Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CP 9. EXAMPLES Particle Kinetics-Force Inertia Method
Hochgeladen von
Jihan Pacer0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
89 Ansichten2 Seitendynamics of rigid bodies
Originaltitel
cp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldendynamics of rigid bodies
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
89 Ansichten2 SeitenCP 9. EXAMPLES Particle Kinetics-Force Inertia Method
Hochgeladen von
Jihan Pacerdynamics of rigid bodies
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
CP 9.
EXAMPLES Particle Kinetics- Force Inertia Method
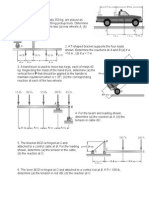
1. The two blocks shown are originally at rest. Assuming
that the coefficients of friction between block A and
the incline are 𝜇𝑠 = 0.25 and 𝜇𝑘 = 0.20 and
neglecting the masses of the pulley and the effect of
friction in the pulleys, determine a) the acceleration
of each block and b) the tension in the cable
2. A 450 g tether ball A is moving along a horizontal
circular path at a constant speed of 4 m/s.
Determine a) the angle θ that the cord forms with
pole BC, b) the tension in the cord.
3. The 15 kg block B is supported by the 25 kg
block A and is attached to a cord to which a
225 N horizontal force is applied as shown.
Neglecting friction, determine the a)
acceleration of block A, b) the acceleration of
block B relative to A.
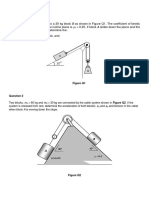
CP 9. EXAMPLES Particle Kinetics- Force Inertia Method
1. The two blocks shown are originally at rest. Assuming
that the coefficients of friction between block A and
the incline are 𝜇𝑠 = 0.25 and 𝜇𝑘 = 0.20 and
neglecting the masses of the pulley and the effect of
friction in the pulleys, determine a) the acceleration
of each block and b) the tension in the cable
2. A 450 g tether ball A is moving along a horizontal
circular path at a constant speed of 4 m/s.
Determine a) the angle θ that the cord forms with
pole BC, b) the tension in the cord.
3. The 15 kg block B is supported by the 25 kg
block A and is attached to a cord to which a
225 N horizontal force is applied as shown.
Neglecting friction, determine the a)
acceleration of block A, b) the acceleration of
block B relative to A.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physics Report PROJECTILE MOTIONDokument9 SeitenPhysics Report PROJECTILE MOTIONHulwan Mukhlis76% (25)
- Robert D. Blevins - Flow-Induced Vibration (2001, Krieger Pub Co) PDFDokument254 SeitenRobert D. Blevins - Flow-Induced Vibration (2001, Krieger Pub Co) PDFDang Dinh DongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsDokument18 SeitenQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Worksheet No.Dokument3 SeitenNewton'S Laws of Motion: Worksheet No.EUGENE ABULOC100% (1)
- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies 2DDokument4 SeitenEquilibrium of Rigid Bodies 2DSyed ShaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages4 41 To 52 PDFDokument12 SeitenPages4 41 To 52 PDFIsmael de PabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- API ExamplesDokument40 SeitenAPI ExamplesChristian Audet25% (4)
- Ista 1aDokument3 SeitenIsta 1ashashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tut1 Part29Dokument1 SeiteTut1 Part29AnmolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tut1 Part29 PDFDokument1 SeiteTut1 Part29 PDFAnmolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test1Review 1Dokument2 SeitenTest1Review 1Cathy NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersDokument4 SeitenPokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DynamicsDokument6 SeitenDynamicsWinter NaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 5Dokument4 SeitenHW 5Quadri Akamo0% (1)
- ERT 250 - Assgmnt 1Dokument4 SeitenERT 250 - Assgmnt 1carl domingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Dokument6 SeitenTUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Hareez FarhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 9 Take HomeDokument2 SeitenCP 9 Take HomeTidal SurgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of NewtonDokument1 SeiteApplications of NewtonAlejandra Carvajal DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Supplementary ProblemsDokument11 SeitenChapter 3 - Supplementary Problems김김김치Noch keine Bewertungen
- Frictionproblems PDFDokument16 SeitenFrictionproblems PDFJannel PaetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsDokument9 SeitenTutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsShubham SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics TutorialsDokument4 SeitenEngineering Mechanics Tutorials2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENoch keine Bewertungen
- ME101 Div3 2017 Tutorial-10Dokument2 SeitenME101 Div3 2017 Tutorial-10ywakadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES 11 - ExamplesDokument2 SeitenES 11 - ExamplesJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Dokument19 SeitenNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDokument4 SeitenCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksManish Shrestha100% (1)
