Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Key Statistical Concepts Summary Sheet PDF
Hochgeladen von
ishtiaque3044Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Key Statistical Concepts Summary Sheet PDF
Hochgeladen von
ishtiaque3044Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Student
Learning Key Statistical Concepts
Centre Summary Sheet
KEY TERMS
Deviation The distance between the mean and a particular data point in a given distribution.
Mean The average score within a distribution.
Median The center score in a distribution.
Mode The most frequent score in a distribution.
Bell curve Normal Distribution is shaped like a bell.
Central Tendency Indicate the centre of a distribution.
Confidence Level The specific probability of obtaining some result from a sample below which the relationship will be
regarded as statistically significant .
Correlation Measures the degree of relationship between pairs of interval variables in a sample. The range of
correlation is from -1.00 to zero to +1.00.
Causality The relation between cause and effect.
ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) A method of statistical analysis broadly applicable to a number of research designs,
used to determine differences among the means of two or more groups on a variable.
Sample The population researched in a particular study. Usually, attempts are made to select a "sample population"
that is considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalised.
Population The target group under investigation, Samples are drawn from populations.
Standard Deviation A term used in statistical analysis. A measure of variation that indicates the typical distance between the
scores of a distribution and the mean; it is determined by taking the square root of the average of the
squared deviations in a given distribution.
KEY FORMULAS
Statistic Formula Used For
Measure of centre; affected
Sample mean (average)
by outliers
n odd: middle value of ordered data
Measure of centre; not
Median n even: average of the two middle
values affected by outliners
Measure of variation;
Sample standard deviation “average” distance from the
mean
Straight and direction of linear
Correlation coefficient
relationship between X and Y
NOTATIONS USED
In general, capital letters refer to population attributes (i.e., parameters) and lower-case letters refer to sample attributes (i.e.,
statistics). For example:
P refers to a population proportion p to a sample proportion
X refers to a set of population elements x to a set of sample elements
N refers to population size n to sample size
Statistics 5/2013 © SLC 1 of 2
Student
Learning
Centre
MAIN CONCEPTS
Bell curve
• Dark blue is less than one standard deviation from the mean. For the normal distribution, this accounts for 68.27% of the
set, while two standard deviations from the mean (orange and dark blue) account for 95.45%.
• Three standard deviations (light blue, orange, and dark blue) account for 99.73%.
• 68-95-99.7 rule — or three-sigma rule, or empirical rule states that for a normal distribution, nearly all values lie within
3 standard deviations of the mean.
STATISTICAL SYMBOLS
μ refers to a population mean; and x, to a sample mean.
σ refers to the standard deviation of a population; and s, to the standard deviation of a sample.
Hypothesis Testing
H0 refers to a null hypothesis.
H1 or Ha refers to an alternative hypothesis.
α refers to the significance level.
Β refers to the probability of committing a Type II error.
TYPICAL QUESTION
A sample of the variable x assumes the following values: 9 11 13 3 7 2 8 9 6 10
x
Compute: (a) n (b) (c) (d) s (e) s2 (f) median & mode (h) range CV
(a) n = 10
(b) ∑ x = 78
∑x 78
(c) x= = = 7.8
n 10
∑ x 2 − nx 2 = 714 − 608.4 = 11.73 = 3.43
(d) s=
n −1 9
2
(e) s = 11.73
n +1 10 + 1
(f) P(med) = th score = th score = 5.5th score
2 2
5thscore + 6thscore 8 + 9
med = 5.5th score = = = 8.5
2 2
(g) mode = 9
(h) range = highest value - lowest value = 13 - 2 = 11
s 3.43
(i) coefficient of variation (CV) = = = 0.44
x 7.8
STUDENT LEARNING CENTRE
REGISTRY BUILDING ANNEXE
TEL: 61-8-8201 2518
E-MAIL: slc@flinders.edu.au
INTERNET: http://www.flinders.edu.au/SLC
POSTAL: PO BOX 2100, ADELAIDE, SA 5001
Statistics 5/2013 © SLC 2 of 2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- A Complete Introduction To Time Series Analysis (With R) - SARIMA ModelsDokument26 SeitenA Complete Introduction To Time Series Analysis (With R) - SARIMA ModelsTeto ScheduleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evans Analytics2e PPT 04Dokument63 SeitenEvans Analytics2e PPT 04sener.asliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics - Probability Q4 Mod1 Tests-of-HypothesisDokument20 SeitenStatistics - Probability Q4 Mod1 Tests-of-HypothesisJoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Definitions: Probability SamplingDokument9 SeitenSome Definitions: Probability SamplingEng Mohammed100% (1)
