Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Principle of Communication Questions
Hochgeladen von
ceazar padillaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Principle of Communication Questions
Hochgeladen von
ceazar padillaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1. Modulation causes the information 12. Which of the following is not 20.
An AM radio station operating at
signal to be _____ to a higher another name for modulation index? 630 kHz is permitted to broadcast
frequency for more efficient audio frequencies up to 5 kHz. The
transmission. upper and lower side frequencies are
a. Modulation reciprocal
2. During modulation, the information fUSB = _____ kHz
signal _____ the amplitude of a high b. Modulation factor
frequency signal called the _____.
fLSB = _____ kHz
c. Degree of modulation
3. The circuit used to produce
modulation is called a _____. Its two 21. The total bandwidth of the signal
d. Modulation coefficient in the above example is _____ kHz.
inputs are _____.
13. The degree or depth of 22. A signal whose amplitude is
4. In AM, the instantaneous _____ of modulation occurring expressed as a
the carrier varies in accordance with displayed with respect to time is
percentage, is computed using the called a _____ domain display. The
the information signal. expression test instrument used to present such
a display is the _____.
5. True or false. The carrier a. 2 Vm
frequency is usually lower than the
modulating frequency. 23. A signal whose amplitude is
b. 100 / m displayed with respect to frequency
is called a _____ domain display.
6. The outline of the peaks of the The test instrument used to present
carrier signal is called the _____, c. m / 100 such a display is the _____.
and it has the same shape as the
_____.
d. 100% x m 24. Complex modulating signals
containing many frequencies
7. Voltages varying over time are produce multiple_____ thus
14. The modulation index is the ratio
said to be _____ signals. occupying more spectrum space.
of the _____ peak voltage of the to
the _____.
8. The trigonometric expression for 25. The AM signal that occupies the
the carrier is Vc = _____. greatest bandwidth is the one
15. An AM wave displayed on an
modulated by a
oscilloscope has values of Vmax=
9. True or false. The carrier 3.8 and Vmin= 1.5 as read from the
frequency remains constant during graticule. The percentage of a. 1-kHz sine wave
AM. modulation is _____ percent.
b. 5-kHz sine wave
10. An amplitude modulator performs 16. The ideal percentage of
the mathematical operation of modulation for maximum amplitude
of Information transmission is _____ c. 1-kHz square wave
percent.
a. Addition
d. 5-kHz square wave
17. To achieve 85 percent
b. Subtraction modulation of a carrier of Ve = 40 26. The composite AM signal can be
volts (V), a modulating signal of Vm recreated by algebraically adding
c. Multiplication = _____ is needed. which three signals?
d. Division 18. The peak-to-peak value of an AM 27. The total sideband power is what
signal is 30 V. The peak-to-peak percentage of the carrier power for
value of the modulating signal is 12 100 percent modulation?
11. Which of the following is the V. The percentage of modulation is
most correct? _____ percent.
a. 25 percent
a. Vm should be greater than Vc. 19. New signals generated by the
modulation process that appear b. 50 percent
directly above and below the carrier
b. Vc should be greater than Vm frequency are called _____.
c. 100 percent
c. Vm should be equal to or less than
Vc. d. 150 percent
d. Vc must always equal Vm
28. Information in an AM signal is 39. The acronym SSB means 48. The average output power of an
conveyed in the SSB transmitter rated at 12W PEP is
in the _____ to _____ range.
a. Single sideband with carrier
a. Carrier.
49. The process of translating a
b. Single sideband with suppressed signal to a higher or lower frequency
b. Sidebands. carrier for more convenient processing is
called _____.
c. Both together. c. Double sideband with no carrier
50. The circuit used for translating
29. The load into which the AM d. Double sideband with carrier the frequency of a signal is referred
signal Power is dissipated is a(n) to as a(n) _____ or _____.
_____.
40. A major benefit of DSB and SSB
is 51. The input signals to a frequency
30. The total transmitted power is the translation circuit are fs = 3.7 MHz
sum of the _____ and _____ and fo = 4.155 MHz. The output
powers. a. Higher power can be put into the signals are _____.
sideband(s).
31. A 5-kW carrier with 60 percent 52. In the example given in the text,
modulation produces _____ kW in b. Greater power consumption. what other local oscillator frequency
each sideband. could be used to produce the 10.7-
MHz output with a 107.1 = MHz
c. More carrier power.
input?
32. In an AM signal with a carrier of
18W and a modulation percentage of d. Double the sideband power.
75 percent, the total power in the 53. Unwanted mixer output signals
sidebands is _____ W. are eliminated by a _____.
41. List four benefits of SSB over AM
and DSB.