- Applied Dynamics QuestionsDokument5 SeitenApplied Dynamics QuestionsKritamMaharjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tut1 Part30Dokument1 SeiteTut1 Part30AnmolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unaizah College of Engineering Qassim University Engineering Statics GE 201 Assignment 4Dokument5 SeitenUnaizah College of Engineering Qassim University Engineering Statics GE 201 Assignment 4Omar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics I - Fall 2013 PDFDokument4 SeitenApplied Mechanics I - Fall 2013 PDFRajeshGupta100% (1)
- Module 6Dokument5 SeitenModule 6John Kennedy EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics IIDokument4 SeitenApplied Mechanics IIsushilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 6Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 6Sean TraverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 8 Motion MIDokument3 SeitenTutorial 8 Motion MIPAWAN SHRESTHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 06Dokument5 SeitenHomework 06Herbert BorjigidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 7 PDFDokument4 SeitenProblem Set 7 PDFGrow RunnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Sheet2 PDFDokument15 SeitenQuestion Sheet2 PDFSaumyak RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 NewtonsDokument4 SeitenTutorial 2 Newtons2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENoch keine Bewertungen
- T2 Force - AccelerationDokument4 SeitenT2 Force - AccelerationDipesh PanditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 7 - Work and Energy-10807Dokument9 SeitenSheet 7 - Work and Energy-10807Bahaa RaghebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics 2Dokument5 SeitenApplied Mechanics 2Bikal BastakotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsDokument10 SeitenPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction (MEC 107)Dokument2 SeitenFriction (MEC 107)Piyush JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MecDokument2 SeitenMecsiddharth yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 Engg. Mechanics-2021 Batch PDFDokument3 SeitenTutorial 1 Engg. Mechanics-2021 Batch PDFARJUN NARAYANAN 21BAS10008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 4Rajkamal NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigid Body 3DDokument6 SeitenRigid Body 3DSyed ShaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics (Dynamics)Dokument4 SeitenApplied Mechanics (Dynamics)Adhikari SushilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 Energy MethodsDokument9 SeitenChapter 18 Energy MethodsnageshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument9 SeitenQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- Problem Set2 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem Set2 PDFMr. DummyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics WorksheetDokument3 SeitenDynamics Worksheetgirma workuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Equilibrium SP With AnswersDokument7 SeitenUnit 2 Equilibrium SP With AnswersGherico MojicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Sheet On DynamicsDokument6 SeitenWork Sheet On DynamicstorsrinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Newtons Laws QuestionsDokument7 Seiten5 Newtons Laws QuestionsAbdullah MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1,2,3Dokument8 SeitenTutorial 1,2,3RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsDokument5 SeitenChapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsSimon ManansalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP Nlm-IDokument8 SeitenDPP Nlm-IMohammed Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemas Cinetica PDFDokument7 SeitenProblemas Cinetica PDFMoisés DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btes103 203 em QBDokument10 SeitenBtes103 203 em QBSurajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 7 Div1A2A2B3BDokument2 SeitenTutorial 7 Div1A2A2B3BAnimesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyVon EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enclosure CoordDokument1 SeiteEnclosure CoordJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math TextbookDokument1 SeiteMath TextbookJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDokument30 SeitenPJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- References For Thesis ProposalDokument6 SeitenReferences For Thesis ProposalJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 DegreesDokument97 Seiten0 DegreesJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES 12 LE4 1920A DRAFT 24nov2019Dokument2 SeitenES 12 LE4 1920A DRAFT 24nov2019Jihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- DesignDokument3 SeitenDesignJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2.0 - Introduction To LRFD Bridge DesignDokument51 SeitenLecture 2.0 - Introduction To LRFD Bridge DesignJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0degrees ProbeDokument13 Seiten0degrees ProbeJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0degrees AreaDokument11 Seiten0degrees AreaJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che 413 - Environmental Engineering: Submitted By: Pacer, Judea SDokument11 SeitenChe 413 - Environmental Engineering: Submitted By: Pacer, Judea SJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- DesignDokument3 SeitenDesignJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES 102 Cluster B TopicsDokument20 SeitenES 102 Cluster B TopicsJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW1 PDFDokument9 