- Implementation of Reliability Centered MDokument10 SeitenImplementation of Reliability Centered MAbdul Raheman MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVM Hands-On ProblemDokument7 SeitenSVM Hands-On Problemishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Data Visualizations Using Tableau Desktop (Beginner) - Map and Data LibraryDokument41 SeitenCreating Data Visualizations Using Tableau Desktop (Beginner) - Map and Data Libraryishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning From Data, Kecman2001 PDFDokument100 SeitenLearning From Data, Kecman2001 PDFIman ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Level Signal DetectionDokument147 SeitenAdvanced Level Signal Detectionishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Risk Modeling in R - ch1 - PDFDokument45 SeitenCredit Risk Modeling in R - ch1 - PDFishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Random Process-Q - TableDokument1 SeiteRandom Process-Q - Tableishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Best First RTutorialDokument17 SeitenBest First RTutorialfrancobeckham23Noch keine Bewertungen
- ARIMA Method AnalysisDokument1 SeiteARIMA Method Analysisishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Box-Jenkins Method Step by Step AnalysisDokument1 SeiteBox-Jenkins Method Step by Step Analysisishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bangladesh Centre For Advanced Studies (BCAS)Dokument2 SeitenBangladesh Centre For Advanced Studies (BCAS)ishtiaque3044Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher Notes: Own Production To Other Peers. This Is PenalizedDokument7 SeitenTeacher Notes: Own Production To Other Peers. This Is Penalizedgabriela acostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP15-A3 Example 2Dokument4 SeitenEP15-A3 Example 2Jenny RosaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistic Hypothesis TestingDokument17 SeitenStatistic Hypothesis TestingFrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- S1Dokument5 SeitenS1AnkitNoch keine Bewertungen
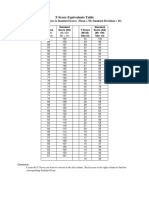
- Conversion Chart T-Scores To Standard Scores PDFDokument1 SeiteConversion Chart T-Scores To Standard Scores PDFcoldfritesNoch keine Bewertungen
- VC-dimension For Characterizing ClassifiersDokument40 SeitenVC-dimension For Characterizing ClassifiersRatheesh P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument77 SeitenChapter 4Dyg Nademah Pengiran MustaphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CÁC BẢNG THỐNG KÊ DATADokument13 SeitenCÁC BẢNG THỐNG KÊ DATAkimmngann04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive Statistics: Numerical Measures: Learning ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenDescriptive Statistics: Numerical Measures: Learning ObjectivesKeight Nueva100% (1)
- CH 4 Multicollearity SDokument24 SeitenCH 4 Multicollearity SHATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Associations Between Maternal and Paternal Parenting Behaviors, Anxiety and Its Precursors in Early Childhood - A Meta-Analysis.Dokument65 SeitenAssociations Between Maternal and Paternal Parenting Behaviors, Anxiety and Its Precursors in Early Childhood - A Meta-Analysis.Leila MargaridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Inferences About Two Populations: Learning ObjectivesDokument26 SeitenStatistical Inferences About Two Populations: Learning ObjectivesIsmail Muktar MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1: Statistical Signal ProcessingDokument2 SeitenAssignment 1: Statistical Signal ProcessingAryan IIITDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isom 351 WelthwrhgDokument74 SeitenIsom 351 WelthwrhgYijia QianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop Brochure and ScheduleDokument2 SeitenWorkshop Brochure and ScheduleRachnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ma3251 - SNM Unit - 1 Testing of Hypothesis Au Questions-1Dokument31 SeitenMa3251 - SNM Unit - 1 Testing of Hypothesis Au Questions-1Abinaya SriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityGrishma BhindoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Applied Statistical Inference With Minitab Second Edition 2nd Edition PDF ScribdDokument41 SeitenInstant Download Ebook PDF Applied Statistical Inference With Minitab Second Edition 2nd Edition PDF Scribdellis.hockman704100% (39)
- 06 SOM 2017 Service Quality Metrics Part II 1X SV 9 Jul 17 ReleaseDokument32 Seiten06 SOM 2017 Service Quality Metrics Part II 1X SV 9 Jul 17 ReleaseAbhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat104 Hw4 Spring2015 V2Dokument6 SeitenStat104 Hw4 Spring2015 V2Karni ShekhawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ID Pengaruh Kualitas Produk Harga Dan LokasDokument12 SeitenID Pengaruh Kualitas Produk Harga Dan LokasAnnisaa DiindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Statistical Analysis of GDP and Final Consumption Using Simple Linear Regression. The Case of Romania 1990-2010Dokument7 SeitenA Statistical Analysis of GDP and Final Consumption Using Simple Linear Regression. The Case of Romania 1990-2010Nouf ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Practice of Statistics Ninth Edition Ebook PDF VersionDokument61 SeitenIntroduction To The Practice of Statistics Ninth Edition Ebook PDF Versionjose.waller368100% (45)
- Chapter 15 Q and A PDFDokument37 SeitenChapter 15 Q and A PDFNanon WiwatwongthornNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhonda Hamilton Case Scenario: Exhibit 1 Hamilton'S Regression Model For Electric Utility IndustryDokument34 SeitenRhonda Hamilton Case Scenario: Exhibit 1 Hamilton'S Regression Model For Electric Utility IndustryĐặng Xuân ĐỉnhNoch keine Bewertungen