33. An AM signal with a carrier of 1 54. True or false. The local oscillator
kW has 100W in each sideband. The is modulated.
percentage of modulation is _____ 42. List two common uses of SSB.
percent. 55. True or false. Any modulation on
43. A common use of DSB is the input signal to be translated is
34. An AM transmitter has a carrier retained.
power of 200 W. The percentage of
a. Two-way communication.
modulation is 60 percent. The total 56. The operation carried out by a
signal power is _____ W. mixer is known as _____.
b. Telephone systems.
35. The total AM signal power is
2800W. The carrier power is 2000 c. FM/TV stereo.
W. The power in one sideband is
_____ W. The percentage of
modulation is_____. d. Satellite communications.
36. The unmodulated carrier current 44. True or false. In SSB, no signal
in an antenna is 1.5 A. When the is transmitted unless the information
carrier is modulated by 95 percent, signal is present.
the total antenna current is _____ A.
45. The type of AM signal that is
37. An AM signal without a carrier is used in TV broadcasting is called
called a(n) _____ signal. _____ transmission.
38. True or false. Two sidebands 46. An SSB signal produces a peak-
must be transmitted to retain all the to-peak voltage of 720V on voice
information. peaks across a 75- antenna. The
PEP output is _____ W.
47. An SSB transmitter has a 15O-V
supply. Voice peaks produce a
current of 2.3 A. The PEP input is
_____ W.
1. translated 22. time, oscilloscope greater efficiency, less
noise, little or no fading
2. varies, carrier 23. frequency, spectrum
analyzer 42. telephone systems,
3. modulator, carrier, two-way radio
modulating signal 24. sidebands
43. c
4. amplitude 25. d
44. true
5. false 26. Carrier, upper
sideband, lower 45. vestigial sideband
6. envelope, modulating sideband
signal 46. 863.7
27. b
7. time-domain 47. 345
28. b
8. Vc = sin 2 fct 48. 3-, 4-W
29. antenna
9. true 49. frequency
30. carrier, sideband conversion
10. c
31. 0.45 50. mixer, converter
11. c
32. 5.06 51. 4.155 MHz, 7.855
12. a MHz, 455 kHz, 3.7 MHz
33. 63.25
13. d 52. 117.8 MHz
34. 236 W
14. modulating signal, 53. filter or tuned circuit
carrier 35. 400 W, 89.44
percent 54. false
15. 43.4
36. 1.8 amperes 55. true
16. 100
37. DSB 56. heterodyning
17. 17.34 V
38. false
18. 66.67
39. b
19. sidebands
40. a
20. 635, 625
41. less spectrum
21. 10 space, more power in
the sidebands with
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsVon EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation (Finale)Dokument20 SeitenInstrumentation (Finale)Jonathan BacusNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEC Definition of Terms FOR ESDDokument2 SeitenPEC Definition of Terms FOR ESDkelleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Fundamentals Part 1Dokument8 SeitenAC Fundamentals Part 1KhatelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECEN 20093 - Lesson 4 Unit 1-4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi DDokument1 SeiteECEN 20093 - Lesson 4 Unit 1-4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi DandreagassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- INSTRUDokument3 SeitenINSTRUStraw Hat luffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEE-BSEE EE 562 L Week 4 5Dokument9 SeitenCEE-BSEE EE 562 L Week 4 5Hazel TardioNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE Laws QuizDokument9 SeitenEE Laws QuizJiever AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebol, Kenn Act 9Dokument3 SeitenEbol, Kenn Act 9Techno HubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebol, Kenn Lloyd EXAM SET BDokument6 SeitenEbol, Kenn Lloyd EXAM SET BTechno HubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab. Equipments FamiliarizationDokument3 SeitenLab. Equipments FamiliarizationashfaqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC&DC Direct Current Electrical Machinery Generalization, December 13, 2016,2nd Semester SY2016to2017TIPDokument58 SeitenAC&DC Direct Current Electrical Machinery Generalization, December 13, 2016,2nd Semester SY2016to2017TIPKatrina Nieto Calanglang-Dayoc100% (1)
- Quiz - TransformersDokument2 SeitenQuiz - TransformersKeneth John Gadiano Paduga50% (2)
- e = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceDokument8 Seitene = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceReniel MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE ReviewerDokument13 SeitenEE ReviewerZZROTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Base RateDokument31 SeitenPerformance Base RateVanvan BitonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine Notes Board ExamDokument14 SeitenElectrical Machine Notes Board Exammarlon mamacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1Dokument22 SeitenTest 1Rinalyn-Oscar Gamboa Magtibay100% (1)