SeitenHW1 PDFJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 Intro To Finite Element Method Part 2Dokument32 SeitenLecture 9 Intro To Finite Element Method Part 2Jihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 252 ResultdDokument123 SeitenCE 252 ResultdJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 252 ProjectDokument1 SeiteCE 252 ProjectJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 252 ResultdDokument123 SeitenCE 252 ResultdJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW1Dokument9 SeitenHW1Jihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 5Dokument2 SeitenCP 5Jihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To PdesDokument16 SeitenIntro To PdesJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Fourier Series PDFDokument15 SeitenComplex Fourier Series PDFJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises PHYSICSDokument2 SeitenExercises PHYSICSJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Date: SN: Quiz 4: D-K Transformation Prove That The Flexibility Matrix For The Given Beam Below IsDokument2 SeitenName: Date: SN: Quiz 4: D-K Transformation Prove That The Flexibility Matrix For The Given Beam Below IsJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decsion TreeDokument13 SeitenDecsion TreeJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- APA 6th EditionDokument5 SeitenAPA 6th Editionfazreen fazil100% (1)
- B, (B) The Number of Revolutions Executed byDokument2 SeitenB, (B) The Number of Revolutions Executed byJihan PacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDM CalibrationDokument6 SeitenEDM Calibrationnfs100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Condition Monitoring Technologies For Steel Wire Ropes - A ReviewDokument15 SeitenCondition Monitoring Technologies For Steel Wire Ropes - A ReviewNixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter No 3 GASES TEXTBOOK EXERCISEDokument21 SeitenChapter No 3 GASES TEXTBOOK EXERCISErehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPH 201Dokument158 SeitenGPH 201ضوسرNoch keine Bewertungen
- 51 Industrial CrystallizationDokument23 Seiten51 Industrial CrystallizationBoris DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barbie Bungee JumpDokument4 SeitenBarbie Bungee JumpReeja MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Getting Started With Code AsterDokument12 SeitenTutorial Getting Started With Code Asterjuanpalomo74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adatlap PDFDokument12 SeitenAdatlap PDFAnuradha SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Woodward Turbine ControlDokument17 SeitenWoodward Turbine Controlprasad5034100% (1)
- Effect of Various Accelerators On Different Strength Parameters of M - 20 Grade of ConcreteDokument10 SeitenEffect of Various Accelerators On Different Strength Parameters of M - 20 Grade of ConcreteTJPRC PublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost-Effective Skyhook ControlDokument9 SeitenCost-Effective Skyhook Controlgloohuis463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamical Systems FinalDokument12 SeitenDynamical Systems FinalBobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novel Separations TechniquesDokument2 SeitenNovel Separations TechniquesSP ManjunathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fulltext01 Matlab Code For Elasticity y Plasticity PDFDokument115 SeitenFulltext01 Matlab Code For Elasticity y Plasticity PDFRory Cristian Cordero RojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20060709leonardo PerspectographDokument5 Seiten20060709leonardo PerspectographTahremNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masel Catalog - Lab SuppliesDokument18 SeitenMasel Catalog - Lab SuppliesOrtho OrganizersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sealed SKF Spherical Roller BearingsDokument13 SeitenSealed SKF Spherical Roller BearingsMohamed Abdou100% (1)
- Library Book ListDokument1.011 SeitenLibrary Book ListKundan SavaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PV Elite Webinar 001Dokument23 SeitenPV Elite Webinar 001MEC_GuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 04 Atomic ArrangementsDokument22 SeitenLecture 04 Atomic Arrangementsantoine demeireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 112-8: Grating and Prism SpectrometerDokument6 SeitenExperiment 112-8: Grating and Prism SpectrometerTuhinVariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4bak 4siz PeruDokument8 Seiten4bak 4siz PeruAnonymous cgKtuWzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Beams: P. AnsourianDokument27 SeitenComposite Beams: P. AnsourianLeonardoMadeira11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philips Sequence PDFDokument1 SeitePhilips Sequence PDFRadiologi RSUKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dcna Fixed Prosthodontics April 2004 PDFDokument236 SeitenDcna Fixed Prosthodontics April 2004 PDFMiki FloreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filter Media Analysis FinalDokument6 SeitenFilter Media Analysis Finalziko23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study of New Type Elliptical Cross Trainer With Symmetrical Driving MechanismDokument9 SeitenStudy of New Type Elliptical Cross Trainer With Symmetrical Driving MechanismAbhishekRajNoch keine Bewertungen