcomesrb YangzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology-1 Department of Physiotherapy: BY DR - Laraib Jameel RPHDokument113 SeitenPhysiology-1 Department of Physiotherapy: BY DR - Laraib Jameel RPHHashir SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Physiology: Ethem Gelir, M.D., Assoc. Prof. of PhysiologyDokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Physiology: Ethem Gelir, M.D., Assoc. Prof. of PhysiologyMohmed El King100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - HomeostasisDokument27 SeitenLecture 2 - HomeostasisAndre Luis CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Physiology Book Aniket .... 1st SemDokument295 SeitenAnatomy Physiology Book Aniket .... 1st SemAnn JulietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Introduction 1Dokument43 SeitenAnatomy Introduction 1raneem fakhouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Physiology By: MulukenwalleDokument73 SeitenHuman Physiology By: MulukenwalleHenok GirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Human Body System Model ProposalDokument4 Seiten3D Human Body System Model ProposalAndre Gere AdsuaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument6 SeitenSyllabusHijrah HatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source For EcolecDokument35 SeitenSource For EcolecJeriz Marie GamboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 HomeostasisDokument13 Seiten3.1 HomeostasisHAFSA RASHEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The Eleven Body Organ SystemsDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding The Eleven Body Organ SystemsReinan Ezekiel Sotto LlagasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 4 Nervous and Circulatory SystemDokument4 SeitenGroup 4 Nervous and Circulatory SystemBrent LorenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDokument149 SeitenIntroduction To Cell PhysiologyAlysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An A Phy TanginaDokument3 SeitenAn A Phy TanginafranzynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Body Systems 3Dokument21 SeitenHuman Body Systems 3JuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Exam 1 Module 1Dokument79 SeitenPhysiology Exam 1 Module 1Derrick ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intorduction To PhysiologyDokument23 SeitenIntorduction To PhysiologyHeswer RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Marketing Strategy of Nestle MILKPAKDokument13 SeitenReport On Marketing Strategy of Nestle MILKPAKAzeem Ahmad100% (1)
- Process Strategy: Powerpoint Slides by Jeff HeylDokument13 SeitenProcess Strategy: Powerpoint Slides by Jeff HeylMuizzNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPM GuidelinesDokument6 SeitenIPM GuidelinesHittesh SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- F5 Chem Rusting ExperimentDokument9 SeitenF5 Chem Rusting ExperimentPrashanthini JanardananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neelima A Kulkarni ResumeDokument3 SeitenNeelima A Kulkarni ResumeAcademics LecturenotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- LS01 ServiceDokument53 SeitenLS01 ServicehutandreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Ares-G2 2Dokument78 SeitenManual Ares-G2 2CarolDiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- OVDT Vs CRT - GeneralDokument24 SeitenOVDT Vs CRT - Generaljaiqc100% (1)
- Engine Controls (Powertrain Management) - ALLDATA RepairDokument3 SeitenEngine Controls (Powertrain Management) - ALLDATA RepairRonald FerminNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument13 SeitenUntitledTestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelors - Harvest Moon Animal ParadeDokument12 SeitenBachelors - Harvest Moon Animal ParaderikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxemias of PregnancyDokument3 SeitenToxemias of PregnancyJennelyn LumbreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan Proses Penyembuhan Luka. Pengkajian Diagnosa Perencanaan Implementasi EvaluasiDokument43 SeitenAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan Proses Penyembuhan Luka. Pengkajian Diagnosa Perencanaan Implementasi EvaluasiCak FirmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Dispatch of Generation: Prepared To Dr. Emaad SedeekDokument7 SeitenOptimal Dispatch of Generation: Prepared To Dr. Emaad SedeekAhmedRaafatNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Angles Are in Degrees: EGR2313 HW SOLUTIONS (2021)Dokument4 Seiten#Angles Are in Degrees: EGR2313 HW SOLUTIONS (2021)SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fmicb 10 02876Dokument11 SeitenFmicb 10 02876Angeles SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ideal Gas Law Lesson Plan FinalDokument5 SeitenIdeal Gas Law Lesson Plan FinalLonel SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advent Wreath Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenAdvent Wreath Lesson Planapi-359764398100% (1)
- BRAND AWARENESS Proposal DocumentDokument11 SeitenBRAND AWARENESS Proposal DocumentBuchi MadukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tree PruningDokument15 SeitenTree Pruningrita44Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zahid Imran CVDokument4 SeitenZahid Imran CVDhia Hadj SassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschDokument28 SeitenInnovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschacairalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life in The Ancient WorldDokument48 SeitenLife in The Ancient Worldjmagil6092100% (1)
- Bigbazaar PDFDokument14 SeitenBigbazaar PDFazhagu sundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- A SURVEY OF ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MIDGE (Diptera: Tendipedidae)Dokument15 SeitenA SURVEY OF ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MIDGE (Diptera: Tendipedidae)Batuhan ElçinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle SOA Suite 11g:buildDokument372 SeitenOracle SOA Suite 11g:buildMohsen Tavakkoli100% (1)
- Cad Data Exchange StandardsDokument16 SeitenCad Data Exchange StandardskannanvikneshNoch keine Bewertungen