- NameDokument4 SeitenNameCzesarinePreciousJadeManibogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candolita - POWER PLANT-ASSIGNMENT 2 PDFDokument3 SeitenCandolita - POWER PLANT-ASSIGNMENT 2 PDFCy CandolitsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 233 2 V Example 13.23.: C B BC BCDokument9 Seiten233 2 V Example 13.23.: C B BC BCmuhammad haseebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistance (R), Inductance (L), and Capacitance (C) CircuitsDokument10 SeitenResistance (R), Inductance (L), and Capacitance (C) Circuitszed cozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Fields & Waves (BEB20303) Chapter 1: Electrostatic FieldDokument32 SeitenElectromagnetic Fields & Waves (BEB20303) Chapter 1: Electrostatic FieldAFiqah Nazirah JailaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acckt Single PhaseDokument6 SeitenAcckt Single Phaseken peligrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. 480 Turns: Transformers Supplementary ProblemsDokument6 SeitenA. 480 Turns: Transformers Supplementary ProblemsDwight Jesser TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines 1 EE05: Engr. Ruben J. Dichoso InstructorDokument17 SeitenElectrical Machines 1 EE05: Engr. Ruben J. Dichoso InstructorAngeli Mae SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE LawsDokument1 SeiteEE LawsMarkAlumbroTrangia0% (2)
- Close Exam 8Dokument4 SeitenClose Exam 8sieged_rj3165Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ener ConDokument5 SeitenEner ConRey Del Castillo Luar Jr.0% (1)
- Open Circuit Saturation Curve of An Alternator-EXPT8Dokument2 SeitenOpen Circuit Saturation Curve of An Alternator-EXPT8Karl Joseph Chua Villariña100% (3)
- Final Requirement IN EE320A/L: (Basic Electrical Engineering)Dokument25 SeitenFinal Requirement IN EE320A/L: (Basic Electrical Engineering)Andre RoqueteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 WattmeterDokument14 Seiten11 WattmeterislahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machines QuizDokument9 SeitenDC Machines QuizDanny MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Alternator TestsDokument20 SeitenModule 2 Alternator TestsJoshua Roberto GrutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Dokument3 SeitenThe Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Tim Picar100% (1)
- Group 11 Case Study 1 Ra 7920 ElectricalDokument9 SeitenGroup 11 Case Study 1 Ra 7920 ElectricalHani NotorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- A304SE PPT Slides T111 - FinalDokument194 SeitenA304SE PPT Slides T111 - FinalEranga Nandana Kumara KudahewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2) SyllabusDokument2 Seiten(ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2) SyllabusMark DasiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Enercon 2nd1718Dokument22 SeitenTransformer Enercon 2nd1718Jaddie Lorzano33% (3)
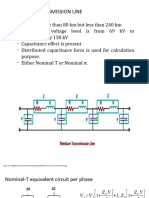
- Medium TransmissionDokument15 SeitenMedium TransmissionPerez Trisha Mae D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDokument7 SeitenReview of Related Literature and StudiesGlaiza GanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Ac PDFDokument128 SeitenDC Ac PDFCedrick PalisocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitance of Transmission LinesDokument3 SeitenCapacitance of Transmission LinesMike AndayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21 MendozaDokument22 SeitenChapter 21 MendozaDaraMendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives Electrical EngineeringDokument21 SeitenObjectives Electrical Engineeringvan eric lardizabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ELECS2) Exp3 - Darlington and Cascode Amplifier CircuitsDokument17 Seiten(ELECS2) Exp3 - Darlington and Cascode Amplifier CircuitsFrodolfre Reginald Lazo100% (2)
- Induction Motor 2Dokument2 SeitenInduction Motor 2Perfectly Amazing VdeosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Designdocx PDF FreeDokument324 SeitenMachine Designdocx PDF FreeJessie DoqueniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examples ExamplesDokument14 SeitenExamples ExamplesWang SolNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Review Advanced MathematicsDokument2 SeitenCE Review Advanced MathematicsRAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument26 SeitenChapter 3Belayneh TadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plates in EnerconDokument38 SeitenPlates in EnerconJevan Calaque100% (1)
- Pass 1Dokument13 SeitenPass 1Jeffsquille YagisgamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1Dokument6 SeitenActivity 1Joshua MenesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- FB Excel Review Math 1 PDF FreeDokument5 SeitenFB Excel Review Math 1 PDF FreePiolo CatiponNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set Circuits 2Dokument3 SeitenProblem Set Circuits 2Vien Ysabel Jasa0% (1)
- Chapter I-Complex Numbers&VariablesDokument10 SeitenChapter I-Complex Numbers&VariablesMico Marvin YturzaetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Supply AgreementDokument15 SeitenPower Supply AgreementVanvan BitonNoch keine Bewertungen
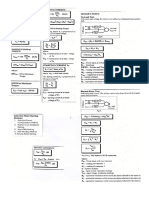
- Modulation Q & ADokument16 SeitenModulation Q & AShanisse AballaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude ModulationDokument43 SeitenAmplitude ModulationAmiel Paul P. GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEG DE351 HD NAS Decoder Product ManualDokument18 SeitenEEG DE351 HD NAS Decoder Product ManualFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Miller and Freunds P PDFDokument4 SeitenSolution Manual For Miller and Freunds P PDFKuttyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormSprint ManualDokument208 SeitenFormSprint Manualronny45Noch keine Bewertungen
- RGB Color Codes ChartDokument6 SeitenRGB Color Codes ChartHermawan UsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tile Hatch Creator2Dokument3 SeitenTile Hatch Creator2Luis HaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whitepapers PostgresDokument298 SeitenWhitepapers Postgrescristina_tudor_ro100% (1)
- S922X Public Datasheet V0.2 PDFDokument1.111 SeitenS922X Public Datasheet V0.2 PDFady_gligor7987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manzana Insurance - Fruitvale BranchDokument10 SeitenManzana Insurance - Fruitvale Branchankit_dadesiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LG LCD CH La73a 47lc7df UbDokument62 SeitenLG LCD CH La73a 47lc7df UbvideosonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiette AR2100 - Service ManualDokument55 SeitenCardiette AR2100 - Service ManualHernan Vallenilla Rumildo MixNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCIR Academy - Application FormDokument6 SeitenCCIR Academy - Application FormYến HảiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft SQL Server To IBM DB2 UDB Conversion GuideDokument558 SeitenMicrosoft SQL Server To IBM DB2 UDB Conversion GuideBupBeChanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX DiagDokument40 SeitenDX DiagRadith FitriansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Home Learning Plan: Empowerment Technologies S.Y 2020-2021 1 SemesterDokument4 SeitenWeekly Home Learning Plan: Empowerment Technologies S.Y 2020-2021 1 SemesterGlenzchie Taguibao90% (10)
- Software Project Management Plan Nexus Rescue Management System Document Revision #: 1.3 Date of Issue: 12 Nov, 2013 Project Manager: Ahsan ShakeelDokument55 SeitenSoftware Project Management Plan Nexus Rescue Management System Document Revision #: 1.3 Date of Issue: 12 Nov, 2013 Project Manager: Ahsan ShakeelChawdhury MashoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iwc DumpDokument1.017 SeitenIwc DumpPeterson MaranhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQL 11g PITB D64258GC11 Ag PDFDokument132 SeitenSQL 11g PITB D64258GC11 Ag PDFUmer Aziz Rana0% (1)
- ServiceNow Interview QuestionerDokument3 SeitenServiceNow Interview QuestionerrajendergrrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco 7841Dokument8 SeitenCisco 7841bbpearlvnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Estimation ToolsDokument13 SeitenCost Estimation Toolsdivya25sep100% (1)
- Workshop 4 (B) - Algos For Humans Dev Gill Marex Spectron - Original.1550055327Dokument7 SeitenWorkshop 4 (B) - Algos For Humans Dev Gill Marex Spectron - Original.1550055327iljanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELS 13 Agustus 2022 RevDokument16 SeitenELS 13 Agustus 2022 RevYANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Label Long Short-Term Memory-Based Framework To Analyze Drug Functions From Biological PropertiesDokument6 SeitenMulti-Label Long Short-Term Memory-Based Framework To Analyze Drug Functions From Biological PropertiesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Drip Irrigation System For Sustainable Agriculture: July 2016Dokument5 SeitenSmart Drip Irrigation System For Sustainable Agriculture: July 2016Shoaib NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Part ListDokument6 SeitenElectrical Part ListdachajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple 1.5-V Boost Converter For MSP430 - Slaa105Dokument7 SeitenSimple 1.5-V Boost Converter For MSP430 - Slaa105Daniel ZancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyg042n10ns1p Hyg042n10ns1bDokument10 SeitenHyg042n10ns1p Hyg042n10ns1brennybenitezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Advisor Webcast: What's New in Financial Reporting 11.1.2.4.900Dokument33 SeitenOracle Advisor Webcast: What's New in Financial Reporting 11.1.2.4.900huyhnNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDP 25-8-2020 - Avnk-SrinidhiDokument26 SeitenFDP 25-8-2020 - Avnk-Srinidhisravan kodemNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMBA Courses For Fall 2018Dokument1 SeiteIMBA Courses For Fall 2018Indrajeet BarveNoch keine Bewertungen